Watercress
Watercress contains a significant amount of protein per calorie.
It is a plant of the cruciferous family that grows in water. It contains a high amount of protein per calorie. Watercress has the following protein content ():
- A standard 35-gram serving of watercress contains 0.8 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of watercress contains 2.3 grams of protein and 11 calories.
- Protein makes up 84% of its calories.
A 35-gram serving of watercress also contains 85 micrograms of vitamin K, which is almost 100% of the recommended daily intake for adults. This vitamin is important for healthy blood and bones ().
Watercress is a rich source of the powerful antioxidant vitamin C and also contains B vitamins, calcium, potassium and vitamin A.
In addition, watercress provides antioxidant protection. It also contains phenolic compounds that may help prevent cancer (, , , ).
Avoid cooking watercress as this will reduce its antioxidant content. Instead, eat raw watercress in salads, add it to sandwiches, or use it to make smoothies ().
The role and rate of protein intake
Protein (protein, polypeptide) is an essential element of human nutrition. Proteins are necessary to regulate biochemical reactions and metabolism. These substances supply the body with amino acids, which contribute to the production of its own proteins and the release of energy.
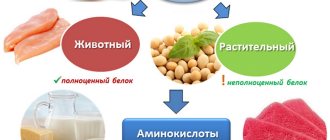
The main sources of protein substances are products of animal and plant origin. First of all, these are meat, eggs, dairy products, nuts, and grains. To a lesser extent, protein is found in vegetables, fruits, berries and mushrooms.
Despite the consensus among experts about the undeniable value of protein, there is an opinion that the existing recommended standards are too low. In any case, generally accepted figures are only general recommendations that should be adjusted in each specific case.
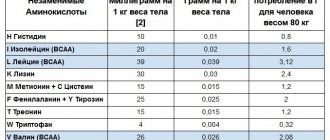
When monitoring your diet, you should always take into account that the amount of protein in it should be at least 30%. A similar number should be for fats , and for carbohydrates - 40%.
| Normal weight 50 kg | 60 kg | 70 kg | 80 kg | |
| Men | ||||
| For weight loss | 165 g | 170 g | 175 g | 185 g |
| To maintain weight | 145 g | 155 g | 165 g | 175 g |
| For gaining muscle mass | 180 g | 190 g | 200 g | 210 g |
| Women | ||||
| For weight loss | 140 g | 150 g | 165 g | 175 g |
| To maintain weight | 115 g | 125 g | 135 g | 145 g |
| For gaining muscle mass | 155 g | 165 g | 175 g | 185 g |
Let's look at some basic foods that contain a lot of protein.
Alfalfa sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts contain very few calories but are rich in nutrients.
Alfalfa sprouts have the following protein content ():
- A standard 35-gram serving of alfalfa sprouts contains 1.3 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of alfalfa sprouts contain 4 grams of protein and 23 calories.
- Protein makes up 69% of the calories in alfalfa sprouts.
This vegetable is a rich source of vitamin K and a decent source of folate, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, copper and vitamin C.
Animal studies have shown that alfalfa sprouts may lower cholesterol levels. This may be due to their high levels of saponins. Saponins are a group of compounds that can lower cholesterol levels (,).
In an earlier study conducted in 1987, researchers gave 15 people with high blood lipid levels 40 grams of alfalfa seeds three times a day for 8 weeks. These people had a 17% reduction in total cholesterol and an 18% reduction in low-density lipoprotein or "bad" cholesterol ().
Research also shows that alfalfa sprouts may reduce inflammation, reduce menopausal symptoms and—thanks to their high vitamin K content—help prevent osteoporosis (, ,).
Spinach
Spinach is one of the most nutrient-rich leafy green vegetables.
Spinach has the following protein content ():
- A standard 25-gram serving of raw spinach contains 0.7 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of spinach contains 2.9 grams of protein and 23 calories.
- Protein makes up 50% of its calories.
The protein in spinach contains all the essential amino acids. One 25-gram serving of spinach contains 121 mcg of vitamin K, which is just over 100% of the recommended daily intake for humans ().
Spinach is also a rich source of folate, vitamin A and vitamin C. It is a good source of magnesium, iron and potassium and a decent source of calcium.
Spinach contains plant compounds that may enhance antioxidant defenses and reduce inflammation ().
In one study, 10 athletes who took spinach supplements for 14 days showed reduced oxidative stress and reduced muscle damage after running a half marathon compared to those who took a placebo ().
In another study, researchers gave nitrate-rich spinach to healthy participants and measured its effect on levels of nitric oxide, which is a signaling molecule that dilates blood vessels. They also measured cell function and blood pressure.
They found that nitrate-rich spinach increased nitric oxide, improved endothelial cell function, and lowered blood pressure—all of which may improve heart health ().
Research has also linked eating spinach to a lower risk of certain types of cancer, including breast cancer ().
What happens when there is a deficiency or excess of a substance?
The above standards apply subject to the following rules:
- The correct ratio of plant and animal foods.
- Complete amino acid composition.
- The presence of additional carbohydrates and fats in the diet.
The lack of proteins in the diet can be determined even by eye. Shortage leads to:
- to sagging skin and the appearance of fine wrinkles.
- loss of muscle mass and sagging muscles on the body.
- deterioration of the condition of the skin, hair and nails.
- problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and obesity.
- decreased resistance to stress and rapid fatigue.
A blood test with a significant protein deficiency shows a lack of hemoglobin and immunoglobulin.
Excess of this substance is also harmful. Excessive consumption is bad for the kidneys. It can cause osteoporosis: calcium is required for the absorption of proteins, and if there is a lack of the mineral in food, it will be extracted from the bones. In addition, abuse increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Chinese collard greens, or bok choy
Chinese collard greens, called bok choy, are also rich in protein.
Bok choy has the following protein content ():
- A standard 70-gram serving of shredded bok choy contains 1.1 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of bok choy contains 1.5 grams of protein and 13 calories.
- Protein makes up 46% of its calories.
Chinese kale is a rich source of vitamins A, C, and K. It is also a good source of folate and a decent source of calcium and potassium.
A number of studies have shown that Chinese kale is rich in compounds with antioxidant activity. Its outer leaves seem to contain most of the antioxidants. It may also have anti-inflammatory properties (, , )
Some research suggests that cabbage vegetables—a group that includes Chinese kale—may contain compounds that reduce the risk of prostate cancer ().
Additionally, an animal study found that taking bok choy powder supplements reduced the risk of liver cancer ().
People use bok choy in many Asian recipes, such as stir-fries, kimchi, soups, and spring rolls.
Asparagus
Asparagus is a very popular vegetable that is high in nutrients.
Asparagus has the following protein content ():
- A standard 135-gram serving of asparagus contains 3 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of asparagus contain 2.2 grams of protein and 20 calories.
- Protein makes up 44% of its calories.
Asparagus is a rich source of vitamin K and a good source of folate and riboflavin. It also contains some magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin A.
Asparagus may also have anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties ().
It also contains fructooligosaccharides, which have prebiotic properties, stimulating the growth of friendly gut bacteria (,).
You can roast, boil, steam or sauté asparagus, and it works well in salads and as a side dish.
Mustard greens
Mustard greens belong to the Brassica family. It is very similar to cabbage, but has a pronounced mustard taste.
Mustard greens have the following protein content ():
- A standard 55-gram serving of chopped mustard greens contains 1.6 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of mustard greens contain 2.9 grams of protein and 27 calories.
- Protein makes up 42% of its calories.
A 55-gram serving of mustard greens also contains 144 mcg of vitamin K, which is more than 100% of the recommended daily intake for humans ().
It is a rich source of vitamin C and also contains calcium, potassium and B vitamins. It is also a good source of vitamin E.
Mustard greens, like many other plants, contain phenolic compounds that give them antioxidant properties (,).
A test-tube study found that steaming mustard greens increased their ability to bind to bile acids. It may help you lower your cholesterol levels ().
The same study also found that steaming may have similar beneficial effects on collards, kale, kale, green peppers and broccoli.
You can steam, boil or stir-fry mustard greens, or you can simply eat them raw.
Cabbage
Kale is a dark green, leafy vegetable in the same family as kale, broccoli, and cauliflower.
Collard greens have the following protein content ():
- A standard 35-gram serving of chopped kale contains 1.1 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of kale contains 3 grams of protein and 32 calories.
- Protein makes up 38% of its calories.
Its vitamin K content is especially noticeable - 157 mcg per 35 gram serving. This is about 131% of the recommended daily intake for humans ().
It is also rich in vitamin C and folate, is a good source of calcium and contains some potassium.
As another member of the Brassica family, kale is a good source of phenolic compounds and antioxidants (,).
Research has linked the high levels of antioxidants in kale to a reduced risk of prostate cancer ().
One study found that people who eat cruciferous vegetables, such as kale, are less likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer ().
Kale can also bind to bile acids in the intestines, which helps lower cholesterol levels. One study found that steaming increased this effect ().
You can enjoy collard greens steamed or sautéed. It is especially tasty mixed with other vegetables, including onions and mushrooms.
Broccoli
Broccoli is a very popular vegetable that also contains protein with all the essential amino acids. You can enjoy it raw or cooked.
Broccoli has the following protein content ():
- A standard 90-gram serving of chopped broccoli contains 2.5 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of broccoli contains 2.8 grams of protein and 34 calories.
- Protein makes up 33% of its calories.
Broccoli is a very rich source of vitamins C and K, a good source of folate, and a decent source of phosphorus and potassium. It also contains some calcium.
Broccoli also contains high levels of plant compounds and flavonoids such as kaempferol. They can have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects ().
Like all cruciferous vegetables, broccoli is high in glucosinolates. These are compounds that may help reduce the risk of cancer ().
Also like mustard greens, broccoli has a greater ability to bind to bile acids when steamed, so eating steamed broccoli may help lower blood cholesterol levels ().
In addition, broccoli may help improve liver health by stimulating detoxification and the production of antioxidant compounds in the liver ().
You can steam, fry, bake or sauté broccoli. It is also good for making soups and sauces, or using as a side dish.
How to Increase Your Protein Intake
- Make a diet of predominantly protein foods.
- As a snack – cheese or a handful of nuts (almonds, peanuts, macadamia). Pay attention to calorie content if you decide to lose weight.
- Replace your usual porridge for breakfast with eggs (omelet).
- After training, give preference to protein shakes.
- For dinner, a vegetable salad with the addition of boiled fish or poultry. And also the option of cottage cheese + not too sweet fruits or citrus fruits (kiwi, grapefruit).
A healthy diet is, first of all, a balanced and varied set of foods every day. It is necessary to alternate and combine the consumption of plant and animal protein. Expand your menu, try new healthy products, cook according to different recipes. This will not only help provide the body with all the necessary substances, but will also lift your spirits. A cheerful mood and a happy smile are the key to health and a slim figure!
Brussels sprouts
Brussels sprouts are a great addition to most diets. It is a good source of protein, fiber and vitamins.
Brussels sprouts have the following protein content ():
- A standard 90-gram serving of Brussels sprouts contains 3 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of Brussels sprouts contain 3.4 grams of protein and 43 calories.
- Protein makes up 31% of its calories.
A 90-gram serving of Brussels sprouts contains 3.3 grams of fiber. It is also very rich in vitamins C and K and is a good source of folate and vitamin B6. It is also a decent source of iron and potassium.
One animal study found that eating Brussels sprouts promoted the growth and health of gut bacteria and stimulated the production of short-chain fatty acids in the intestines ().
You can cook Brussels sprouts by boiling, steaming, grilling, or sautéing and frying. It goes well as a side dish.
Why is protein food important?
Although amino acids are different chemicals found in many different foods, they are held together in the body by peptide bonds.
Without enough varied protein sources in your diet, you risk becoming deficient in certain amino acids. Low energy, complex muscle mass structure, poor concentration and memory, mood swings, unstable blood sugar levels and problems maintaining or losing weight.
Proteins are used every day to keep the body moving. Because they are used to develop, grow, and maintain virtually every part of our body—from our skin and hair to our digestive enzymes and antibodies to the body's immune system—they are continuously broken down and must be replaced.
Cauliflower
Like broccoli, cauliflower contains a large amount of protein for the number of calories it has.
Cauliflower has the following protein content ():
- A standard 105-gram serving of cauliflower contains 2 grams of protein.
- 100 grams of cauliflower contains 1.9 grams of protein and 25 calories.
- Protein makes up 31% of its calories.
Cauliflower is a rich source of vitamin C and a good source of vitamin K. It also contains some calcium, iron, magnesium and phosphorus.
Cauliflower also contains high amounts of a glucosinolate compound called sinigrin, which may have anti-cancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties ().
The glucosinolate content of cauliflower can be significantly reduced when you cook it. Therefore, cauliflower may be healthier when eaten raw ().
However, cauliflower also contains many other antioxidants that are retained during cooking and their levels may even increase after steaming or baking ().
Like some of the other vegetables on this list, cauliflower can lower cholesterol levels through its ability to bind to bile acids. Steaming cauliflower increases this ability ().
Cauliflower is a versatile vegetable that can be used in a variety of recipes. In many cases, it can replace starchy carbohydrates such as pasta or bread.
Fruits
Not everyone knows that protein can be found not only in vegetables and nuts, but also in fruits. The leaders in this list are avocado, dried apricots and dates. There is slightly less of it in coconut, kiwi, figs and bananas.
There are contraindications! Dates should not be eaten by diabetics due to their high glycemic index. The high calorie content of avocado can interfere with the fight against extra pounds. Kiwi is not suitable for those with high acidity.
Having a correct idea of which vegetables have a lot of protein, you can replace animal protein with plant protein without compromising your health.