What is fatty liver?
Fatty liver, fatty hepatosis, liver steatosis - all these concepts reflect the same pathological condition, which can develop as a result of exposure to a wide variety of factors. At the same time, the literal translation of the English term “fatty liver” – “fatty liver” – attracts attention because it is understandable to both the doctor and the patient. Like an obese person, a “fatty liver” is subject to a whole range of diseases. However, in most cases, fatty liver is completely reversible if the causes leading to its formation are eliminated. It is this indisputable fact that should first of all be drawn to the attention of both doctors and patients, since timely recognition of fatty hepatosis makes it possible to prevent the development of inflammation, which is much more difficult to treat.
What causes fatty liver?
There are many reasons for the deposition of fat in the liver, but in two thirds of patients it is still alcohol. In second, third and subsequent places are diabetes mellitus, obesity and hyperlipidemia (increased levels of certain fractions of fat in the blood due to genetic reasons and corresponding food preferences). Less common causes of fatty liver include taking certain medications, gastrointestinal surgery, and hereditary diseases. In addition, these factors can be combined.
Fat in motion. Lipid metabolism
Perhaps you imagine excess fat as a static, frozen mass. This is a serious misconception, since fat travels through fat cells day and night. Adipose tissue may appear amorphous, but in fact it is constantly in motion.
Some scientists believe that obesity is not a consequence of excess calories , but the result of a violation of the process of fat storage . But what promotes the transformation of fat into fat cells and retains it in them?
Fat enters fat cells through the blood in the form of triglycerides. One triglyceride molecule consists of three fatty acid molecules attached to a glycerol molecule. Triglyceride is too bulky to enter fat cells on its own. It must be broken down so that its fatty acids can enter the fat cell. Having penetrated there, fatty acids and glycerol are again combined into a triglyceride, securely holding fat in the fat cell.
Fat can come out of the fat cell, but for this to happen, the triglyceride must again be broken down into its components. This process (lipolysis) allows fat to be returned to the bloodstream.
So what regulates the breakdown of fat in fat cells? And, most importantly, who is responsible for the fact that more fat enters fat cells than comes out?
Alcohol and liver – enemies?
So, back to alcohol. It doesn't matter what you prefer - mumbling or Hennessy. Fatty liver has become a common diagnosis for representatives of high strata: politicians, businessmen, diplomats, artists. They are not alcoholics, they do not even abuse alcohol in the generally accepted sense. It’s just that for these categories of citizens, a glass of cognac or vodka is either an indispensable attribute of buffets and presentations, or a means of relieving stress after a working day, and sometimes during it. They feel great the next morning and are completely unaware of the need to reduce their drinking. Such patients are very surprised when examination reveals pathological changes in the liver.
Each person's reaction to alcohol is individual; this is due to genetically determined enzyme activity, gender, age, etc. Thus, in women, hormonal levels contribute to increased damage from alcohol to the liver, and in half of the representatives of the Mongoloid race, the toxic breakdown products of ethyl alcohol are neutralized much more slowly than in Europeans. In addition, a person may have concomitant diseases that he is not even aware of, for example, viral hepatitis or diabetes. At the same time, these diseases significantly increase the sensitivity of liver cells to alcohol. When talking about liver diseases, you should always remember that the liver is a very reliable, silent and patient organ, which often makes its suffering known when there are no more reserves for recovery. If you drink and don't eat, fatty liver disease will appear faster. However, even the most exquisite delicacies with a full range of vitamins will not save you from fatty liver - this has been proven both in animal models and in numerous clinical studies.
Why is fat deposited in the liver?
The fact is that the liver bears the main burden of oxidizing fatty acids, as a result of which the body is replenished with energy reserves. Alcohol damages the membrane of liver cells and disrupts the function of enzymes involved in the transport and oxidation of fatty acids. This leads to disruption of their normal metabolism and accumulation in the cell. In type 2 diabetes mellitus (typical of middle-aged and elderly people), obesity and hyperlipidemia, the relationship between the amount of fat penetrating the liver cell and the cell’s ability to utilize it is also disrupted.
Water retention on the stomach
2% subcutaneous fat consists of triglyceride fatty acids and 90% water. Sweet, salty and fatty foods retain fluid in the body. Visually, the stomach becomes larger in those who move little and eat junk food.
Under a microscope, adipose tissue looks like a porous sponge of cells filled with fluid. With proper nutrition and mechanical impact on problem areas of the body, tissues become more elastic. Lymphomassage will help get rid of excess fluid in the cells and reduce volume.
Why is fatty liver dangerous?
The main danger of this condition is that excess fat, under the influence of various factors, begins to oxidize with the formation of highly active compounds that further damage the cell. And this is the next stage of the disease – hepatitis, that is, inflammation of the liver. In this aspect, it is appropriate to compare fatty liver with a warehouse of fuels and lubricants, which must be guarded by an armed guard, since one spark is enough to start a fire. The progression of inflammation leads to the death of liver cells (hepatocytes), their replacement with skeletal connective tissue, and ultimately to impaired blood circulation in the liver and the development of liver failure. These, in fact, are the main manifestations of cirrhosis.
Weight and fat gain
Holidays are usually spent at the table. Experts from the University of Oklahoma calculated how much is eaten, drunk and stored as fat during this time. They weighed 94 students before and after the Thanksgiving holiday. The vacation dedicated to him lasted about two weeks, during which time the young people gained, on average, half a kilogram, with participants with a body mass index of less than 25 kg/m2 gaining 0.2 kg, and overweight people gaining about a kilogram. In itself, such weight gain is safe for health. But if they ate so intensely all year, they would gain 7 kg, especially those who are already overweight.
The consequences of overeating depend not only on the amount eaten, but also on genetic predisposition. In 1990, employees of the University of Laval (Canada) conducted an experiment on overfeeding twins. It involved 12 pairs of identical male twins aged 19 to 27 years old, without excess weight or chronic diseases. Scientists do not write what prompted them to agree to such a study. The twins were under strict supervision and received a thousand extra kilocalories six days a week. After 100 days, the couples were found to differ significantly in weight gained (from 4.3 to 13.3 kg), fat content and distribution. Differences within pairs were small, indicating a significant contribution of genetic factors. Thanks to them, it is not possible to predict the effect of long-term overfeeding: according to calculations, the twins should have gained 17 kg, but no one gained that weight.
Refined, processed foods are high in carbohydrates and contribute to weight gain.
It is even more difficult to predict the results of a short-term spree than a long-term one. For example, none of the University of Oklahoma students had to have an extra hole pierced in their belts, even though they gained weight. Their waist size remained the same, which is great, because an enlarged waist is a stronger predictor of health problems than body mass index.
Nine calories eaten and not consumed results in one gram of fat. Therefore, consuming 3,500 calories daily instead of the required 2,500 would result in the storage of 111 grams of fat. However, the twins did not reach the calculated targets. The fact is that the body’s ability to utilize calories is limited. Nutrients that it cannot convert into fat are eliminated through the excretory system. After a heavy meal, a person visits the toilet much more often, and the portions allocated are larger.
When you overeat, your body takes on water. Its volume in the blood and in the body depends on physical activity, medications taken, and the amount of salt and carbohydrates consumed. Excess carbohydrates eaten are converted into the polysaccharide glycogen, and each gram of it binds 3-4 grams of water. An adult weighing 70 kg can store about 100 g of glycogen in the liver and 400 g in the muscles. To this amount should be added 1.5 - 2 kg of water. Various detoxification diets are so effective because they allow you to quickly get rid of this water, that is, lose a couple of kilograms.
So, those who eat a lot gain weight, but only part of this weight is fat. The rest is water, which will quickly drain. Therefore, short-term holiday gluttony, measured in a thousand or two extra calories, will not cause a significant increase in fat depot.
The outcome of a meal depends on the components included in it. Consumption of carbohydrates leads to water storage. But if you eat very few carbohydrates at all, or limit your carb intake for another day, or go on a couple of long runs, you can afford half a kilo of carbohydrates, and almost all of them will be stored as glycogen, not fat. However, carbohydrates are usually eaten with proteins and fats. Let's see what this combination will lead to.
Protein may promote fat loss by suppressing appetite and stimulating thermogenesis. Specialists from Nova Southeastern University (USA) kept 12 trained men on a high-protein diet (more than 3 g of protein/kg per day) for 16 weeks. This is about four times the recommended amount, but the excess protein did not harm the participants and did not increase body fat or blood lipids. As for fatty foods, its excess will lead to fat deposition: experiments show that excess fat eaten does not oxidize. But our body burns alcohol to reduce its toxicity, which slows down the oxidation of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. And since it also increases appetite, drinking makes you fat.
If you eat too much protein, for example a good portion of turkey, less fat will be deposited than from wine or fat (pies and cakes). Having decided not to limit yourself at the holiday table, start with meat as the most harmless food, and fill up on it. Consume other products according to the residual principle.
However, no matter what you eat, one day of excess won't hurt. With prolonged overeating, the situation is different. Russians are condemned for the long New Year holidays. Americans traditionally indulge in gastronomic excesses for six weeks: from Thanksgiving to New Year. Continuing the study of students from Oklahoma, scientists found that although body weight did not change over these weeks, body fat increased by about 1%. Fat deposition takes time.
However, a long celebration does not always lead to obesity. Experts from the University of Utah examined 34 people of different ages before Thanksgiving and after the New Year. Twenty-four participants believed they had gained weight during this time. However, only four actually gained weight. For the rest, neither body weight nor fat content changed.
Not only subjective sensations can deceive; body weight sometimes changes significantly during the day depending on digestion, the amount of water or the weight of clothing. And even the scales lie sometimes.
How does fatty liver affect your health?
Fatty liver is insidious in that it often does not manifest itself in any way. Some people are brought to the doctor by a feeling of heaviness or dull pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Having a rough idea of the location of the organs, patients believe that their liver hurts. But there is nothing to hurt in the liver, because there are no nerve endings there, they are only present in the capsule and bile ducts. Typically, painful sensations are associated with impaired motor activity (dyskinesia) of the biliary tract. In most people, signs of fatty liver are detected by chance during an examination for some other reason. For example, a patient undergoes an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs or he consults a doctor about some other disease (coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc.), and during the examination the doctor reveals abnormalities in the structure and function of the liver.
How to identify fatty liver?
Diagnosis of fatty liver and its complications is complex. An experienced doctor always begins by carefully collecting anamnesis (memories of the patient’s life), paying special attention to the dose and regularity of alcohol intake, as well as concomitant diseases. Then the patient is examined to identify external signs of damage to the liver and other organs, determine the size of the liver and spleen. And only after this comes the stage of laboratory and instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound allows you to detect indirect signs of fat deposition in the liver, accurately assess its size, and sometimes identify changes characteristic of cirrhosis.
- A biochemical blood test provides valuable diagnostic information about the presence and nature of inflammation, impaired bile metabolism and functional reserves of the liver.
- Testing for the presence of hepatitis viruses is mandatory: this is due both to the fact that viral hepatitis is the most common cause of liver damage in the world, and to the fact that, in particular, the hepatitis C virus can disrupt fat metabolism in the liver.
- Additional examination, including determination of immunological parameters, computed tomography and liver biopsy, is prescribed if there are special indications.
Fat is good for you
The effect of fat on insulin levels and body fat was clearly demonstrated by the results of an experiment in which participants were given two diet options. In the first stage, participants fasted for 84 hours (they were given only saline solution). During this time, insulin levels fell and the rate of lipolysis (fat breakdown) increased, which was confirmed by an increase in the level of free fatty acids in the bloodstream. Fasting lowered insulin levels, which allowed fat cells to shed fat. Nothing surprising yet.
But the most interesting part of the experiment began when the same participants were intravenously injected with a solution consisting almost entirely of fat. The fat injection provided volunteers with 2,000 calories a day, enough to maintain a stable weight.
As in the first stage, insulin levels dropped. The rate of lipolysis and the level of fatty acids in the bloodstream increased. Moreover, these indicators were almost the same as during fasting. Saturating the body with pure fat caused the same metabolic state as when completely giving up fat.
If it is not fat that stimulates insulin production, what is responsible for this? It turns out that the main stimulator of insulin production is carbohydrates . Sugar is precisely carbohydrates, just like starch.
If you choose a diet limited in fat but rich in carbohydrates, then even with strict calorie control, the basis of your diet will be foods that stimulate the deposition of fat in fat cells and retain it in them. This can delay the process of reducing fat mass indefinitely or even slow down the process of losing weight.
Nuts are fats that you shouldn’t be afraid of. Nuts are rich in fats, and they also have plenty of calories. That is why many nutritionists recommend keeping their consumption to a minimum. However, when scientists examined the effects of nuts on body weight, they found no evidence that nuts make you fat. Nuts are generally low in carbohydrates, which means they do not stimulate insulin production. There are other arguments in favor of nuts: they effectively satisfy hunger, they are difficult to overeat during a snack, and at the same time they keep us from overeating during main meals. And finally, it turned out that nuts stimulate metabolism.
How to treat fatty liver?
First of all, it is necessary to either eliminate or minimize the effect of the factor that led to the deposition of fat in the liver. This is almost always possible in relation to alcohol, unless we are talking about the formation of addiction, when the help of a narcologist is required. Patients with diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia should be monitored jointly by an endocrinologist and a cardiologist, respectively. All patients require a low-fat diet as well as adequate daily physical activity.
When these measures are not enough, the doctor prescribes special medications that affect fat metabolism in the liver. Only an experienced doctor can determine what causes liver changes in a particular patient and how severe they are. If you have any suspicions, consult a gastroenterologist or hepatologist.
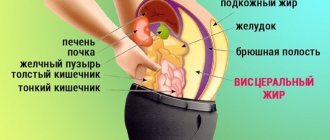
// Visceral fat - what is it?
Visceral fat is fat located directly in the abdominal area and surrounding the internal organs (primarily the liver and stomach). It is he who squeezes the stomach forward, giving the figure the shape of an apple. Having large amounts of this fat is a key characteristic of obesity.
Moreover, if subcutaneous fat (located under the layer of skin and accessible to palpation) is associated only with aesthetic problems and does not affect metabolism, then the presence of visceral fat impairs the body’s ability to properly produce insulin¹.
The development of insulin resistance requires both the production of additional amounts of insulin (which increases the load on the body) and is associated with an increase in blood glucose. Ultimately, these factors influence the development of prediabetes, full-blown diabetes, and then metabolic syndrome.