( 3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
The healing properties of this plant were first discovered by the Indians, long before the 16th century, in which the first research on stevia was published. The benefits and harms of the sweet herb stevia a few years ago continued to cause controversy in scientific circles: some biologists called it carcinogenic, others argued otherwise. By the way, even legends were made about its sweetness. According to one of them, stevia is the name of a fragile girl who sacrificed herself for the good of her own people. The ancient gods did not remain in debt and, as a sign of respect, gave people a sweet and healthy herb of the same name. Let's find out how useful stevia is and for what properties doctors, including nutritionists around the world, especially value it. Let's start from the beginning and turn to researchers who for a long time could not come to a consensus: is stevia harmful or beneficial?
What scientists say - debunking myths about unusual grass
Stevia petals contain over a hundred different phytochemical elements that not only give the plant a sweet taste, but also have beneficial effects on the body. For example, steviosides in the composition have a unique property - they significantly reduce blood sugar levels. On the subject: How to reduce food cravings However, researchers have differing opinions. Some argued that the plant has a carcinogenic effect due to a mutagen, which leads to mutations. Others, on the contrary, considered stevia safe. Meanwhile, it has firmly entered into gastronomic “everyday life” and is especially loved by followers of a healthy diet, because sweet grass can completely replace harmful sugar. The increased popularity has led to new research. Thus, in 2006, the World Health Organization conducted a comprehensive experiment that unconditionally proved: in moderate quantities, stevia is absolutely harmless to the body.
Stevia sweetener for weight loss: benefits and harms
In order for the extra pounds to go away, you need to not only include healthy natural substitutes in your diet, but also adhere to a healthy diet, and do not forget about moderate physical activity. The first step can be taken now - by giving up sugar and replacing it with a healthy extract of “honey” grass. It contains virtually no calories and is recommended for diabetics.
What foods can you add all-purpose sweetener to?
- porridge;
- compotes;
- confectionery;
- mousses and jams;
- jelly;
- tea and coffee.
The result is the discovery of new tastes and incredible benefits given by nature itself. There are no chemicals in the composition - only vitamins, minerals, flavonoids and other substances that help strengthen our health, slimness and vigor.
What does sweet grass consist of and how many calories does it contain?
Stevia petals are distinguished by a rich vitamin composition, over a dozen micro- and macroelements, various acids and minerals. Let's note the key ones:
- vitamins A, B, C, D, E and PP;
- iron, zinc, chromium and manganese;
- calcium, potassium, phosphorus and selenium;
- caffeic and humic acids;
- essential oils and over 17 amino acids;
- flavonoids, glycosides and steviols.
The latter, by the way, give stevia a very sweet taste, which is 30 times higher than regular sugar in terms of sweetness quality: literally 1/4 teaspoon of crushed petals replaces a full spoon of sugar. At the same time, honey herb (the second and quite justified name for stevia) is recommended even for diabetics, since it does not increase blood sugar levels. Calorie content directly depends on the form of release of the drug. The benefits of stevia in all cases depend on the dosage - this is important to remember (we will tell you in more detail below). So, the leaves of the grass contain only 18 kcal per 100 g. Despite the fact that only 1 leaf of this plant can add sweetness to a large pumpkin! If used in tablets, the calorie content will increase to 272 kcal/100g, in syrup – 128 kcal/100g. Stevia has taken a special place in dietary nutrition, replacing loose and refined sugar, as well as its artificial chemical-based substitutes. The glycemic index of the herb is 0 units, therefore it does not interfere with the body’s processing of glucose and further distribution to cells and tissues. Insulin remains normal, so there is no glycemic load.
Simply put, our system does not need to urgently process excess glucose, because it simply does not exist.
On the contrary, if you replace stevia with regular sugar, insufficient insulin will be produced to process glucose in a timely manner, which will end up turning into unsightly fat on the sides, belly and other most vulnerable areas of the body. The uniqueness of this herb lies in its rich composition, which no other plant in the world can boast of. The combination of dozens of useful elements allows it to be used as a substitute for sugar. It is incorrect to compare the benefits and harms of the sweetener stevia, since there are simply no negative effects with moderate consumption. Find out the causes of excess weight and ways to quickly lose weight
Sign up for a free initial appointment with a nutritionist!
By the way, a zero glycemic index is an excellent assistant in the fight against excess weight - we continue to eat sweets, but remain slim. Now let's find out how stevia improves the functioning of our entire system, and in some cases has a healing effect.
Stevia-based sugar substitute: why was it recognized as one of the best?
As we have already said, the sweetness of the purified extract of this herb exceeds the similar property of the sweetener that we eat daily by 150-300 times. At the same time, it does not seem cloying - it just has a specific taste that is easy to get used to, especially if you gradually include this product in your diet - for example, starting with baked goods or drinks.
The plant, which came to us from the Indians, contains glycosides, which give the powder, tablets or syrup made from it a special sweetness. These substances are isolated from the leaves of the "honey" grass using one of several extraction methods. All known methods are patented. The most commonly used method is aqueous extraction from dried herbs, after which the resulting raw material is purified and crystallized.
Stevia – the extent of its beneficial effects on the body
One of the main advantages of sweet grass was discovered in 2003 by researchers from Taipei Medical University. A number of experiments have shown that stevia copes excellently with surges in blood pressure, bringing the levels back to normal. The herb is equally beneficial for people of all ages who suffer from hypertension and high blood pressure. Thanks to researchers from Texas, it became known that stevia is an excellent cancer prevention agent. It's all about kaempferol - a natural flavonoid that grass contains in large quantities. This substance prevents the development of cancer cells, naturally prolonging life. Note that to achieve a positive effect, it is important to use stevia constantly. The gradual saturation of the body with the components of this plant acts in the long term, and the first results can be obtained only in the third year after using the herb.
Briefly and succinctly about all the advantages of consuming stevia:
- relieves joint pain, relieves muscle spasms;
- helps fight swelling and inflammation;
- strengthens the body's immune defense, increasing resistance to seasonal colds;
- restores intestinal microflora after infectious diseases;
- normalizes metabolic processes, improves the functions of the pancreas and liver;
- prevents the development of diseases of the skeletal system;
- strengthens the cardiovascular system, normalizes blood flow;
- reduces cholesterol levels in the blood, preventing the formation of plaques;
- promotes mental activity and relieves physical fatigue.
It is also known that stevia promotes the healing of small wounds and is an excellent antibacterial agent. An infusion of this herb is recommended for inflammatory gum diseases, as it effectively relieves inflammation and protects teeth from damage by caries. The herb is truly unique, but it is worth remembering that we are not talking about a magical transformation of the body. Only regular intake of stevia brings tangible results due to the systematic enrichment of the entire system with useful substances, which slowly but surely begin to act.
Contraindications
Perennial honey grass is considered a safe natural product. But, like any remedy, it has contraindications:
- intolerance of individual components in the plant by a specific person;
- the possibility of a reaction in those who are allergic to plants of the Astrov family (chrysanthemums, stevia, tagetes and others);
- dyspepsia when using herbal preparations simultaneously with dairy products (cow's milk).
Preparations are produced with the addition of a certain amount of plant leaves, pure extracts that differ in chemical composition. Their effect on the human body is different, and this must be taken into account.
How does stevia help you lose weight?
In an effort to get rid of excess weight, some of us are constantly haunted by the desire to eat something sweet, because it both lifts our mood and enhances brain function. However, on a diet (even the most gentle one) sweets are prohibited, and tea with honey becomes terribly boring. On the subject: Products that reduce appetite In such a situation, stevia comes to the rescue - sweeten tea, oatmeal for breakfast, or prepare a very sweet, but dietary dessert. In addition to the ability to replace high-calorie sugar with low-calorie stevia and enjoy the taste of food every time (which especially pleases those with a sweet tooth), the plant also brings practical help to the body.
The benefits and harms of the sugar substitute stevia and its fight against excess weight:
- accelerates metabolic processes, helping to effectively lose unwanted pounds;
- due to its low calorie content, it is an excellent preventive measure against obesity;
- dulls the feeling of hunger and reduces appetite, disarming the main enemies of weight loss.
If we talk about the quality of the effect, it is better to take the plant in the form of syrup or dried leaves. The benefits and harms of the stevia sweetener, based on the form of release, are obvious here: flavors and other less useful components are often added to powders and tablets based on this herb. However, in all cases it is important to follow the dosage so that the positive effect does not turn into a negative effect. In order not to make a mistake with the portion, we have prepared a detailed table for you. It will help you clearly understand how much sugar stevia can replace without loss of taste:
| Sugar | Crushed stevia leaves (dried) | Stevioside (substitute in tablets) | Stevia extract (syrup) |
| 1 teaspoon | ¼ teaspoon | A little pinch | 2 to 5 drops |
| 1 tablespoon | ¾ teaspoon | A little pinch | 5 to 8 drops |
| 1 cup (200 g) | ½ tablespoon | ½ tablespoon | ½ tablespoon |
Stevia will help you lose up to 10 kg of weight without much effort if you completely replace sugar with it - in drinks, cereals or desserts. For example, just a couple of drops of sweet grass extract reduces the calorie content of a dish by an average of 30%. A special herbal tea for weight loss is also produced based on stevia, which is drunk half an hour before meals. As a result, the stomach is not only filled with liquid, but its capacity is reduced, but a feeling of fullness comes. You can prepare this tea yourself: brew a spoonful of stevia leaves in boiling water and let it steep for 20 minutes. Let us remind you that, like any other plant, stevia has contraindications, depending on your health condition.
Facts about natural sweetener
- This perennial plant is a small bush. Its stems are similar to the stems of nettles due to the shape of the leaves - whole, with jagged edges. The height of such a bush can reach 1 meter. Every year the shoots die off and are replaced by new ones.
- The main value of stevia is the sweetness of its leaves. The harvest collected from 1 bush sometimes reaches 1200 pieces.
- This plant can be grown anywhere, not forgetting several conditions: the soil must be constantly moistened, like the air, and the temperature should not fall below 15 degrees Celsius. So you can even plant this useful herb on your windowsill.
- In total, science knows more than 80 varieties of natural sweetener grown in North America, and approximately 200 South American species.
- Stevia rebaudiana (namely, its pre-purified extract) is 300 times sweeter than refined sugar or purified highly digestible carbohydrate in the form of sand. The sensation of sweetness does not appear immediately, but lasts longer.
- The calorie content of the powder obtained from the leaves of this perennial plant is zero. In addition, this product has an antibacterial effect and many other beneficial properties, which we will discuss below.
In what cases can stevia harm the body?
As we found out, this unusual plant brings comprehensive benefits if it is constantly present in the diet as a sugar substitute. But it is important to take into account individual intolerance to the components in its composition and health characteristics. There are no serious restrictions on the use of sweet grass - both adults and children can use it as a sweetener. However, in 5 cases, stevia has contraindications and side effects:
- Allergy. In a mild form or with severe consequences (anaphylactic shock). If you have noticed a negative reaction in your body to chrysanthemums, marigolds or chamomile, the likelihood of getting anaphylactic shock increases.
The first signs of an allergy include shortness of breath, dizziness, difficulty swallowing and general weakness. If they appear after taking stevia, an urgent visit to the doctor will be required to prevent complications.
- Disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. Steviosides are the main sweeteners in the plant and can lead to bloating, diarrhea or nausea. The advantage is that negative reactions are mild and do not cause major difficulties. If the process is prolonged, it is important to seek the help of a doctor.
- Metabolic disorder. Abuse of stevia can “suppress” metabolic processes due to poor absorption of carbohydrates. This means that the conversion of food into energy for the body will be reduced, and the result of such a disorder will be reflected in the form of excess fat. Therefore, it is so important not to overestimate the daily dosage.
- Diabetes. Doctors’ recommendations to use stevia for this disease are entirely individual. The beneficial property of lowering blood sugar levels also has a downside. In some cases, the sweet plant reduces the body’s ability to control “sugar” levels on its own.
Therefore, if there is the slightest change in the health of a diabetic who uses stevia, he will need to consult a doctor. He will conduct the necessary research and find out how safe the sweetener stevia is for a particular person.
- Low blood pressure. The beneficial effect of stevia is precisely to reduce blood pressure if it exceeds the norm. But if a person initially suffers from low blood pressure and uses stevia, the risk of lowering blood pressure to a critical point increases.
In this case, a herbal sweetener can be used only after the recommendation of a doctor who can assess the risks and make the right decision. Despite the lack of full-fledged studies on the harmfulness of stevia during pregnancy and lactation, we note: if you are expecting a baby or breastfeeding, it is better to limit the use of the sweet herb.
What is stevia?
This subshrub, commonly called grass, is native to South America. It loves a lot of sun, warmth and moisture, so it grows naturally in the fertile soils of the plateaus of Paraguay and Brazil. The plant is not tall - up to 70 cm, the oblong, oval foliage accumulates a huge amount of sweet substances - glycosides. Stevia leaves are picked shortly before flowering, during which time they are at their sweetest. The classification places the grass in the Asteraceae family. The genus "Stevia" (https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A1%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%8F) includes many subspecies, but only one of Among them, honey stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) is used as a natural sweetener (Fig. 1).
Did you know that...?
Japan firmly holds the leading position in stevia consumption. Here, up to 40% of all sweet products are produced using it. This product policy is yielding results. There are practically no obese people in the country, the incidence of diabetes is low, and life expectancy is the highest on the planet.
For ease of use, we produce dry extract in prepackaged bags of 0.8 g each. The Dolce Vita Light package contains 50 such sachets, the cost is 128.70 rubles. Enough for a long time!
Use by healthy people
Supporters of a healthy diet position stevia as a modern sweetener. When a healthy person eats it, the sugar level drops quite quickly (by about 1-2 mmol). At the same time, insulin production begins.
For diabetics, this effect (hypoglycemic) is important, since the process of producing insulin for processing glucose is disrupted in their body. But healthy people do not have such a pathology, and increased insulin production must be taken into account.
Frequent consumption of sweet grass-based products leads to a certain stress for the body. Reactions occur and the processes of processing calories that come with sweet foods are started. But pure stevia has zero calories, so the body has nothing to process.
Therefore, healthy people are advised to use stevia-based products in limited quantities. It is advisable not to look for a substitute for sugar, but to reconsider your eating habits by limiting harmful sweets.
Honey herb for weight loss
A plant with natural sweetness is used as an additive in menus for various diets. There are no calories in the leaves of the perennial, while various elements in stevia contribute to weight adjustment.
Benefits for weight loss:
- strengthening the autoimmune system;
- metabolism optimization;
- stimulation of intestinal motility;
- acceleration of lipid breakdown;
- removal of excess water;
- removal of waste and harmful toxins.
Replacing sugar with this wonderful herb significantly reduces the calorie content of food. At the same time, you can change your nutrition system to a minimum and calmly “lose” 2-5 kg per month without mental discomfort. A person does not feel constant hunger, which is typical for those “on a diet”; he consumes desserts and at the same time loses weight.
Stevia-based preparations can be included in the menu for any diet: carbohydrate and non-carbohydrate, protein and others. The choice of form when taking stevia is determined by personal preference:
- powder;
- pills;
- herbal teas;
- dry leaves.
On a note!
When preparing drinks based on stevia leaves, take into account that in cold water the sweetness develops more slowly than in boiling water.
To lose extra pounds, drink teas with stevia, add it to salads and various desserts.
Use in cooking
Culinary experts appreciate all the beneficial properties of the sweet perennial plant. In addition to its sweet taste and lack of calories, stevia components dissolve in liquid and do not lose their qualities during heat treatment. At the same time, adding a natural product to baked goods, drinks, and desserts enhances their taste.
Stevia as an ingredient is included in:
- cookies;
- ice cream;
- yoghurts;
- desserts;
- bakery products;
- chewing gum.
Uses in cooking:
- in powder form;
- syrup;
- tea;
- concentrated infusion.
In many recipes, this herb successfully replaces sugar. Suitable for preparing sauces, first courses, meat.
On a note!
The sweetness levels of products vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Before use, you must carefully study the composition in order to dose stevia correctly.
Cooking
You can prepare many dishes with honey herb. It is added wherever sugar is traditionally used:
- porridge;
- beverages;
- dairy products;
- yoghurts;
- bakery.
At home, stevia is used as an ingredient in canning and pickling vegetables and fruits, for preparing compotes, syrups, tinctures, and when making jam.
Features of application:
- Herbal powder or infusion is suitable for baking and desserts;
- for tea, tinctures, marinades, compotes - crushed plant leaves;
- Leaves are placed in compotes and marinades just before seaming;
- To balance the taste of dishes, it is necessary to increase the amount of other ingredients (the dose of stevia is much less than sugar).
Stevia tincture at home
Dried herb leaves retain the entire range of useful components. Infusions are prepared from them, then adding liquid to tea, coffee, pastries, and desserts.
The recipe is simple:
- prepare a liter of boiled water;
- pour 100 grams of dry leaves with water;
- leave for 24 hours;
- pour into another container;
- the leaves are carefully poured with water (0.5 liters), boiled over a fire for about an hour;
- the resulting liquid is poured into the first infusion;
- mix, filter.
The resulting infusion is stored for 5-7 days and added to drinks.
Instead of water, you can use vodka:
- per liter you will need 100-150 grams of dry raw materials or 300 grams of fresh leaves;
- pour vodka over the raw materials;
- shake gently;
- stand for 48 hours in a dark place;
- filter;
- place the container with the infusion on low heat and evaporate the alcohol for 15 minutes;
- cool, filter, bottle.
When evaporated, the infusion may become thick and darken. This product can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 5-6 months.
Sweetgrass Syrup: Making at Home
Another product that is easy to make at home is sweet syrup. Its shelf life is up to two years, so you can immediately make a couple of liters.
Preparation:
- the infusion (water or vodka) is poured into a saucepan;
- put on low heat and heat;
- the infusion should not boil,
The total time for evaporation of liquid from the infusion is 5-6 hours. Do not leave the saucepan unattended; carefully stir the contents. As soon as the syrup slowly drips from the spoon, turn off the heat and remove the pan. Pour the syrup into bottles and store in the refrigerator.
Honey herb for diabetes: application possibilities
According to WHO research, there is a pharmacological effect after taking stevia in people suffering from a serious illness - type 2 diabetes. This is explained by the fact that honey grass contains no carbohydrates (accordingly, the plants do not contain glucose).
Therefore, people suffering from diabetes can consume various foods and desserts with stevia without fear of an increase in glucose levels. In addition, the herb helps reduce the dosage of hypoglycemic drugs and insulin.
Features of taking sweet grass for various types of diabetes:
- in the first type, stevia normalizes the activity of insulin-producing cells. Also, regular use of tablets or extracts based on it allows you to reduce the dosage of glucose-lowering hormones;
- in the second type, when stevia-based products are consumed, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism is normalized. It is possible to reduce the doses of tablets taken by diabetics. An excellent means of prevention for various vascular pathologies.
- in case of gestational diabetes (occurs in pregnant women), stevia replaces “fast” carbohydrates, helps to equalize glucose levels in pregnant women, and correct carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
Examples of sweet stevia products for diabetics:
| Forms of sweetener | Titles | Peculiarities |
| Pills | Stevioside | Per glass – 2 tablets. Daily norm – 7-8 tablets |
| Stevia plus | No more than 8 tablets per day are recommended | |
| Stevilight | Per glass – 2 tablets. Norm per day – 6 pieces | |
| Herbal teas | Dried leaves in bags, as well as teas in sachet bags Steviasan, Green Slim | Brew in hot water. |
| Concentrated syrup | General strengthening | In addition to stevia, it contains: leaves of horsetail, St. John's wort, linden. Additive to drinks – four drops |
| Stevia syrup | Contains extract, vitamins, distilled water. For tea, coffee, desserts. Add 5 drops to a glass | |
| Honey grass syrup (contains pineapple and fucus extracts) | Take in courses, 5 ml every day. Course – 4 weeks | |
| Extract | Stevioside | Add to tea, sachet per glass |
Who shouldn't you trust?
The organizing and disciplining force of any civilized society is bureaucracy. Therefore, in the USA, if your health is contraindicated or your beliefs do not allow you to drink some kind of “cola” with aspartame and saccharin (with sugar too), you will have to buy a bottle of extract or a pack of stevia leaves, fruits in different departments, come home and brew the drink yourself . It is difficult to explain why this cannot be immediately mixed, like aspartame, in one bottle, so the discussion with the FDA on this topic is not published and is conducted, so to speak, on a routine basis. However, a good joke was made by an unknown named FDA official: “If we wanted, we could ban carrots too.” A good hundred studies have been carried out on the toxicity of stevia and its individual components, so you can select suitable ones and draw the necessary conclusions for different cases. However, last spring the first international conference on the safety of stevia was held in Belgium, which was organized by the European Stevia Research Center located there. As follows from her works, it’s all a matter of doses.
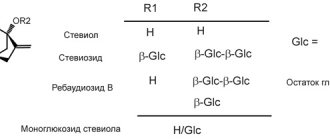
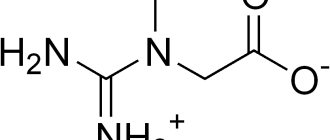
Stevia is suspected of three crimes: antiandrogenicity, mutagenicity and, as a consequence, carcinogenicity. The work of researchers, equipped with the most advanced equipment that allows them to find picograms of stevia glucosides in samples, helped to construct the following diagram of the biochemistry of stevia in the body of rats, mice, chickens and people. As it turned out, its glucosides, once in the body of a mammal, do not turn into anything - there are no corresponding enzymes in the intestinal tract, and those hundredths of a percent that seeped inside, unchanged, leave the body along with the urine. In any case, with an accuracy of picograms, no products of stevioside transformations could be found either in the blood or in the urine. The only exception is steviol, that is, that fragment of the stevioside molecule that remains after the elimination of glucose. However, this cleavage occurs before steviol passes through the intestinal wall: it is carried out by our cohabitants - bacteria of the intestinal tract, which utilize small amounts of stevia glucosides. And it was this steviol that became the main suspect. The accusations are as follows: firstly, it is capable of causing mutations in some E. coli, and secondly, it deprives experimental rats of the opportunity to have offspring.
Suspicions of the latter were caused both by the structure of steviol, which is similar to steroid hormones, and by legends that Paraguayan women use stevia as a contraceptive. The first data on the antiandrogenic abilities of steviol appeared in the experiments of Dorfman and Nes, carried out in 1960 on chickens - their crest growth is convenient for monitoring the decrease in the activity of male sex hormones. (There is a special “capon unit” of hormonal activity.) At a dose of 1.2 g/kg (for a person, this dose in terms of sweetness corresponds to a bag of sugar per day), a decrease in activity was actually recorded. Eight years later, G. Planas and J. Kuch prepared an infusion from dried stevia powder (5 g/100 ml, that is, approximately 100 teaspoons per glass) and, apart from it, did not give female mice anything to drink. The result was 0.5 g of stevioside per kg of animal weight. Neither the weight nor the health of the mice was affected, but their fertility was reduced by almost half, which the authors told the whole world about with the help of Science magazine. However, already in 1975, H. Akashi and Y. Yokoyama did not notice any effects at a dose of 0.1 g/kg, and in 1996, S. Shiotsu tried to reproduce Kucha’s experiments with the greatest accuracy on a larger number of mice and also did not find the effect of stevia on their fertility. The corresponding article was published in Tech. J. Food Chem. Chemicals". In 1999, M. Melis fed male mice with stevia infusion for two months, and the weight of fresh plant leaves they consumed daily exceeded half the weight of the animals themselves. In other words, the dose of stevioside was 5.3 g/kg. These males have problems with reproduction. But reducing the dose five times, to an equally monstrous 1 g/kg in the experiments carried out by J. Geuns in 2004, eliminated these problems.
Numerous experiments carried out with both stevioside and rebaudioside have shown that they not only do not cause cancer, but, on the contrary, reduce the likelihood of experimental animals getting adenoma or breast cancer and reduce the rate of development of skin cancer. As for mutagenicity, steviol was noticed in it: under its influence, cells of one of the salmonella strains mutate. However, only these cells - many other strains of both salmonella and E. coli do not respond to it. Even huge doses of pure steviol - 4 g/kg - did not cause any signs of mutations in the tissues of the mice. And even with that single strain, the activity of steviol was not so high: three thousand times less than, say, benzopyrene. And the latter, by the way, is necessarily present in the smoke of a burnt tree, and, therefore, anyone who has been on a picnic and tasted meat roasted on coals at the fire has inevitably dealt with it. Also, mutagenic activity was noticed in steviol derivatives, for example, in its methyl ester, but, as already mentioned, no derivatives were found in the blood of volunteers.
In general, the lethal dose (LD50) of stevioside is 15 g of stevioside per 1 kg of live weight. This level could probably be achieved by feeding mice only stevia, because for humans this LD50 sweetness value corresponds to 300 kg (twelve bags) of sugar per day. Rebaudi, in his experiments on animals, which convinced him of the harmlessness of stevia, did not use such large doses. Obviously, the normal dose - two or three leaves per cup of tea - is as far from harmful in its harmfulness from the doses used in the experiments as a pinch of table salt is from a pound of it. Moreover, during a thorough examination of the blood of volunteers who tasted stevia extract, the metabolic products of steviol were not found as well as stevioside derivatives, and all of it, intact, was excreted in the urine in the form of a monoglucoside. And the highest content of this monoglucoside in the blood was 100 ng per mg of plasma.
Biochemists did not pay attention to the taste sensations of experimental animals, but in vain. As V. Dzhakinovich established in 1993 for gerbils chosen as a model rodent, the series of sweets looks like this: rebaudioside A = stevioside > hernandulcin > sucrose. Moreover, sugar itself serves as an effective taste stimulant for them. That is, the bags of sugar mentioned above per experimental mouse were indeed bags of sweetness, which could well cause a sweet shock.