Body mass index
Quetelet index (body mass index, BMI ) is a more progressive option. The body mass index indicator was developed by the Belgian sociologist and statistician Adolphe Quetelet in 1869.
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]2 For example, a person’s weight = 60 kg, height = 170 cm. Therefore, the body mass index in this case is equal to: BMI = 60: (1.70 × 1.70) = 20.7 The results are compared with the tabular data.
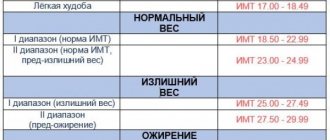
In accordance with WHO recommendations, the following interpretation of BMI indicators has been developed:
| Body mass index | Correspondence between a person's mass and his height |
| 16 or less | Severe underweight |
| 16—18,5 | Insufficient (deficit) body weight |
| 18,5—24,99 | Norm |
| 25—30 | Excess body weight (pre-obesity) |
| 30—35 | Obesity of the first degree |
| 35—40 | Obesity of the second degree |
| 40 or more | Obesity of the third degree (morbid) |
The body mass index should be used with caution, solely for indicative assessment - for example, an attempt to evaluate the physique of professional athletes with its help may give an incorrect result (a high index value in this case is explained by developed muscles).
How to lose extra pounds
Reading time 6 min. Data from numerous studies are alarming and obesity is already reaching epidemic proportions and is being referred to as the disease of the 21st century. Every fourth man and every fifth woman are classified as overweight. It's time to make an important and perhaps too often postponed decision about your own health, get rid of those extra pounds and give up bad eating habits.
1.How can you check if there is a problem with obesity?
There are several simple methods for determining the correct weight: 1. The BMI index takes into account height and weight. Based on it, it is possible to determine whether weight parameters are within normal limits. You can find your BMI by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. BMI = body weight (kg) / height (m) 2 Example: weight 90 kg and height 1 m 80 cm, then BMI is calculated as follows: BMI = 90 / 1.8 2 = 90 / 3.24 = 40 BMI value – 27.7. BMI below 18.5 - underweight if it is in the range from 18.5 to 24.9 - correct weight exceeds 25 - overweight if more than 30 - obesity. However, this indicator is not suitable for athletes - a muscular bodybuilder or a slender runner, despite being in excellent shape, will have the wrong weight according to the indicator
Broca-Brugsch formula.
Depending on the height, it is calculated as follows: for people with a height of 155 – 164 cm: height (in cm) – 100 = proper body weight, for people with a height of 165 – 174 cm: height (in cm) – 105 = correct body weight, for persons taller than 174 cm: height (in cm) – 110 = proper body weight. 3. analysis of body mass and composition. To see what your body fat ratio is, it's best to take a simple test with a body mass and composition analyzer. Such devices are found in many fitness clubs and nutritionists' offices. The device resembles a scale and uses electrical bioimpedance (BIA) to analyze the water and fat content of the body. After a few seconds of testing, you can get an accurate result.
2.What is the relationship between excess weight and a person’s psychological state?
Problems with maintaining a healthy weight affect not only adults, but also children and teenagers, who often learn poor eating habits from home. It is in the family that a child from an early age learns an approach to nutrition and acquires certain forms of behavior associated with caring for health - physical and mental. Obese people are more likely to become depressed and feel inferior. It happens that children are ridiculed at school, which can affect their future life and character development. Obesity is not only problems with daily functioning, discomfort when performing various activities or decreased satisfaction with appearance, loss of self-confidence. It's not just resentment and embarrassment that your favorite shirt doesn't fit or you need to buy a new suit. Obesity, first of all, poses huge health problems.
3.Why is it necessary to fight obesity?
Obesity is not only an aesthetic and psychological problem, but also a health problem. Unnecessary pounds increase the risk of developing many diseases, such as type II diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension, asthma, sleep apnea, spinal degeneration and others. The fight against obesity can be beneficial not only in terms of getting rid of excess weight, but also the opportunity to overcome your own weaknesses and increase your libido level. People who were able to overcome the problem have changed not only on the outside, because the silhouette of the body already looks different, but their health and well-being have improved; they set goals and life priorities, gain self-confidence and enter into new social relationships.
4.What is the most common cause of obesity?
Lack of control over what you eat and how much you eat is the biggest cause of obesity. If you don’t approach the issue of nutrition wisely and don’t understand that nutrition directly affects your health, fitness and well-being, it will be difficult to give up bad habits. It will be difficult to resist the temptation to eat unhealthy food. Unfortunately, a product's packaging is often more interesting than its contents. Many foods that are on the table and eaten every day - certain types of breakfast cereals, yogurts, fruit juices - can contain a lot of so-called "hidden" sugar. If you unreasonably consume excessive amounts of highly processed foods, do not avoid high-calorie snacks, chips, sweets, do not eat regularly or eat constantly, and lead a sedentary lifestyle, then you may be at risk of turning excess fat into full-fledged obesity. Another reason is lack of exercise. Physical activity for an obese person is not a waste of time; better results can only be achieved by combining exercise with proper nutrition. No one can guarantee that it will be easy at first, but it is worth overcoming the barrier of reluctance to engage in physical activity. For many people, this is a serious problem, especially if they have previously consistently avoided exercise.
5.How to take the first step?
You shouldn’t put it off until later, arguing that it’s winter or summer, better from the beginning of a new week or already a month. It's always a good time to commit to a healthy lifestyle and start changing your habits so you can finally live a "simply healthy" life. If you have doubts about the exact direction of changes, or you are not sure that you can lose extra pounds on your own, you can seek help from a nutritionist. The doctor, based on knowledge and experience, will help you avoid dietary mistakes and motivate you to achieve results - losing extra pounds. The most important thing is to follow certain (and proven) rules. If you put in the effort and are consistent in taking the actions you have taken, you can achieve success.
6.How to create a weight loss program?
A good program for normalizing weight consists of several components and a series of sequential actions: for a good start, you need to choose the right, most suitable diet and become familiar with its rules. It may turn out that it is enough to reconsider, and perhaps slightly adjust, eating habits and develop a new plan of action. If you can’t make up your mind, you should make an appointment with a nutritionist; you will definitely need two more ingredients: motivation (will help you start losing weight and will support you in moments of doubt) and perseverance (the desire to go all the way); you should be patient and not rush to conclusions, it is possible that you will have to wait for the results of losing weight; you must not forget about regular exercise; diet and physical activity must be included in the daily routine; psychologically tune in to the desired result - weight loss; when the effect is achieved, you do not need to abruptly stop following the rules; the achieved weight indicators still need to be maintained for a long time.
Broca's formula
Ideal weight for men = (height in centimeters – 100) · 1.15. Ideal weight for women = (height in centimeters – 110) · 1.15.
Example: Ideal weight for a woman 170 cm tall = (170 – 110) · 1.15 = 69 kg.
Broca-Brugsch formula
The previous formula was modified taking into account body type and non-standard height.
So, hypersthenics add 10% to the form, and asthenics subtract 10%. As for height, now it is proposed to calculate as follows (X is height in centimeters): less than 165 cm: X - 100 165-175 cm: X - 105 more than 175 cm: X - 110.
Already in this form the result is more optimal. So, a girl with a normosthenic physique and a height of 168 cm should weigh: 168-105 = 63 kg.
How to calculate ideal weight using Broca's formula
This method of determining normal weight indicators is known to most as “height minus 100”, while the main parameter is taken in centimeters, but the formula itself is more accurate and requires taking into account the person’s gender:
- The weight norm for women in kilograms is “(height (cm) - 100) * 0.85.”
- The weight norm for men is calculated as “(height (cm) - 100) * 0.9".
Broca's formula is not universal - it is not suitable for very petite (up to 155 cm) or tall (from 170 cm) people. It does not take into account indicators that affect the qualitative composition of the body: weight of muscles, fluid, bone tissue. According to experts, there is no point in calculating normal weight using Brock’s formula:
- pregnant women (the weight of the child, placenta, amniotic fluid is added);
- nursing (breasts are heavier due to milk);
- bodybuilders (muscle is heavier than fat);
- adults over 50 and teenagers under 18.
Other indices for determining normal weight
Breitman index. Normal body weight is calculated using the formula - height [cm] • 0.7 - 50 kg.
Bernhard index. Ideal body weight is calculated using the formula - height [cm] • chest circumference [cm] / 240.
Davenport Index . A person's mass [g] divided by height [cm] squared. An increase above 3.0 indicates the presence of obesity (obviously, this is the same BMI, only divided by 10).
Oder index. Normal body weight is equal to the distance from the crown to the symphysis [cm] • 2 - 100.
Noorden index. Normal weight equals height [cm] • 420/1000.
Tatonya index . Normal body weight = height − (100 + (height − 100) / 20)
In clinical practice, body mass index is most often used to assess body weight.
We must not forget that body weight also depends on a person’s age. The following chart will also help you determine your weight category.
How to calculate ideal female weight using Broca's index
so simple
It is believed that a woman's ideal weight is fixed when she reaches 18 years of age. And this number of kilograms should serve as a guide for the young lady for the rest of her life. In fact, only a few manage to maintain ideal parameters through a balanced diet, proper metabolism and regular physical activity.
But weight also depends on other parameters. That’s why today the editors of “So Simple!” will demonstrate the relationship between weight and height for each female body type. We will also tell you how to calculate your correct weight as you age.
Weight table of academician A.A. Pokrovsky
You can also use a table developed by the Soviet biochemist, academician A.A. to determine normal body weight, taking into account gender, age and body constitution. Pokrovsky Normal body weight at the age of 25-30 years (according to A. A. Pokrovsky)
| Height cm | Men, kg | Height cm | Women, kg | ||||
| Narrow chest | Normal rib cage | Wide chest | Narrow chest | Normal rib cage | Wide chest | ||
| 155.0 | 49.30 | 56.00 | 62.20 | 152.5 | 47.80 | 54.00 | 59.00 |
| 157.5 | 51.70 | 58.00 | 64.00 | 155.0 | 49.20 | 55.20 | 61.60 |
| 160.0 | 53.50 | 60.00 | 66.00 | 157.5 | 50.80 | 57.00 | 63.10 |
| 165.0 | 55.50 | 61.70 | 68.00 | 160.0 | 52.10 | 58.50 | 64.80 |
| 162.5 | 57.10 | 63.50 | 69.50 | 162.5 | 53.80 | 60.10 | 66.30 |
| 167.5 | 59.30 | 65.80 | 71.80 | 165.0 | 55.30 | 61.80 | 67.80 |
| 170.0 | 60,50 | 67.80 | 73.80 | 167.5 | 56.60 | 63.00 | 69.00 |
| 172.5 | 63.30 | 69.70 | 76.80 | 170.0 | 57.80 | 64.00 | 70.00 |
| 175.0 | 65.30 | 71.70 | 77.80 | 172.5 | 59.00 | 65.20 | 71.20 |
| 180.0 | 68.90 | 75.20 | 81.20 | 175.0 | 60.30 | 66.50 | 72.50 |
| 182.5 | 70.90 | 77.20 | 83.60 | 177.5 | 61.50 | 67.70 | 74.90 |
| 185.0 | 72.80 | 79.20 | 85.20 | 180.0 | 62.70 | 68.90 | 73.70 |
Note. At the age of over 30 years, it is permissible to increase weight compared to the table for men by 2.5 - 6 kg, for women - by 2.5 - 5 kg.
The influence of body weight on human health
It is believed that weight directly affects a person's health, but in reality, health and life expectancy are more closely related to body composition.
Conventionally, we can distinguish 2 main components - fat and muscle mass (muscles, bones, organs and water). It's important to understand how body composition affects your health and learn how to optimize it.
A person's weight can be influenced by many factors: environment, family history and genetics, metabolism, behavior and habits. Although some factors, such as family history, are beyond your control, you can make positive lifestyle changes to lose weight and maintain a healthy weight. These include a healthy eating plan and increased physical activity.
People who are preobese, obese, or underweight are susceptible to health problems. A healthy weight reduces your risk of developing diseases.
Egorov-Levitsky table
The table shows the maximum weight for this height.
Maximum permissible body weight
| Height, cm | 20–29 years old | 30–39 years old | 40–49 years old | 50–59 years old | 60–69 years old | |||||
| husband. | wives | husband. | wives | husband. | wives | husband. | wives | husband. | wives | |
| 148 | 50,8 | 48,4 | 55 | 52,3 | 56,6 | 54,7 | 56 | 53,2 | 53,9 | 52,2 |
| 150 | 51,3 | 48,9 | 56,7 | 53,9 | 58,1 | 56,5 | 58 | 55,7 | 57,3 | 54,8 |
| 152 | 51,3 | 51 | 58,7 | 55 | 61,5 | 59,5 | 61,1 | 57,6 | 60,3 | 55,9 |
| 154 | 55,3 | 53 | 61,6 | 59,1 | 64,5 | 62,4 | 63,8 | 60,2 | 61,9 | 59 |
| 156 | 58,5 | 55,8 | 64,4 | 61,5 | 67,3 | 66 | 65,8 | 62,4 | 63,7 | 60,9 |
| 158 | 61,2 | 58,1 | 67,3 | 64,1 | 70,4 | 67,9 | 68 | 64,5 | 67 | 62,4 |
| 160 | 62,9 | 59,8 | 69,2 | 65,8 | 72,3 | 69,9 | 69,7 | 65,8 | 68,2 | 64,6 |
| 162 | 64,6 | 61,6 | 71 | 68,5 | 74,4 | 72,7 | 72,7 | 68,7 | 69,1 | 66,5 |
| 164 | 67,3 | 63,6 | 73,9 | 70,8 | 77,2 | 74 | 75,6 | 72 | 72,2 | 70 |
| 166 | 68,8 | 65,2 | 74,5 | 71,8 | 78 | 76,5 | 76,3 | 73,8 | 74,3 | 71,3 |
| 168 | 70,8 | 68,5 | 76,3 | 73,7 | 79,6 | 78,2 | 77,9 | 74,8 | 76 | 73,3 |
| 170 | 72,7 | 69,2 | 77,7 | 75,8 | 81 | 79,8 | 79,6 | 76,8 | 76,9 | 75 |
| 172 | 74,1 | 72,8 | 79,3 | 77 | 82,8 | 81,7 | 81,1 | 77,7 | 78,3 | 76,3 |
| 174 | 77,5 | 74,3 | 80,8 | 79 | 84,4 | 83,7 | 83 | 79,4 | 79,3 | 78 |
| 176 | 80,8 | 76,8 | 83,3 | 79,9 | 86 | 84,6 | 84,1 | 80,5 | 81,9 | 79,1 |
| 178 | 83 | 78,2 | 85,6 | 82,4 | 88 | 86,1 | 86,5 | 82,4 | 82,8 | 80,9 |
| 180 | 85,1 | 80,9 | 88 | 83,9 | 89,9 | 88,1 | 87,5 | 84,1 | 84,4 | 81,6 |
| 182 | 87,2 | 83,3 | 90,6 | 87,7 | 91,4 | 89,3 | 89,5 | 86,5 | 85,4 | 82,9 |
| 184 | 89,1 | 85,5 | 92 | 89,4 | 92,9 | 90,9 | 91,6 | 87,4 | 88 | 85,9 |
| 186 | 93,1 | 89,2 | 95 | 91 | 96,6 | 92,9 | 92,8 | 89,6 | 89 | 87,3 |
| 188 | 95,8 | 91,8 | 97 | 94,4 | 98 | 95,8 | 95 | 91,5 | 91,5 | 88,8 |
| 190 | 97,1 | 92,3 | 99,5 | 95,6 | 100,7 | 97,4 | 99,4 | 95,6 | 94,8 | 92,9 |
Many consider this table to be the most comprehensive and balanced approach to determining the presence of excess weight.
Main categories
Conventionally, a person’s weight is divided into 4 categories, which are calculated using the body mass index (BMI).
It is a useful indicator of overweight and obesity. It is calculated based on your height and weight. Although BMI (aka Quetelet index) can be used for most people, it has some limitations:
- it may overestimate body fat in athletes and muscular people;
- it is not suitable for disabled people and pregnant women;
- it may underestimate body fat in older people and those who have lost muscle mass.
Shortage
Underweight is characterized by a BMI <18.5. Experts consider low weight to be the most dangerous for health, because... in this case, the risk of mortality from diseases increases.
Low weight can be dangerous to your health.
Possible problems:
- insufficient shock absorption of organs;
- suppressed immune health;
- impaired ability to recover from illness;
- insulin resistance and poor glycemic control;
- bone fragility;
- disruption of normal hormonal function.
Norm
With normal weight, BMI = 18.5-25. Such people have an ideal weight associated with the longest life expectancy, the lowest incidence of disease, and are also perceived as more physically attractive than people with BMI in the higher or lower ranges.
Obesity
Overweight people have a BMI of 25-30. This is an intermediate stage between normal body weight and obesity. This condition is characterized by an increase in weight by 15-20% of normal. The disease is manifested by fatty deposits, shortness of breath, increased sweating, increased blood pressure, and impaired glucose tolerance.
Pre-obesity is an intermediate stage before obesity.
Obesity
For obesity, BMI>30.
Problems with obesity:
- shorter life expectancy;
- high blood pressure;
- glucose dysregulation and diabetes;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;
- increased risk of various types of cancer;
- shortness of breath and other respiratory disorders.
Physical activity should be part of a comprehensive weight management program because it promotes weight loss in preobese and obese people.
Features of determining normal weight for women
Using the Quetelet index Ideal body weight is associated not only with a person’s body type, but also with his age. One of the calculation options is the Quetelet index. So, for example, for girls 15-18 years old it is equal to the following values: for asthenics - 315 g, normosthenics - 325 g, hypersthenics - 355 g for every 1 cm of height. For girls 19-25 years old, the Quetelet index will be equal to, respectively: 325 g, 345 g and 370 g. For women 26-39 years old – 335 g, 360 g and 380 g per 1 cm of height. In addition, for those girls and women whose height is below 1m 60 cm, the weight should be 10-15% less. This is especially necessary for girls under 20 years old.
Lorenz formula Ideal weight of a woman = (height in centimeters – 100) – (height in centimeters – 150) / 2. Or a simplified version: X/2-25, where X is height in centimeters. Example: Ideal weight for a woman 165 cm tall = (165 – 100) – (165 – 150) / 2 = 65 – 15/2 = 57.5. The obvious simplicity of the method has both a positive and a negative side. The Lorenz formula does not differentiate people by type (asthenic, normosthenic, hypersthenic), and does not take into account age and the presence of physical activity. The result can be considered quite average. Please note that this formula was developed only for women and is in no way suitable for the stronger sex. At first glance, it is too demanding on weight compared to the improved Brocca formula and rather indicates exactly the ideal weight when you were eighteen years old. However, it is completely consistent with the body mass index (BMI), so it is quite possible to use it. If you are upset by the proposed numbers, then just forget about it and use another formula. By the way, it still won’t suit women taller than 175 cm
Features of the figure The percentage of fat in a woman's body is of great importance. Trying to create an ideal body, like the professionals, with 5% body fat is unrealistic, since these values are achieved with the help of special diets and special pharmacology. But 10% is ideal. If we compare two girls with the same weight of 60 kg and different percentages of body fat - 10 and 20%, then the first will have 6 kg more muscle tissue than the second. The appearance of both beauties will be strikingly different! If girls with an hourglass figure just need to lose weight so that their ideal body proportions become visible, then “pears” need to focus on strength training in order to slightly build muscle on their narrow shoulders, and “apples” need to give preference to aerobic exercise and exercises for lower body.
Psychologists strongly advise ignoring BMI and other standardized indices. If your reflection makes you happy, but the test showed a slight deviation from the norm, do not be upset about it. It is difficult not to notice excess weight, and a harmonious figure does not require additional confirmation. Use your own common sense when critically assessing appearance. And don't put too much emphasis on dry standard numbers, which are very relative.
Ideal weight according to Broca's formula
I don’t know about you, but I’ve never been good at math, so calculating my ideal weight using complex formulas has always been a big problem for me.
However, my torment ended only when I became acquainted with Brock’s formula, which allows me to calculate ideal weight indicators for different weight categories without much hassle.
However, first, it is better to get acquainted with the main body types, since this factor also affects the final result of the formula.
Three body types:
- Asthenic: elongated face, thin nose, long and thin neck, narrow shoulders, flat and narrow chest, long arms and legs, poorly developed muscles; with the asthenic type there is a minimal tendency to be overweight.
- Normosthenic: harmonious figure, thin waist and slender legs; usually average weight.
- Hypersthenic: heavy and wide bones, wide and short chest, slightly shortened arms and legs, voluminous shoulders; height, usually below average; there is a high tendency to be overweight.
Method for determining body type:
Determining your body type is very simple: you just need to measure your wrist at the narrowest point.
Results for women:
- up to 14 cm - asthenic type;
- from 14 to 18 cm - normosthenic type;
- from 18 cm - hypersthenic type.
Results for men:
- up to 17 cm - asthenic type;
- from 17 to 20 cm - normosthenic type;
- from 20 cm - hypersthenic type.
There is another way to determine belonging to a certain body type - the ratio of height and leg length. Leg length is measured from the tuberosity of the femur (opposite the hip joint) to the floor.
The ideal length should match the following parameters:
- asthenic type: legs are 2-4 cm longer than half the height;
- normosthenic type: legs are 4-6 cm longer than half the height;
- hypersthenic type: legs are 6-9 cm longer than half the height.
Ideal weight according to Broca's formula
So, Broca’s formula (the French surgeon and anthropologist Paul Broca developed it back in 1871) sounds like “height minus 100” and is by far the simplest and fastest way to determine the amount of excess weight.
The calculation formula is simple:
- “height minus 100” (for height up to 165 cm)
- “height minus 105” (with height 166–175 cm)
- “height minus 110” (for height over 175 cm)
Why then do you need information about your body type?
The author of the formula clarifies:
- for asthenics, the resulting value should be reduced by 10%;
- for hypersthenics - increase by 10%;
- normosthenics do not need to add or decrease anything.
As an example: 3 women of the same height (165 cm), but different builds. This means, according to the formula “height minus 100” - 65 kg. But, based on the constitution of each of them, the final results will differ from each other: asthenic type: 65 kg - 10% = 58.5 kg; normosthenic - 65 kg; hypersthenic: 65 kg + 10% = 71.5 kg.
There is one more indicator that should be taken into account when calculating weight using Brock's formula - age. Experts claim that Broca's index is ideal only for women 40-45 years old. Girls 20-30 years old need to reduce the resulting figure by 10%, and ladies over 50 need to increase it by 5-7%.
And yet, experts assure, no formulas can reflect the individual characteristics of a person and his state of health, which means you should not blindly believe the results obtained. Calculating the ideal weight using Brock's formula is not worth it, for example, for pregnant women, people under 18 years of age, bodybuilders and athletes who are purposefully building muscle mass.
Since the advent of Brock's formula, science has developed modern methods for determining recommended weight. One of them is bioimpedance analysis of body composition. It can be used to determine the ratio of water, fat and muscle in the human body. In addition, this technique allows you to very accurately determine excess and lack of body weight. Based on the data obtained, specialists decide to review a person’s diet and the need to increase his physical activity.
Methods for calculating body fat percentage
Body analysis provides insight into your health.
The methods range from simple and fast to complex and highly accurate. Some calculations cannot be done on your own and require a medical professional to carry out the analysis and interpret the results. The most common methods for calculating body fat percentage are:
- Thickness of the skin fold. A method of measuring subcutaneous fat by pinching the skin and using a caliper to measure the thickness of the skinfold. The measurements are entered into a formula used to estimate body fat percentage. This method is fast, accessible and inexpensive. But its ability to accurately depict overall body characteristics is limited because it only measures subcutaneous fat.
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). This method uses electrical impulses to determine your lean body mass level. BIA machines range from simple home scales with electrodes under each foot to more complex devices with electrodes for the arms, legs and other parts of the body. The devices send tiny electrical impulses through the body and measure how quickly they return.
- Underwater weighing. First, the mass is measured outside the water on a scale, then determined when a person is completely immersed under water. Because muscle tissue is denser than fat tissue, the difference in weights can be used to determine body density. The accuracy and reliability of this method are high, but it is not always accessible and convenient.
- Air displacement plethysmograph. The air displacement method for assessing body composition is a more recent development. Using a similar principle to underwater weighing, the device, called BodPod, measures body weight and air displacement to determine body density. It then calculates body composition and indicates the percentage of lean body mass and fat mass. It is fast, safe and accurate, but requires access to a machine and an experienced physician.
- Ultrasound. Used for accurate assessment of adipose tissue. The portable device is capable of quickly assessing body composition. The method is reliable and accurate.