The “bicycle” exercise for the abs is in some sense unique. You engage the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles at the same time, work both the lower and upper rectus abdominis, and increase calorie expenditure due to the fact that the movement is performed dynamically. There are several “bicycles”. In Soviet school physical education, this was the name for simulating the rotation of pedals while lying down, and today in fitness, “bicycle” is the name for simultaneous twisting, in which the shoulder reaches towards the opposite hip.
The exercise is used in regular fitness, as well as in group aerobics classes. But it came to fitness from gymnastics. There, the bicycle is an easy way to teach the young athlete to control the center of the body.
In addition, the movement is used as a physical training tool in strength sports such as weightlifting and powerlifting.
What muscles work in the bicycle exercise?
The lying bike exercise is a complex movement that focuses on the abs and lower body. The movement involves most muscle groups, although they are usually divided into primary (directly involved) and secondary (help stabilize the body or work partially).
The main burden falls on:
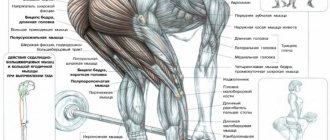
- Press – straight, external and internal oblique, transverse.
- Back – erector spinae, semispinalis, deep muscle group.
- Pelvis – straight femoral, iliopsoas, pectineal, sartorius.
- Legs – hamstrings, gluteals.
Even though the movement is performed to develop the abs, it is important to understand which muscles work in the bicycle exercise. This will allow you to correctly distribute the load and better think through recovery.
Auxiliary:
- Quadriceps femoris muscle.
- Calf.
- Soleus.
- Latissimus.
- Deltoid.
- Big round.
- Diamond-shaped.
- Trapezoidal.
Which muscles the bike works directly depends on the technique used. Some of the auxiliary groups are included only in cases where the exercise is performed with the pelvis lifted off the floor (hands supporting the lower back).
Common mistakes when doing the exercise
Proper cycling is the key to a healthy body. If done correctly, a person will not be able to harm himself.
Beginners make mistakes that must be avoided so as not to cause harm to health.
The main ones:
- choosing a soft surface for performing the exercise - a sofa or bed puts additional stress on the lumbar region;
- making sudden movements, the speed of the lesson does not contribute to development - the useful properties of the bicycle are lost;
- holding your breath - blood pressure rises, heart function is disrupted;
- It is recommended to thoroughly and efficiently warm up before class - this will relieve sprains and prepare the joints for the load;
- it is necessary to rest between approaches - the body should rest well and prepare for the next approach;
- pain during exercise - move on to another exercise, consult a doctor;
- pulling your head up with your hands injures your neck.
The benefits and harms of exercise
Benefits of cycling exercise:
- Tones muscles, improves posture, strengthens core.
- Accelerates fat burning, improves muscle definition.
- Significantly increases endurance.
- Simultaneous training of the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles.
- Visual narrowing of the waist.
downside is how many calories cycling burns. Due to the difficulty of performing the movement, it can only be done for short sessions, so in terms of calorie loss it loses to running, cycling and other types of cardio (and is ideal for the HIIT method).
How to do an ab bike while lying on your back
In the classic version, the movement is performed without lifting the pelvis from the floor. The benefits of the bicycle exercise lying on your back in this version are optimal, taking into account the complexity, efficiency and other criteria.
Execution technique (regular version):
- Lie on the floor with your arms along your body to maintain balance (you can hold on to any support if you cannot stabilize your body).
- Raise your legs at a 45 degree angle.
- Perform alternate rotational movements (imitation of spinning pedals in the air).
The higher your legs rise, the harder the execution becomes. Therefore, before doing cycling exercises for the first time, check your physical capabilities. If you can easily perform 3-4 sets of 60 seconds, gradually increase the load.
Inclusion in the training plan
The “bicycle” exercise can become an independent workout if you do it 10-15 times in 4-5 approaches per day. The main thing is to do it correctly, without trying to simplify the task. You can also include it in your training plan:
- as part of morning exercises;
- for warming up before strength training;
- as part of interval training;
- as a cool-down after a run or intense exercise at home.
Cycling is an exercise with which you can significantly correct your figure. It is useful for everyone who wants to have a strong and sculpted abs, slender legs and a healthy back. For people with imperfect posture, training will be a real boon.
The main thing is not to be lazy and not to give up. At first it will be difficult, since you will have to put in a lot of effort and experience pain in the muscles that are involved in the process of performing the exercise. But once you get used to it, it will be easy and comfortable to practice.
Exercise Bicycle: technique of execution.
Technique for lying down bicycle with body elevation
This version is aimed at maximizing the inclusion of the oblique abdominal muscles. However, in order to properly do an ab bike in this version, you need to control the pace of rotation of the legs (synchronize with the work of the arms).
Technique:
- Lie down on the floor. Place your hands at the back of your head, spread your elbows to the sides. Raise your legs up at an angle of 45 degrees.
- Start slowly rotating your right leg. At the moment when the knee comes as close to the chest as possible, slightly rotate the body and try to bring the left elbow to the knee.
- After this, do the same bringing your right elbow to your left knee.
Despite the fact that the speed of rotation of the legs in the exercise is much slower, this technique is considered quite difficult. By 40-50 seconds, a strong burning sensation will be felt in the abdominal muscles, which indicates that the abs are receiving sufficient load. It is best to perform this option in short but intense sessions (30-60 seconds each).
Contraindications
“Bicycle” - an exercise for the legs - is quite harmless, it is even used in physical therapy. But there are still cases when it should be performed with caution or it is better to completely abandon it:
- During pregnancy;
- For infections in the acute stage;
- For problems with the respiratory system;
- Severe gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Phlebeurysm;
- At elevated body temperature;
- If you have cancer;
- After surgery and fractures, you can only exercise with the permission of a doctor;
- With thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities;
- For heart pathologies, you also need to consult a doctor.
If you have any pain or alarming symptoms, you should not exercise. You need to see a doctor as soon as possible and undergo an examination; at the same time, you can check with the doctor whether it is worth doing the “bicycle” exercise in a particular case, or whether it is better to replace it with something.
How to do a standing bike
The standing bicycle exercise is not the most popular option. But it can be shown to beginners to strengthen the muscle corset and gradually move on to more complex versions.
Technique:
- Stand up straight, back straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Hands are brought together at the back of the head, elbows to the side.
- Begin to raise your right leg (bending at the knee) as high as possible. Closer to the peak point, tilt your body so that your left elbow is as close to your knee as possible.
- Return your leg to the floor and repeat the movement on the other side.
It is important that when trying to bring the elbow to the knee, the back remains straight. This will strengthen the obliques and improve performance.
Recommendations for execution technique[edit | edit code]
- As in the “Scissors”, in the 1st phase of the bicycle exercise, simultaneously pull up the front and back of the pelvis using the abdominal and back muscles to create a slight deflection in the lumbar region. Maintain this position of the pelvis and spine throughout the entire bicycle exercise.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades and straighten your shoulders. The upper arm applies constant pressure to the mat so that the shoulder extensor muscles help keep the torso in an elevated position.
- While keeping your torso stable, try to spread your legs as far apart as possible. Use your knee extensor muscles to straighten your legs and your plantar flexion muscles to pull your toes up.
- In phases 2 and 4, the hip extensor muscles keep the lower leg from falling to the mat, and the hamstrings flex it at the knee. At the same time, the muscles that flex the upper leg at the hip joint are activated when it is above the head (similar to the “Scissors” exercise). This allows you to keep it motionless when moving the lower leg.
- In the 3rd and 5th phases of the bicycle exercise, the knee of the lower leg is pulled towards the chest. To do this, first use the muscles that flex the leg at the hip joint. The upper leg is simultaneously lowered due to the muscles that extend the leg at the hip joint. When the leg crosses the vertical line, antagonist muscles are activated, preventing it from falling under the influence of its own weight. The muscles that extend the leg at the knee joint do not allow it to bend at the knee. At the end of the phase, the muscles that started the movement are reactivated to increase leg extension and stretch the hamstrings of the upper leg and the hip flexor muscles of the lower leg.
- Mental image. As the name of the exercise suggests, leg movements should be smooth, rhythmic and coordinated, like when riding a bicycle.
Common Mistakes
Despite the simple technique, athletes often make a number of mistakes. They not only reduce the efficiency of movement, but can also have a detrimental effect on the condition of the spine.
Main mistakes:
- Raising your head - if your hands are not behind the back of your head (as in the usual version), it is correct to do the movement with your head firmly pressed to the floor. This will ensure the natural position of the spine and avoid injuries to the cervical region.
- Pulling the head with your hands - in variants when the hands are brought together at the back of the head, it is necessary to completely relax them. Athletes often pull their body with their arms, trying to bring their head closer to their legs. This not only reduces the benefit of the entire work, but is also guaranteed to lead to problems in the cervical spine.
- Lack of concentration and tension - a large number of muscles work in movement. If you do not focus on the abdomen, maintaining tension, the load will be distributed to other areas.
- Fidgeting body - your back should be close to the floor. A destabilized body significantly reduces efficiency and reduces stress on the press.
Notes[edit | edit code]
Exercise bicycle
The bicycle exercise is characterized by the same difficulties as the “Scissors”, but more complex leg movements are added to them. This makes it much more difficult to maintain stability of the pelvis and lumbar spine. Like the Scissors, the Bicycle, when performed correctly, provides the opportunity for dynamic stretching of the hip flexor and hamstring muscles.
Modifications[edit | edit code]
If you are unable to maintain pelvic stability or feel discomfort in your lower back, try doing a bicycle exercise with your pelvis and lumbar spine in a neutral position and using your arms to support your lower back rather than your pelvis.
Option[edit | edit code]
Variations of the bicycle exercise
The bicycle exercise can be performed by creating stronger hyperextension in the lumbar spine. In this variation, the goal is to touch the toes of your lower foot to the mat as you bend your knee while maintaining core stability. This variation allows you to better prepare for more advanced Pilates exercises that require your back extensor muscles to interact precisely with your abdominal muscles, such as belly rolls and Swan Dives. However, you should refuse this option if you feel discomfort in the lower back or spinal hyperextension is contraindicated for you.
In addition to the classic version of bicycle crunches, there are several variations of the exercise, in particular:
- with weights in hands (weighted ball);
- holding the fitball near your feet;
- standing cross step.