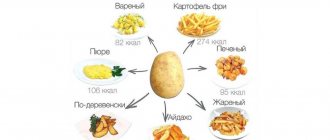
Kinds
Numerous varieties of hard cheeses are produced using two methods: boiling or drying with the addition of lactic acid bacteria and enzymes that stimulate the milk coagulation process. This product can mature from three months to three years.
A special niche is occupied by extra-hard cheeses (Italian Parmesan or Swiss Sbrinz), which wait from two to ten years to be ready. The famous Parmesan cheese becomes the hardest product when ripe. It is split with a knife resembling a chisel, as well as with a special hammer that hits the metal insert on the handle of the knife. If the calorie content of Swiss hard cheese of the Sbrinz variety is 429 kcal per 100 g of product, then Italian parmesan is a more dietary option, its energy value is 292 kcal per 100 g.
Extra-hard cheeses are used to prepare gourmet dishes either in grated form or in small crushed pieces. They are also served ready-made in thin shavings as an appetizer with wine. The varieties of hard cheeses include: naturally ripened cheeses (Gouda, Edamer, Maasdam), gourmet blue cheeses (Blau Bastianse, Delfts Blau), peasant cheeses (Beemster, Stolweiker) ), smoked (“Gouda”) or with a red rind (“Doruvael”). The calorie content of hard cheese depends on its fat content, which in Parmesan is 32%, in Dutch cheese - 45%, in Swiss cheese - 50%. It is known that the higher this indicator is for a popular fermented milk product, the tastier it is.
Hard cheeses in Russia are produced: “Dutch”, which corresponds to “Edamsky” from the Netherlands, “Swiss”, English “Cheddar”, “Kostromskoy”, “Rossiysky”, “Sovetsky”, “Yaroslavsky”, “Altaisky” and “Gornoaltaisky” ", "Moscow", "Caucasian", Brie President cheese, smoked varieties and others.
Types of tofu cheese
There are several types of tofu cheese.
They differ in moisture content, protein content and other properties:
- Japanese (silken) tofu
. It has a smooth and silky structure, and in appearance resembles pudding. If you open the product package, you may find a soft mass. This is due to the high liquid content in the cheese. Unlike other varieties, it is not pressed. Any attempt to prick a piece with a fork will be unsuccessful. Japanese tofu is best pureed and prepared into sauces, omelettes, and creamy desserts. It is not suitable for baking or frying in a pan. - Soft tofu.
Quite often, soft tofu is confused with silken tofu. However, these varieties are not interchangeable. When purchasing a product, it is important to pay attention to the label, which clearly indicates the type of product. When making soft tofu, a press is used to remove excess liquid. Despite the high moisture content, it does not have the creamy texture of the silk version. It is rarely used in culinary recipes. - Regular tofu.
This is a dense cheese that holds its shape well when cut. Usually sold in the form of bars and stored in refrigerators. He is very sensitive to smells and tastes. Therefore, before starting cooking, it should be held under pressure and squeezed out. The use of spices is allowed as in the case of any other protein product. However, it is better to avoid marinades with vegetable oil. The cheese will not absorb them. - Firm tofu.
This product option is considered the most popular. It contains little moisture and the structure is dense. During the manufacturing process, a double dosage of coagulant is used. Firm tofu is well suited for dishes that require a crispy crust when cooked. It can also be used in salads and baked. - Extra-firm tofu.
The product has a high density. It practically does not crumble or disintegrate during cooking, so it is ideal for frying. There is no need to squeeze it further to remove excess liquid. Just blot with a paper towel.
Today, exotic versions of tofu are increasingly appearing in stores. Some cheeses are prepared in the traditional way using soybean puree. For others, a special type of cottage cheese is used as a raw material. A prime example is black tofu. In reality, it is purple in color, and in the cooking process, black beans are used instead of the classic yellow ones. It has a smooth structure and contains a lot of protein. You can also find non-soy tofu. It is made from chickpeas and almonds.
Compound
Cheese contains 26–28% protein, which is absorbed by the human body much better than meat. Nutritionists call solid varieties “concentrated milk” because sometimes a small piece of cheese for breakfast (30–50 g) can replace 300–400 ml of valuable liquid. The high calorie content of hard cheese is associated with the high lipid content in milk (20-28%). They are also rich in vitamins: A, group B (B1, B2, B6, B9, B12), PP, E and C. The product described contains many minerals: zinc, calcium, copper, manganese, sodium, iron, magnesium, potassium , phosphorus. Milk fat has a low-melting structure and a large amount of phosphotites, which contribute to its almost complete absorption (98-99%).
Processed cheeses
- The Swiss didn’t have enough of their ordinary cheeses, so back in the 50s of the last century they invented a way to make “processed” cheese with a calorie content of 294 kcal, by heat treating rennet (again this is a funny word) cheeses. And they still produce such a product under the Kraft brand. Flavoring fillers are added to the mass - salt, spices, butter, sugar, mushrooms, bacon. The result is a tasty paste or layer with different flavors.
- And if you form “sausages” from the processed cheese mass (hence the name) and smoke it in special smokehouses-chambers, you get “sausage” cheese with a calorie content of 275 kcal. As a result, we get what we are used to having for breakfast - a refined aroma of smoked meat with a high content of vitamins A, folic acid, phosphorus, calcium and potassium.
Benefit
When consuming hard cheese, which is high in calories, you need to monitor portions in moderation and a sufficient amount of physical activity. This will help burn off the excess energy gained from the nutritious product.
But hard cheeses, if eaten regularly in sufficient quantities, provide a person with the essential amino acids they contain: tryptophan, methionine and lysine. The first helps reduce appetite and is involved in the synthesis of vitamin B3, which is necessary for brain activity. In turn, lysine and methionine help break down fats and slow down the aging process of cells.
Calorie table for different types of hard cheese
Despite the benefits that hard cheese provides to the body, the calorie content in 100 grams of any type of this product is 17-20% of the total daily diet. Anyone who is watching their figure or their blood cholesterol levels should consume no more than 20–50 g of mature cheese per day.
| Cheese varieties | Fat content | Energy value in kcal per 100 g |
| "Dutch" "Gouda" "Edamian" | 45 % | 340-356 |
| "Gouda" | 48% | 361-362 |
| "Kostroma" | 45% | 345 |
| "Russian" | 45-50% | 337-366 |
| Kondrovo Russian "Olterber" | 50% | 355 |
| "Dobryan" Russian | 50% | 360 |
| "Soviet" | 50% | 356 |
| "Poshekhonsky" | 45% | 350 |
| "Uglichsky" | 45% | 335-347 |
| "Yaroslavsky" | 45% | 361 |
| "Swiss" | 50% | 335-380 |
| "Altaic" | 50% | 355 |
| "Ozerny" | 50% | 350 |
| "Steppe" | 45% | 362 |
| "Cheddar" | 50% | 392-405 |
| "Kaunas" | 30% | 355 |
| "Latvian" | 45% | 316 |
| "Lithuanian" | 30% | 250-338 |
| Lithuanian "Gouda", "Edam" | 45% | 334 |
| "Altaic" | 50% | 356 |
| "Chester" | 50% | 363 |
| Cheese with mushrooms | 50 % | 395 |
| "Emmental" | 45 % | 420 |
| "Parmesan" | 32% | 292 |
| "Gruyere" | 49% | 396 |
| "Munster" | 45% | 365 |
| "Lambert" | 50% | 377 |
| "Appenzeller" | 50 % | 400 |
| "Edamer" | 40 % | 340 |
| "Etorki" (sheep) | 50% | 401 |
| "Roquefort" | 45% | 332-369 |
| "Limburger" | 28% | 327 |
| "Oltermani" | 55% | 400 |
| "Maasdam" | 45% | 340-360 |
When preparing dishes or snacks, hard cheese is often grated to create an appetizing crust. A teaspoon of this delicacy contains 8 g, from which you can get 30 kcal. A tablespoon of grated hard cheese contains 25 g, the calorie content of the product is 94 kcal.
A glass (200 ml) contains 320 g of hard grated cheese with a calorie content of 1200 kcal, and a cup (250 ml) contains 400 g and 1500 kcal, respectively.
Russian cheese BZHU. What is the calorie content of Russian cheese and how to eat it
From this article you will learn what chemical composition, energy value, and calorie content hard Russian cheese has. It will benefit the human body if consumed in a regulated manner.
Calorie content and consumption rate, BJU
- Russian cheese is high in calories, so you shouldn’t get carried away with it. To get the maximum benefit that a dairy product provides to the human body, it is enough to eat from 50 to 100 grams per day. The amount of calories you will get varies, it all depends on the type of food.
- The calorie content of Russian cheese with 50% fat content is 358 kcal per 100 grams of product. BJU (g): proteins – 23, fats – 30, carbohydrates – 0.3.
- The calorie content of cheese with 45% fat content is 337 kcal. BJU (g): proteins – 22, fats – 28, carbohydrates – 0.2.
- Russian cheese "Como" contains 363 kcal. BJU (g): proteins – 27, fats – 29, no carbohydrates.
How it is used in dietetics and for weight loss
Despite the fact that the calorie content of dairy products is high, nutritionists still recommend consuming it during weight loss diets. A slice of whole grain bread with hard cheese for breakfast will fill your body with useful substances and satisfy your hunger for a long time. Therefore, those who are watching their figure are recommended to eat up to 20 g of dairy products in the morning.
The main contraindications for diets will be the maximum consumption of cheese up to 20 grams per day in the morning, twice a week. The best time to eat will be 9-11 o'clock in the afternoon. Before going to bed, avoid this delicacy, as it takes a long time to digest and can cause heaviness in the stomach.
The food should be a natural, non-cheese product.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a sample diet menu for weight loss, which includes Russian cheese:
- In the morning, drink a glass of warm water, after half an hour, eat a sandwich of whole grain bread with cheese, natural coffee without sugar or tea.
- Have a snack with a glass of kefir or low-fat natural yogurt.
- Have lunch with low-fat soup or borscht.
- Snack on an orange or any other favorite fruit.
- Dine with fresh cabbage salad with cucumber and herbs, or stewed cabbage with beef.
When dieting, be sure to exclude foods that contain harmful carbohydrates, canned vegetables, fruits, confectionery, and fried foods. Drink up to 2 liters of water per day. By following this diet for 5-7 days, you can get rid of 3-5 kg without much effort.
Energy value of “Russian” cheese
One of the most popular domestic cheeses, Rossiysky, is produced today in Russia and some neighboring countries. The characteristic features of this type of hard cheese are its pronounced, delicate taste and “fine lace” pattern. “Russian” cheese is prepared from pasteurized milk obtained from cows with the addition of rennet and lactic acid bacteria. The product is aged for 2.5 months and then goes to stores.
The calorie content of Rossiyskiy hard cheese can vary from 337 to 366 kcal. Milk protein is approximately 23%, lipids - about 30% (in dry weight, the fat content of the product does not exceed 50%). This type of cheese is rich in vitamins B, A, E, D and PP. Per 100 g of product there are 0.88 g of calcium, 0.81 g of sodium, 88 mg of potassium and 0.5 g of phosphorus. “Russian” cheese with 45% fat content contains 337 kcal per 100 g of product, the calorie content of hard cheese with 50% fat content (of the same variety) is 358 kcal, and the energy value of Russian “Como” is 363 kcal.
Calorie content Hard cheese. Chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Hard cheese”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 364 kcal | 1684 kcal | 21.6% | 5.9% | 463 g |
| Squirrels | 23.2 g | 76 g | 30.5% | 8.4% | 328 g |
| Fats | 29.5 g | 56 g | 52.7% | 14.5% | 190 g |
| Organic acids | 2 g | ~ | |||
| Water | 41 g | 2273 g | 1.8% | 0.5% | 5544 g |
| Ash | 4.3 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 288 mcg | 900 mcg | 32% | 8.8% | 313 g |
| Retinol | 0.26 mg | ~ | |||
| beta carotene | 0.17 mg | 5 mg | 3.4% | 0.9% | 2941 g |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.04 mg | 1.5 mg | 2.7% | 0.7% | 3750 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.3 mg | 1.8 mg | 16.7% | 4.6% | 600 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 15.4 mg | 500 mg | 3.1% | 0.9% | 3247 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.3 mg | 5 mg | 6% | 1.6% | 1667 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.1 mg | 2 mg | 5% | 1.4% | 2000 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 23.5 mcg | 400 mcg | 5.9% | 1.6% | 1702 g |
| Vitamin B12, cobalamin | 1.5 mcg | 3 mcg | 50% | 13.7% | 200 g |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 0.7 mg | 90 mg | 0.8% | 0.2% | 12857 g |
| Vitamin D, calciferol | 0.96 mcg | 10 mcg | 9.6% | 2.6% | 1042 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.5 mg | 15 mg | 3.3% | 0.9% | 3000 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 2.3 mcg | 50 mcg | 4.6% | 1.3% | 2174 g |
| Vitamin K, phylloquinone | 2.3 mcg | 120 mcg | 1.9% | 0.5% | 5217 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 6.1 mg | 20 mg | 30.5% | 8.4% | 328 g |
| Niacin | 0.2 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 88 mg | 2500 mg | 3.5% | 1% | 2841 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 880 mg | 1000 mg | 88% | 24.2% | 114 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 35 mg | 400 mg | 8.8% | 2.4% | 1143 g |
| Sodium, Na | 810 mg | 1300 mg | 62.3% | 17.1% | 160 g |
| Sera, S | 232 mg | 1000 mg | 23.2% | 6.4% | 431 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 500 mg | 800 mg | 62.5% | 17.2% | 160 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 1249 mg | 2300 mg | 54.3% | 14.9% | 184 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Iron, Fe | 1 mg | 18 mg | 5.6% | 1.5% | 1800 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.1 mg | 2 mg | 5% | 1.4% | 2000 g |
| Copper, Cu | 50 mcg | 1000 mcg | 5% | 1.4% | 2000 g |
| Selenium, Se | 14.5 mcg | 55 mcg | 26.4% | 7.3% | 379 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 3.5 mg | 12 mg | 29.2% | 8% | 343 g |
| Essential amino acids | 8.56 g | ~ | |||
| Arginine* | 0.71 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 1.69 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 1.49 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.97 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 1.93 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 1.53 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.54 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.75 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.92 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.66 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 1.22 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 2.57 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | 14.23 g | ~ | |||
| Alanin | 0.6 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 1.35 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.38 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 4.6 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 2.32 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 1.2 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 1.35 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.21 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Cholesterol | 88 mg | max 300 mg | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 15.9 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| 6:0 Kapronovaya | 0.1 g | ~ | |||
| 8:0 Caprylic | 0.39 g | ~ | |||
| 10:0 Kaprinovaya | 1.26 g | ~ | |||
| 12:0 Lauric | 1.16 g | ~ | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 2.42 g | ~ | |||
| 15:0 Pentadecane | 0.29 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 6.19 g | ~ | |||
| 17:0 Margarine | 0.19 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 3.38 g | ~ | |||
| 20:0 Arakhinovaya | 0.19 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 7.64 g | min 16.8 g | 45.5% | 12.5% | |
| 14:1 Myristoleic | 0.39 g | ~ | |||
| 16:1 Palmitoleic | 0.48 g | ~ | |||
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 6.77 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.68 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 6.1% | 1.7% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.68 g | ~ | |||
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.68 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 14.5% | 4% |
The energy value of hard cheese is 364 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Harm and contraindications
When buying your favorite product, you need to pay attention to its natural composition: adding vegetable fats (palm oil) reduces its cost and significantly deteriorates its quality. It should also be taken into account that people suffering from gastrointestinal problems are prohibited from eating spicy varieties of the described product. Sometimes hard cheese, whose calorie content may be small, causes headaches, migraine attacks or nightmares. This harm is caused by an excess of the amino acid tryptophan coming from cheese. If you overuse solid varieties of the product, this can become a trigger for the occurrence of excess cholesterol in the blood, blood thickening, hypertension or atherosclerosis.
Blue cheese (hard), the calorie content of which is 340-353 kcal per 100 g of a savory product, is prohibited in the diet of pregnant women, since some products with mold contain a dangerous amount of bacteria that cause listeriosis. This disease can lead to problems with pregnancy and birth.
The benefits of cheese for weight loss
- Regular consumption leads to fat burning.
- Milk fats activate metabolism.
If you are trying to lose weight, then you should stop eating Dutch, Kostroma, Smetankova (the calorie content of which is 340-360 kcal per 100 g). Goat cheese, which contains 364 kcal, is also contraindicated during the diet.
Instead choose:
- Mozzarella cheese (280 kcal per 100 g).
- Gouda 7% (calorie content of Gouda cheese is 200 units). Camembert has the same nutritional value.
- Feta and cheese.
- Ricotta (since it is made from whey and its fat content is very low - from 8 to 24%). The calorie content of Ricotta cheese per 100 g is 174 kcal.
- Tofu (76 kcal.).
Although Pigtail and Chechil (which have 313 calories) are recommended as low-fat foods, you should be careful with them. They contain a considerable amount of salt and hot spices, which can cause a burning appetite and cause water retention in the body. The same applies to Suluguni (290 kcal).
For fitness nutrition
The beneficial properties of hard cheeses are a godsend for a vegetarian menu or for those who want to diversify their protein diet. They act as a replacement for meat or fish. Protein is involved in the formation of muscles and organs, and phosphorus and calcium strengthen the structure of joints and bones. When choosing hard cheeses for your diet while losing weight, you need to pay attention to the product label, which indicates the exact energy value of the product in calories. For example, the calorie content of hard cheese with 45% fat content can vary from 310 kcal to 420 kcal.
At the same time, Cheddar cheese can be produced with either a fat content of 49-50% (405 kcal) or 33%. The calorie content in the second case will be only 380 kcal. A dietary version of this cheese called “Cheddar” contains only 18% fat and has only 282 kcal. At the same time, milk fat is absorbed by the human body quite easily, but a high percentage of lipids can hinder weight loss. Therefore, when losing weight, it is more advisable to eat no more than two cheese slices (plates) in the first half of the day. You can also consume no more than 20 g of your favorite hard cheese before lunch, but no more than twice a week.
The product helps maintain muscle mass and health while fighting extra pounds, but it is necessary to ensure sufficient physical activity.
Dietary dish of zucchini with grated cheese
Products you will need: 1 kg of zucchini, 15 g of sunflower oil, 40 g of corn flour, 1-2 eggs, 200 g of Adyghe cheese and 150 g of “Russian” cheese, 1-2 cloves of garlic (to taste), fresh parsley. In order to prepare a delicious dietary casserole, grate the zucchini on a coarse grater and sprinkle with salt. Then they are allowed to settle and the excess liquid is drained, squeezing out the mass. Add grated cheese, chopped parsley, favorite spices, squeeze out the garlic. Mix with flour and egg, giving the mass homogeneity. Grease a baking tray with oil, pour the future casserole onto it and level the surface. Sprinkle with cheese and bake at 180 degrees for 30-40 minutes. The calorie content of this dish is 156 kcal per 100 g of casserole.
Mass fraction of fat in cheese
The mass fraction of fat in a popular fermented milk product, on average, is about 30% of the total mass. One standard serving of cheese (100 g) can satisfy one third of the daily requirement for this nutrient.
The calorie content of a product is determined mainly by fats, mostly represented by saturated fatty acids.
There has been a direct relationship between the amount of lipids in cheese and the milk used to make it. The higher the fat content of the milk, the greater the energy value. The least amount of lipids is in very hard varieties, for example, “Parmesan” - less than 27%, in the semi-hard “Russian” - 30%, in “Adygei” - 20%. The latter refers to brine varieties, which are distinguished by a small amount of fat compared to the others. Read more about the calorie content of cheese in our publication.
( 2 ratings, average 4.5 out of 5 )