October 17, 2012
We tell you how to calculate your individual calorie needs and how many calories you need to burn to lose one kg of fat.
Science defines one calorie as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius. In practice, calories measure the amount of energy a person receives from food and spends on physical activity and metabolic processes, such as breathing. By the way, when it comes to caloric intake or energy expenditure, it is more correct to use the term “kilocalorie”. The calorie itself is too small, and the average diet when calculated in such units becomes millions. However, the abbreviated term “calorie” is used in everyday life.
Where do calories come from?
The only fuel that supplies calories to the human body is food. Drinks also contain calories
, for example, juices, milk, sweet soda.
Some drinks, particularly the aforementioned soda, contain empty calories
. They don't provide any nutritional value, but they still need to be considered. Calories are found in the three main components of food: fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Fat has about twice the calorie content of proteins and carbohydrates, but this is not a reason to give it up completely - the body needs fats.
Got enough sleep - burned calories
We calculated how many calories a person spends while performing daily activities. Simply enter keywords (such as "office work" and "sleep") to determine your body's energy expenditure.
Myths associated with counting calories
- The lower your daily caloric intake, the faster the weight will come off. This is true for the first days, when mostly water will go away. Further, your weight will either rise or become more, because the body will put aside reserve reserves of energy for its vital functions, since the amount of calories consumed is below the basic norm - a huge stress.
- When stopping weight, you need to constantly reduce calories. The body adapts to everything, including a constant lack of energy, so you should periodically change your caloric intake. But sometimes it’s worth forgetting about calories for a couple of days, eating whatever you want, and then returning to the norm where you stopped. These swings often help shift the weight.
- Calorie deficit as a lifestyle. This is fundamentally wrong. In order to avoid unpleasant consequences, every two months of deficiency you need to take a break of 2-4 weeks.
- With high daily activity, calorie counting is not necessary. Counting calories is not needed only if you can visually determine the number of calories in a serving and remember everything you eat. Very often people forget that while drinking coffee with a colleague, they ate a couple of cookies (200-250 kcal) or on the way to work they stopped at a fast food restaurant and drank only a cappuccino (100-150 kcal). Such little things can add up to a decent amount, and during an intense workout you burn an average of 500-700 kcal.
- Once you see the treasured number on the scale, forget about counting calories. You can forget about the deficit, but not about counting. But many people are beginning to determine the energy value of a dish by eye, which makes the calculation much easier; it is not necessary to constantly have scales and a calculator.
How to gain and lose weight?
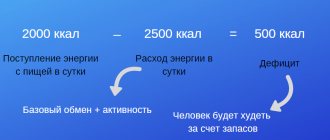
To form one kg of fat reserves, about 7700 kcal are needed. It follows that to lose a kilogram of fat you need to spend about 7700 kcal
.
True, refusing food does not bring the desired result. You need to lose weight wisely: by moderately reducing your caloric intake and burning excess calories through exercise. Reducing calories and/or spending about 500 kcal per day
leads to a loss of about 450 grams of excess weight per week.
Nutritionists consider losing weight at such a speed to be the healthiest
and emphasize that the weight lost in this way will not return quickly.
Starvation diets, on the contrary, not only harm the body, but are also ineffective
. The weight will drop quickly, but with a return to normal nutrition it will instantly return.
What is the role of calories in the body?
Calories allow us to survive. All processes occurring in the body (breathing, the work of the heart to pump blood, tissue repair, digestion, etc.) require energy, which calories give us when breaking down food. In simple terms, a lack of calories is a lack of nutrition, and absolutely everyone understands that a person cannot survive without food. At first, you won’t even have the strength to move, and after using up the calorie reserves in your body (the proportion of fat), it will have no resources left to perform vital functions. Therefore, it is very important to correctly calculate the number of calories for weight loss per day so as not to go into a large deficit.
In addition, the number of calories received and spent shapes our figure. Therefore, it is very important to calculate calories by weight. If the consumption is higher, then you will lose weight, if on the contrary, then you will gain weight, and if these indicators are the same, then you will remain in your current shape.
Determining the basic need
There are many formulas for calculating individual calorie intake, but most often experts use the Harris-Benedict formula
.
It was created back in 1919 and adjusted in 1984, taking into account the fact that over 75 years people began to lead a much less energy-intensive lifestyle. First, we calculate the basic energy requirement necessary for the body to function normally. A person uses about 60 percent of the calories entering the body only to maintain the vital functions of the body. The main factors that influence basic energy requirements are height, weight, age and gender. Basic energy requirement for women = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kilograms) + (3.098 x height in centimeters) - (4.330 x age in years). Basic energy requirement for men = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kilograms) + (4.799 x height in centimeters) - (5.677 x age in years). Please note that this formula only works for adults
.
For example, for a 35-year-old woman weighing 65 kilograms and 165 centimeters tall, 1409 kcal is required daily to maintain the vital functions of the body. Attention:
even with minimal physical activity, the need for energy increases significantly!
The whole truth about metabolism
How do excess calories turn into fat? Why should you reduce your caloric intake as you age? What hormone helps men spend more energy? Read about what metabolism is and how it relates to body weight.
How to calculate your daily calorie intake?
Here are some examples of calculating daily calorie intake using the Harrison-Benedict formula:
1. Male, 25 years old , height 178 centimeters, weight 72 kilograms, plays sports three times a week, the rest of the days he works in the office:
- BMR = 88.36 + (13.4 x 72) + (4.8 x 178) – (5.7 x 25) = 1765 kcal
- Calorie Value = BMR x Activity Level = 1765 x 1.55 = 2735 kcal
2. Woman, 25 years old , height 172 centimeters, weight 50 kilograms, goes in for fitness four times a week, leads an active lifestyle, being on the move most of the day:
- BMR = 447.6 + (9.2 x 50) + (3.1 x 172) – (4.3 x 25) = 1333
- Calorie Value = BMR x Activity Level = 1333 x 1.725 = 2299 kcal
// Online calculator for calculations
How to use a calculator to calculate calorie intake:
- Select metric system
- Please indicate your gender (“male” – male, “female” – female)
- Enter the number of complete years (“age”)
- Enter your height in centimeters (“height”)
- Enter your current weight in kilograms (“current weight”)
- Specify your activity level (“sedentary” – sedentary lifestyle, “light activity” – sedentary, “moderate” – mobile, “very active” – very active).
- Click the button to calculate (“calculate”)
Determining daily needs
Now let's calculate the daily calorie requirement taking into account the level of physical activity. Be objective
and don’t overestimate her!
If you spend 8-12 hours a day at the computer and have long forgotten what the gym looks like, your physical activity can be assessed as very low or even classified as a sedentary lifestyle. Sedentary lifestyle:
daily calorie requirement = basal calorie requirement x 1.2.
Low physical activity
(half an hour of walking and light housework per day): Daily calorie requirement = base calorie requirement x 1.375.
Moderate physical activity
(daily 1-hour walk, 20-minute jog, or housework): Daily calorie requirement = basal calorie requirement x 1.55.
Daily Workout:
Daily Calorie Need = Base Calorie Need x 1.725.
Professional sports Thus, for the woman mentioned above with low physical activity, the daily energy requirement is 1937 kcal. This is enough to maintain your current weight. To lose weight, our hypothetical heroine would need to either increase her physical activity or reduce her calorie intake.
Calculation of calorie intake - formula
Calculating your daily calorie intake begins with determining your basal metabolic rate (BMR)—the energy your body needs to function. The figure includes calorie needs for brain function, maintaining body temperature, digesting food and metabolic processes.
However, BMR does not take into account physical activity - and from 20 to 90% of daily calories are spent by the body not on metabolism, but on everyday movement. Depending on the level of load, an additional human activity coefficient is selected (from 1.2 to 1.9), by which the BMR figure is multiplied.
Harris-Benedict formula
The first version of the formula for calculating calorie intake was presented in 1919 by anthropologists James Arthur Harris and Francis Gano Benedict. To compile the formula, they studied 239 subjects of different genders and ages with different percentages of body fat. The formula was revised and refined in 1984².
// Formula for calculating the basic calorie intake:
- for men: BMR = 88.36 + (13.4 x weight, kg) + (4.8 x height, cm) – (5.7 x age, years)
- for women : BMR = 447.6 + (9.2 x weight, kg) + (3.1 x height, cm) – (4.3 x age, years)
To determine the body's daily caloric needs, you need to multiply the BMR corresponding to your gender, age and weight by the activity factor. In turn, this coefficient is determined depending on the level of physical activity on a particular day.
Daily activity rate
The Harris-Benedict formula for calculating daily calories defines five types of physical activity. Minimum level (no exercise), low level (physical activity 1-3 times a week), medium level (3-5 days a week), high level (6-7 times) and very high level (exercise more than once a week). day).
However, it is in the activity coefficient that the key problem with any calorie calculation formula lies. Once your BMR is accurately calculated (eg 1765 kcal), you need to multiply the figure by your activity factor, which ranges from 1.2 to 1.9. The final result will be from 2118 kcal to 3354 kcal - a difference of 1236 kcal.
// Activity coefficients when calculating calorie intake:
- Minimum activity level - 1.2
- Low activity level - 1.375
- Average activity level - 1.55
- High level - 1.725
- Very high - 1.9
Basics of Dietetics
This is the science that studies proper nutrition.
In dietetics there is such a thing as energy balance. Its meaning is to ensure that the amount of incoming nutrients is completely consumed by the body. The diet should consist of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the correct proportion. Along with food, the body must receive vitamins and microelements every day. Nutritional deficiencies lead to diabetes, hypertension and other diseases, which negatively affects life expectancy.
Balanced diet
To create the right diet, you need to know your metabolic level: how much energy your body uses. Nutritionists use the term basal metabolism (basal metabolism) - the caloric intake required by a person to perform basic vital functions.
When determining the daily amount of calories, basal metabolism, gender, height, and body weight are taken into account.
It must be remembered that metabolic processes in men are faster than in women.
A young body requires more energy than an older one. The average metabolic rate per day for an adult is 25 kcal per 1 kg of body weight. Based on this, the daily protein intake is determined. For athletes and young people leading an active lifestyle, it is recommended from 1.5 to 2.5 g per 1 kg of weight. The norm for moderate activity is no more than 1.5 g, and for a sedentary lifestyle - a maximum of 1 g.
Daily calorie intake depending on a person’s weight.
What you need to know about kcal
Daily calorie intake is the optimal number of kcal consumed per day. Following this norm every day helps to keep yourself in perfect shape.
Many people mistakenly think that weight gain directly depends on the amount of food eaten. Therefore, the less you eat, the greater the chances of maintaining a beautiful figure. However, it is not. Three candies sometimes contain as many calories as a full meal. Excessively high-calorie foods lead to extra pounds, while a lack of daily intake can harm the body.
For this reason, it is so important to count the calories in the foods you eat daily.
The amount of energy a person needs per day
Each person's energy needs are individual, but there are average daily caloric intake standards.
The nature of the female body is such that it creates energy reserves that are needed during pregnancy. This explains the tendency of women to become obese due to poor nutrition. At the same time, losing weight is difficult and takes a long time. The average daily intake for women is from 1600 to 2400 kcal.
Men's metabolism is faster, so more energy is required - from 2000 to 3000 kcal.