Foods high in animal protein
1 eggs
Long before the invention of synthetic protein, eggs were indispensable in the diet of athletes. However, in terms of protein content, any meat steak will surpass an egg, since this figure does not exceed 7 grams. The secret of success is this:
- Egg protein is 95% digestible,
- The egg contains a minimum of fats and carbohydrates,
- Easy to prepare.
They are also full of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants necessary for vision, and nutrients necessary for brain activity, which we do not get in sufficient quantities.
A whole egg is a source of protein, and egg white is protein in its purest form.
1 whole large egg is 6 grams of pure protein, 78 kcal.
2 Chicken breast
Chicken breast is a very famous product with the highest protein content and is considered a dietary product due to its low amount of fat (below 8%). But the protein content per 100 g of meat exceeds 24% . Thanks to this, the body receives 130 kcal.
Chicken breast is very easy to prepare and incredibly tasty if you make it following simple cooking rules.
Foods High in Iron
3 Turkey breast
Turkey breast is very similar in its characteristics to chicken breast meat and is simply irreplaceable for those who want to lose weight without reducing muscle mass.
It is extremely tasty and low in calories.
Boiled turkey contains selenium, which is extremely important for maintaining hormonal levels.
100 g of turkey contains 19 g of protein, which provides the body with 84 kcal.
4 Red meat
Beef is an important and incredibly appetizing source of protein. Moreover, it contains a large amount of vitamins B3 and B12, iron and zinc.
100 g of lean beef contains 16 g of protein and 150 kcal.
Red meat
Red meat typically comes from large animals. It contains higher levels of myoglobin, resulting in a red color. Red meat is associated with heart disease and diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and obesity. Red meat is also linked to colorectal cancer. This is because red meat contains more saturated and trans fats than white meat. Because red meat has more fat, it also has more calories. There are reduced fat and additional lean options. However, red meat contains more iron, zinc and vitamin B compared to white meat. The iron found in red meat is called heme iron, which is easily absorbed by the body.
Protein-rich dairy products
1 Cheese “Cottage” (Curd cheese)
Curd cheese, or “Cottage” cheese, is a grain cottage cheese with the addition of fresh salted cream. This cheese is extremely low in calories. But at the same time, it contains a lot of calcium, phosphorus, selenium, vitamin B12, riboflavin (vitamin B2) and other variety of microelements.
100 g of cheese contains 11 g of pure protein.
The following cheeses are also rich in protein : Parmesan, Swiss cheese, mozzarella and cheddar.
2 Greek yogurt, or filtered yogurt
Low in calories, fortified with calcium and probiotics, this yogurt has an incredible flavor and thick, creamy texture.
100 g of low-fat yogurt contains 10 g of protein (exactly as much protein as 40 g of chicken breast).
Moreover, yogurt is a source of magnesium, riboflavin, and pantothenic acid.
Its calorie content is 53 kcal per 100 g.
Just make sure you choose yogurt without added sugar. Full-fat yogurt is also very rich in protein, but higher in calories.
The following foods are rich in protein: regular fat yogurt (24%) and kefir (40%).
Foods that slow down metabolism
3 Milk
Milk is a very important source of protein, but a large number of adults have problems absorbing cow's protein. But if you're not one of them and can enjoy milk to its fullest, it's an ideal source of high-quality protein.
Milk contains small quantities of almost all the nutrients our body needs.
The milk is enriched with calcium, phosphorus and riboflavin (vitamin B2).
There is approximately the same amount of protein in a glass of milk as in 1 egg, namely 8 g.
Due to the different percentage of fat content, calorie content ranges from 44 to 64 kcal per 100 g of milk.
4 Whey protein
It is made from whey, which is formed during the production of cheese.
And as you know, whey is a high-quality protein from dairy products, which has proven itself to be a very effective muscle builder, as well as an assistant in the fight against excess weight.
This product is very quickly absorbed by the body and is rich in amino acids.
1 serving (35g) contains 27g of pure protein.
It is taken depending on your weight.
Nuts and grains are the main sources of protein
1 Almond
Almonds are the richest in protein compared to other types of nuts - 18%.
100 g of almonds contain 19 g of pure protein.
However, it is very high in calories: 645 kcal per 100 g of nuts. The main caloric content consists of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. It also contains vitamin A, thiamine, many B vitamins and other microelements.
Pistachios (13%) and cashews (11%) occupy a respectable second and third place among protein-rich nuts.
2 Peanut
Peanuts have an optimal ratio of amino acids, so they are perfectly absorbed by the human body. It is also rich in various vitamins, liooleic and folic acid, antioxidants and other useful microelements.
The nutritional value of peanuts is 552 kcal per 100 g.
100 g of peanuts contain 26 g of protein.
3 Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkins contain edible seeds, called pumpkin seeds.
Pumpkin seeds are incredibly healthy: they contain a lot of zinc, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and manganese, as well as a wide variety of vitamins (groups B, A, E, K)
100 g of seeds contain 19 g of protein.
Flax seeds (12% of calories), sunflower seeds (12%) and chia seeds (11%) are not far behind pumpkin seeds in protein content.
4 Hercules
Hercules is a protein-rich product that is amazing in its nutritional value and content of nutrients, which is ideal as a breakfast.
100 g of rolled oats contain 352 kcal.
The flakes are especially rich in B vitamins, magnesium, iron, selenium, phosphorus and many other microelements.
100 g of rolled oats contains 10-12 g of pure protein.
5 Quinoa
Few people have heard such a name, much less are fully aware of the usefulness of this cereal. By the way, quinoa is one of the top 20 healthiest foods with a high protein content.
100 g of cereal contains more than 14 g of protein; it is an excellent source of protein.
This culture is also rich in all kinds of vitamins (A, B, C, E) and microelements such as iron, sodium, zinc - to name just a few.
6 Lentils
Dishes prepared from lentils are distinguished by excellent taste and an unimaginable range of microelements. Boiled lentils contain vegetable protein ( approximately 8 g per 100 g of product ), but due to the low amino acid content, its absorption by the body is very slow.
It is rich in iron, magnesium, folic acid. Another important feature of lentils is their inability to accumulate toxins, so we can safely call them an environmentally friendly product.
The calorie content of lentils is 112 kcal per 100 g.
7 Ezekiel bread
Nutritious and easily digestible, Ezekiel bread is made from sprouted grains and legumes, including millet, barley, wheat, soy and lentils.
Ezekiel is unique in that it is a very rich source of protein, fiber and other various microelements.
1 slice of bread contains 4 g of protein and 80 calories.
Meat proteins
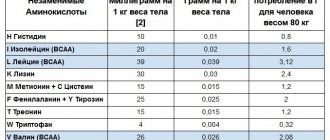
Meat proteins vary in their biological properties. The proteins of muscle tissue that have the greatest value are myosin and myogen (50%), actin (12-15%) and globulin X (about 20%). They contain all essential amino acids, which are favorably balanced.
The approximate content of essential amino acids in high-value meat proteins of the main types of slaughtered animals is on average (in grams per 100 g of product):
- Tryptophan - 0.26
- Lysine - 1.62
- Phenylalanine - 1.65
- Methionine - 0.86
- Leucine - 2.40
- Greonine - 0.86
- Valine - 0.70
- Arginine - 1.08
- Histidine - 0.60
- Isoleucine - 0.70
Meat proteins are distinguished by a high content of amino acids that have growth properties (tryptophan, lysine, arginine).
Under the influence of heat treatment, the content of amino acids in meat proteins changes little.
Less valuable meat proteins are characterized by a high content of amino acids that have the growth properties of tryptophan; meat proteins include connective tissue proteins (stromal proteins). They contain albuminoids - collagen and elastin, lacking a number of essential amino acids.
These proteins do not contain the important essential amino acid tryptophan. In addition, collagen and gelatin do not contain cystine, which, although a non-essential amino acid, has important biological significance.
The resistance of collagen to hydrothermal and other influences depends on the age of the animal. As we age, collagen turns into “mature” collagen. In the latter, intermolecular cross-links occur in addition to intramolecular cross-links, which increase the stability of the mature collagen structure. The meat of young animals, poor in mature collagen, is tender and soft.
With a high proportion of collagen in lean meat, its nutritional value sharply decreases. The presence of 12-25% collagen in food does not ensure tissue protein synthesis even with the addition of the missing amino acids. Collagen, when heated with water, turns into glue - glutin (gelatin).
Consumption of foods containing large amounts of collagen in the form of gelatin has a negative effect on kidney function. Elastin makes up about 1% of the total meat.
The high content of connective tissue in meat negatively affects the organoleptic properties of culinary products obtained from such meat. To improve the quality of meat products with a high content of connective tissue, various methods of preliminary exposure are used - fermentation, grinding, trimming (separation of connective tissue), physical methods of exposure - mechanical and ultrasonic. The use of these and some other pre-treatment methods makes it possible to reduce the hardness of culinary products and increase their taste.
Currently, to determine the nutritional value of meat, a ratio of two amino acids - tryptophan and hydroxyproline - has been proposed. In this ratio, tryptophan characterizes the content of complete proteins, and hydroxyproline characterizes the content of incomplete ones. The table shows data on the values of this indicator in relation to beef of different fatness.
The ratio of tryptophan to hydroxyproline and the content of connective tissue in muscle tissue (longissimus dorsi muscle) of cattle
| Indicators | Fatness | ||
| highest | average | below average | |
| Tryptophan/hydroxyproline | 5,8 | 4,8 | 2,5 |
| Connective tissue proteins (% of total protein) | 2,1 | 2,4 | 3,5 |
From the above data it is clear that the ratio of tryptophan to hydroxyproline is inversely dependent on the content of connective tissue proteins.
Extractives >>>>
Plant-based high protein foods (vegetables)
1 Broccoli
This variety of cabbage occupies a leading place in protein content among vegetables ( 100 g of cabbage contains 3 g of pure protein ), and it is also a storehouse of vitamins and minerals so necessary for our health - vitamins A, B, E, C, K, fiber , iodine, phosphorus and other trace elements.
Broccoli also contains bioactive nutrients that help fight cancer cells.
In addition, broccoli is low in calories: only 30 kcal per 100 g.
2 Brussels sprouts
This miniature cabbage contains a significant amount of high-quality and easily digestible protein ( about 4 g per 100 g of cabbage ).
It is also rich in fiber, vitamin C, phosphorus, and provitamin A.
Like most vegetables, it is low in calories, which allows it to fit perfectly into the diet of people trying to lose extra pounds. Nutritional value is 43 kcal per 100 g of product.
Calorie content of meat. Chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “meat”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 460.8 kcal | 1684 kcal | 27.4% | 5.9% | 365 g |
| Squirrels | 51.2 g | 76 g | 67.4% | 14.6% | 148 g |
| Fats | 27.9 g | 56 g | 49.8% | 10.8% | 201 g |
| Carbohydrates | 1.4 g | 219 g | 0.6% | 0.1% | 15643 g |
| Organic acids | 0.3 g | ~ | |||
| Alimentary fiber | 0.6 g | 20 g | 3% | 0.7% | 3333 g |
| Water | 219.15 g | 2273 g | 9.6% | 2.1% | 1037 g |
| Ash | 3.15 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 600 mcg | 900 mcg | 66.7% | 14.5% | 150 g |
| Retinol | 0.6 mg | ~ | |||
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.105 mg | 1.5 mg | 7% | 1.5% | 1429 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.3 mg | 1.8 mg | 16.7% | 3.6% | 600 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 136.2 mg | 500 mg | 27.2% | 5.9% | 367 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 1.05 mg | 5 mg | 21% | 4.6% | 476 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.75 mg | 2 mg | 37.5% | 8.1% | 267 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 18.45 mcg | 400 mcg | 4.6% | 1% | 2168 g |
| Vitamin B12, cobalamin | 5.1 mcg | 3 mcg | 170% | 36.9% | 59 g |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 1.05 mg | 90 mg | 1.2% | 0.3% | 8571 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 1.2 mg | 15 mg | 8% | 1.7% | 1250 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 6 mcg | 50 mcg | 12% | 2.6% | 833 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 15.2409 mg | 20 mg | 76.2% | 16.5% | 131 g |
| Niacin | 6.75 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 560.25 mg | 2500 mg | 22.4% | 4.9% | 446 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 28.2 mg | 1000 mg | 2.8% | 0.6% | 3546 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 51.6 mg | 400 mg | 12.9% | 2.8% | 775 g |
| Sodium, Na | 109.8 mg | 1300 mg | 8.4% | 1.8% | 1184 g |
| Sera, S | 486.15 mg | 1000 mg | 48.6% | 10.5% | 206 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 425.7 mg | 800 mg | 53.2% | 11.5% | 188 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 129.3 mg | 2300 mg | 5.6% | 1.2% | 1779 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Aluminium, Al | 44.9 mcg | ~ | |||
| Bor, B | 25 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vanadium, V | 6.6 mcg | ~ | |||
| Iron, Fe | 6.3 mg | 18 mg | 35% | 7.6% | 286 g |
| Yod, I | 15.6 mcg | 150 mcg | 10.4% | 2.3% | 962 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 15.15 mcg | 10 mcg | 151.5% | 32.9% | 66 g |
| Lithium, Li | 0.45 mcg | ~ | |||
| Manganese, Mn | 0.1 mg | 2 mg | 5% | 1.1% | 2000 g |
| Copper, Cu | 391.65 mcg | 1000 mcg | 39.2% | 8.5% | 255 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 25.65 mcg | 70 mcg | 36.6% | 7.9% | 273 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 18.6 mcg | ~ | |||
| Tin, Sn | 158.7 mcg | ~ | |||
| Rubidium, Rb | 28.1 mcg | ~ | |||
| Fluorine, F | 137.55 mcg | 4000 mcg | 3.4% | 0.7% | 2908 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 17.55 mcg | 50 mcg | 35.1% | 7.6% | 285 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 6.8658 mg | 12 mg | 57.2% | 12.4% | 175 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Starch and dextrins | 0.15 g | ~ | |||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 1 g | max 100 g |
The energy value of meat is 460.8 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.