Many people look at people who desperately fight for every kilogram they gain with obvious surprise. Is it really possible to want to gain weight when everyone around you is only thinking about losing weight? In fact, being underweight can be no less a serious problem than being overweight or obese. It carries a hidden or already obvious threat to life and health.
Nutritionists and nutrition consultants know very well how difficult it is sometimes to persuade a client to gain at least a little weight, and how difficult it can be to gain weight in the context of a habitual diet and lack of proper motivation. Today, experts from Lara Serebryanskaya’s school of nutritionists will talk about why underweight occurs, and what nutrition should be like to get rid of thinness...
Where does underweight come from?
This problem can have several different causes or a combination of them. Thus, underweight most often occurs when:
- insufficient nutrition, when its caloric content is lower than the basic needs of the body (small portions, only low-calorie foods, rare meals, for example, only 2 times a day);
- poor absorption of nutrients by the body (most often a consequence of certain metabolic problems and diseases);
- lack of healthy appetite (reduced reaction of the hunger center, lack of hormones responsible for the desire to eat, post-morbid or painful state);
- eating disorders (ED), for example, anorexia, orthorexia, selective disorders;
- hormonal disorders;
- long fasting and frequent fasting days;
- serious illnesses.
Before prescribing examinations and tests for a client, simply talk to him about his diet. Find out what he usually eats, at what time and how often. You can ask him to keep a diary of food and physical activity for a week to see the whole picture.
If a person complains of poor appetite, then try to understand what is causing it: deliberate dietary restriction or possible health problems. This is especially important for underweight children or adolescents, who often do not admit that they do not want to eat at all and can hide the real volumes of their diet.
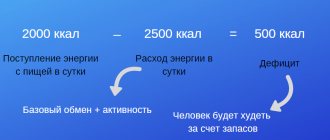
In cases where the client is simply malnourished and provided that he does not have an eating disorder or other mental disorders, weight gain is most often achieved by simply creating a daily calorie surplus. This will work for people who do not have serious health conditions that caused them to be thin in the first place.
However, it is possible that you are dealing with vegans, raw foodists and other restrictive dieters, as well as with clients who have primary symptoms of eating disorders. Working with them will be long and multifaceted.
Vegetarians will have to develop a sufficiently high-calorie diet, taking into account their food preferences and principles, but the correction of eating disorder will largely take place in the plane of psychotherapy.
There is another interesting category of clients - professional athletes and dancers, for example, gymnasts, ballerinas, who are prohibited from gaining weight above a certain norm. Long-term strict dietary restrictions and grueling training lead to the fact that a person’s weight becomes noticeably below adequate levels.
It is also often necessary to involve psychologists in weight correction among athletes, since their eating behavior may be based on deliberate dietary restrictions. If you do not intervene in time, this position will eventually lead to the development of anorexia or bulimia.
How to understand that a person is underweight
Here you can use the usual assessment of body mass index (BMI). To calculate it, the following formula is used:
BMI = weight (kg) / (height in meters)²
Thus, if a girl is 175 cm tall and weighs 55 kg, then her BMI will be 55 / (1.75 × 1.75) = 18.3. Note that for women, underweight is stated if the BMI is less than 19, for men - if the BMI is below 20.
To estimate the weight of children, the body mass index is not used; here it is necessary to use special centile tables, in which the analysis is carried out depending on the sex and age of the child. However, keep in mind that all children are different, each has its own build and physiology.
Therefore, when checking weight standards, pay attention to the child’s height. In some cases, conditional underweight in children is associated only with the fact that their height does not reach age standards. If a child is shorter than he should be for his age, then, therefore, his weight will also not correspond to age standards.
In this case, you need to correlate the parameters of height and weight. If the ratio does not deviate from the norm (even if it is at the lower limit), then there is no reason to state that the child is underweight.
Lack of body weight with normal nutrition
It also happens that the client’s diet is quite high in calories, he has no problems with appetite and eating disorders, but at the same time his weight is below normal. Then you should look for the cause in your health condition.
Here is a list of diseases that can potentially lead to underweight:
- hyperthyroidism and other problems in the production of thyroid hormones;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus (in some cases, instead of weight gain, it leads to rapid weight loss);
- severe stress and prolonged depression, when the nervous system is depressed;
- tuberculosis;
- long-term infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- celiac disease (celiac enteropathy or severe gluten intolerance);
- oncological diseases;
- chronic intestinal infections;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including insufficient enzymatic activity of the pancreas and underdigestion of food;
- helminthiasis (in other words, worms).
However, without appropriate tests and examinations, it is impossible to say exactly what could have caused the loss of weight and appetite. Therefore, advise your clients to go through the following:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and consultation with a gastroenterologist.
- Fluorography or x-ray of the lungs and consultation with a family doctor or TB specialist.
- Take a general and biochemical blood test, as well as blood tests for thyroid hormones, gluten tolerance, and worms.
- Make a tumor marker.
- Kaprogram and analysis for intestinal dysbiosis.
- Electroencephalogram and consultation with a neurologist.
- Consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist.
If certain diseases are identified, the client will have to begin treatment for them. Otherwise, without eliminating the cause of weight loss, gaining additional kilograms can be very difficult. And, nevertheless, people with underweight need to adjust their diet in any case.
Causes
There are many reasons that lead to this condition: obsession with diets, diseases, poor nutrition. But it is important to know that the reasons typical for women are not typical for men.
The reasons for thinness in adults are different than in children. Therefore, the reasons for lack of weight for women, men and children should be considered separately.
Among women
- Neuropsychic exhaustion. The psyche of women is highly susceptible to stress, and with nervous tension the body tends to refuse food;
- Hormonal disorders. The hormones produced by the pituitary gland and thyroid gland directly affect the metabolism in the body. If the functioning of these organs is disrupted, body weight increases or decreases. In such cases, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary;
- Overwork. If you lead an overly active lifestyle, forget to eat and fall exhausted in the evening, then overwork is your diagnosis. The body spends too much energy, which contributes to weight loss. With this regimen, anemia is the least that can happen. To avoid the consequences of neglect of your body, start eating right and don’t allow yourself to overwork;
- Parasites . Helminths are a common cause of weight loss. Therefore, doctors recommend getting tested for worms.
In men
- Increased carbohydrate metabolism. If a man has a congenital high metabolism, he needs to properly plan his diet so that the body has enough carbohydrates to maintain body weight;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to insufficient production of enzymes, food entering the body is not completely absorbed;
- Diseases of the endocrine system. Men are no less susceptible to hormonal disorders than women. Diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland or thyroid gland cause underweight.
In children
- Disruption of internal organs. The development of a child is disrupted due to serious diseases: heart disease, immunodeficiency, central nervous system damage. It is necessary to examine the child to see if there are any serious disorders in the body;
- Genetic diseases with malabsorption syndrome. Such diseases include cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, lactase deficiency. Because of them, the child’s body does not fully absorb vital elements;
- Nutritional factor . Incorrect diet or poor nutrition;
- Infections. Intestinal infections and frequent colds disrupt the child’s metabolism and food absorption. The feeling of hunger with such diseases is dulled.
Lack of weight causes irreparable harm to the health of an adult, and even more so to the health of a child. To restore your child to a normal weight, you need to carefully monitor your diet, activity, and overall physical well-being.
If you suspect that you or your loved ones are severely underweight, consult a doctor for a diagnosis. You cannot make a correct diagnosis on your own. The doctor will advise you on how to properly gain weight and maintain your body.
Underweight: consequences
Low weight is just as dangerous to your health as obesity. Here is just a small list of what awaits a person if he does not normalize his body weight in time:
- hypovitaminosis due to a sharp lack of nutrients and nutrients;
- decreased general immunity and associated susceptibility to infectious diseases with severe course and complications;
- difficulties in treating diseases due to weakness of the body and lack of energy resources for the functioning of the immune system and recovery processes;
- prolapse of internal organs due to a lack of fat and muscle mass;
- menstrual irregularities in women and the development of infertility in both sexes;
- serious hormonal imbalances with all the ensuing consequences;
- prolonged depression, up to the appearance of suicidal thoughts;
- dizziness, weakness, loss of consciousness, hypotension (low blood pressure);
- lack of strength to move, which will force you to lead a completely recumbent lifestyle;
- neurological and mental disorders, including paralysis of limbs, seizures, coma;
- extreme form of dystrophy with possible death.
After such a list, it becomes clear why you need to quickly get rid of underweight. The best way to do this is with a properly balanced diet.
Weight deficiency treatment in Almaty
Weight deficiency, or lack of body weight, is a disease that is expressed in a person’s body weight decreasing below the critical level of the body mass index. Weight deficiency can occur in both women and men, as well as in children, including newborns. In particularly serious cases, being underweight can be fatal.
Causes of underweight
The causes of underweight are very diverse. The most common of them are:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that prevent the normal breakdown of food and the consumption of sufficient amounts of nutrients;
- diseases of the endocrine system that cause hormonal imbalances: hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, the onset of diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency, including as a result of taking hormonal medications without medical supervision;
- lifestyle: insufficient or unbalanced diet with low amounts of fats and carbohydrates, stress, lack of sleep, smoking, excessive physical activity. In this case, body weight deficiency is observed more often in women and can be caused, among other things, by psychological reasons - the peculiar ideas of modern culture about a beautiful body, leading to the development of neuroses and anorexia;
- In children, underweight can be observed at an early age due to underfeeding (lack of milk from the mother or when feeding with incorrectly selected formulas). In some cases, lack of weight can be observed already at the fetal stage and is caused by an improperly proceeding pregnancy - poor nutrition of the mother, bad habits, etc.
What are the dangers of being underweight: complications
Lack of weight is a disease with a large number of serious consequences, including:
- loss of not only fat, but also muscle tissue, resulting in developing muscle weakness;
- decreased immunity and general resistance of the body, including psychological: frequent illnesses, long-term inflammatory processes, nervous breakdowns and depression, fatigue, decreased performance and mental activity;
- damage to various body systems, cardiovascular, nervous, sexual: lack of nutrition can cause the development of chronic diseases. In men, underweight can lead to a decrease in sperm production and further to complete infertility; in women, interruptions in the menstrual cycle are observed, up to the complete cessation of menstruation;
- critical underweight can cause death due to extreme exhaustion;
- In children, lack of weight is dangerous both in early childhood (including at the fetal stage) and in adolescence: it can also cause various kinds of disorders, including developmental delays.
Lack of weight: symptoms
Modern scientists distinguish several types of underweight (especially when determining this disease in children). Thus, degree 1 body weight deficiency, calculated as a percentage, implies a deviation from the norm by 10-15%, the second - by 15-30%, the third - by more than 30%.
In adults, underweight is diagnosed when the body mass index (BMI) decreases to less than 18.5 kg/m2.
Symptoms of underweight are most often visual: there is a pronounced loss of fat on the chest, abdomen, limbs, and also on the face (in the later stages of the disease). Patients may experience weakness, including muscle weakness, fatigue, irritability, and a tendency to depression.