- What is compulsive overeating
- Causes of the problem
- Symptoms of the disorder
- Consequences
- Treatment
- Inpatient therapy
- Is it possible to deal with the problem on your own?
- Nutritional Features
Attention! Drug use causes irreparable harm to health and poses a danger to life!
Eating disorders affect about 10% of the population. Some diseases, such as anorexia, bulimia, are known and discussed by scientists and doctors around the world. Others, such as compulsive or psychogenic overeating, remain little known and therefore are often not perceived as a dangerous disease. However, compulsive overeating is a mental disorder that requires treatment.
What is compulsive overeating
Binge eating disorder is also known as binge eating disorder, binge eating disorder, and hyperphagic stress response. All of these synonyms describe an eating disorder in which a person eats a lot, which causes excess body weight. As a rule, compulsive overeating is a defensive reaction to various stress factors. A feature of the disorder is the absence of real hunger, and food is necessary in order to drown out emotions.
Unlike bulimia, episodes of exacerbation do not end with vomiting. The disease affects about 2-5% of the population, while 75% of patients are women and adolescents.
Overeating reasons
The first and main reason for most cases of overeating and gluttony is the presence of mental and psychological problems that a person has developed at the moment.
The main reason is the manifestation of the consequences of various stressful situations that a person can experience during the day, both small ones, in the form of minor conflicts in transport, shops, on the street, etc., and more significant ones that can radically change a person’s life ( both negative and positive).
You work all day, come home tired, and the only thing you want is to eat well and lie down. And if after work you found the strength to take a walk in the park, play sports, i.e. Find yourself other pleasant activities, then you will have much less thoughts about food. In short, find a hobby you like!
For many people, especially women, overeating occurs in an unstable home environment. Quarrels, scandals with their spouse, worries about children, lack of harmony in family life (stress factors) - all this forces them to find solace in food. By gorging yourself on pies and sweets, and especially chocolate (which has an anti-stress effect), life begins to seem more rosy and it seems that not everything is so bad. But you get sucked into this pool very quickly - when even the smallest problem arises, you run to the refrigerator to find solace in the next portion of the food you like and love.
The main reasons for overeating
- Decreased background mood, depression.
- Stressful and post-stressful conditions.
- Anxiety, anxiety disorders.
- Various forms of neuroses.
- Endogenous mental disorders.
Diet errors
Now let's look at the mistakes that provoke overeating. Many people have the habit of washing down any meal with large amounts of tea and water, but this seriously disrupts digestion. Food is not processed as it should in the stomach, gastric juice is diluted and further in the intestines the absorption of nutrients is disrupted, as a result of which you feel hungry and continue to eat again.
Another bad food habit is eating in a hurry, on the go, quickly putting food in your mouth without chewing it thoroughly. In this case, the feeling of fullness comes after 20 minutes. So compare - how much you can eat when eating leisurely and feel full, and how much you swallow during the same time when eating hastily.
The historically established and main problem of early development is the desire to feed the child more nourishingly at any cost! It is mainly grandmothers who instill this habit and persuade them to eat “a spoon for mom and dad.” Children's small stomachs quickly stretch, and unhealthy eating behavior is established, which subsequently leads to overeating.
And one more thing: older people should remember that with age, the amount of food they eat must be reduced. Otherwise, you risk developing atherosclerosis. It’s not for nothing that they say that when you’re old, you’re young.
Causes of the problem
Psychogenic overeating is associated with internal and external factors. It is impossible to reliably name the cause of the disorder, but it is known that the trigger may be one or more of the following reasons:
- genetic predisposition, namely the presence of close relatives with a history of obesity or any eating disorder;
- acute or chronic stress (problems at work, school, frequent conflicts in family, friends);
- uncontrollable hunger, following strict diets for an extended period of time;
- dissatisfaction with one's own body;
- emotional instability;
- the presence of endocrine diseases, obesity;
- depressive disorders;
- postoperative recovery.
Get help now
Do any of your relatives or friends have an addiction? Have you tried in every possible way to help, but as a result the person still returned to his past life?
You are not the first to encounter this problem, and we can help you.
We guarantee anonymity, we will persuade you to undergo treatment, and we will help you choose a center.
Call us
+7
or
Call me
Causes of bulimia symptoms
Symptoms of bulimia nervosa can be recognized in childhood and adolescence. As a rule, they develop against the background of pathological relationships in the family. For example, a dominant mother, having formed a symbiotic relationship with her child, can unconsciously inhibit his physical development and prevent social contacts. Often in such families there are conflicts and neglect of the child’s personality. In turn, the child develops:
- guilt;
- feeling of loneliness;
- apathy and despair;
- internal tension.
Pathological relationships in the family are the basis for the development of various mental disorders. However, symptoms and signs of bulimia most often occur in those families where increased attention is paid to the issue of eating behavior, diets and attempts to lose weight; where they discuss the child’s own and weight and give him an assessment. Also, an important role in the development of symptoms of bulimia is played by the assessment of the appearance of children and adolescents: a greater likelihood of developing an eating disorder occurs in those whose weight and figure were subjected to critical assessment by their parents.
Sadness–overeating–anger
Carroll Ellis Izard, Ph.D., who specializes in the psychology of emotions, has made connections between sadness, fear of gaining weight, and anger. Thus, bulimic behavior is an ambivalent mechanism consisting of a “cycle”:
- feelings of anxiety rooted in childhood;
- uncontrollable hunger as a way to cope with anxiety;
- anger, which entails inducing vomiting, other ways of getting rid of food taken.
Neurotic need for love
Karen Horney, a prominent representative of neo-Freudianism, associated the symptoms of bulimia with a neurotic need for love: bulimic behavior, caused, in fact, by the need for such love (food is a symbol of reward, encouragement), is very often accompanied by the development of an anxious state and anger.
Aggression is a food instinct
Frederick Perls, a psychiatrist and the founder of Gestalt therapy, saw overeating (the food instinct) as a manifestation of aggression. In other words, bulimic behavior represents the suppression of high levels of anger, and vomiting represents its rejection. A person who resorts to this method of coping with anger controls his psycho-emotional state without taking out aggression on other people.
Symptoms of the disorder
The severity of the clinical picture depends on the severity of the disease, provoking factors, as well as other situational circumstances. Characteristic signs of compulsive overeating are:
- eating large amounts of food in a short period of time;
- there is a relationship between gluttony and stress factors;
- loss of control over the frequency of food and the method of eating it;
- craving for food in the absence of physiological hunger;
- a person gives preference to “harmful”, unhealthy food, drinks, and sometimes taste does not matter;
- eating food alone, at night, which is associated with the presence of a feeling of shame;
- the appearance of feelings of self-hatred after every meal;
- lack of a sober perception of your body, yourself as a person;
- After attacks, a person can go on a diet, but they are quickly accompanied by breakdowns.
Consequences
Most perceive psychogenic overeating as a harmless addiction to food. However, as the disorder progresses, it leads to mental and physical health problems. The patient constantly experiences feelings of anxiety, fear, restlessness, which causes the development of panic attacks, persecution mania, depressive disorders, anxiety-phobic disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. Often, a patient begins to fight a severe psycho-emotional state with the help of alcoholic beverages and drugs. This leads to the formation of another severe addiction. Against this background, thoughts of suicide may also appear.
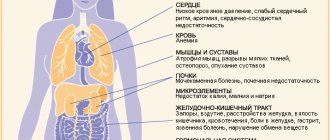
Overeating also negatively affects physical health. Excess body weight, which is inevitable when overeating, causes complications:
- cardiovascular diseases: hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, coronary heart disease;
- diabetes mellitus, other endocrine pathologies;
- sleep problems;
- stopping breathing during sleep;
- alveolar hypoventilation;
- destruction of bone and muscle tissue due to excess body weight, poor nutrition, and lack of physical activity;
- diseases of the stomach, intestines;
- inhibition of fertility, impotence, menstrual irregularities, infertility.
Rarely, poor nutrition, a gradual disruption of the functioning of internal organs can lead to multiple organ failure, disability and death.
A person suffering from psychogenic overeating must remember that food is a means to satisfy hunger, but not emotions.
Treatment
The manifestation of bouts of overeating 2-4 times a week for three or more months suggests that a person suffers from a compulsive disorder. The diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by a psychiatrist, psychologist, as well as somatic specialists. Mandatory during the diagnosis are clinical tests of blood, gastric juice, as well as instrumental studies of the endocrine, digestive, cardiovascular and respiratory systems. A complete diagnosis allows you to assess the patient’s condition, promptly recognize complications, and take measures to eliminate them.
Inpatient therapy
Treatment of eating disorders is carried out individually based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease. Psychotherapy is considered the most effective, namely cognitive behavioral therapy. Work with the patient is carried out using group and individual trainings. During the classes, it is possible to find the cause of pathological cravings for food, assess the psycho-emotional state, cope with existing internal conflicts, regain faith in oneself, find goals in life and learn to realistically evaluate oneself and food.
In severe forms of the disorder, the patient, along with psychotherapy, is prescribed medication, namely antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, tranquilizers, and antidepressants. These groups of drugs help to cope with established mental disorders, causeless fear and anxiety, and normalize the psycho-emotional state. To improve the general condition, vitamin and mineral complexes are used.
In addition to psychotherapy, a mandatory stage of treatment is examination by other specialists, for example, a gastroenterologist, nutritionist, urologist, cardiologist, as well as doctors of other somatic profiles, from whom complications have arisen.
Is it possible to deal with the problem on your own?
With a mild form of compulsive disorder, as well as at the initial stage of its formation, you can cope with the disease at home. Outpatient therapy is based on the following activities:
- eliminate the causes that may provoke an exacerbation of the pathology;
- in stressful situations, try to remain calm and not take everything that happens to heart;
- play sports - physical activity helps to forget negative emotions, improve your psycho-emotional state and cope with excess weight;
- with the help of nutritionists, choose the right, rational diet;
- find a hobby that will bring you pleasure and help you cope with emotional stress;
- take time for self-care;
- do not be categorical about yourself, learn to mobilize energy and direct it in the right direction, and meditation, reading, new acquaintances and active recreation will help with this.
In any large locality there are mutual aid groups where you can seek help, share a problem, find the strength to start fighting a problem, listen to the experience of treating others, and find life goals and priorities. During the treatment of psychogenic overeating, the help and support of relatives and friends is important.
Nutritional Features
In the fight against psychogenic overeating, the patient must work with nutritionists who help restore a conscious attitude towards food, paying attention to the following points:
- adequate daily calorie intake;
- eating 3-5 times a day in small portions;
- the diet should be dominated by fiber, dairy products, fish, fresh fruits and vegetables;
- you need to eat slowly, and while eating it is recommended to pay attention to the taste of foods and their smell;
- It is advisable to boil, steam, stew or bake all products in the oven;
- While eating, you should not read books, watch TV or sit at the computer.
It is also recommended to remove from the house all foods that the patient liked to overeat. This helps reduce disruptions. At first, the nutritionist prepares a menu for the patient every day, which he must strictly follow.
Overeating or gluttony?
Overeating can come in various forms. At the same time, food preferences can often change and emphasis may be placed on foods that the person has not previously consumed. When a disorder of higher nervous activity develops, the level of the “happiness hormone” begins to decrease. Eating is always associated with the release of this hormone. Therefore, a person, to compensate for the lack of this hormone, begins to eat food in increased quantities and in the intervals between main meals. This disrupts the body’s metabolic processes and a “habit” begins to form, which gradually intensifies.
Therefore, overeating, and especially gluttony, leads to serious consequences associated not only with brain disorders. Gradually, concomitant somatic diseases are formed, which a person notices and to which he pays most attention. Naturally, he is trying to get rid of, for example, excess weight, hypertension, etc., paying attention only to the somatic component, which reduces the quality of his life. But, unfortunately, it does not pay attention to the main source of all existing problems.
Complaints of overeating or gluttony
- Various types of sleep disorders - insomnia, nightmares.
- Difficulty falling asleep, early or night awakenings.
- Feeling guilty that you yourself are largely to blame.
- Headache.
- Attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Panic attacks.
- Poor appetite.
- Premature morning awakenings.
Many of us feel heavy after eating. After a hearty lunch, you really want to sleep and there’s no time for work.
And if overeating overtakes you every day, then you risk stretching your stomach, which will certainly reduce the secretion of gastric juice, and the slowdown in stomach and intestinal motility will not keep you waiting long.
The signal of satiety comes after the stomach is completely filled, but in an extended state of food, more and more food needs to be put into it each time. And you will be surprised that after a good dinner you remain hungry, and add an extra portion.
Consequences of overeating
What is the risk of decreased intestinal motility if you overeat every day?
With too much food, the work of almost all internal organs is disrupted. The food mass in the intestines will decompose, causing bloating, and toxins will begin to poison your body. The gallbladder, liver, and endocrine system suffer. Overeating does not have the best effect on your figure. It is better to leave the table hungry than overfed. But few people understand that the causes of major heart problems are banal overeating, including overeating and gluttony during various holidays and celebrations. It is precisely those people who have noticed attacks of angina pectoris or arrhythmia who need to pay attention to their diet.