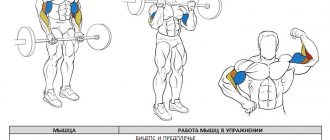
The biceps curl is considered one of the main exercises for developing the biceps brachii muscle. It loads both bundles, as well as the forearm, and is considered basic.
It can be performed by both beginners and more experienced athletes, both in combination with other exercises and as a single exercise, especially if the goal is to gain muscle mass.
Rules for performing exercises
The exercise is considered basic, that is, the main one for the development of biceps. It is included in almost all training programs if it is possible to work with a barbell. Its peculiarity is that it allows you to pump both biceps bundles at once, as well as, to some extent, the forearms.
When performing the movement, you need to follow some recommendations:
- It is better to perform the exercise first, only after it do other movements on the biceps;
- the body must be straight, swaying and bending are not allowed;
- Elbows cannot be moved to the sides;
- It is better to use a small working weight and gradually increase it.
Attention! The exercise is often used in practice, it is not difficult to master due to its relatively simple technique, but its importance cannot be overestimated.
Be sure to watch: How to pump up biceps at home: strong and sculpted arms Training chest and biceps: list of exercises and nuances of pumping Intensive workouts for growing biceps and triceps Arms toned: biceps exercises for girls
Disadvantages of the exercise
For beginners, the movement has two serious disadvantages:
- Possibility of injury due to technical violations;
- Risk of falling
Some athletes simply do not have time to “unhook” their hands from the apparatus and therefore fall back along with the barbell. This usually happens if the weight taken is too heavy. For novice athletes, movement carries many dangers, especially if a person cannot adequately assess training volume. We are not talking about injuries and falls. Many athletes really want to build up their shoulders faster, so they do a monstrous amount of work on them. This causes inflammation in soft tissues and pain.
They say that the reason is the military press itself, and they forbid doing it. But in fact, the reason is the abundance of different presses, and insufficient time and resources of the body for recovery.
A beginner whose strength is not yet sufficient to adequately stabilize the lower back in an exercise may also experience a back injury. Usually this is a vertebral displacement, protrusion or hernia. It is impossible to assume that this movement alone is the cause. In practice, there are many more reasons, and one of them is weakness of the anterior abdominal wall. Until the abs become stronger, it is recommended to wear an athletic belt. But this is not a panacea. The skill of keeping your back neutral will still have to be developed, no matter how much you would like to exercise safely all your life using only a belt.
Hand injuries are common due to improper technique. Many people do not place the bar in the middle of the palm, and do not provide even pressure, but simply try to redistribute the weight so that it is comfortable to lift. This is not always optimal for the wrists. Wrist bandages partly solve the problem of such athletes.
Standards for training in powerlifting
Powerlifting is a sport aimed at lifting a barbell in various movements. The classic version involves three movements: bench press, deadlift and squats, but there are other variations, such as strict biceps curls.
The standards will differ depending on gender, weight, and the federation in which the athlete competes. For example, in WRPF the standards for men are as follows:
| Athlete's weight in kilograms | Projectile mass (3, 2, 1 category, KMS, MS, MSMK) |
| 52-56 | 25, 27,5, 30, 32,5, 40, 47,5 |
| 60-67,5 | 32,5, 35, 37,5, 40, 47,5, 55 |
| 75-82,5 | 42,5, 45, 47,5, 50, 57,5, 65 |
| 90-100 | 55, 57,5, 60, 62,5, 70, 77,5 |
| 100-125 | 65, 67,7, 70, 72,5, 80, 87,5 |
| 125+ | 75, 77,5, 80, 82,5, 90, 97,5 |
The movement must be performed once, but with strict adherence to the correct technique. For women, the standards are slightly different:
| Athlete's weight in kilograms | Projectile mass (3, 2, 1 category, KMS, MS, MSMK) |
| Up to 44 | 12,5, 15, 17,5, 20, 25, 32,5 |
| 48 | 15, 17,5, 20, 22,5, 27,5, 35 |
| 52 | 17,5, 20, 22,5, 25, 30, 37,5 |
| 56 | 20, 22,5, 25, 27,5, 32,5, 40 |
| 60 | 22,5, 25, 27,5, 30, 35, 42,5 |
| 67,5 | 25, 27,5, 30, 32,5, 37,5, 45 |
| 75 | 27,5, 30, 32,5, 35, 40, 47,5 |
| 82,5 | 30, 32,5, 35, 37,5, 42,5, 50 |
| 90 | 32,5, 35, 37,5, 40, 45, 52,5 |
| Over 90 | 35, 37,5, 40, 42,5, 47,5, 55 |
Standards are assigned when movements are performed at competitions and there are judges of a certain rank. Specific requirements are set by each federation individually.
Features of the technique
The technique for performing the exercise will differ slightly depending on the execution option. The classic standing version is performed as follows:
- stand straight, feet approximately shoulder-width apart. Grab the barbell with an overhand grip, palms up, shoulder-width apart;
- arms are bent at the elbows, approximately to chest level;
- Elbows must be pressed to the body; they are not allowed to be pulled to the sides or brought together;
- The bar goes down slowly.
The technique of performing the exercise may differ depending on the movement option. For example, you can perform a movement with a “crooked” bar, taking it narrower.
In this case, the emphasis of the load will shift slightly to the long biceps bundle. The rest of the technology will remain the same.
Barbell curls for biceps. Execution technique
I will consider the classic biceps curl with a straight bar, because... This is the basic exercise, and all its variations are performed in the same way.
And besides, I will write separate articles about each variation of this exercise, so that it is as clear as possible and broken down into atoms.
So, let's talk about the technique of performing this exercise.
- Starting position: Hang a weight on a barbell that you can lift for 6-12 repetitions (8-15 for girls), take the barbell at shoulder width, place your legs about the same, you can slightly bend your knees. The palms are facing forward, the hands are EXTENSION, and the elbows are pressed tightly to the body (the elbows are either pushed forward (the inner head works) or pushed back (the outer head works), but, nevertheless, pressed to the body). The abdominal muscles are tense.
- We draw air into the lungs (inhale), after which, fixing the shoulders and pressing the elbows, we begin UNDER CONTROL, feeling the biceps at each point of the amplitude, and begin to bend the arm using the biceps. At the same time, our hands are still in an extended state (we are not trying to help ourselves with our hands). Continue curling your arm until you feel a peak biceps contraction (your arm can no longer bend) and the barbell is just below shoulder level. Stay in this position for 1 second. Bending your arm, gradually exhale the air from your lungs.
- We exhale completely at the top point of the amplitude (the point of maximum tension).
- Slowly, under control, lower the barbell back towards your hips, almost fully straightening your elbow joint, but KEEPING TENSION in your biceps. As you lower the barbell, gradually inhale air until your chest is completely filled.
- We do the required number of repetitions.
Useful tips:
- The back is FIXED! There should be no swaying of the body, no throwing of the barbell, movement should be carried out only with the help of the elbow joint.
- We lift the barbell in a wide arc, rather than trying to quickly bend the joint.
- At the top point of the amplitude we perform a PEAK CONTRACTION, i.e. We additionally strain the biceps to give it additional load.
- We lift faster than we lower. 1-1.5 s to rise, 2-2.5 s to lower.
- There is no need to throw the barbell; always lower it down under control and smoothly.
- At the bottom of the movement, you should straighten your elbows until you lose tension in your biceps. Where the tension starts to go away, stop. Biceps are always tense!
- Perform a fascia stretch after performing biceps curls (biceps stretch).
- This is the best exercise to train your biceps, start your arm workout with it.
- Additionally, use a weightlifting belt to avoid unnecessary tension in the lumbar spine.
For your convenience, I made a cool picture for you so that you can clearly see how to perform a barbell curl:
As you can see, in the picture above I am performing the barbell curl in its classic form (with the elbows slightly pushed forward) and lifting the barbell in a large arc, and not in a shortened version.
Now I'll show you what I mean.
Here are two options for performing barbell curls:
- The first (classic version): more difficult in terms of lifting, because a large load is additionally created at point “B”. This option will allow you to take less weight, but the time the muscle is under load is longer, all other things being equal.
- Second option (reduced amplitude): I will give it to you not to make your life easier, but so that you can take more weight, but at the same time the movement (bending) must be carried out more slowly to compensate for the shorter time under load due to the smaller amplitude of movement.
For example, if you are already stuck with one working weight and cannot progress the load even by 2.5 kg, then it will be useful to perform the exercise in the second version, which will give you further progression and help you take on a new weight.
How to lift while sitting on a “prayer bench”
The exercise can also be performed on the so-called “prayer bench,” which is more often called the Scotus bench. The execution technique will be as follows:
- sit on a bench, adjusting the height to your own height;
- rest your elbows on a special support;
- take the barbell from below, lift it upward with force by bending the elbow;
- Slowly lower the barbell back after reaching the top point and pause for a couple of seconds.
In this case, it is better to choose a light weight. The bench helps to isolate the biceps as much as possible by fixing the arm in a stationary position.
What is the difference and types of grip
You can change the load by changing the grip, that is, the distance between the hands when holding the barbell. A different grip allows you to shift the emphasis of the load to individual parts of the muscles.
Important! Also, the grip may differ depending on the position of the palms. They can grasp the barbell from above or below, respectively, certain parts of the biceps muscle and forearm are included in the work to a greater or lesser extent.
In general, with any grip, all parts of the biceps are used, as well as the forearm; only the degree of load changes when performing a certain version of the exercise.
Narrow
The narrow grip is most often used with a curved bar, but can also be used with a straight bar. In this case, the brachialis is worked to a greater extent, as well as the outer part of the biceps muscle.
The technique for performing the exercise with a narrow grip will not differ fundamentally from the standard version with a medium grip. You also need to stand up straight, take the projectile, lift it sharply, pause and lower it slowly, while not bending your arms anywhere except your elbows, and also moving your back or arching it.
Wide
When performing the exercise with a wide grip, the main load falls on the inner part of the biceps, that is, its short brachialis muscle. The rest of the body, as well as the forearm, also receives some load; we are only talking about shifting the emphasis of the load.
Overhand raises (reverse)
You can also perform exercises with a reverse grip. In this case, you need to take the barbell not with your palms up, but with your palms down. Otherwise, the general technique for standing biceps exercises is followed.
When performing biceps curls while standing with a reverse grip, the load is shifted to the forearm, as well as the brachialis.
Built-in circuits for training strict biceps curls
This instruction includes built-in circuits for training strict biceps curls. Despite the fact that such a movement as strict lifting has recently been gaining popularity, it is nevertheless difficult to imagine an athlete who will train only in this discipline. From this, built-in circuits have been developed, namely circuits that can be built into any plan and add sufficient strict lifting training. This will make it possible to fully prepare for a strict biceps curl and at the same time not interfere with the athlete’s main specialization. And this can be triathlon or bench press, or any other.
The first thing you need to pay attention to if an athlete wants to use built-in cycles is their sports level and experience. If an athlete is just starting to train for strict biceps curls, then it would be advisable for him to use the BicBeginner.xlsm cycle. This program will give him sufficient load for the initial increase in results and will help him quickly master the technique.
If an athlete has been preparing for a strict biceps curl for some time, and has a result at the I-KMS level, then you can take on a cycle for intermediate-level athletes, namely BicIntermdiate.xlsm In this plan, a load of greater magnitude is implemented and will allow the athlete to effectively increase results.
For athletes who are preparing to perform MS-MSMC in a strict biceps curl, have already competed in competitions and strive for high sporting achievements, the BicExperienced.xlsm cycle has been written. It already implements quite high loads and this plan can only be used if you have well-trained hands and the desire for significant achievements in this movement.
It is assumed that the athlete builds the exercises of the cycle at the end of the workout after other exercises of the training day. No other biceps or wrist flexor exercises are suggested during the week. If the athlete is an arm wrestler, then you need to carefully dose the load in those movements that involve the forearm flexor group. In the body of the cycle you can find the line “Exercise of the complex”. This means that the last exercise of the complex needs to be placed in this place to give the arms time to recover and then load them again.
For example, on the second day of the BicBeginner.xlsm cycle, the structure of the exercises is as follows: strict biceps curl, complex exercise, strict biceps curl, concentrated curl. The athlete planned the following plan for training: squat, bench press, standing press, French press. Then the final plan will look like: squat, bench press, standing press, strict biceps curl, French press, strict biceps curl, concentrated curl. That is, the circuit will be built into the end of the workout, and the last exercise will be placed in the place of the “complex exercise”.
Video about organizing biceps curl training
It is also necessary to mention one important detail when preparing for biceps. Namely, if an athlete, after systematic heavy biceps training, feels severe pain in the forearms, it is necessary to give long-term unloading and use exercises for preparation that do not cause accentuated pain, for example, hammer curls for biceps, dumbbell lifts, and the like. You cannot do the exercise through severe pain, however, minimal accumulation of fatigue is allowed.
The cycles used do not have strict restrictions on level, weight-to-height ratio or others. The main requirement is that the athlete eats well and ensures an adequate sports training regime. Adequate protein intake is necessary.
It is also recommended to master the trapezius technique and work on the biceps in an explosive style when it comes to strict lifting. The necessary technical advice can be obtained from this video.
Video on strict biceps curl technique
Cycles can be used both in the off-season and in preparation for competitions. Considering that the cycle mode is power, it would be reasonable to integrate them specifically into power cycles or peaking cycles. It is also not expected to perform more than 6 repetitions in any lead-up or warm-up sets of biceps work.
Instruction text:
- Assess the athlete’s initial parameters and cycle compliance conditions. If there is a match, a decision can be made to introduce a built-in biceps cycle into the training process;
- Depending on the athlete’s level, download the file:
- for beginners – BicBeginner.xlsm
- intermediate – BicIntermediate.xlsm
- high – BicExperienced.xlsm;
- When starting, familiarize yourself with the splash screen, turn it off with a single click and, if necessary, allow editing, then enable the content (this notification is requested by Microsoft Excel when downloading documents from the network);
- Review the exercises being used and make sure that the athlete’s technical skills allow them to be performed;
- Proceed to design the downloaded cycle for yourself;
- Estimate the level of the maximum maximum in the strict biceps curl with an accuracy of 5 kg and enter the value in the “RM” column of the first microcycle. The field is marked with a thick border and yellow shading;
- The weekly microcycle, depending on the cycle, will include from 3 to 4 days. Optimal mode: Mon, Wed, Fri or Tue, Thu, Sat for three training days. For four training days: Mon, Tue, Thu, Fri or Tue, Wed, Fri, Sat;
- Pay attention to the adjustment percentage column. The optimal value is 0.5. The adjustment percentage is set for each week separately and can change during the period in order to regulate the load;
- Save the file and start implementing the loop.
We pump our arms correctly with a projectile
When performing the exercise, it is important to follow a number of recommendations, which will allow you to fully load the muscles and ensure their development:
- It is better to perform the movement first if we are talking about the standard version of lifting with a medium grip. After this, other exercises can be performed: dumbbell lifts, deadlifts, and so on;
- Compliance with safety regulations plays a primary role. You should not increase the working weight if you cannot perform the movement with normal technique with the previous one;
- elbows should remain motionless throughout the entire exercise;
- It is best to use a straight bar as the main exercise.
It will be enough to perform 4 sets of exercises of 8-12 repetitions. Then you can include 1-2 other exercises, performing them for 10-15 repetitions. One biceps workout per week will be enough.
Scott Bench Dumbbell Curls
This biceps exercise targets the middle and bottom of the biceps. An isolating exercise, used to highlight the lower part of the biceps and its peak. Recommended for advanced and more experienced athletes to complete their biceps training.
Exercise technique
1. Adjust the height of the desk so that its upper edge rests against your armpit, your back is straight, and your body position remains fixed throughout the entire approach. 2. Take a dumbbell of the desired weight and place one hand so that the triceps are pressed firmly to the desk. 3. In the starting position, the back is straight, the elbow lies on the desk, the arm with the dumbbell is straightened, but not to the point of locking in the elbow joint. The palm faces up. 4. Take a deep breath and, holding your breath, lift the dumbbell up. At the top point it should be at chin level. 5. You can exhale after overcoming the most difficult section of the amplitude. Then immediately, slowly, return the dumbbell to its original position. 6. At the bottom point, the arm is fully straightened again, and the dumbbell changes its direction of movement without delay. 7. After completing all repetitions for one arm, proceed to perform the exercise with the other arm. This will be one approach.
Technique tips
- Throughout the entire approach, the elbow should be pressed tightly to the desk. By tearing your elbow off, you put a lot of stress on the joint, which can lead to injury.
- The elbow should always be pointed straight down. If it is directed inward or outward, there is a possibility of dislocating the joint.
- Make sure that at the lowest point the arm does not extend until it locks in the elbow joint. Locking is dangerous not only for the elbow, but also for the biceps ligament.
- Holding your breath while performing the exercise helps not only keep your back straight, but also develop significantly greater force while lifting the dumbbell.
- Keep your body still throughout the entire approach. Adjust your seat and desk so that you don't have to lift your butt off the bench or your elbows off the desk.
- If possible, use a Scott bench to perform the exercise while standing. This way you can better fix your posture and avoid unnecessary body movements.
- To maximally work out your biceps, you can pause for literally 1-2 seconds when passing the most difficult section.
- Do not twist or bend your wrists while raising or lowering the dumbbell. This can cause a wrist dislocation.
- The option of performing the exercise with both hands at the same time is more preferable. This way you stabilize the position of the body and eliminate unnecessary body movements.
- Variations of the exercise with different grips are possible. Turning the hand upward with your thumb shifts the load on the brachialis. Turning the hand palm down loads the brachioradialis muscle.
- A variation of the exercise on the back side of the desk is possible. But be careful. In this position, the arm will hang freely, which can lead to excessive extension at the elbow.
Main conclusions
Before pumping up your biceps, you should do a warm-up, as well as other exercises, if they are planned for this training day. It is better to train the biceps at the end or together with the triceps, combining them into a general arm workout.
The technique for performing the movement is simple, but requires a little practice. It is better to start with a small weight, gradually increasing it.
Lifting the barbell is carried out with the first movement, as it works the entire muscle at once, after which isolated movements are added.
Anatomy exercises
Lifting the barbell is aimed at developing both bundles of the biceps muscle of the arm - the biceps. The load is distributed unevenly, so the long (inner) beam does more work. Short (external) – loaded using other movements with additional weights.
Biceps exercises with dumbbells or a barbell are classified as isolating movements. Their action is maximally aimed at loading the biceps muscle, but not only. Before you start training, you need to figure out which muscles work in parallel:
- brachyradialis;
- anterior delta;
- brachialis;
- wrist extensors and flexors;
- round shoulder.
Lifting a barbell that is too heavy for your biceps or performing the exercise uncontrollably and quickly will cause irreparable damage to your joints. Uneven load, sudden movement, lack of warm-up before training can lead to muscle rupture. In such cases, further surgical intervention will be required.