An athletic body - a sculpted, lean one - will most likely never go out of fashion, and our modern society will probably not live to see the time when fatness will again be held in high esteem. Therefore, fitness clubs are growing like mushrooms. But people don’t mind losing extra pounds, so not only equipment and exercise machines come to the rescue, but also various fat-burning techniques. One of these is interval training. We have already looked at similar examples of HIIT and Tabata, now we will take a closer look at what this technique is.
What is interval training
The essence of this training is to perform interval sessions in which intense load alternates with less intense, which is more of a rest. Interval training is performed either on one of the cardio machines - it can also be running at a stadium, or alternated with strength and cardio exercises.
And also read how to do cardio training at home →
Thus, the intervals are performed among themselves without a pause - the second interval will serve as a rest. Such sessions can be from 5 to 15, depending on the complexity of the program and physical fitness. Strength exercises can be done for quantity, but the next interval can be either moderate-paced cardio or simple walking. The duration of such a workout can take an average of 15-30 minutes.
The next important point is the duration of the intervals:
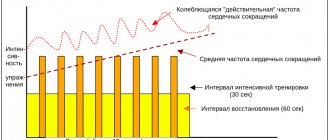
- an intensive session lasts from 10 to 30 seconds, a maximum of a minute;
- the second part of the interval is performed two to three times longer for recovery and can last 2-3 minutes.
To understand at what intensity to train, you need to exercise with a heart rate monitor or calculate your heart rate using the formula, which is described in detail in the article on heart rate zones. Thus, the intensive part should be performed in the range of 80-95% of the maximum heart rate, and the rest interval in the region of 40-60%.
For example, running on a treadmill: after warming up, increase the speed until you see that your heart rate has risen to the desired level - on average 80-90%, and maintain the pace for 30 seconds. Then slow down to jogging or walking until your heart rate drops to about 50-60%. You can track your heart rate on both treadmills and a heart rate monitor. The main thing is to know your heart rate zones in advance. Everyone’s speed will be individual, so here you need to build on the indicators on the heart rate monitor.
How to Create Your Own HIIT Workout Plan
When designing a HIIT program, keep the following in mind:
- Lead time;
- Intensity;
- Recovery;
- The ratio of intensity and recovery process (low intensity);
- Frequency.
The ACSM, ACE, and NASM general recommendations for HIIT suggest the following:
| Duration | From 5 seconds to 2 minutes for women (for men up to 3 minutes) |
| Intensity | 80% to 95% of a person's maximum heart rate. |
| Recovery | 40% to 50% of a person's estimated maximum heart rate |
| Relationship between intensity and recovery period | From 1:1 to 1:3 |
| Periodicity | from 3 to 5 times a week |
A little more about intensity
When performing HIIT, the interval should be greater than or equal to your intended heart rate. A good subjective measure is the interval of work at which you seem to move from “difficult” to very “difficult.”
Using Joel Dowdell's "Talk Test" in his book "Ultimate You", you should find it challenging when moving to another level.
Another way to determine intensity is to use a point system.
According to ACE, intensity is measured on a scale of individual perceived exertion from 1 to 10. A level of 7 is considered high intensity.
A few words about low intensity and recovery
The intensity of recovery intervals should be 40%-50% of maximum heart rate. This is a physical activity during which a person feels comfortable and does not feel out of breath.
Think of your workout as an active holiday where you work on your body and take a break from putting in the effort.
Let's take a closer look at the ratio of high- and low-intensity efforts. The connection between work and recovery periods is important.
Keep in mind that the numbers will vary depending on the guidelines you follow during HIIT.
ACSM suggests a 1:1 ratio, while NASM suggests 1:2 to 1:3. (big number: recovery)
The Tabata protocol and Chris Jordan's seven-minute training are based on the inverse ratio: high-intensity periods are almost 2-3 times longer than recovery periods.
Let's focus on the ACSM 1:1 ratio and look at how it works:
Example:
- A 1:1 ratio of 3 minutes of hard training (or high intensity training) followed by 3 minutes of rest (or low intensity training).
- Workouts with a 1:1 ratio often last around 3, 4 or 5 minutes with a similar recovery period.
This combination of exercises can be repeated 3 to 5 times.
During sprint intervals, higher intensity efforts typically last for a shorter amount of time (20-30 seconds).
Combining the above exercise principles will help you maximize fat loss and build muscle in significantly shorter workouts.
Since time is of the essence for most women, good time management is a valuable feature of HIIT.
A little more about frequency
ACSM suggests exercising 3-5 times per week, with each session lasting less than 60 minutes.
The benefits and harms of interval training
Advantages and benefits of interval training:
- Allows you to burn subcutaneous fat even after finishing your workout.
- Strengthens the heart and blood vessels.
- It takes less time and is more effective compared to long-term moderate-intensity cardio exercises.
- Increases the body's endurance.
- Speeds up metabolism.
- Tones muscles.
- It is universal, suitable for lovers of both cardio and strength training.
- You can exercise in the gym or at home; such training can be done without special equipment.
Disadvantages and harm:
- The workouts are high-impact, requiring you to perform high-intensity sessions at 90-95% of your maximum, which for many people puts a lot of strain on the heart. Therefore, unprepared people should not start with such classes ; general strengthening preparation is necessary in advance.
- Even strength interval training is more designed for fat burning, so in order to gain muscle mass, you should not choose this technique .
Advantages
Interval training has a huge number of advantages:
- Increased endurance. During exercise, the body works hard. At the same time, for a permanent effect, it is necessary to regularly increase the load - the body should not have time to adapt to environmental conditions.
- Fat burning. One well-done session consumes a huge amount of calories. No strength training provides such an effect. But interval training is the best and only way to quickly get rid of visceral fat.
- Figure correction. With the help of interval training, men and women not only get rid of fat deposits, but also form a beautiful, slender figure with elastic, properly pumped muscles.
- Health promotion. A gradual increase in physical activity, the correct choice of scheme and exercise equipment ensure the development of not only the body, but the internal organs. The cardiovascular and respiratory systems do not wear out in the process, but, on the contrary, become stronger and become immune to many diseases. The risks of injury are also minimized.
Types and methods of interval training
Varieties of interval training include:
- Interval cardio training , including HIIT. The training is performed as in the example of running on a treadmill. Any of the cardio equipment, a jump rope and your own body weight can also be used as a load. Acceleration takes 1 minute, recovery takes 2 minutes. You can perform the complex for 5-10 cycles.
- Tabata Protocol. This popular method also applies to interval training. Exercises are performed with your own body weight or equipment. But the load is performed according to the following principle: 20 seconds of intense load, 10 seconds of rest. Or a list of exercises is performed for 30 seconds without pauses between them, and rest only at the end of the circle.
- Strength interval training. The principle of training is to alternate strength and cardio exercises. For example, 2-3 strength exercises are performed 15-30 times, and between them any of the cardio exercises: jumping, running, and jumping.
Oxygen consumption and calorie burning
According to scientific research, it takes about five calories to consume 1 liter of oxygen.
As HIIT programs alternate between short bursts of intense exercise and moderate to low intensity exercise, researchers around the world are trying to figure out how to get more with less.
After extensive research into the effectiveness and efficiency of HIIT compared to monotonous workouts, it has been found that you can achieve comparable or greater results in less time using this method.
One study from the scientific journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism found that high-intensity interval training increases the metabolic activity of fats and carbohydrates in human skeletal muscle, without long sessions in the gym.
This means that the body successfully converts carbohydrates and fats into energy to fuel muscles. In simpler words, it is effective for fat burning.
The American authority on sports medicine, the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), states that HIIT provides the same fitness benefits as continuous aerobic endurance exercise, but in a shorter period of time.
They elaborated, commenting, "This is because high-intensity interval training tends to burn more calories, especially post-workout, than traditional long-term, steady-state exercise."
If there's one mystery or secret to HIIT, it's the calorie burn that comes with it.
Indeed, at this moment the full effectiveness and efficiency of this method is revealed.
By exercising intensely with minimal rest periods, you successfully kick-start your metabolism for several hours after your workout.
The professional term for this effect is EPOC or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption.
This means the body is working hard and it will take several hours and additional energy (calories!) for the body to return to its pre-workout state.
The exact amount of time your body burns calories at a higher level depends on the intensity and duration of the activity. Various studies have been conducted with a wide range of figures.
Some believe this occurs within 2 hours, while others have found that this effect can last for up to 48 hours after exercise.
Regardless of how many hours it actually lasts, this expenditure can add 6 to 15% more calories to your total energy expenditure.
For most women, the goal of exercise is to burn calories and lose weight/weight, but there are other benefits of HIIT.
According to the ACSM, HIIT affects:
- Aerobic and anaerobic fitness;
- Blood pressure;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Insulin sensitivity (which helps exercising muscles more readily use glucose as an energy source);
- Cholesterol levels;
- Abdominal fat and body weight while maintaining muscle mass.
How to exercise correctly
- Is it worth reminding that any lesson begins with a warm-up ? You need to do light cardio for 5-10 minutes; if the workout is carried out on a treadmill, then the warm-up, accordingly, looks like walking on the same machine. You can also choose an exercise bike, orbitrack, stepper and more.
- Be sure to monitor your pulse. Having a heart rate monitor is a prerequisite for such training. Determine your heart rate zones in advance by calculating your heart rate for an intense session and a non-intense session.
- Since the training involves high loads, the optimal training duration is about 20-30 minutes . This should not be confused with regular aerobic exercise.
- Perform the load, maintaining a clearly established time or number of repetitions. Exceeding the intensity risks overtraining and putting a lot of stress on the heart.
- After completing the last training cycle, do not rush to complete the load - get off the machine or throw the apparatus. If the workout was a running workout, continue to walk quietly for 7-10 minutes, gradually reducing your speed until your heart rate is completely restored.
- At the end of your workout, stretch your muscles.
Read more about stretching muscles after a workout →
So let's get started
When creating an interval training plan, it is important to consider a few things. Think about what you want to get out of this workout and where you start.
The training should be challenging but realistic. Calculate your strength if you are a beginner or have had a short break in training. An injury or illness will simply put your activities on the back burner, so be careful. There is always an opportunity to do something next time.
Here is a list of the best interval training, in our opinion:
#1. Aerobic interval training
A great place to start training as aerobic exercise is less intense than other types of interval training. They are suitable for both beginners and those who have taken a long break.
First, you will need to decide on the intensity of the work and recovery intervals. The intensity of the working interval should be about 70% of the maximum heart rate, and you must learn to maintain this pace and be able to talk. The intensity of the recovery period should be as low as possible, but do not stop moving (running and walking are suitable).
It does not matter how long the working interval lasts, but the recovery period should be either equal in time or half as long in a ratio of 1:1 or 2:1.
Aim for a total of 5-10 work intervals. Once it becomes easy, add more reps, increase the speed or duration of the work interval, or shorten the recovery period.
#2. Fartlek workout
This method of training can be loosely called interval training, since there is no set period of time between working sets and recovery periods. Instead, there is freedom of choice; you choose the structure and intensity of the workout at your own discretion.
This type of exercise combines continuous training with random intervals. This is an unstructured workout and is completely up to you.
Try to make it as varied as possible. Here's an example of a short fartlek session on a bike:
- Ride at an average pace for 3 minutes, slightly lifting your buttocks from the seat;
- Shift to a heavier gear and rest for 1 minute;
- Gradually increase speed every 30 seconds while sitting;
- Ride at an average pace for 2 minutes, slightly lifting your buttocks from the seat;
- Slow driving pace with gear changes every 30 seconds;
- Average riding pace for 1 minute while standing;
- Ride at a fast pace for 2 minutes while seated.
As you can see, the style, speed and intensity change regularly, the whole process is controlled solely by you and invented on the fly. The only things you can plan ahead of time are what equipment you'll need, how long the session will last, and how difficult it will be overall. This is all.
#3. Cruise Interval Training
They can also be classified as not quite ordinary interval training, since they are not as intense and longer, but extremely effective.
Choose an intensity that is about 80% of your maximum heart rate. You need to hold out at this pace for 3-5 minutes. Quite difficult to do.
During the recovery period, you continue to move, preferably at a slightly higher than average intensity - about 70% for 3-5 minutes. Try to do the ratio of intervals with a ratio of 1:1.
This training structure quickly increases the amount of lactic acid in the blood, which makes the exercise difficult and not entirely comfortable. However, it is an excellent stimulus for the release of anabolic hormones, namely growth hormone (GH) and testosterone (T).
Both hormones enhance the fat-burning effect through a process called partitioning . Sprints of 30 seconds or more can increase GH levels by 450% and testosterone levels by over 90%.
#4. Wingate training
This training method first appeared in 1970 and was specifically designed for cycling. The intense phase will last only 30 seconds at maximum , and the recovery period will be 4 minutes. There is no need to stop; just continue at a slow pace.
In one workout, try to complete 4-6 approaches and 3 sessions per week.
You'll soon start to get better at 30-second high-intensity intervals, so you can extend your recovery period to 15 to 20 minutes with low-intensity exercise. After some time you will see how effective this training is.
#5. Tabata
This is the training system that started the revolution called high-intensity interval training (HIIT) .
This is a very short 4-minute session, but make no mistake, as it is one of the most difficult types of interval training.
In 1996, Izumi Tabata of the National Institute of Fitness and Sports in Tokyo studied the effects of HIIT on his students. He asked volunteers to perform 8 rounds of jump squats at their maximum capacity. Each work interval lasted only 20 seconds , and the recovery period was only 10 seconds .
The results of the study showed that the volunteers spent 13.4 kcal per minute, which led to an increase in metabolism that doubled compared to the pre-workout period.
There are several different methods of interval training, each of which has its own specifics, time frame and ratio of work and rest periods. The beauty of high-intensity interval training is that it is productive and versatile. They guarantee quick results. Numerous video reviews confirm this. Below are some more plans for these workouts.
General strengthening of the body
Increases and strengthens such qualities as:
- Muscular endurance, strength, increased power;
- Reaction, speed;
- Improved coordination;
- Lose fat and get the figure of your dreams;
- Improvement of the vascular-cardiac system.
Interval fitness what is it?
This is a type of training where the intensity and type of load constantly changes, with a rest interval of two to three minutes - this is the interval in fitness. An example of such fitness is dancing (sports aerobics).
Interval in fitness, what is it and what does it include?
In this form of training, there must be a warm-up for at least 10 minutes and cardio exercise. Interval training, what is it in fitness, is the same interval fitness only with double the load.
Step interval in fitness what is it?
A type of training that produces maximum results in a slightly short period of time. It looks like various climbs to a step pad accompanied by invigorating and catchy music. Allows people with different physical fitness to exercise in one group. Helps develop coordination and increase endurance, burns fat from the most problematic areas: stomach, legs and butt.
interval class fitness what is it?
This is an activity with a constant change of strength loads and cardio load. The main exercises are jumping, push-ups and running.
What can be achieved with such training?
- Strengthening the vascular-cardiac system;
- Improved coordination;
- Getting in excellent physical shape;
- A good mood is a nice bonus.