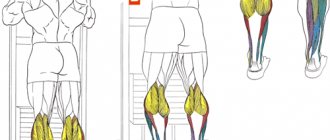
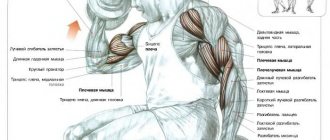
If you set yourself the task of pumping up your pectoral muscles as much as possible, then visiting the gym seems to be the best option. The presence of special equipment, qualified instructors - all this will help you achieve the desired results. But often a situation arises when regular visits to the gym are impossible. In this case, home exercises can serve as an alternative to the gym.
If you want to focus on swaying the pectoral muscles, then you need to take into account that they consist of several symmetrical groups, including:
- pectoralis major muscle
- pectoralis minor muscle
- anterior serratus.
Do not forget that when training the pectoral muscles, the body spends a huge amount of energy, which has a beneficial effect on burning fat tissue.
Home workouts
The modern life rhythm of many people nowadays is such that it is often very difficult to find time to regularly visit the gym. The training process at home can be considered as an adequate replacement for the gym. The desire of the student to achieve his goal should come first.
First of all, you need to decide on the number of classes per week. Many beginners mistakenly believe that daily exercise can lead to the desired result in a minimum amount of time. But the characteristics of the pectoral muscles are such that during active work, the muscles receive multiple microtraumas and after each exercise time is needed for their complete recovery. Therefore, at the initial stage, the number of training sessions should not exceed two sessions per week.
You should also adhere to a certain dosage in the number of approaches for exercises to develop the chest muscles. Depending on individual physical fitness, their number should be from four to eight approaches per workout. For those who are just starting to exercise, the best option would be one or two exercises of two or three approaches. And remember, excessive overload of the pectoral muscles does not give good results. To achieve the desired result, create a training program and try to stick to it on a regular basis.
4 week training program
Follow this 4-week program, paying attention to the volume and intensity of your training to meet your target. In the first week of classes, there is a general development of strength and mass of the chest muscles. Further, at weeks 2, 3 and 4, the work is aimed at the middle, lower and upper parts of the muscles, respectively. Although each week includes working on a different area of the chest, the program also includes exercises for all parts of the chest.
In addition to this, we have added several techniques to increase the intensity of the workout. Stick to the plan, add one of the techniques to increase intensity on the last set and if there is an * symbol.
Techniques for increasing exercise intensity
Weight loss
After completing a set with maximum weight, remove the weight from both sides of the barbell or select lighter dumbbells. Continue performing reps to the limit, then remove more weight and do even more reps.
Forced replays
Ask a partner to help you with reps at the end of the set, when the muscles are at their most tired. It should help you lift the barbell precisely so that you overcome the moment when lifting becomes difficult.
Partial repeats
Perform repetitions only within a certain range—at the top, middle, or bottom—of the movement.
Pauses
During one set of a particular exercise, pause briefly to perform more repetitions. Lift the weight 2-3 times, pause for 20 seconds, then do another 2-3 repetitions. Rest again, then perform as many repetitions as possible and repeat again.
Negative repetitions
Slow down as your arms lower down with the barbell. For example, when bench pressing, use a weight that is 15% to 25% heavier than normal and slowly lower the barbell down toward your chest. Let your partner help lift the barbell up.
Week 1: for general chest muscle development
| Exercises | Picture | Sets and reps |
| 1. BENCH PRESS Equipment : barbell, bench Perform for warm-up, if possible in 3 sets. | 2 x 15-20 — pause | |
| 2. BENCH PRESS Equipment: barbell, bench * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last set | 3 x 6-8* — pause | |
| 3. BAR PRESS ON AN INCLINED BENCH Equipment: barbell, incline bench | 3 x 8-10 — pause | |
| 4. DUMBBELL FLIES ON AN INCLINED BENCH Equipment: dumbbells, incline bench | 3 x 10-12 — pause | |
| 5. BENCH PRESS ON A SMITH MACHINE Equipment: Smith machine | 3 x 12-15 — pause | |
| 6. Push-ups | 3 x maximum — pause |
Week 2: Midsection Exercises
| Exercises | Picture | Sets and reps |
| 1. BENCH PRESS Equipment: barbell, bench Perform as a warm-up, in 3 sets if possible. | 2 x 15-20 — rest | |
| 2. DUMBELL PRESS Equipment: dumbbells, bench | 3 x 8-10 — rest | |
| 3. Bent-over rows on the “CROSSOVER” MACHINE * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last approach | 3 x 6-8* — pause | |
| 4. “PULLOVER” WITH DUMBBELL Equipment: bench, dumbbell | 3 x 8-10 — pause | |
| 5. INCLINE DUMBBELL PRESS Equipment: incline bench, dumbbells * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last set | 3 x 10-12* — rest | |
| 6. Push-ups | 3 x maximum — rest |
Week 3: Upper Exercises
| Exercises | Picture | Sets and reps |
| 1. BAR PRESS ON AN INCLINED BENCH Equipment: barbell, incline bench Perform for warm-up, if possible in 3 sets. | 2 x 12-20 — pause | |
| 2. INCLINE BAR PRESS Equipment: barbell, incline bench * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last set | 3 x 6-8* — pause | |
| 3. DUMBELL PRESS Equipment: dumbbells, bench | 3 x 8-10 — pause | |
| 4. STANDING CROSSOVER * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last approach | 3 x 10-12* — pause | |
| 5. DUMBBELL FLIES ON AN INCLINED BENCH Equipment: dumbbells, incline bench | 3 x 15-20 — break | |
| 6. STEP PUSH-UPS Equipment: step | 3 x maximum — break |
Week 4: Lower Exercises
| Exercises | Picture | Sets and reps |
| 1. BAR PRESS ON AN INCLINED BENCH Equipment: barbell, incline bench Perform for warm-up, if possible in 3 sets. | 2 x 12-20 — rest | |
| 2. INCLINE BAR PRESS Equipment: barbell, incline bench | 3 x 6-8 — rest | |
| 3. STANDING BLOCK PULL ON THE CROSSOVER MACHINE * + 1 technique to increase intensity on the last approach | 3 x 8-10* — rest | |
| 4. BENCH PRESS Equipment: barbell, bench | 3 x 10-12 — rest | |
| 5. TRICEPS PUSH-UPS Equipment : parallel bars | 3 x maximum — rest |
Exercises for training
The simplest and most universal exercise available to anyone starting to develop their body is simple push-ups. If we take a closer look at the mechanism of the push-up process, we will see that this is a kind of variation of the bench press. In addition, push-ups are an optimal general developmental exercise. When doing push-ups, the muscles of the arms are also involved, which ensures uniform development of the muscles of the upper body. In addition, there is an active effect on the abdominal muscles, which has a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole. The leg muscles are used to a lesser extent, but they also receive a small share of the load.
Like many physical exercises, push-ups have different variations, using which you will load different groups of pectoral muscles.
What you need to grow your pectoral muscles
Effective muscle growth depends on several factors:
- A well-designed set of exercises that takes into account the initial physical data.
- Balanced fractional nutrition, which contains all the nutrients the body needs.
- Quality rest, because muscles grow during the recovery period after training.
But the most important factor, without which a qualitative increase in muscle mass is impossible, is the athlete’s brain. Only a competent approach to training and exercise technique will give an acceptable result and protect you from injury.
For example, a chest push-up training program has many advantages. But a technically unprepared athlete will negate all the advantages of the program, since the load, instead of the chest, will be distributed to the triceps and back with the abdominal muscles. The same principle works in nutrition and the use of sports supplements.
Pushups
The simplest and most universal exercise available to anyone starting to engage in the process of developing their body is simple push-ups. If we take a closer look at the mechanism of the push-up process, we will see that this is a kind of variation of the bench press. In addition, push-ups are an optimal general development exercise that affects a huge number of muscles. When doing push-ups, the muscles of the arms are involved, which ensures uniform development of the muscles of the upper body. In addition, there is an active effect on the abdominal muscles, which has a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole. The leg muscles are used to a lesser extent, but they also receive a small share of the load.
Like many physical exercises, push-ups have different variations, using which you will load different groups of pectoral muscles.
Narrow push-ups
One such option is narrow push-ups. The difference between narrow push-ups and regular push-ups is the width of your arms. In the case of narrow push-ups, the hands are placed so that the fingers of both hands are facing inward and touching each other. When lowering, you need to touch your chest with your hands and maintain a second pause in this position. When performing this exercise, you should pay special attention to the straight position of your back. The movements during push-ups are smooth without jerking, breathing is uniform, without delays.
The best exercises for chest muscles at home
The main basic chest exercise performed with your own weight is push-ups. It is around them that we will build the entire home training process. Let's look at the most common variations of this exercise.
Push-ups with wide arms
This exercise is often called the “reverse bench press” - the biomechanics of the movements are almost identical, so as part of home training, classic push-ups will be basic.
Use the maximum possible amplitude: at the lowest point between your body and the floor there should be no more than 5 cm. If your physical fitness for this exercise is not yet enough, first perform push-ups from your knees - this way you will strengthen the muscle frame and prepare the joint-ligamentous apparatus for more serious work.
Plyometric push-ups
Plyometric push-ups are an explosive movement that works all the fibers in the pectoral muscles. The most common variation is clap push-ups. Excellent for developing explosive power and strengthening the entire shoulder girdle. More complex variations: with two claps, with a clap behind the back, superman push-ups, etc. Alternate them from workout to workout.
Deep push-ups
For this exercise you will need a pair of dumbbells (weight is not important) or a small elevation (alternatively, you can use two chairs). The amplitude is greater than in classic push-ups, so you stretch the muscles more strongly at the bottom. The result is new stress and more incentives to grow.
© kucherav — stock.adobe.com
If you have special sports equipment at home (dumbbells, weights, barbell), then you can do more strength work. This will create even more prerequisites for gaining muscle mass.
Dumbbell floor press
This is the only strength exercise for pumping up the pectoral muscles at home, which does not require a special bench or other equipment. You simply lie down on the floor, bend your knees for greater stability, and press the dumbbells up, then lower them until your hands touch the floor. The amplitude will be less than when pressing on a bench, so if it is available, it is better to perform the exercise on it.
A combined option is possible: bench press + fly-out. To do this, you need to spread your arms further to the sides and bend your elbows less.
It is possible to perform this exercise using two weights. You can press them similarly to dumbbells or one at a time:
Dips
Often at home there is a wall bars with bars, or a similar apparatus is in the nearest yard. These push-ups are one of the main basic exercises for the pectoral muscles.
To maximize the load on your chest, the distance between the bars should be slightly wider than your shoulders, and when performing the movement, lean forward slightly and do not fully extend your arms. This is how you can almost completely “turn off” the triceps.
Pullover with dumbbell
This exercise perfectly forms the “collar” - the middle of the upper part of the pectoral muscles. It does not require a lot of weight; it is much more important to feel the work of the pectoral muscles, and not the serratus or latissimus dorsi muscles. To create the correct angle of inclination of the body, an ordinary chair or stool will be enough.
© Nicholas Piccillo — stock.adobe.com
Also, the pectoral muscles work indirectly when performing some abdominal exercises, for example, when rolling on a roller, running in a prone position, or lifting from a plank. To further strengthen your core, we recommend performing one of these exercises at the end of each at-home chest workout.
Push-ups on stools
The next push-up option is push-ups on stools. Two stools are placed shoulder-width apart, and a sofa or chair is used as a footrest. Starting position is the same as for a regular push-up. The main difference is that in this variation of push-ups the depth of lowering the body increases. Also in this exercise it is possible to work with weights, for example, you can use a backpack with books as an additional load.
Simple yet effective chest workout in 8 weeks
This eight-week workout program will help you tone your chest with push-ups using only your own body weight.
How to pump up your pectoral muscles at home in 1 week? Most likely, this is not possible in such a short period of time, but it is quite possible to make the muscles more expressive and prominent. And with our program, you can pump up your pectoral muscles in 8 weeks by training at home without going to the gym and using exercise equipment, heavy dumbbells and barbells.
Train in three phases to get toned within 8 weeks. The first stage will build endurance, the second will increase strength, and the last stage will increase explosiveness and speed so you can increase your size. The entire program is based on variations of standard push-ups. It is so simple.
Try to maintain consistent training and adjust your caloric intake for bulking according to your needs and training goals.
25 types of push-ups
Before starting the complex, watch a video with the best variations of push-ups, which you can use to diversify your home exercises, and at the same time learn the correct technique.
Did you think that training with barbells and dumbbells was the only way to develop a strong, muscular chest? Think again. You can pump up without lifting a barbell or dumbbells. Just follow our recommendations and the result will surprise you.
Perform these exercises 2 or 3 days a week, resting at least 1 day between workouts. Perform three full sets, resting 1-2 minutes in between. Each set contains 10-15 repetitions. If this exceeds your capabilities, then perform the maximum number of repetitions possible for you.
With arms wide
Week 1 and 2
A. Wide-arm push-ups
Do regular push-ups, but place your hands wider than shoulder-width apart.
Offset to the side
Week 1 and 2
B. Sideways push-ups
Start in the classic push-up position. Move your right hand to your left so that they are side by side. Move your left hand further to the left so that your hands are shoulder-width apart. Push up and repeat, moving to the right. That's two push-ups, but one rep.
With narrow hand position (Diamond)
Week 1 and 2
C. Push-ups with narrow arms (Diamond)
Do a push-up by placing your palms close enough that the tips of your thumb and index finger touch, forming a diamond shape.
With one hand on a stand
Weeks 3, 4, 5 and 6
Perform these variations 2 days a week, 4 sets, resting 1-2 minutes between sets. Again, the goal is 10-15 reps, or as many as possible. You will need a box 10-20 cm high. Or steps. Just make sure the box won't tip over.
A. One-arm push-ups
When performing push-ups, your right hand should be on the floor and your left hand on the box. Switch hands and repeat. This is just one repetition. Sorry.
With arms crossed on the box
Weeks 3, 4, 5 and 6
Train 2 days a week, doing 4 sets of each exercise with 1-2 minutes of rest. It is advisable to do 10-15 repetitions or as many as you can.
B. Push-ups with arms crossed on a box
Do push-ups with your left hand on the box. From the starting position, move your right hand towards your left. Lower your left hand to the floor, placing your hands shoulder-width apart. Do push-ups. This is one repetition.
With hands on a stand (Brilliant)
Weeks 3, 4, 5 and 6
Exercise 2 times a week, 4 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
S. Diamond with hands on the box
The key is in the name: perform diamond push-ups, but with your hands on the box.
Dynamic box push-ups
Weeks 3, 4, 5 and 6
Perform this variation 2 days a week, 4 sets of each variation, resting about 1-2 minutes between sets. Again, you need to do 10-15 reps per set, or as many as you can. To help, take a box 10-15 cm high or a thick book.
Dynamic box push-ups
Place your hands on the box in a diamond position. Lower your body and quickly push up from the box so that your hands land on the floor on either side of the box. Watch your chin. Immediately lower yourself and push up sharply, returning your hands to the box to the starting position. This is one repetition. This will take you to the level of Private Balboa. Keep up the good work, champion.
We enhance the effect with circuit training
Weeks 7 and 8
Thanks to hard work, you have increased muscle endurance (weeks 1-2) and added strength to them. This final stage develops the explosive power and speed that will give you an edge in any sport. They will also increase the size of the muscles and improve the relief, which will provide you with an aesthetic appearance.
This is not very simple: do the same exercises as in the second stage (weeks 3-6), but in a circle without stopping to rest. Try to do 10 repetitions of each exercise. This is a set. Rest 1-2 minutes and repeat again for a total of 4 sets. Exhaustion is not necessary. Exercise twice a week, allowing yourself 3 days of rest for complete recovery and intensive growth.
Bend push-up
The point of this exercise is to keep your legs higher than your head. You need to put your feet on some kind of elevation and do regular push-ups. This exercise will involve the upper chest, as well as the main muscle groups of the arms. When performing this exercise, you should pay attention to the correct placement of your elbows. If possible, try to move them apart to provide maximum load to the chest muscles.
Dumbbell floor press
Having regular dumbbells will allow you to significantly diversify your training program. The most universal exercise is the following: take the starting position lying on your back, bend your legs at the knees, and stretch your arms with dumbbells up. Then, as you inhale, slowly lower your arms until your elbows touch the floor. Try not to rush, perform this exercise at a smooth, even pace. A regular folding athletic bench, which you can buy at any sports store, can significantly diversify such exercises with dumbbells.
Remember that nothing is impossible. With a certain amount of desire, even at home you can achieve excellent results. Find for yourself an additional incentive for regular exercise, allocate free time, and the results you will receive will pleasantly please you.
What exercises to do for the pectoral muscles?
Lifehacker selected chest exercises based on data from scientific experiments with electromyography (EMG). With this research method, special sensors are attached to the athlete in the area of the working muscle. A person performs an exercise, and devices record the electrical activity that occurs in the muscles during their contraction.
Using this method, scientists find out which exercises best load muscles and determine the most beneficial technique for pumping them up.
Bench press
This is an immortal classic. The press has been studied inside and out, and it engages the pectoral muscles 100% by Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises.
The bench press works multiple joints and stresses not only the chest, but also the shoulder muscles. Do the bench press at the beginning of the workout: there is no need to Neuromuscular activity during bench press exercise performed with and without the preexhaustion method to tire the muscles with other exercises before it.
Lie down on a bench press with your feet flat on the floor. Grasp the barbell with an overhand grip 1.5 times shoulder width. A grip twice as wide as shoulder width is only slightly The influence of grip width and forearm pronation/supination on upper-body myoelectric activity during the flat bench press increases the load on the chest, but at the same time greatly increases The Affect of Grip Width on Bench Press Performance and Risk of Injury risk of injury to the shoulder joint.
As you inhale, lower the barbell to the bottom of your pectoral muscles, as you exhale, press it back down and repeat.
You can also do incline bench presses. This option better pumps up the upper chest than the bench press on a horizontal bench. Set the bench at a 45 or 60° angle and lower the bar to your upper chest.
As for the reverse bench press, it will pump up Influence of bench angle on upper extremity muscular activation during bench press exercise the lower chest no better than horizontal, so it makes no sense.
Dumbbell Bench Press
Scientists do not agree on which press is more effective for the chest - barbells or dumbbells. Some say Maximal Strength Performance and Muscle Activation for the Bench Press and Triceps Extension Exercises Adopting Dumbbell, Barbell, and Machine Modalities Over Multiple Sets that dumbbells place more stress on the pectoral muscles, others say Electromyographic activity of the pectoralis major and anterior deltoid muscles during three upper -body lifts exercises are equivalent and it is recommended to alternate them to avoid a plateau. This is a good solution because the bench press will provide you with heavier weights, and the dumbbell press will provide additional tension from instability.
Sit on the edge of the bench, pick up the dumbbells from the floor. Lie with your back on a bench, press your feet to the floor, bend your elbows at right angles, point your wrists away from you. As you exhale, press the dumbbells up while turning your palms with your fingers towards each other.
By turning your arms, you increase the range of motion of the shoulder: it not only moves from the side forward, but also crosses the line of the body, providing greater load on the muscles.
As with the barbell press, you can also do it with dumbbells on an incline bench. This will increase the load on the upper muscle bundle.
Reduction of arms on a butterfly simulator
This is an isolated exercise: it moves only one joint and works mainly the pectoral muscles. Bringing your arms together on this machine loads the muscles a little worse Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises than the bench press, but it is almost impossible to get injured on it.
Sit on the machine, press your feet to the floor, lower your shoulders. Grasp the handles, slightly bend your elbows. As you exhale, bring your arms together in front of you, hold for a second and slowly move them back.
Crossing your arms in a crossover
This exercise pumps up the chest just as well Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises as the “butterfly”. In addition, here you can adjust the position of your arms and shift the emphasis to different muscle heads.
Place weights on two crossover blocks, grab the handles of the top block with an overhand grip and stand in the middle. Place one leg forward for stability and lean your body forward slightly, keeping your back straight. Stretch your arms out to shoulder level and bend your elbows slightly to protect the joint.
As you exhale, cross your arms in front of you. Hold for a second and slowly move back out.
To shift the emphasis to the lower part of the muscle, bring your arms down.
You can also load the upper part well, but to do this you need to change the upper block to the lower one. Grab the handles and pull them from bottom to top and crosswise. The body position and execution rules are described above.
The following exercises are inferior to the first four in effectiveness or have not been sufficiently studied. But they are quite suitable for diversifying your workout and “finishing off” your muscles. This means that you will perform the exercise at the very end, after the main presses and data.
Bench press
There is such a simulator in almost any gym. Performing the Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises exercise on it is as easy as shelling pears: set the desired weight, sit down, press against the back, grab the handles and move them forward.
If you finished the exercise with effort, but did not bend your whole body, then the weight was selected correctly.
Dumbbell flyes on a bench
Dumbbell flyes pump up the chest worse Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises than presses, but better than push-ups.
Sit on the edge of a bench and lift the dumbbells off the floor. Lie down on a bench and extend your arms with dumbbells in front of you, fingers facing each other. Bend your elbows slightly to protect the joint.
As you inhale, slowly move your arms with dumbbells to the sides of your body. As you exhale, bring your arms in front of you, returning them to their starting position.
Dips
Exercise Electromyographical analysis of the pectoralis major muscle during various chest exercises works well on the lower part of the pectoral muscles. You can do it without weights or with a weight belt.
Jump onto the parallel bars, lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together. Bend your elbows and go down until your shoulders are parallel to the floor. As you exhale, push yourself up and repeat.