What is an intragastric balloon?
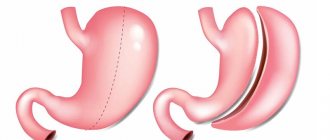
The balloon is a smooth ball made of high quality silicone rubber. The balloon has a radiopaque valve through which it is filled with water.
BIB balloon in stomach
Bloated
- balloon in the stomach - 1
- Cylinder valve - 2
- Gastric lumen - 3
- Esophagus - 4
- duodenum - 5
The volume of injected liquid is set only once, at the time of installation. You cannot add or remove a little extra liquid. As a rule, the standard volume is administered - 500 ml. This volume is used by most specialists.
Mechanism of action of the cylinder
The presence of a balloon in the stomach leads to the fact that it fills a significant part of its volume. Consequently, the amount of food a person can eat decreases. In addition, an inflated balloon stretches the wall of the stomach, which leads to irritation of satiety receptors. Such irritation leads to an early feeling of satiety.
How long does it take to place the balloon?
The balloon can be placed in the stomach for a maximum of 6 months. After this, it must be removed. This is explained by the fact that the hydrochloric acid present in the gastric juice gradually destroys the balloon, and it wears out. If the patient wants to continue treatment in this way, the old one must be removed and a new balloon placed in its place.
Who can have such a balloon placed in their stomach?
In order to understand who can have a balloon placed in their stomach for weight loss, you need to have an idea of the Body Mass Index.
So, the first group of patients who can have a balloon placed in their stomach are patients with a BMI from 30 to 40. As a rule, these are people who have already tried many times to lose weight in a variety of ways, but could not get sufficient effect. Many of them ask for a surgical operation to put a ring on the stomach, but with such a BMI, it is premature to perform the operation (it should be done when the BMI is 35-40 or higher). It is in such cases, when it is too early to perform the operation, but it is necessary to reduce weight, and the installation of a balloon is used.
Another group of candidates for balloon placement are patients with a BMI of 40 or higher if they are in poor health. Of course, they need to have weight loss surgery, but the risk of surgery is high. Installation of a balloon and weight loss lead to improved health and, accordingly, a reduced risk of surgery. That is, in this case we are talking about preoperative preparation. Sometimes a balloon is placed in obese patients who are undergoing joint surgery (joint replacement for arthrosis), surgery for hernias and other operations. Even a slight weight loss in them leads to a reduction in the risk of any surgery.
Another group of patients are people with a BMI of 40 and above who have extremely severe cardiovascular diseases. Due to severe cardiopulmonary failure, these patients will never undergo surgery.
If they need to achieve rapid and significant weight loss, they can have a balloon placed in their stomach.
Contraindications
Which patients should not have a balloon inserted into their stomach?
- You cannot install a balloon only for cosmetic reasons.
- Balloon installation is contraindicated in patients with a body mass index less than 30 (except in cases where patients have concomitant diseases, the course of which may improve with a decrease in body weight).
- The use of the BIB system is contraindicated in patients who have previously undergone abdominal or gynecological surgery.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including esophagitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, Crohn's disease, and malignant tumors of the stomach.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated in the presence of potential sources of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, such as varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach, congenital and acquired telangiectasia, and other congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract, such as atresia and stenosis.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated in the presence of large hiatal hernias.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated in the presence of strictures and diverticula of the pharynx and esophagus.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated if there are other medical problems that may make gastroscopy difficult.
- Also, a contraindication to balloon placement is the presence of mental disorders.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated in the presence of alcoholism and drug addiction.
- Balloon placement is contraindicated for people with low discipline, who cannot follow the prescribed dietary regimen, and cannot come for medical supervision 2 times a month.
- Contraindications include chronic use of aspirin, other anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, drugs that irritate the stomach, and anticoagulants (medicines that reduce blood clotting).
- A contraindication to balloon placement is pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Installation method
The balloon is installed under gastroscopy control. This is not an operation, but an endoscopic procedure. It is performed under complete anesthesia. The patient may lie on their back or left side, depending on the physician's preference. A special medical dye, methylene blue, is introduced into a container of water intended for inflating the balloon (it is needed for timely recognition of leaks from the balloon). First, a gastroscopy is performed - an examination of the esophagus and stomach for the presence of diseases that may be a contraindication for the installation of a BIB. The balloon is then inserted through the mouth. A syringe is connected to the catheter, and under visual control, the balloon begins to inflate. In this case, the cover in which the cylinder is located is torn, and the cylinder is released. When the balloon is filled to the required volume (500 ml), the catheter is pulled out of the balloon and the valve closes. The balloon becomes a free ball in the lumen of the stomach. The catheter and gastroscope are removed from the patient. This concludes the procedure.
Longitudinal gastrectomy
During surgery, the doctor removes the part of the stomach that produces the hunger hormone, ghrelin. After surgery, the volume of the stomach decreases, the patient's appetite decreases and therefore the feeling of fullness occurs faster. Longitudinal gastrectomy is performed in two ways: abdominal and laparoscopic. Laparoscopic resection is performed through small punctures in the abdominal cavity, and the next day after the operation the patient moves independently and does not experience pain. During abdominal surgery, the surgeon reduces the volume of the stomach through an incision in the abdominal wall. After the operation, doctors recommend staying in the hospital room for 5 days.
How to live after installing a balloon
A few hours after installation of the balloon, the patient can go home, although many authors recommend staying in the clinic until the morning. The fact is that the first night after installing the balloon can be very unpleasant. There may be severe nausea and repeated vomiting. We must survive this first night. And if the patient remains in the clinic, he can be given a drip and given an injection of drugs for nausea and vomiting. If a person goes home, he will have to deal with it himself.
So, for the first 3 days the patient receives the following treatment.
- If there is repeated vomiting, 1.5 liters of Ringer's solution or saline is prescribed intravenously.
- In the presence of vomiting, Cerucal (metoclopramide) 2 ml (10 mg) 2 times a day intramuscularly. If there is no vomiting, Cerucal (metoclopramide) is prescribed in tablets of 10 mg three times a day.
- A very good medicine against nausea and vomiting is Torekan (thiethylperazine). It is prescribed in capsules of 6.5 mg three times a day. If there is severe vomiting, the drug can be administered into the rectum in the form of suppositories.
Every day, for the entire time the balloon is in the stomach (that is, 6 months), the patient should receive omeprazole 30 mg per day (1 tablet at night).
Unpleasant sensations in the stomach may remain for another 3-4 days, then the body adapts to the foreign body in the stomach, and the person stops feeling anything.
Nutrition with the balloon installed can, in principle, be normal, but it should be borne in mind that the best results were obtained if the patient consumed 1000-1500 kcal per day.
Biliopancreatic shunt (BPSh)
This operation combines a reduction in the volume of the stomach and bypass surgery - reconstruction of the small intestine to reduce the absorption of food. BPS is considered one of the most difficult, but at the same time effective operations for the treatment of obesity. In 75% of cases, patients achieve the desired weight loss. In addition, the operation helps to cope with type 2 diabetes and normalize blood glucose levels. Already 3-4 weeks after surgery, the patient can eat without any restrictions.
How does a person lose weight after installing a balloon?
Body weight loss begins immediately after installation of the balloon. On average, patients’ weight loss over 6 months looks like this (average data, analysis of results from several clinics):
- Patients lost from 0 to 40 kg
- Average weight loss was 15 kg
- Excess body weight decreased by 40%
- Body mass index decreased by 5.
Decrease in body mass index (BMI) against the background of standing balloon
Patients' adherence to diet influenced the results achieved:
- Patients who followed the diet and consumed 1000-1500 kcal/day lost an average of 18 kg.
- Patients who did not follow the diet lost an average of 9.6 kg.
This means that the patient's personality plays a big role in achieving the result. A person with high discipline who is willing to put in real effort to lose weight is likely to get better results than the patient who relies on the balloon to do everything for him. There are no miracles. All principles of weight loss, namely following a diet with limited fats and carbohydrates and reducing the total calorie content of food, and rational physical activity remain basic principles in the case of using a balloon. That is, a person loses weight through his own efforts, and the balloon only helps him.
Laparoscopic gastric banding
Gastric banding is a surgical procedure in which a band is installed on the upper part of the stomach - a dense ring made of biologically inert material based on silicone.
The main purpose of installing a band is to divide the stomach into two parts: the upper, with a volume of 15-20 ml, and the lower. Food, passing down the esophagus, enters the formed “small stomach”, which, due to its small size, quickly fills. Its wall stretches and sends saturation signals to the brain. Due to the resulting feeling of satiety, the patient stops eating. Due to the constant reduction in the number of foods taken, and, therefore, the calories they contain, excess body weight is reduced, and the main goal of the intervention is achieved - weight loss.
Removing the balloon
After 6 months, the balloon must be removed. If the patient does not tolerate the balloon well, removal has to be done earlier than planned.
How is the balloon removed? You need to come for removal on an empty stomach. The procedure is again done under complete anesthesia.
After sleep occurs, the doctor inserts a gastroscope into the stomach for examination. Interestingly, while it is in the stomach, the balloon changes its color - instead of white and transparent, it becomes brownish. This is due to the fact that the wall of the balloon is stained with bile pigments. The balloon is pierced with a needle and the liquid is sucked out of it. After the fluid is sucked out, the balloon collapses. After this, the empty balloon is removed together with a gastroscope using a special clamp. The picture below shows the balloon after it has been removed from the stomach.
2-3 hours after removal of the balloon, the patient can go home; there is no need to stay in the clinic overnight.
On this day, however, you should not drive a car yourself.
The essence of the operation
First of all, you need to understand why you need a stomach band for weight loss.
The bandage, unlike the intragastric balloon, can be installed on the patient for life and does not require replacement over time. It is made of silicone and, if necessary, can be removed without any consequences for the stomach, if necessary. Today, manufacturers produce various types of bandages. Each of which is selected strictly individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient: the structure of his gastrointestinal tract, clinical data, and also based on the experience of a bariatric surgeon. As a rule, the patient is offered several bandage systems, then at the appointment the patient and the doctor choose the optimal one based on the advantages or disadvantages of each.
The bandage operates on the principles of a hydraulic system, which includes: a cuff, a connecting tube and a port. After the cuff is installed on the upper part of the stomach, it can be filled with an isotonic solution using a connecting tube. Through the port, which is part of the bandage system and is installed in front of the stomach under the skin, fluid flows into the connecting tube and from there into the cuff. The amount entering the port regulates the pressure in the cuff, thus increasing or decreasing the lumen in the stomach.
For each patient, the width of the lumen in the stomach is strictly individual and is adjusted empirically. Food that lingers in the upper part of the stomach (before the band) brings a faster feeling of fullness, putting pressure on its cardiac region. Thanks to this effect, the feeling of hunger is satisfied with much less food, in turn, a decrease in the amount of food leads to a decrease in calorie intake, which leads to gradual weight loss.
Preparation rules
In order to minimize all risks associated with the operation, the patient must be properly prepared for it. Ideally, the preoperative period consists of several successive stages, at each of which the doctor or the patient himself can decide to refuse the procedure.
Survey
A thorough examination is necessary to ensure that there are no medical contraindications, as well as to identify and prevent possible complications during the operation and the recovery period.
The list of necessary tests and analyzes in each case is determined by the doctor, but usually its integral part is:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood clotting studies;
- tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- fluorogram and ECG;
- gastroscopy and/or x-ray of the stomach.
A good doctor will definitely require that you first consult with a therapist and bring him an opinion about your general health.
Diet
Diet is needed already in the preoperative period. Its main task is to prepare the body for the transition to fractional nutrition, reduce the load on the liver and kidneys, and eliminate part of the visceral fat that covers the liver and interferes with the installation of the ring.
Doctors recommend that those losing weight stick to the following diet for at least a month:
- animal protein must be dietary - chicken breast or lean fish, boiled or steamed, no more than 200 grams per day;
- porridge and pasta with a minimum amount of oil and salt - 350-400 grams per day;
- fresh or boiled vegetables, salads with lemon dressing (no mayonnaise!) – 350-400 grams per day;
- 2-3 fresh apples or oranges, 1 grapefruit, a glass of fresh berries per day;
- vegetable soup 250-300 ml per day, meat, mushroom and fish broths are prohibited;
- dairy products - with a minimum percentage of fat content.
Sugar, sweets, canned fruits and packaged juices, soda, smoked meats and pickles, baked goods and confectionery are completely excluded from the diet.
Important! Those who manage to survive a month on such a diet often refuse surgery. It gives excellent results and has absolutely no contraindications.
Special training
A few days before the operation, it is necessary to take additional preparatory measures:
- stop taking aspirin and other blood thinners;
- do not use strong painkillers “Ibuprofen”, “Nurofen”, etc.;
- temporarily stop taking estrogens, even if they are prescribed to you by your doctor;
- 12 hours before surgery, do not drink or eat any food;
- Be sure to take a shower in the morning before surgery.
Even if you are very worried, do not take sedatives or sleeping pills - they can affect the quality of anesthesia. Warn the anesthesiologist at the clinic about this, and he will give you safe means in this situation that will help you relax.