Why pump up your lower back?
Athletic achievements in almost any sport depend on the development of the lumbar muscles. When performing exercises, tricks and other sports elements, a colossal load falls on the spine.
All coaches know this well. And that is why performing athletes regularly and persistently pump up their lower back muscles. This creates a natural muscle corset that protects the spine from possible injuries.
In strength sports such as powerlifting, bodybuilding, weightlifting, CrossFit, etc., the spine is subjected to compression loads every workout.
Without a strong lower back, the risk of injury increases significantly. Moreover, for this it is not necessary to lift heavy weights, it is enough just to have weak lumbar muscles.
Lower back exercises are one of the main elements of training methods in all strength sports.
Ordinary gym goers who “work out for themselves” often naively believe that they don’t have to work out their lumbar muscles. After all, they are not going to train with a heavy barbell or compete.
But the fact is that the spine is anatomically predisposed to injury and damage.
This can happen not only when lifting heavy objects, but also during sudden, awkward movements. Or simply over time, from wear and tear of the osseous-ligamentous apparatus of the spine.
With age, the back muscles begin to atrophy and cease to perform one of their main functions - to support the spine in its natural position. Therefore, back health is directly related to its muscle development.
This means that pumping up the lower back muscles and maintaining their tone throughout life is important for everyone! And regular strength exercises come first here.
Exercise Atlas: Lower Back
You need to enable JavaScript to vote
Lower back and lumbar muscles
In the first part, “Atlas of Exercises: Back,” we talked about the muscles of the upper back. In the second part we will look at the muscles of the lower back, the muscles of the lower back, as well as the deep back muscles that are important for proper posture.
Strong muscles in the spine and lower back not only provide additional protection to the torso during many exercises, they are also important in creating that coveted and masculine “triangle” silhouette.
Straightening your back and correcting your posture - exercises and techniques. How to learn to maintain a sporty posture with wide open shoulders?
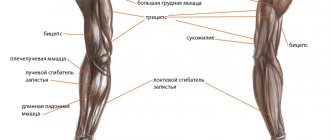
A short anatomy lesson
The deep back muscles consist of long, short and subvertebral fascicles. The three largest long muscles are marked in the figure. All three are located on either side of the spine and stretch from the back of the head to the tailbone.
The iliocostalis muscle is located farthest from the vertebrae (1), the longissimus muscle is located in the middle (2), the spinalis muscles are located exactly in the middle of the back (3).
Each muscle consists of several muscle bundles: those close to the skull, located directly on the neck, lying in the middle of the back, located in the lower back. They are all responsible for protecting and moving the spine.
Seated row of block to the waist
A basic exercise that involves a large muscle mass, especially the pectoral and latissimus muscles. One of the best for giving your back visual width. The position of the handle determines which muscle bundles are more involved in the work.
When performing an exercise for the internal back muscles, hold the handle with both hands, with your palms facing each other. Keep your back straight; if you can't do this, use less weight.
Deadlift with dumbbells
Lean forward, back and legs straight, dumbbells in your hands, arms hanging down freely. Slowly, keeping your back straight, straighten up. To make the exercise more challenging, perform it while standing on one leg, but with lighter dumbbells.
Single leg lift on a bench
Lie on the bench with your stomach, transfer your body weight to your bent knee, keep your other leg straight and suspended. Then lift that leg as high as possible, pause at the top, and slowly lower it down. Repeat for the second leg.
Back straightening (hyperextension)
Fix your legs in the machine, fold your arms in front of your chest. Place your body weight on your hips. From this position, keeping your back straight, slowly rise up. To make the exercise more challenging, rotate your torso as you lift.
Raising straight arms to the sides while lying down
Lie on the bench on your stomach, so that your torso above your hips is unsupported. Hold onto the bench with your toes. Straighten your arms to the sides, then slowly twist your torso to the left, brace yourself, then twist to the right.
Raising the body while lying on the ground
Lie on your stomach, arms extended behind your back at the level of your buttocks
Very slowly and carefully lift your shoulders up as high as possible, fixate at the top point, then return to the starting position
Flying on the ground
Lie on your stomach with your legs straight and slightly raised up. Straighten your arms and extend them in front of you, then slowly lift your upper torso, spreading your arms out to the sides while alternately bending your knees. Do one set to failure.
One-arm pull-down
Perform the exercise by holding the handle with one hand, with your palm facing inward.
Remember that the recommended exercises for the back muscles (both upper and lower) do not need to be done all at once and in one workout. This is just a recommendation for various exercises.
Best exercises
There are not so many truly effective exercises for the lumbar muscles.
Basically these are various options and modifications of just 3 movements:
- Hyperextension
The most effective and at the same time simple and accessible exercise for the lower back.
Here the load is more isolated and targeted. Additionally, the gluteal and hamstring biceps are involved in the work.
They begin to master the exercise with their own body weight. Therefore, this movement is suitable for absolutely everyone, regardless of the level of physical fitness.
- Bent-overs with a barbell on your shoulders
The next in degree of complexity, it involves the use of weights and the presence of a certain muscle tone of the lumbar muscles. Therefore not suitable for beginners.
The same muscle groups work - lower back, buttocks, hamstrings.
By the way, an interesting modification of this exercise is bending over with a barbell on your shoulders while sitting. Quite a rare exercise for the gym, but quite popular among weightlifters.
- Deadlift
The deadlift is a complex basic exercise that involves about 70% of the muscles of the entire body (more than 400 muscles contract at the same time).
In terms of the unique impact on the human body, only squats can be compared with deadlifts.
The deadlift works the legs, buttocks, back, abs and forearms.
This exercise is valuable for the back muscles because it simultaneously pumps up all of its muscle groups:
- trapezius (responsible for the health of the cervical spine)
- lats (thoracic region)
- psoas muscles (lumbar)
But as effective as deadlift is for comprehensive back training, it is also dangerous for injuries. Especially if the execution technique is very poor.
This exercise is definitely not suitable for beginners. And even advanced gym-goers should be careful when performing this movement.
It is better to have the equipment controlled by someone who is good at it. For example, a coach.
How to do exercises for the trapezius muscles of the back
These exercises load the trapezius muscles Comparative electromyographical investigation of the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius muscles during five pull exercises; Effect of grip width on electromyographic activity during the upright row; Surface electromyographic analysis of exercises for the trapezius and serratus anterior muscles; ACE-SPONSORED RESEARCH: What Is the Best Back Exercise? the best thing.
Barbell row to the chin
Grab the barbell with Effect of grip width on electromyographic activity during the upright row. 1.5–2 times wider than shoulders. As you exhale, pull it up to the level of your collarbones, pointing your elbows up. Lower back down and repeat.
Do 3-5 sets of 8-10 reps.
Reverse dumbbell swings lying on your stomach
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, take dumbbells, turn your hands back to front. As you exhale, spread the dumbbells to the sides, while simultaneously turning your hands with your thumbs up. Lower back down and repeat.
Do 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
IYT climbs
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, hold dumbbells in your hands. As you exhale, raise your arms above your head with the backs facing up and then lower them to the starting position.
Now raise your arms up diagonally so that your posture resembles the letter Y, with your palms facing upward with your thumbs. Lower to the starting position.
Then spread your arms out to the sides with your thumbs up so that your body resembles the letter T. Lower to the starting position. This was one approach.
Do the same 3-5 times for 4-5 repetitions.
Recommendations for lower back training
Before training, be sure to warm up.
This will warm up the muscles and ligaments and prepare them for the upcoming loads.
The lumbar muscles are strong, but medium and light weights are used to target them, with an emphasis on correct execution technique and smooth movement.
Rep Range:
- for hyperextension - 10-20 repetitions in 1 approach
- for slopes - 8-15
Optimal training frequency:
- for beginners – 3 times a week
- for intermediate level – 2 times
Beginners usually use hyperextension.
The average level alternates 2 exercises - in 1 lesson hyperextension (2-3 sets of 15-20 times), in 2 - bending over with a barbell (or, as an option, deadlift).
Bends are performed in 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions, deadlifts are performed in 3 sets of 6-10 repetitions.
As for the advanced level, they usually train the lower back once a week, performing 1-2 exercises on it.
You can also pump up your lower back at home. For this, as a rule, the “Boat” exercise is used.
At the beginning, it is performed with your own body weight, and later pick up a light weight. The main thing is to make smooth and controlled movements.
There are many options for implementation. These are lifts of opposite arms and legs, lifting the body with straight arms, with bent arms, and so on. Read more about how to replace hyperextension at home here.
How to pump up your lower back at home
Of course, you don't need to go to the gym to pump up your lower back , although it's much faster to do it there. But even at home there is a whole range of exercises necessary for the lower back that will effectively and safely allow you to achieve results.
At home, it is advisable to pump your lower back every other day to give it some rest and not overload it, so as not to harm your health.
We recommend reading: Carbohydrates after a workout
Work your lower back slowly for the first time, gradually increasing the load.
Make a plan and schedule for training every other day at the same time, following your diet and exercise routine. And also, knowing immediately what exercises you will perform and in what sequence.
Contraindications for lower back training
If you are just starting to train in the gym, it is better to sign up for several training sessions with a personal trainer to establish the correct exercise technique.
If you are at an advanced level, you may need help adjusting your bends or deadlifts.
But in any case, tell the instructor about problems with the spine, if any.
When training the lumbar muscles there are many contraindications and restrictions:
- Spinal curvatures (lordosis, kyphosis)
- Vertebral displacements
- Pinched nerve roots
- Intervertebral hernias and protrusions
All this often prohibits training the lumbar muscles.
This usually happens when back pain progresses. Doctors' help is needed here.
When the acute phase of the disease subsides, begin moderate loads, performing movements in a small amplitude.
However, if back problems are only in the initial phase, doctors strongly recommend going to the gym and pumping up your lower back. But correctly, competently and under the supervision of instructors.
Exercises on how to pump up your lower back at home or on a horizontal bar
Bend the torso forward. Take a lightly weighted barbell or a simple stick and bend your torso, keeping your back straight. Lower and rise slowly, fixing the load. Don't lift too much weight at first.
We recommend reading: How to start working out in the gym for a man
Squats with dumbbells. You can also do simple squats, but using dumbbells. Try to do squats not quickly as usual, but slowly, trying to put the load not on your legs, but on your spine.
Pull-ups on the bar. You need to pull yourself up not as usual, with your chin touching the bar, but on the contrary, pulling up the back of your neck and back. This exercise is the most effective for pumping up your lower back on the horizontal bar or at home. Find out what it is: gymnastics for the lower back.
Exercises to strengthen your back muscles
Why do you need to strengthen your back muscles? The answer to this question lies on the surface. First of all, you need to strengthen the core muscles, which include the long extensor muscles on the back. Along with your abdominal muscles, a trained core will give you the confidence to avoid injury when performing any strenuous exercise. Secondly, a trained, strong back is the key to the health of your spine. Thirdly, a trained back creates balance for the often over-inflated pectoral muscles, which in turn is fraught with injuries to the deltoid muscles of the shoulder joint.
The very first exercise you should include in your training program is hyperextension.
Classic hyperextensions are performed in a special simulator. Having rested your heels on special supports, we begin extensions, maintaining a slight deflection in the spine. At the top point of the amplitude, we avoid excessive lordosis - hyperextension of the spine. We make movements smoothly, without jerking. As you inhale, lower your body down for 2 counts, and as you exhale, lift your body up for one count. We do 15-20 repetitions. When the extensor muscles are sufficiently strengthened, you can use weights - pick up a disc, dumbbell or weight.
There are many variations of hyperextensions (on a fitball, on a horizontal bench, etc.). Some of them concentrate the load on the hamstrings and gluteal muscles; take this into account and when training to strengthen the back muscles, use hyperextensions specifically on the extensors of this part of the body.
Lower back pain: what causes it and what to do?
The most common cause of lower back pain is a sedentary lifestyle and poor development of the corset muscles, which are unable to support the spine. In addition, the cause may be various pathologies, excessive stress, or simply a sudden awkward movement that provoked pain. Most of these problems can be neutralized with lower back exercises.
What can cause lower back pain:
- staying in one position for a long time;
- weak back and core muscles;
- excessive loads or non-compliance with exercise technique;
- hypothermia of the body;
- rachiocampsis;
- osteochondrosis;
- large excess weight;
- improper diet and vitamin deficiency.
To prevent lower back pain from causing serious problems with the spine, it is necessary to perform special exercises for the lower back, which will help relieve discomfort, reduce pain, improve the health of the body and serve as a good preventive measure. It is not for nothing that the basis of rehabilitation after back injuries is physical therapy and gymnastics for the spine.
Why it is useful to perform exercises for the lower back:
- pain in the lower back is reduced due to muscle stretching and relaxation
- the spine is strengthened and its flexibility increases
- blood circulation increases, which saturates the joints and vertebrae with nutrients
- strengthens the corset muscles that support the spine
- posture improves
- improves the functioning of the heart and lungs
- hormonal levels are normalized
- the risk of hernia, osteochondrosis and other pathologies is reduced
- the functioning of the pelvic and abdominal organs improves
A set of exercises for lower back pain should include: muscle stretching exercises, muscle strengthening exercises. During exacerbations, tension in the muscles is observed, so first of all, they need to be relaxed - for this, a muscle stretching complex is performed. To prevent lower back pain, it is necessary to strengthen the muscles. When strengthening the back muscles, the load on the spine decreases, since a significant part of the load is taken on by the muscle corset.
Rules for performing exercises for the lower back
- You should not force the load and overload your lower back with exercises in order to achieve your goal faster. Start with light loads, gradually increasing the duration of exercise.
- Exercises for the lower back should be done with the load and amplitude that is comfortable for you. Do not make sudden jerks or movements while performing exercises for the lower back, so as not to aggravate the problem.
- One or two workouts will not help solve the problem; try to perform a set of exercises for the lower back on an ongoing basis. It will be enough to train 3 times a week for 15-20 minutes.
- If you have a cold floor or cold weather outside, then dress warmly and lay a rug or blanket on the floor to prevent your lower back from getting cold.
- Perform exercises on a hard surface: a bed or soft mat is not suitable. During exercises lying on your back, your lower back should be pressed to the floor.
- Do not forget about breathing while performing a set of exercises for lower back pain. The training should be accompanied by deep, even breathing; perform each static exercise for 7-10 breathing cycles.
- If while performing any exercises you feel discomfort in the lower back or spine, then it is better to skip such exercises. If during the exercise you feel acute pain, then in this case it is better to stop training altogether.
- You should not perform the proposed set of exercises for the lower back during pregnancy, after a spinal injury or with chronic diseases. In this case, consultation with a doctor is required.
- Remember that if you have some kind of chronic disease, then a set of exercises for the lower back must be selected individually. For example, for scoliosis, exercises to straighten the spine are indicated, and for osteochondrosis and hernia, exercises to stretch it.
- If discomfort in the lumbar region does not go away within a few weeks, consult a doctor. Lower back pain may be a sign of a serious illness. The sooner you begin the treatment process, the easier it will be to avoid irreversible consequences.