Amino acid complexes are sports nutrition, where not individual types are present, but all amino acids. These supplements should not be confused with BCAA. Protein is also an amino acid, so the sports nutrition in question is practically no different from it. However, given the characteristics of each, they exist. What is the difference? What to give preference to?
Benefits of Amino Acids
The following advantages speak in favor of the use of complexes:
- Does not require digestion. Complexes are absorbed much faster than proteins. The latter first require preliminary breakdown into amino acids. The difference in the assimilation process is up to one hour. It may be longer or shorter. It all depends on the type of protein. This difference is not significant even for a training person, so this advantage cannot be called significant.
- Contain a minimal amount of carbohydrates and fats. Most of the complexes on sale contain virtually no impurities. Proteins contain about 5% fat and 10-15% carbohydrates. Amino acids are great for those who want to lose weight. There are proteins with a minimum amount of fats and carbohydrates that are not inferior to complexes in this aspect.
- Much more convenient to use. To take complexes you do not need to use a shaker, mix cocktails and then wash dishes. There is no need to purchase milk for preparation. The use of amino acids comes down to taking tablets with water.
The differences are not significant, but they are there.
Amino acids or protein. What's better.
Benefits of Proteins
The main advantages of protein over amino acids:
- Better feeling of fullness. This property allows you to reduce appetite and suppress hunger. Replacing some meals or parts of a meal with protein can increase the amount of protein and reduce the percentage of fats and carbohydrates. This makes proteins an ideal choice for weight loss. Amino acids are not suitable for these purposes. It is almost impossible to get enough of tablets and capsules.
- Certain types of protein take a long time to break down in the body. Casein is one of these proteins. This protein quality is a significant advantage in some situations. Proteins that break down over a long period of time can be taken at night. They will gradually saturate the body with amino acids, promoting the growth and restoration of muscle fibers. The complexes are quickly broken down, so they are absorbed into the blood within the first hour after administration.
- Greater availability. Amino acid complexes are more expensive than regular protein powder. The difference reaches one and a half times. A kilogram of inexpensive protein will cost about 1,000 rubles, and the most affordable complex will cost no less than 1,500 rubles.
The last point should be discussed in more detail. Cheapness is the main advantage of protein over complexes, but here a reasonable question arises: where does such a big difference come from if both types of sports nutrition are almost identical. The higher price is due to the fact that the tablets require pre-compression into tablets, scattering into capsules or adding to syrup.
Protein or amino acids: which is better?
Protein or amino acids ? This question can often be heard from novice bodybuilders or people who have just started going to the gym and getting acquainted with sports nutrition. In this article we will talk about how protein differs from amino acids and what is better to take.
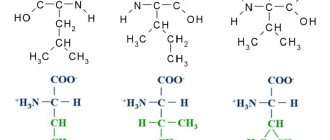
To begin with, let us clarify that by the word “ amino acids ” we mean amino acid complexes , that is, sports supplements that contain all amino acids (essential, conditionally essential and non-essential) or only essential amino acids (EAA). Let us also recall that protein is an organic substance that consists of amino acids connected by peptide bonds. After these important clarifications, we can move on to the main topic of this article.
Protein is a sports supplement that is typically produced in powder form. The protein composition may include various types of protein (whey protein, egg white, casein, etc.) or combinations thereof. The most popular type of protein is whey protein , which has a balanced amino acid profile and high bioavailability. The most popular form of whey protein is whey protein concentrate, which contains up to 80 percent protein. Also popular are whey protein isolate, which contains up to 95 percent protein, and whey protein hydrolysate, a protein that is partially broken down into chains of two to three amino acids.
Whey Protein Isolate
Amino acids or amino acid complexes are sports supplements that are produced in the form of powder, tablets, capsules or liquid. The main component of amino acid complexes is, oddly enough, the same whey protein . Most often, whey protein isolate is used in the production of amino acid complexes, and whey protein hydrolyzate is used a little less often. Whey protein concentrate is also used in the production of amino acid complexes. Sometimes sports nutrition manufacturers, to increase the effectiveness of their product, add free-form amino acids to amino acid complexes, in addition to whey protein concentrate, isolate or hydrolyzate - these can be branched chain amino acids (BCAAs), L-glutamine, taurine or others amino acids. Also, there are amino acid complexes that consist exclusively of amino acids in free form, but such amino acid complexes are quite expensive and are not so easy to find in stores.
Amino acid complex
So what is the difference between protein and amino acids? The answer is that there is no fundamental difference between protein and amino acids . There is no difference between a protein that contains whey protein isolate or hydrolyzate and an amino acid complex that contains whey protein isolate or hydrolyzate.
In practice, this means that you can take both protein and amino acids. With a similar composition and similar dosages, the effectiveness of protein and amino acids will be the same. In this case, protein will cost a little less than amino acids, but amino acids in the form of capsules or tablets are more convenient to take.
But, there is one nuance that is worth paying attention to. Since whey protein isolate and hydrolyzate are quite expensive (whey protein hydrolyzate is especially expensive) and taking 30 gram servings of these forms of whey protein unless you are a professional athlete is simply not practical, the optimal solution is to take whey protein concentrate, which costs a significant amount cheaper, and amino acid complexes.
For example, immediately after finishing a workout, it is advisable to take 5-10 grams of an amino acid complex, which will quickly be absorbed and within five minutes will begin to saturate the muscles with amino acids, and 15-30 minutes after the amino acid complex, take 30 grams of whey protein concentrate, which will be absorbed longer and will saturate muscles with a large amount of amino acids. Also, it is advisable to take 5-10 grams of the amino acid complex in the morning, immediately after waking up, in order to activate anabolic processes as quickly as possible and lower cortisol levels. In all other cases, it is advisable to take protein.
Subscribe to our social networks to be the first to receive the most interesting and useful information on bodybuilding and fitness: Telegram, Facebook, Instagram, Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki, Twitter.
Share this article:
The best proteins and amino acids
You should always select sports nutrition taking into account not only cost, but also quality. The following additives demonstrate a good relationship between these two criteria:
- Proteins . Mutant Whey with 61% protein, Syntrax Whey Snake and Syntrax Matrix with 77% protein, Maxler Whey Protein with 73% protein.
- Amino acid complexes . Scitec Nutrition: Amino 5600, Dymatize Super Amino 6000, Hardlabz Aminoz.
This is not a complete list of protein supplements. You can always look at various reviews and tops that describe a wide variety of complexes and proteins. When choosing a specific product, you can watch reviews and even videos that allow you to make your final choice.
EAA and protein
The combination of a balanced EAA formulation and a high-quality concentrated protein should provide the beneficial effect of a rapid and significant increase in leucine concentration to activate protein synthesis at the molecular level, as well as provide sufficient amounts of other essential amino acids to maintain the long-term availability of all precursors necessary for protein synthesis. In this study, researchers determined the acute protein kinetics response to two doses of a formulation containing free form EAA and whey protein, as well as the response to consuming amounts of a popular whey-based protein supplement.
Study of the effect of a mixture of EAA and protein on protein synthesis
The study involved 16 healthy men and women not involved in exercise, 8 of them took a serving of whey protein isolate containing 12.6 grams of protein, the other 8 took in one case a mixture consisting of essential amino acids EAA in free form with whey protein, total weighing 6.3 g and in another case the same mixture, twice the dose - 12.6 g. The composition of the additives is shown in the figure below.
Thus, the effects of pure protein were compared with a mixture of protein and EAA, equal in weight, and half the weight of a portion of the mixture. Overall anabolic response, or net protein balance (whole body protein synthesis minus breakdown), was measured in all subjects over a 4.5-hour fasting period and 4 hours after supplementation. The second parameter measured was the fractional rate of muscle protein synthesis within 4 hours after drinking the drinks. The concentration of amino acids in the blood was also recorded.
Results of the study of amino acid-protein mixture (Low EAA)
The researchers saw that within the first 4 hours of supplementing with 6.3 grams of amino acid-protein supplementation (Low EAA), muscle protein production increased similar to that of 12.6 grams of whey protein. The administration of 12.6 grams of the amino acid-protein mixture had a significantly greater muscle effect than whey and half the mixture. Moreover, a 12.6 g portion of the mixture increased both protein synthesis and significantly reduced its breakdown. Which led to an almost 6 times greater net protein balance.
The change in total EAA concentration after consumption of the mixture was directly related to the dose of the study product. Both doses of the EAA/protein mixture product caused significantly greater increases in EAA concentrations than protein alone. Plasma leucine increased to significantly higher levels at both doses of the formula compared to the protein product even though the amount of leucine obtained from the smaller portion of the formula was less than the amount of leucine in the protein product.