What is this?
As we noted above, behind this diagnosis lies nothing more than a separation of the rectus abdominis muscles. And it just so happened that the main reason for its appearance is pregnancy.
During this exciting period, the constantly growing baby puts pressure on the anterior abdominal cavity, literally stretching the abdominal muscles. The hormone relaxin, the main task of which is to increase the elasticity of ligaments and joints, which simplifies the process of childbirth, adds fuel to the fire of the formation of the disease.
Based on the above, it can be determined that all pregnant women are at risk. But most often, diastasis occurs in women with large, multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, second and subsequent births, unfavorable heredity, problems with posture, and in overweight women in labor.
Maternity capital in 2021
What can you spend the money on, and what is the payout amount?
Go to article
Should diastasis be treated?
You may decide that diastasis is nothing more than a cosmetic defect.
But for some women, this is quite enough for the appearance of serious psychological complexes. However, this pathology can result in other problems. The fact is that the purpose of the abdominal muscles, contrary to widespread belief, is not at all limited to flexing the torso
. They have a number of perhaps more important tasks.
Firstly, these muscles are a protective shell for the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. In addition, they play an important role in maintaining an upright body position. And it is precisely this function that suffers the most during diastasis, since the abdominal muscles are uncoordinated. The body is forced to redistribute the load, primarily to the back muscles. The result is poor posture, back and lower back pain.
How to determine?
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, but you can conduct a preliminary diagnosis yourself.
- Lie on the floor, bend your legs, press your feet tightly, moving your heels towards your buttocks. Raise your head and shoulders so that your abdominal muscles are tense (as if you are pumping your abs), place one hand behind your head.
- With your other hand, feel the midline of the abdomen and the muscles radiating from it (feel like rollers).
- Use your fingers to determine the width of the strip between the muscles near the navel.
It is customary to distinguish three stages of diastasis, depending on the size of the muscle discrepancy:
- 5-7 cm. This degree is quite common after the first birth. Usually it does not bring any problems to a woman, but sometimes it can be accompanied by abdominal discomfort.
- More than 7 cm. At this stage, the lateral abdominal muscles relax.
- More than 10 cm. A dangerous situation for health, the skin becomes saggy, hernias and muscle atrophy may occur.
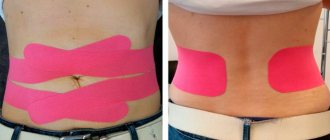
As you might guess, the treatment method for diastasis depends on its degree. If the first and second stages can be dealt with naturally with the help of exercises and corrective gymnastics, then the third stage will most likely require surgery.
Rehabilitation after surgery
If the muscles diverge by more than 10 cm, surgical treatment may be required, which has strict indications. But even after such treatment there is a period of rehabilitation. Already 10-14 weeks after surgical treatment, patients are advised to return to their normal lives, and exercise is allowed. But therapeutic exercises, that is, a set of exercises aimed at speedy recovery, are allowed much earlier. The recovery scenario and set of exercises are selected individually, and this depends on a number of factors: • surgical treatment method: endoscopic, classical surgical; • degree of diastasis and discrepancy in centimeters; • patient's condition; • etc. But even after surgical treatment, the probability of relapse is high, so there is no way to do without therapeutic exercises. Only a correctly selected set of exercises, supervision by a specialist and their regular implementation are the key to complete recovery and normalization of the condition.
It is important that a set of preventive exercises be compiled by a specialist. Some of them require some training. It is important to perform them correctly, otherwise there will be more harm than good.
Abdominoplasty
In some cases, diastasis can only be removed surgically. Do not forget that without treatment the disease will progress, which can lead to an even greater expansion of the line, loss of waist, growth of a “pregnant” tummy, prolapse of internal organs, urinary incontinence, etc. It is important to note that such plastic surgery is not a contraindication for subsequent pregnancy .
Let's talk about modern methods of treating diastasis.
Abdominoplasty
A procedure in which excess skin and fat are removed and the abdominal muscles are returned to their original position. There are several types of such intervention:
- Mini abdominoplasty. Excision of excess skin, correction of the lower abdominal wall.
- Standard. Suturing of muscles, tightening of skin, in some cases correction of the navel area.
- Endoscopic. Used when suturing muscles without removing excess skin is required.
Hernioplasty
A procedure indicated for patients who develop hernias due to divergence of the abdominal muscles. There is an open method of hernia repair, when the intervention occurs through a small incision, and an endoscopic method, with the elimination of pathology through an opening in the abdominal wall.
In addition, hernioplasty can be:
- Stretch using your own fabrics.
- Tension with the use of a mesh implant - endoprosthesis.
- Combined, combining both methods.
In our city, several companies offer diastasis treatment services. Let's talk about some of them:
- Institute of Medical Cosmetology, st. Kirova, 19, t. 212-09-75
- Krasnoyarsk Center for Plastic Surgery and Outpatient Medicine, Mira Ave., 93, t. 211-21-13
- Krasnoyarsk Institute of Traumatology, st. Mechnikova, 49, t. 22-33-999
- Effi, st. Historical, 111 art. 3/2
Reviews, photos and prices for abdominoplasty and hernioplasty in Krasnoyarsk can be found on the companies’ website.
In any case, a woman should make a decision about surgery and the technique used together with her doctor. The main thing is not to let the problem take its course and contact specialists in a timely manner.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
What is diastasis recti?
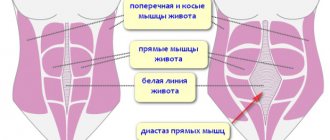
The rectus abdominis muscles are separated by a dense connective tissue septum - the linea alba, formed by tendon stretches of the oblique and transverse abdominal muscles on both sides. Normally, the inner edges of the rectus abdominis muscles are quite tightly adjacent to each other, and the width of the white line usually does not exceed 1 - 2 cm. Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is a divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles, an increase in the width of the white line by more than 2 cm.
Is diastasis recti a hernia?
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is not a classic abdominal hernia, since it does not have a hernial orifice and there is no risk of strangulation of internal organs. But traditionally, diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is considered within the framework of herniology (a surgical discipline that studies abdominal hernias), since the principles of reconstruction of the anterior abdominal wall and abdominal hernias are similar. In addition, diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is often combined with hernias of the white line and umbilical hernias.
Who gets diastasis recti?
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is more common in middle-aged or older men with abdominal (central) obesity and in slender women after pregnancy. Moreover, in men, diastasis of the rectus muscles most often occurs in the epigastric region (upper abdomen), and in women - in the mesogastrium and hypogastrium (in the middle and lower abdomen).
Why does diastasis of the rectus abdominis occur?
The main causes of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles are congenital weakness of connective tissue (connective tissue dysplasia) and stretching of the linea alba as a result of increased intra-abdominal pressure or mechanical load. If for men the risk factors are heavy physical activity and obesity, then the main risk factor for diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in women is pregnancy and childbirth. During pregnancy, significant stretching of the anterior abdominal wall and the white line occurs. In addition, during pregnancy, as a result of hormonal changes, softening and stretching of the ligaments occurs. Additional risk factors are pregnancy with a large fetus, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, and repeat pregnancies.
What kind of diastasis of the rectus muscles occurs?
Depending on the severity of the expansion of the white line of the abdomen, 3 degrees of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles are distinguished: I degree - the width of the white line is up to 5 - 7 cm, II degree - the width of the white line is more than 5 - 7 cm, III degree - a combination of diastasis of the rectus muscles with a saggy abdomen .
In plastic surgery, another classification of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is used:
- A – diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in women after pregnancy and childbirth
- B – diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in combination with “relaxation” of the lateral abdomen and lower part of the anterior abdominal wall
- C – diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles, extending in the epigastrium to the xiphoid process and costal arches
- D – diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in combination with the absence of a waist
The most common type A diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles occurs, that is, in women after pregnancy and childbirth.
How does diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles manifest?
A small diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles usually does not cause any complaints, except for the presence of a protrusion in the midline of the abdomen, which appears during physical activity and disappears with rest. With large diastasis, discomfort and abdominal pain may periodically occur. But in general, diastasis recti is an aesthetic problem, and most operations are performed for cosmetic reasons. If diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is combined with a hernia of the white line of the abdomen or an umbilical hernia, then surgical treatment is indicated as planned, for the same indications as for other hernias.
What examination is necessary for diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles?
To diagnose diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles, an examination of the patient is usually sufficient. If you try to raise your head and upper half of your body while lying down, a characteristic keel-shaped protrusion will appear in the midline of the abdomen, disappearing with rest. In cases of severe diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles and its combination with hernias, it may be advisable to perform an ultrasound examination of the anterior abdominal wall (US) or computed tomography (CT) of the abdominal cavity. These studies provide accurate information about the distance between the rectus abdominis muscles, the size of the hernial orifice in the presence of an umbilical hernia or white line hernia, the nature of the hernial contents, and allows one to calculate the volume of the hernial sac and the volume of the abdominal cavity. This data is extremely necessary for choosing an operation. All patients with diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles must undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvis before a planned operation, so as not to miss the presence of other pathology of the abdominal organs.
What are the treatment tactics for diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles?
In most cases, the indications for surgical treatment of diastasis recti are cosmetic. But with grade III diastasis, accompanied by complaints, limitation of physical activity, combined with hernias, there are absolute indications for planned surgical treatment.
In women after childbirth at the initial stage of the disease, diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles can be corrected with the help of special physical exercises. However, if conservative treatment does not bring any effect or there is diastasis of II – III degree, combined with abdominal hernias, surgical treatment is performed.
Considering that the indications for surgical treatment of diastasis are often cosmetic in nature, preference is given to minimally invasive surgical operations. Most often, a small semilunar skin incision is made in the navel area or a transverse incision up to 6–7 cm along the skin fold above the pubis. If there is a scar after a cesarean section, it is usually used for surgical correction of diastasis. Using special elongated instruments, subcutaneous fat is separated from the linea alba of the abdomen throughout this diastasis (if necessary, from the costal arches to the pubis). Then, using a continuous suture using long-absorbable suture material, the separated inner edges of the rectus abdominis muscles are sutured. Thus, the linea alba is reconstructed and diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is eliminated. If necessary, a synthetic mesh implant is additionally used, which further strengthens the suture line. In some cases, it is possible to use endoscopic support to fix a synthetic implant to the anterior abdominal wall from the abdominal cavity.
In the presence of overstretched skin with striae (stretch marks) in the lower abdomen, it is advisable to combine correction of diastasis with abdominoplasty. This is a surgical intervention in which excess overstretched skin and subcutaneous fat are removed, and the waist and contours of the abdominal wall are formed.
Pathogenesis
During the period of bearing a baby, the fetus puts pressure on the abdominal wall, which leads to stretching of the muscles and their lateral divergence.
After childbirth, muscle groups, due to their high contractility, quickly return to their original state.
However, the connective tissue frame that holds them, when strongly stretched, is not capable of independent contraction.
The result is a clear perforation in the area of the white line, determined both by palpation and visually.