General rules
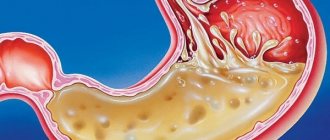
The basis of pancreatic disease is an inflammatory process with degenerative changes in the parenchyma of the organ, which in acute pancreatitis can lead to pancreatic necrosis , and in a chronic, often recurrent form - to the development of fibrosis of the parenchyma and sclerosis of the gland tissue. In this case, the digestive function of the gland (mainly proteins) is disrupted, and then the intrasecretory function, in which the insular apparatus is involved in the pathological process, which is manifested by a violation of carbohydrate metabolism and the development of hyperglycemia , glucosuria .
The main symptoms of the disease: nausea, an attack of pain (acute girdling or radiating to the left half of the lower back or chest), general weakness, bloating , diarrhea , vomiting, increased body temperature and, much less frequently, jaundice . Treatment of pancreatitis is complex, the most important component of which is nutritional therapy. Moreover, it is proper therapeutic nutrition that can normalize metabolic processes in the body, including the pancreas, and improve its function.
Diet for pancreatic disease, basic principles
A diet for pancreatic disease should, first of all, be aimed at reducing pain, reducing the secretory function of the pancreas, reducing hyperenzymemia , and restoring impaired metabolic . The basic principles of diet therapy for patients with acute/chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage include:
- hunger and parenteral nutrition with pronounced metabolic and clinical signs of the presence of an autolytic process in the pancreas;
- transferring the patient to a nutritious diet as soon as possible (especially regarding protein levels);
- gradual expansion of the diet by including new foods and dishes in the diet;
- a gradual increase in caloric intake and the volume of the daily diet as the diet expands;
- ensuring maximum protection of the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract from adverse factors.
Along with bed rest and drug treatment in order to reduce the secretion of enzymes of the stomach and pancreas, a patient with acute/chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage is prescribed a 2-3 day fast. During this period, it is allowed to drink non-carbonated Borjomi mineral water at room temperature, 250 ml fractionally 4-5 times - a total of 1-1.5 l/day and rosehip decoction (1-2 glasses).
From the 3rd day, in case of mild pancreatitis, patients are prescribed the pureed (first) version of Diet No. 5P . The diet is low-calorie (1500-1800 Kcal: 60-80 g of proteins (25 g of animal proteins), 50-60 g of fats, 200-300 g of carbohydrates), as gentle as possible, the daily diet includes products that provide the physiological norm of protein with a sharp limitation in diet of fats and easily digestible carbohydrates.
Refractory fats and simple carbohydrates (honey, sugar, confectionery, jam) are limited. Avoid foods that stimulate the secretion of pancreatic juice and contain a lot of fiber.
The menu includes dishes of semi-viscous, liquid and semi-liquid consistency; 50 g white crackers; 5–6 g of table salt: these are cereal soups with a weak vegetable broth or water (slimy or thoroughly pureed), cream soup made from well-cooked meat; steam cutlets, soufflé, quenelles; soft-boiled chicken eggs, egg white omelet (1-2 per week); steam pudding made from fresh cottage cheese; puddings/purees from steamed vegetables (cauliflower, zucchini, potatoes, carrots), pureed porridge with water, jelly, jellies, pureed fresh/dried fruit compotes, mousses with aspartame , fructose , weak tea, rosehip decoction; Butter is added to prepared dishes.
It is prohibited to introduce other foods and dishes into the diet. The drinking regimen for patients is 2 l/day of free fluid. Meals for pancreatic disease are fractional (6–8 times/day), the volume of food consumed in one serving is no more than 300 g.
After 5-10 days, when the exacerbation subsides, the patient is transferred to the untreated (second) version of the 5P Diet , which the patient must follow throughout the entire period of the disease and the transition to the stage of stable clinical remission (3-12 months). Its goal is to prevent relapses and progression of pancreatitis, correcting nutritional disorders that have arisen.
The basis of the diet during the period of subsiding exacerbation and the stage of remission in chronic pancreatitis is an increased content of protein in the diet (110–120 g/day, 60% animal proteins) with a sharp restriction of fats to 60–70 g/day (20% vegetable ), and in some cases (with severe steatorrhea) up to 30–50 g/day and limiting carbohydrates to 300 g/day, mainly mono- and disaccharides, and in cases where diabetes mellitus they are completely excluded.
It is also strictly forbidden to include in the diet foods that stimulate the secretion of digestive juices and are rich in extractive substances. vitamins to the diet of such patients . The amount of table salt is reduced to 6–8 g/day. The energy value of this version of Diet No. 5P is 2500-2700 Kcal.
The menu and range of products in the second version of the diet have been expanded. The diet includes dried wheat bread or crackers up to 200-300 g per day. Vegetable soups with the exception of cabbage and cereal soups (except millet), also with the addition of vermicelli, are allowed. Outside the period of exacerbation, you can add a little sour cream or butter. Meat dishes are prepared from lean varieties of meat or poultry in boiled form (meatballs, cutlets, dumplings, rolls, mashed potatoes), fish dishes from lean river fish in pieces or steamed, boiled, chopped; chicken eggs only in the form of a white omelet; Among fats, it is allowed to consume vegetable oils (olive, sunflower) and unsalted butter.
Dairy products are presented in the diet in the form of homemade non-sour cottage cheese, mild cheese, and fermented milk products. Potatoes, beets, carrots, zucchini, and pumpkin are introduced into the diet as vegetables and dishes made from them. xylitol jelly , weak tea, and a decoction of wheat bran and rose hips are allowed.
treatment with diet for symptoms of severe insufficiency of the exocrine function of the pancreas (syndrome of impaired absorption and digestion, steatorrhea ) with the use of specialized products for dietary nutrition - pureed and homogenized products from veal, beef, chicken meat, beef tongues, vegetables and fruits.
After operations on the pancreas (especially often with a cyst, which is a tumor - a capsule with liquid contents), the passage of contents through the intestines is disrupted, which contributes to the development of dysbiosis and constipation . Signs of malabsorption are often absent. In such cases, the basic Diet 5 for the pancreas is modified. The diet increases the content of vegetables and unsweetened fruits, and reduces the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates to avoid fermentation and flatulence .
For pancreatic lipomatosis Table No. 5 according to Pevzner. Diet for exacerbation and deterioration of the patient’s condition who is in remission - the first version of Table 5P . At the same time, during an exacerbation, nutrition should be started again with a period of fasting.
Vegetables and fruits
Dietary nutrition for inflammation of the pancreas is based mainly on the consumption of animal protein and complex carbohydrates. Recommended for inclusion in the diet:
- potato,
- beet,
- zucchini,
- pumpkin,
- cauliflower,
- Bell pepper.
The following vegetables are considered generally safe:
- tomatoes ,
- legumes (peas, beans),
- White cabbage,
- cucumbers
During the acute period, vegetables are consumed only in the form of puree soups without adding oil and spices. Raw vegetables can be eaten in rare cases and only during a period of stable remission.
The consumption of fruits can only be permitted by the attending physician, because one of the concomitant diseases in people suffering from pancreatitis is diabetes mellitus. If your blood sugar level is normal, you can try introducing the following foods in small quantities:
- apples ,
- pears,
- apricots.
Before eating, it is recommended to thoroughly wash, peel and boil or bake fruits. Thermally processed foods are absorbed much better without causing damage to health.
It is not recommended to eat berries, but if desired, you can add them to compotes.
Varieties
If there are problems with the appearance of clinical signs of diabetes mellitus , diet therapy is adjusted taking into account impaired carbohydrate metabolism, approaching the physiological norm of nutrition as much as possible. In such cases Diet 5P/9 , which excludes in the diet:
- purines (extractive nitrogenous substances);
- foods that promote bloating and fermentation processes in the intestines (cabbage, legumes);
- products formed during the frying process;
- foods rich in lipotropic substances and calcium;
- products containing a lot of essential oils and irritating the mucous membrane of the digestive tract (pepper, onion, garlic);
- salt - up to 6 g per day.
In terms of energy value and nutrient composition, the main diet for diabetes mostly coincides with the 5P Diet , however, the latter is more gentle. In terms of nutritional composition, Diets 5P and 5P/9 are identical. 5-6 meals a day are prescribed, simple carbohydrates are excluded from the diet by increasing the fiber content (bran, pectin), and more than 50% of fats should be vegetable fats. Small meals throughout the day equalize the relationship between blood glucose and insulin .
In the diet, up to 50% of the daily energy requirement should be covered by the carbohydrate portion of the diet. For this purpose, sweeteners are widely used - xylitol , sorbitol , saccharin , aspartame , taking into account individual tolerance.
The diet includes foods containing complex carbohydrates: bread, cereals (excluding semolina and rice); fruits, berries and vegetables that contain less than 5 g of carbohydrates per 100 g of product (cucumbers, zucchini, cauliflower) and vegetables/fruits containing 5-10 g of carbohydrates per 100 g of product (beets, carrots, oranges, tangerines) are limited. The ability of any food to increase blood glucose levels is characterized by the glycemic index . And the lower the index, the more suitable this product is for a patient with diabetes.
There is a special table containing the necessary information, using which the patient can navigate when choosing products. The fat content in the diet of such patients should be less than the physiological norm due to the exclusion of refractory animal fats and foods containing a lot of cholesterol (geese, ducks, pork, liver, lamb, brains, yolks). The 5P/9 diet should contain a sufficient amount of vitamins, especially thiamine (vitamin B1), which is actively involved in carbohydrate metabolism, as well as myco/macroelements.
Diet features
Nutrition for pancreatitis of the pancreas has its own characteristics. The main goal of the diet is to reduce the activity of the organ. How to eat with pancreatitis so as not to worsen your health? The main principles are:
- complete rejection of fatty or fried foods and sweets;
- lack of coarse fiber products in the diet;
- in the process of preparing the dish, only boiling and steaming methods are used;
- fractional diet - food intake is carried out in six to seven meals in small portions;
- The food served must be pureed or thoroughly chopped.
During the day, the patient should consume at least 2 liters of any liquid.
Authorized Products
The diet of patients with pancreatitis includes dried bread, unsweetened cookies and white wheat crackers in a total volume of 200-300 g/day, pureed or slimy cereal/vegetable soups with vermicelli, noodles with the addition of butter or sour cream. The diet must include lean meat (rabbit, lean young lamb, beef), boiled or steamed poultry (chicken, turkey), steamed, boiled or baked rabbit (mashed potatoes, cutlets, dumplings, soufflé, roll).
During the period of remission, lean meat, rabbit, and chicken can be served boiled in pieces. Fish dishes are prepared from low-fat varieties of fish (cod, pike, icefish, perch, pike perch, carp) boiled, chopped or in pieces. Chicken eggs are included in the diet in the form of a soft-boiled egg or a steam omelet (up to 2 eggs per day).
It is important to include in the diet dairy dishes and especially non-acidic cottage cheese (preferably homemade), as well as dishes based on it - puddings, casseroles. As side dishes, the diet should include porridge from various cereals and viscous or pureed pasta, vermicelli, homemade noodles, pasta, which is prepared with the addition of milk in a ratio (1:1) or in water.
For vegetable side dishes, beets, carrots, cauliflower, young beans, and boiled, baked or pureed pumpkin are recommended. Fats are mainly unsalted butter and refined vegetable oils, which are added directly to prepared dishes. Sweet dishes in the diet include compotes from pureed fresh and dried fruits, jellies, jelly, mousses from juices with sorbitol or xylitol. Non-carbonated mineral water, rosehip decoction, unsweetened fruit juices, and weak tea with lemon are used as drinks.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| green beans | 2,0 | 0,2 | 3,6 | 24 |
Fruits | ||||
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1.8% (low-fat) | 18,0 | 1,8 | 3,3 | 101 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Detailed diet for a week
During an exacerbation of the disease, the body needs complete rest for the first three days. Any consumption of food is extremely undesirable; you can only drink non-carbonated liquid. After the end of the fasting days, the patient’s diet begins to expand. The calorie content of food consumed daily should not exceed 850 kcal. After a week, calories can be raised to 1100 kcal.
On the fourth day, you can slowly introduce natural foods:
- Dry bread or crackers.
- Kissel or fruit drink.
- A decoction based on rice or oatmeal.
- Mashed potatoes, only in liquid form.
- Ground porridge, only in liquid form.
If no complications arise, then from approximately 8-10 days you can move on to diet number 5.
The first day
.
- Steam omelette (one egg), weak tea without sugar, a slice of bread.
- Four pieces of dry biscuits, low fat cheese.
- Buckwheat porridge 200g, boiled and grated zucchini 150g, curd mass no more than 8% fat.
- Applesauce 100g.
- Oatmeal 200g, grated beets.
Second day
.
- Low fat cottage cheese 200g, weak tea.
- A small portion of salad 100g (boiled green peas with boiled carrots) can be seasoned with vegetable oil.
- Boiled beef 200g with stewed tomato without seasoning, two slices of bread, oatmeal 200g.
- Kissel 200g.
- Vegetable soup 350g (potatoes, carrots, zucchini), fermented baked milk 200g.
Day three
.
- Milk rice porridge 200g, one cracker.
- Low fat cottage cheese 100g, applesauce.
- Chicken broth with meat and potatoes 250g, one slice of bread, boiled zucchini.
- Drinking yoghurt 200g, dried apricots three pieces.
- Boiled grated carrots 100g, steamed meat cutlet 100g (minced beef).
Day four
.
- Curd casserole 100g, weak tea with a little sugar.
- Low fat hard cheese 50g.
- Vermicelli soup 400g (meat broth, vermicelli, oatmeal), one slice of bread, steamed meat cutlet 100g (minced beef).
- Fruit puree 200g.
- Mashed potatoes 200g, boiled lean fish 200g, cauliflower 80g.
Day five
.
- Steamed cutlet 100g (any lean meat), boiled grated beets 100g, weak tea.
- Still water 200 ml, dry biscuits three pieces.
- Chicken broth with grated vegetables 150g (potatoes, carrots, zucchini), 100g buckwheat porridge, chicken meat 150g, two slices of bread.
- Drinking yoghurt 200g.
- Hard boiled pasta 150g, salad 150g (boiled green peas, beets, carrots, olive oil), one marshmallow.
Day six
.
- Pumpkin baked with honey 150g, kefir 200g.
- Low fat cottage cheese 150g.
- Boiled rice with chicken 250g, boiled zucchini, tea.
- Apple or pear puree 200g.
- Oatmeal 200g, boiled veal 150g, weak tea, two dried apricots.
Day seven
.
- Semolina with milk 200g, a slice of bread, tea.
- Curd mass 150g.
- Vegetable mass 200g (boiled zucchini, potatoes, carrots), two steamed fish cutlets, drinking yoghurt 200g.
- Kissel 200g.
- Broth with chicken, potatoes and carrots 350g, boiled beets, a slice of bread.
Remember - during a diet, you cannot overload your stomach, so it is better to undereat a little and overeat.
Fully or partially limited products
It is prohibited to use soups with meat/mushroom/fish broth in the diet. Excluded are pork, lamb, goose, duck, fried foods, solid refractory animal fats (lard, cooking fats), smoked meats, canned fish/meat, salted and fatty fish, sausages, fresh bread, chum salmon caviar, stellate sturgeon, sturgeon, salmon, catfish, carp, pickles, marinades, spices, mushrooms.
Spicy and fatty snacks, whole milk, strong tea, fatty cottage cheese, coffee, cranberries, cocoa, chocolate, mature legumes, sorrel, spinach, lettuce, radishes, turnips, raw vegetables and fruits are prohibited. Fried or hard-boiled chicken eggs, flour and confectionery products, garlic, sorrel, radishes, green onions, white cabbage, rye bread, carbonated drinks, spinach, cold dishes and drinks, any dough (butter, puff pastry), ice cream, and alcoholic drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Restrictions
Despite the fact that the list of permitted foods is quite wide, the amount of prohibited foods for inflammation of the pancreas is also high.
A therapeutic diet should be taken very seriously, because it is what allows you to relieve unpleasant symptoms and return to your normal life
To restore the functions of the pancreas and liver, and to avoid exacerbation of the disease, it is not recommended to consume the following products:
- strong meat and mushroom broths;
- fatty meats and fish;
- canned products (meat, fish, vegetables and fruits);
- salt (in the initial period of exacerbation, it is recommended to completely avoid it in order to relieve swelling of the inflamed gland);
- processed and spicy cheese;
- sausages, lard, smoked meats;
- fried foods;
- hot and sour vegetables (garlic, onions, radishes, sorrel);
- sour fruits;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- strong tea and coffee;
- chocolate and cocoa;
- sweets.
All purchased products that can be replaced with home-cooked food must be made yourself. Thus, your own cottage cheese and yogurt are much healthier because they do not contain preservatives that can harm health due to an inflamed pancreas.
Menu (power mode)
Since the time period for prescribing the pureed version of the diet is short (3-5 days) and it is prescribed in a hospital, it is more advisable to provide a nutrition menu for the non-mashed (without mechanical sparing) version of the 5P Diet, which should be followed for 6-12 months in case of pain and discomfort. It is necessary to organize split meals 5-6 times a day. For the whole day, the patient is allowed 200 g of wheat bread, 30-40 g of sugar (or 20-30 g of xylitol in sweet dishes) and 20 g of butter.
Monday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Tuesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Wednesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Thursday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Friday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Saturday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Sunday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Nutrition for combined pancreatitis with gastritis or cholecystitis
If the underlying disease is accompanied by the development of cholecystitis, then the menu is allowed to include:
- slimy soups made from rice, oatmeal or semolina;
- pureed porridge cooked in water; adding milk and butter is strictly prohibited;
- vegetable juices, compotes;
- homemade white bread croutons;
- pureed boiled meat, fish;
- low-fat cottage cheese.
With a combined course of pancreatitis and gastritis, the menu should include pureed soups from oatmeal, rice and semolina, to which you can add egg yolk and a little butter, pureed vegetables - potatoes, carrots, beets - with the addition of milk or cream, steam soufflés, cutlets and dumplings made from minced meat and fish.
The strict option is recommended only during the acute period of the disease. After the condition has stabilized, the person switches to the diet recommended for chronic pancreatitis.
[node:field_field_doprekl2]
Recipes
First meal
Vegetarian soup with zucchini
Vegetables: chop onions and carrots and simmer in a saucepan in water with added oil. Add water and potatoes, cook for 15 minutes. 5 minutes before the potatoes are ready, place the potatoes in the soup, add chopped zucchini, add salt and bring until ready. Sprinkle with herbs on the table and top with sour cream if desired.
Oatmeal soup with cauliflower
Chop carrots and onions in the usual way for soup, simmer in water with vegetable oil. Add water to the volume you need, add chopped potatoes. Boil for 15 minutes, add cauliflower, disassembled into inflorescences, and oat flakes. Cook for 5 minutes. Serve with chopped herbs.
Second courses
Chicken meatballs with mashed potatoes
Wash and cook the rice. Add an egg, rice, a little sautéed onion, and salt to the prepared minced chicken fillet. Knead thoroughly, form meatballs and bake in a mold with sour cream sauce.
Fish quenelles with milk sauce
Beat the fish fillet in a blender. Add wheat bread crumb soaked in milk or semolina. Mix everything and beat again. Gradually add a little cream and whipped egg white, add salt. Use two tablespoons to form quenelles from the dumpling mass, place them on a baking sheet and bake. Can be steamed. Serve with milk sauce.
Dessert
Lapshevnik with cottage cheese
Boil the noodles, add grated cottage cheese, sugar, egg and knead. Place in a suitable pan and bake in the oven until a rough crust forms. Serve with sour cream.
Cheesecakes with carrots and dried apricots
Grate the carrots and simmer with the addition of water and butter. Finely chop the dried apricots, add the grated cottage cheese, add the egg, sour cream, flour, dried apricots and carrots. Form cheesecakes from the curd and carrot mixture and bake them in the oven.
Types of pancreatitis
The most general classification of pancreatitis is based on the nature of the disease: acute attack or prolonged chronic pancreatitis with periodic relapses. The two forms differ in the severity of symptoms and require different treatment approaches.
Acute pancreatitis
The inflammatory process in acute pancreatitis develops very quickly and is always accompanied by severe pain. In most cases, the disease occurs due to alcohol abuse or after eating large amounts of fatty foods. Sometimes an exacerbation is preceded by an attack of acute hepatic colic.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis:
- Severe pain in the left hypochondrium, radiating to other organs. The painful attack lasts about half an hour to an hour. The pain is felt especially strongly when lying on your back. The attack intensifies after eating food, especially fried and spicy food, and any alcoholic beverages.
- Vomiting, often uncontrollable with an admixture of bile and a bitter taste. Constant nausea that does not go away after vomiting.
- Low-grade or high fever.
- Sometimes, due to a violation of the outflow of bile, yellowing of the eye whites is observed, very rarely - a yellow tint to the skin.
- In some cases, the pain syndrome is accompanied by heartburn and bloating.
An attack of acute pancreatitis requires immediate medical attention. Painkillers provide only temporary relief, but do not affect the cause of inflammation. In the absence of qualified assistance, the risk of severe complications quickly increases: infection in inflamed tissue, necrosis and abscesses.
Severe acute pancreatitis can lead to shock and multiple organ failure.
Chronic pancreatitis
If, after an attack of acute pancreatitis, a person does not follow doctors’ recommendations and continues to drink alcohol and eat poorly, the disease is highly likely to enter the chronic stage. Chronic pancreatitis develops when there is significant damage to the pancreas during the first episode of the disease.
The disease is characterized by gradual pathological changes in the structure of pancreatic cells. Over time, it begins to lose its main function - the production of enzymes necessary for digesting food. Exocrine insufficiency manifests itself:
- diarrhea,
- bloating,
- a change in the nature of feces - they acquire a sticky consistency due to the large amount of fat in them and are poorly washed off the walls of the toilet.
Chronic pancreatitis can be asymptomatic for a long time: acute pain appears when significant pathological changes have already occurred in the pancreas. During an attack, chronic pancreatitis manifests itself with the same symptoms as acute:
- severe girdle pain,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- disturbances in intestinal function.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The examination usually reveals narrowed pancreatic ducts due to the formation of stones in them - calcifications. Hardware techniques also make it possible to detect cysts in place of atrophied tissue. Laboratory blood tests for chronic pancreatitis are not very informative.
Pancreatic insufficiency is determined by analyzing stool. If they contain a specific enzyme, pancreatic elastase, a diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis is made.
Comments from nutritionists
In order to prevent the development of chronic pancreatitis, therapeutic nutrition for pancreatic disease after acute pancreatitis must be observed for 6-12 months until stable clinical remission.
Many “advanced” patients with pancreatitis, trying to find alternative methods of treatment, mainly ask on the Internet whether and how they can treat the disease on their own and whether cleansing the pancreas with folk remedies is effective. Their desire, especially during pain, is understandable. However, it is necessary to warn that the authors of articles on the Internet, where there is a lot of all kinds of advice and recommendations (cleansing with buckwheat, treatment with kvass on celandine, flax seeds, juice therapy, and so on) do not bear any responsibility for them, and you may get an aggravation pancreatitis with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, it is not recommended to use folk remedies without consulting a gastroenterologist.
Diet for acute pancreatitis
If acute pancreatitis is confirmed, it is necessary to completely abstain from food for several days. Only alkaline mineral water without gas is allowed for consumption (about 1.5 liters per day), and if necessary, droppers with glucose, albumin and other supporting medications are given. As soon as the condition has stabilized, the doctor, based on the characteristics of the course of a particular disease, will prescribe a therapeutic diet, which will need to be followed for quite a long time, and sometimes throughout life.
Reviews and results
For symptoms of pancreatic disease, treatment with diet gives positive results. The diet is gentle and compensates for the necessary protein needs. Meals are prescribed for a long period, and various methods of processing foods (boiling, baking, steaming) allow you to diversify the menu and, according to patients, it is not very boring.
Reviews from patients indicate that dietary nutrition is very important, and some note that they are constantly forced to follow a diet - deviations from it cause a deterioration in their health.
- “... In case of a mild exacerbation, if IVs are not needed, I do not go to the hospital, but carry out the treatment at home and include therapeutic nutrition. I know what to eat and what to exclude, since this is not the first time. The only way out is to give rest to the pancreas and remove broths, fatty and fried foods. The transition to steamed and baked dishes is immediately felt: bloating and discomfort in the left hypochondrium disappear. I tolerate all porridges well, I don’t even exclude boiled vegetables, so the diet is quite complete and not difficult to follow. I try to hold out for a month or two and during this time I also lose weight”;
- “... When my pancreas hurts and mushy stools appear, I switch to this diet. The first time I was in the hospital, they told me to stick with it for at least a year. Dietary restrictions affected my weight, I lost 6 kg. I will be very careful about my nutrition and treatment; in the hospital I was on a very strict diet”;
- “... For problems with the pancreas, the very first thing is diet and regimen. I know that I eat irregularly, often eat fried and fatty foods, which causes aggravation. Moreover, drinking alcohol on holidays has an immediate effect. The doctor warned that you need to constantly follow a diet. It’s difficult for me to stick to it, but what to do if there are frequent exacerbations. Therefore, I decided to endure a year without any disturbances and I can say that during this time I forgot what an exacerbation is and where the pancreas is located”;
- “... When I was in the hospital for the first time with an attack, they told me what the diet for the pancreas should be so as not to burden it and not provoke an exacerbation. Since then, I switched to boiled and baked dishes, introduced my family to them, and I think that this only makes everyone healthier. What is the use of smoked meats and fatty, fried foods? My condition is normal and there have been no exacerbations for 3 years. Of course, sometimes you want to break your diet for a holiday, and this happens, but I allow errors in moderation.”
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Prohibited foods and diet violations
Violation of diet principles can cause a number of negative consequences for the patient. Firstly, dietary nutrition is an integral part of the treatment of pancreatitis (the symptoms of the pathology cannot be eliminated with medications alone). Secondly, the dietary nutrition program is designed to restore the functional state of the pancreas. Following a diet will allow you to achieve stable remission and reduce the risk of sudden attacks. Thirdly, the menu contains products that are beneficial for the digestive system.
Failure to comply with recommendations for adjusting the diet can provoke complications and the need for urgent surgical intervention.
| Vegetables | Radish, radish, turnip, eggplant, white cabbage, bell pepper |
| Cereals | Barley, corn, millet cereals |
| Meat | Pork, waterfowl meat, fatty meats, offal |
| Fish | Fatty fish, carp, mackerel, sturgeon, salmon |
| Milk products | Whole and baked milk, products with added dyes |
| Mushrooms | All types of mushrooms |
| Legumes | Peas, beans, lentils |
| Sweets | Chocolate, sweet pastries with cream, pastries, cakes, halva, confectionery |
| Beverages | Coffee, strong tea, carbonated drinks |
How does exacerbation of pancreatitis affect nutrition?
Exacerbation of pancreatitis is a significant reason for adjusting the diet. From the moment of the attack until the period of remission, the patient should follow a diet. In the first days of an exacerbation, therapeutic fasting is recommended (complete exclusion of any food is necessary). From the third or fourth day of therapy, you can gradually restore the diet, but only if there is a tendency to recovery.
Important principles:
- during the stages of improvement and recovery of the patient, the amount of fat and salt in the diet is limited;
- the calorie content of food should not exceed 1000 kcal;
- eat food at least six times a day (in small portions);
- The menu should contain only products from the approved list.
What can you drink if you have pancreatic disease?
If you have diseases of the digestive tract, you should not drink coffee, strong tea and carbonated drinks. Permitted options include fruit drinks, compotes, rosehip decoction, diluted juices and alkaline mineral water (still).
It is acceptable to drink weak tea (black, green). You can add milk to the drink.
Is it possible to drink alcohol if you have pancreatitis?
Alcoholic beverages should not be consumed at all stages of pancreatitis. Even a single violation of this rule can cause an attack of exacerbation of the inflammatory process. Alcohol contains components that have a negative effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive tract and the process of food digestion. If you consume such drinks during pancreatitis, there will be not only a decrease in the tendency to recovery, but also the risk of serious complications (including those incompatible with the patient’s life).
Patients need to exclude fatty foods and alcohol from their diet.