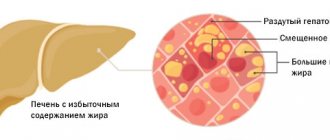
World Diabetes Day is celebrated on November 14th. This is an endocrine disease that is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. With diabetes, the body's metabolism is disrupted, blood vessels and the nervous system are affected, and other organs are affected. Elena Khilko, an endocrinologist at the 14th central district clinic of the Partizansky district, told a correspondent of the Minsk-News agency about the main symptoms and causes of diabetes.
“At least 25% of people suffering from diabetes do not know about their disease: they calmly go about their business, do not pay attention to the symptoms, and at this time the disease gradually destroys their body,” explains the interlocutor. — Diabetes mellitus is of several types: 1st, 2nd, gestational (diabetes mellitus in pregnant women) and specific. Each type has characteristic symptoms, but there are also common signs.
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Sudden weight loss
This is one of the first signs of a developing disease, which should alert you. You seem to be eating as usual, not on a strict diet and not torturing yourself with daily exercises in the gym, but at the same time you are melting right before your eyes. Losing weight can be exciting at first. But the joy will be short-lived, since rapid weight loss is a sure sign of some kind of disease. In the case of diabetes, weight is lost due to a lack of insulin needed by the body, which breaks down food and facilitates the absorption of valuable substances and calories.
Thirst
Constant dry mouth does not go away even when consuming large volumes of liquid. You are thirsty all the time. You drink water, tea, juices - whatever you like and catches your eye, but the result is zero: you still feel thirsty. And it doesn’t matter whether it’s a hot summer or a frosty winter.
Incredible fatigue
Waking up one “beautiful” day, you suddenly realize that you cannot get out of bed. Loss of physical strength, weakness, exhaustion are some of the sure symptoms of diabetes. There is nothing surprising in the fact that the body loses vitality, because, as already mentioned, due to a dysfunction in the production of insulin, the nutrients necessary for the body are not absorbed, you lose weight, and along with it, strength.
Constant feeling of hunger
You suddenly have a brutal appetite, you greedily pounce on food, although only an hour has passed since a hearty lunch. Even when you eat a lot of food, you are constantly hungry. The cause of increased appetite is metabolic disorders.
Frequent urination
You constantly want to go to the toilet. A similar situation occurs with cystitis. But in this case, the cause is not kidney inflammation, but the body’s inability to cope with high blood sugar. Attempts to remove excess sugar lead to a constant urge to urinate.
“Sand” in the eyes and blurred vision
Suddenly your vision begins to double or you feel foggy. Vision deteriorates due to dysfunction of the retina due to increased blood sugar.
Non-healing wounds and abrasions
Have you noticed that even small wounds and abrasions do not heal for a very long time and cause you a lot of inconvenience and discomfort? Or are you bothered by itching in some places of the body, often intimate? Women usually go to a dermatologist or gynecologist with these symptoms, but they can be signs of diabetes.
How to know if you have high blood sugar
Only by laboratory means, that is, you need to take a blood test for sugar. This test will accurately determine the presence of the disease even without obvious symptoms. Self-control is also needed in order to timely identify prediabetes - a condition in which carbohydrate metabolism is impaired, but not yet to the extent that the pathology develops into diabetes mellitus.
What is diabetes like: who are you - thin or fat?
The disease, otherwise called diabetes mellitus or diabetes, is manifested by an increase in blood glucose levels.
Type I diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, pancreatic cells reduce insulin production. The disease often manifests itself in childhood and adolescence and is hereditary. The disease is treated by constant administration of insulin, which is why this type of diabetes is called insulin-dependent. Since patients with this form are rarely overweight, and some, once ill, lose weight sharply, type I diabetes is called “diabetes of the skinny.”
Type II diabetes
Type II of the disease occurs, as a rule, in obese people with normal pancreas function. The insulin produced is not enough for the patient’s large body weight—and this is how relative insulin insufficiency occurs. This type of diabetes is called non-insulin dependent and “fat man diabetes”. The disease develops mainly after 40 years. If a patient loses weight at the initial stage of the disease, he recovers.
Diabetes mellitus in pregnant women occurs when a woman’s glucose concentration increases precisely while she is expecting a child. After childbirth, the signs of diabetes disappear.
What are the dangers of losing weight?
A sharp change in a patient's body weight downward carries many health hazards.
First of all, with sudden weight loss, there is a disruption of metabolic processes that ensure normal human life, and secondly, the development of degeneration of muscle and fat tissues is observed.
In addition, a decrease in body weight can threaten the appearance of severe intoxication. In the patient's plasma, there is an increased accumulation of products of incomplete breakdown of fat and muscle tissue. The body is not able to fully cope with the process of removing decay products, which negatively affects the condition of all organs and their systems. The negative impact of toxins is especially strong on the brain, which can ultimately lead to death.
When a diabetic loses body weight, the digestive system begins to suffer first. The patient exhibits disturbances in gastric motility, such a disturbance is accompanied by the appearance of:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- pain;
- feelings of heaviness and some others.
All of these changes affect the functioning of the pancreas and gall bladder. For this reason, the appearance and progression of pancreatitis and gastritis become frequent companions of patients suffering from diabetes and rapidly losing weight.
New Information: Signs and Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
As a result of metabolic processes disturbances and the accumulation of large amounts of toxins in the blood plasma, it leads to changes in water-salt metabolism. This violation provokes a malfunction in the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
Such pathological changes lead to serious consequences:
- Kidney failure.
- Hepatitis A.
- Urolithiasis, etc.
In addition to these disorders and pathologies, a diabetic who is rapidly losing body weight may experience the following complications:
- the appearance and progression of hypoparathyroidism;
- the formation of severe edema;
- increased fragility of hair and nail plates appears, which develops against the background of a lack of vitamins and mineral compounds in the body;
- development of hypotension;
- problems with memory and concentration.
In addition to these problems, diabetics with weight loss are accompanied by psychological disorders. Patients become irritable, sometimes aggressive, and there is a tendency to develop depressive states.
It is impossible to cure diabetes, but it is possible to prevent complications. To do this, you must strictly follow the recommendations of your endocrinologist and regularly take prescribed medications.
If there is a need to reduce body weight, this process should be strictly controlled by the attending physician.
Causes of diabetes
Diabetes is often inherited. There are families where the disease occurs in every generation. In 95% of cases, hereditary diabetes mellitus is type I. Type II occurs as a result of hereditary pathologies of the liver, kidneys and thyroid gland. Genetic diabetes may not appear until it is triggered by stress, pregnancy, infection, excessive exercise or weight gain.
Excess weight
It is believed that diabetics are prone to obesity, but people confuse cause and effect. Excess weight provokes diabetes, and not vice versa. Those who simultaneously suffer from overweight, atherosclerosis and hypertension often get sick. People with a body index of more than 30 kg/m2 and apple-type obesity, when fat is deposited on the abdomen, are at greatest risk. Obese people are usually prone to type II diabetes.
Age
Over the years, pancreatic function declines and insulin production decreases. According to scientific research, the risk of diabetes doubles with each passing decade. By age 80 it is 80%. Older people mainly develop type II diabetes.
Hormonal diseases
Diseases of the pancreas provoke the death of cells that produce insulin, and, as a result, diabetes. Can cause disease and deficiency of the thyroid gland, leading to hormonal imbalance in the body and obesity. Such people develop type I and type II diabetes.
Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases can also be the cause: rubella, mumps, measles, hepatitis. These diseases are a trigger for diabetes for people with a hereditary predisposition. Complications of infections that cause dysfunction of the endocrine glands and lead to type I and type II diabetes are dangerous.
So “horror stories” about the dangers of eating sweets are outdated. There is no direct relationship between the love of sugar and the occurrence of diabetes. Cakes and pastries cause excess weight, but you can get sick by overeating on butter, fatty sausage, rolls or fast food. Only the onset of obesity is important, and its nutritional cause does not matter.
Basic principles of nutrition for sudden weight loss due to type 2 diabetes
Nutrition plays a huge role in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. If it is organized correctly, taking into account all the recommendations and requirements of the attending physician, then the course of the pathology is much more favorable.
In order for nutrition to be rational and meet all requirements, its completeness and calorie content should be controlled. In addition, the food ration during the day should be distributed in accordance with the loads placed on the body and the periods of maximum glucose-lowering effect from the drugs used in antidiabetic therapy.
This approach to nutrition will ensure a normal level of sugar in the blood plasma for a diabetic, which will be as close as possible to the physiologically normal level.
Additionally, you should ensure that the food consumed by a sick person is varied and tasty.
A special balanced diet and recipes for type 2 diabetics help gain weight if you have diabetes and stop the process of losing weight.
The amount of carbohydrates in the diet should be strictly balanced. When developing a diet, preference is given to foods with a low glycemic index. This is due to the fact that the lower this indicator, the less the food product releases sugars into the blood.
The list of recommended products includes the following:
- Legumes.
- Whole grain cereals.
- Low-fat yogurt.
- Milk with a fat content of no more than 2%.
- Green bananas.
- Apples.
- Walnuts.
- Figs
- Dried apricots.
- Tomatoes and cucumbers.
- Cabbage, lettuce, green peppers and radishes.
It is best to eat food in small portions, using the principle of fractional meals, the number of meals per day should be up to 5-6 times.
New information: Diabetic foot prevention
In order to begin to gain weight and get rid of thinness, it is recommended that malnourished patients introduce natural honey and goat milk into their diet.
The menu must be designed in such a way that the food contains about 25% fat, about 15% protein, and about 60% carbohydrates.
If a woman suffering from diabetes is pregnant, then the proportion of proteins in the diet should be increased to 20%. At the same time, the proportion of fats in consumed foods should be reduced. This requirement also applies to elderly patients.
The carbohydrate load should be distributed evenly throughout the day.
The amount of calories for lunch, dinner and breakfast should be about 25-30% of the daily calorie intake for each meal; second breakfast should account for about 10-15% of the daily calorie intake.
In order to recover from sudden weight loss due to diabetes, you should consult with an endocrinologist, who will advise how to adjust your diet to combat diabetic weight loss. The doctor will first conduct an examination to identify all the factors contributing to weight loss, this will avoid further aggravation of the situation and prevent the development of pathologies.
Bottom line
Having found out why people with type 2 diabetes and type 1 diabetes lose weight, we can conclude that when the first signs of the disease appear, including sudden weight loss, it is necessary to urgently seek help from a specialist.
Despite the fact that a large number of people die in the world every year from this terrible disease and its complications, it can and must be fought. With proper treatment and a well-chosen diet, diabetics have the opportunity to feel good, lead a normal lifestyle, work and even play sports.