The core muscles (translated from the English “core” - center) perform certain functions: stabilizing the pelvis and spine, maintaining balance and maintaining the health of the entire musculoskeletal system. For the Russian-speaking population, it is easier to associate “core muscles” with the main consonant function of these muscles, which are a corset for the skeletal system. Performing the function of a corset, the “centre muscles” hold the body in the correct (physiological) position. Training these muscles is necessary not only for athletes to improve athletic performance, but also for those who want to keep all body systems healthy.
Where are the core muscles located and what functions do they perform?
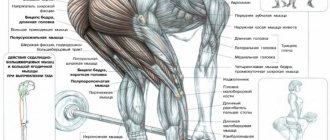
The core muscles (or core muscles) are a conditional group of muscles that hold the spine and pelvic region in a stable position. It is impossible to master any sports discipline, doing strength sports or fitness, with weak core muscles. Without tone of the muscles that fix vulnerable parts of the spine and joints, increasing loads can only injure or aggravate problems.
Core muscles include:
- rectus abdominis muscle;
- external oblique abdominal muscles;
- internal oblique muscles of the abdomen;
- transverse abdominis muscle;
- back extensors;
- gluteal muscles;
- hamstrings;
- tensor fascia lata;
- rectus femoris muscle;
- tailoring;
- leading.
Thus, the muscles of the center can be both external and internal. These muscles are conventionally located in the center of the body and hold the spine, pelvis and hips not only under load, but also at rest. They are interconnected, uniform tone of the core muscles ensures balance between the front and rear groups, maintaining correct posture in an upright position.
Barbell exercises
These exercises are suitable for experienced athletes. If you are a beginner, use a barbell without weights to perform these exercises.
Lying leg raise
Lie on the mat, grab a barbell, hands at shoulder width. Extend your arms with the barbell up. Tighten your core and keep your legs straight. Lift your legs up to the right side, keeping your back on the mat. Slowly lower your legs back and repeat to the left. Do 10-12 repetitions on both sides.
Simplified version : Practice proper technique without a barbell.
Barbell crunches
In addition to the barbell, you will also need an incline bench. Lie down on the bench and hold your feet firmly. Grab a barbell with your hands shoulder-width apart. Press the dumbbell upward while keeping your arms fully extended. Essentially, this exercise is similar to crunches, only with a barbell overhead. Keep your back straight. Return slowly to the starting position and repeat the exercise 8-10 times with heavy weight . If you choose a light weight, do 10-12 repetitions.
Simplified version : Try doing incline crunches without a barbell. Feel each muscle and stick to the correct technique.
Incline bench press with head up
Start in the same position as in the previous exercise. Lie down on an incline bench, hold your feet firmly, and grab a barbell. Swing down, but don't go all the way down; your shoulder blades and back should be above the bench and your buttocks on the bench. Tighten your core and slowly press the barbell up. Inhale and pull the dumbbell toward your chest, keeping your elbows wide apart. Perform 8-10 presses and return to the starting position, lower your back onto the bench.
Simplified version : Do the exercise without weights.
Taken from greatist.com
Will you try any of these exercises in your next workout? What abdominal exercises do you find most effective? Share your tips in the comments. If you liked our article, please support us by reposting.
Consequences of core weakness
With atony or hypotonicity (weakening), the core muscles do not hold the vertebrae or joint in the correct position, and the unfixed section seems to bulge forward. Hypertonicity is also not a plus for muscles, which, being in an overstrained and pinched state, pull the “blanket” over themselves and compensate for the state of atonic muscles.
For example, consider core muscle dysfunction:
- Weakness of the gluteal muscles , the posterior or anterior group of thigh muscles provokes a forward displacement of the pelvis, visual flattening (smoothing, leveling) of the buttocks.
- Weakness of the transverse and rectus abdominis muscles forms a bulging abdomen and hypertonicity of the lumbar extensors, which are in a enslaved state and increase lordosis, that is, the lower back is in an unnatural deflection.
The benefits of core training
By training your core muscles you can get a number of benefits:
- In strength sports, when lifting heavy weights, the core muscles maintain stability of the spine and pelvis, preventing injury.
- Strong core muscles allow you to build strength and endurance faster.
- Core training helps you achieve proper posture.
- Improves coordination and balance, increasing the level of stress where it is necessary to maintain balance.
- The tone of these muscles directly affects the condition of the internal organs, increasing blood circulation and relieving tension due to incorrect position of the spine and pelvis.
Benefits of Core Training
Anyone can benefit from these workouts, no matter your level of physical fitness or the purpose of the workouts themselves. As for specific advantages, there are many of them.
A strong core improves performance in the gym, and in all sports, as it produces more energy in the limbs to facilitate the transfer of torque. Simply put, a strong core will allow energy to be transferred from the lower body to the upper body.
When the muscles are weak, all the stress is placed on the spine, which often leads to pain in the hips and/or back. Strengthening muscles takes pressure off the spine and reduces the risk of injuries to the hips, knees and ankles.
Helps burn fat and lose weight
How much weight and/or fat will be burned during exercise will depend entirely on the type of activity. If the plan includes only planks and crunches, it will not be possible to pump up all the necessary groups. On the other hand, if you add a few higher intensity exercises such as mountain climbers, burpees or strength training, it is likely that results will be seen much faster.
If your goal is to lose extra pounds, then the key to achieving results is not just abdominal exercises, but movements that involve the whole body. Performing such exercises in a circuit or interval mode is the best option to achieve your goals.
Tones and builds muscles
Gaining muscle mass will also depend on the type of training. Performing a variety of movements that involve all parts of the body but focus on strengthening the core (squats, deadlifts) is the most effective way to gain muscle mass.
Isometric exercises won't do much to build muscle simply because they target muscles that are needed for endurance rather than strength. To gain muscle mass, you need dynamic strength exercises, first of all.
General recommendations for core training
To strengthen your core muscles, it is important to focus on sensations, being aware of which muscles are working at the moment. For girls, core muscle training does not involve working with weights. In the future, both men and women can use the equipment. Exercises can be either static or dynamic.
Important! You can't train your core muscles every day.
The complex, including warm-up and stretching, should last no more than an hour.
- For beginners, all exercises are performed once with multiple repetitions.
- If you are prepared, you can perform the complex in 3 approaches.
- If the exercise is performed statically , it must be held for approximately 5-7 breathing cycles (1 cycle: inhale-exhale) or 30-60 seconds, depending on preparation.
- Dynamic exercises should be performed for 16, 24, 32 repetitions.
The Best Exercises to Train Your Core Muscles at Home
Plank
A static exercise that involves all the muscles of the center at the same time.
- Place your hands under your shoulders, your feet the width of your pelvic bones.
- Tighten your stomach, tighten your buttocks, squeeze your shoulder blades together.
- Pull the top of your head forward.
- Hold the position without holding your breath.
Learn more about the plank exercise →
Exercise "swimming"
Strengthening the core of the body, stretching and strengthening the back, arms and legs.
- Starting position on all fours: hands under the shoulders, knees under the pelvis.
- At the same time, extend your arm and the opposite leg, straightening it until it is parallel to the floor as you inhale.
- Exhale, lower your arm and knee and switch sides.
- Keep your stomach tense, avoiding arching in the lumbar region.
Concentrate on lengthening your muscles.
Twist up/down
The transverse abdominal muscle is strengthened and the hamstrings are stretched.
- Sitting on your buttocks, bend your knees, place your heels on the floor, and keep your hands in front of you.
- Having stretched the top of your head, inhale, then as you exhale, slowly lower yourself onto your back, vertebra by vertebrae, starting from the tailbone.
- At the bottom, take a breath and just as slowly lift your neck, and so on, each section one by one, without jerking or using your hands.
Fully straighten your spine at the top.
Shoulder bridge
The shoulder bridge exercise develops the muscles of the thighs and buttocks.
- Lie on your back, place your heels under your knees, the width of your pelvic bones.
- Inhale, and as you exhale, lift your buttocks, as if you were twisting your pelvis, tearing off vertebrae by vertebrae, but do not collapse your chest towards your neck.
- Inhale at the top, and just as slowly lay your back on the floor.
Oblique crunches
Strengthens the core muscles, mainly the obliques and rectus abdominis, shaping the waistline.
- Lie on the floor, keeping your shins parallel to the floor.
- Place your hands behind your head.
- Lift your shoulder blades off the floor and hold the position until the end of the approach.
- Inhale, and as you exhale, twist your body to the side: elbow to the opposite knee.
- As you inhale, return to the center and repeat the twist in the opposite direction.
Exercises on the horizontal bar
Circular Leg Raise
Make sure the bar is high enough so that your feet don't touch the floor while hanging. Grab the bar with both hands at shoulder width. Tighten your abdominal muscles and raise your legs at a right angle. Then start drawing circles clockwise with both feet. Keep your abdominal muscles tense at all times. Perform 8-10 repetitions and then repeat in the opposite direction. Repeat 8-10 times on each side.
Simplified version: Try doing the exercise on the wall bars, this will make it easier to maintain balance.
Bicycle hanging
Grasp the bar with your hands shoulder-width apart. Raise your legs at a 90-degree angle parallel to the floor. Instead of bringing your knees together, lift them up one at a time, as if you were riding an imaginary bicycle. Perform the exercise at maximum speed for 30 seconds.
Hanging lateral crunches
Hang on the bar, tighten your abdominal muscles. Bend your knees at a right angle. Slowly bend your knees to the side, trying to raise your feet as high as possible. Then slowly return to the starting position. Repeat on the other side. Perform 8-10 repetitions.