Gastric juice helps the digestion of food. “Stomach acidity (acidity of gastric juice) is a characteristic of the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the lumen of the stomach or in gastric juice,” says Olga Khafisova, gastroenterologist at the MEDSI Clinical Diagnostic Center on Belorusskaya, Ph.D. — The main constituent unit of gastric juice is hydrochloric acid, which is produced by the parietal cells of the fundic glands of the stomach. Normal acidity in the lumen of the body of the stomach on an empty stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH; accordingly, an increase in gastric acidity is said to occur when pH measurements tend to decrease. The breakdown of large peptide molecules by hydrochloric acid is essential for their complete absorption. The enzyme pepsin, which is found in gastric juice, also breaks down proteins, but its activity requires normal stomach acidity. In addition to digesting proteins, hydrochloric acid directly affects a multiple cascade of reactions converting inactive digestive enzymes into active ones, and also destroys pathogenic microorganisms ingested with food.”
Diet
Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which without proper treatment becomes chronic and can lead to serious pathological changes, including anatomical restructuring of tissues. The main symptoms of gastritis with high acidity - pain and heartburn - are characteristic of other gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, the diagnosis is made exclusively by a doctor after examination. Diet and timely treatment can stop the process, relieve symptoms, and provide the patient with complete digestion.
The nutrition menu for gastritis of the stomach with high acidity is compiled individually, taking into account the state of health. However, there are general rules that apply to all patients.
The basic principle of dietary nutrition for gastritis with high acidity is thermal, chemical, mechanical sparing of the mucous membrane.
- Nutrition should be balanced and contain all the nutrients the body needs.
- Avoid fried and fatty foods. Steam, boil, stew, bake.
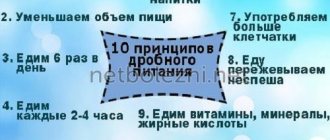
- Follow the regime. It is better to take food at the same time, then the digestive system will adjust to a certain rhythm and will better cope with its “responsibilities”.
- Eat at least five meals a day. Small meals reduce the load on the digestive tract.
- Limit your portions and don't overeat.
- Dishes should not be too hot or too cold. The optimal temperature is 15-600C.
The menu limits hot seasonings and spices, cereals and vegetables containing coarse fiber. Sour berries and fruits. Baking and brown bread and whole grain bread are also not recommended. Avoid products that have a toxic and irritating effect: hot seasonings, smoked foods, canned food, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
In case of exacerbation of gastritis, diet No. 1 is prescribed. It is as gentle as possible on the stomach, helps reduce inflammation, improve the healing of erosions, and normalize secretory and motor functions. In the remission stage, treatment of gastritis with high acidity with a diet is not stopped; the diet is gradually expanded, adhering to the principles and rules of a healthy diet.
Why does my stomach hurt?
There are many diseases that cause pain in or near the stomach. It is important for the doctor to determine the nature and location of the pain. Here is a list of some diseases and a description of the nature of the accompanying pain:
- pancreatitis, cholecystitis and duodenal ulcer cause sharp pain in the stomach area. Pain, which patients characterize as acute, usually indicates ulcer perforation (the appearance of a hole in a hollow organ due to a chronic pathological process in its wall). This can happen with a stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- gastritis and stomach ulcers are usually accompanied by a burning sensation in the epigastrium (the part of the abdominal cavity below the breastbone). If the process becomes chronic, the pain becomes dull and aching. With gastritis and ulcers, there is a clear relationship with food intake: pain appears a couple of hours after eating or on an empty stomach;
- “shooting” pain, short-lived (a couple of seconds), which occurs when inhaling or quickly getting out of bed, is characteristic of diaphragm spasm. A spasm is provoked by a violation of the blood supply to the diaphragm;
- patients with malignant tumors in the stomach complain of mild but constant pain. If the tumor has metastasized to the pancreas, the pain turns into shingles;
- Poisoning is characterized by sharp, severe, cramping pain in any part of the abdomen;
- Colitis (inflammation of the large intestine) is accompanied by intense pain in the upper abdomen, which usually subsides after a few days, but does not disappear completely.
These are the most common causes of abdominal pain. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after certain diagnostic tests. In addition to the above conditions, pain occurs with dissection of the abdominal aorta, trauma after a blow to the stomach and intestines. There are cases when the pain from a heart attack moves to the epigastric region. The main symptoms of gastritis of the stomach: heartburn, vomiting, belching, frequent release of gas, bloating, headache, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, increased salivation or extreme thirst; chronic gastritis is sluggish.
Some diseases require quick response and immediate surgical intervention to save the patient's life. For example, if surgery is not performed in time for perforation of a stomach or duodenal ulcer, complications develop (peritonitis, sepsis) that directly threaten the patient’s life.
Important! If you have abdominal pain of any location, you should not take painkillers. The nature of the pain will tell the doctor which organ to check, and the spontaneous disappearance of pain may indicate that the pathological process is progressing and something needs to be done urgently, although subjectively the patient will feel that he is feeling better. A similar condition can occur with ruptured appendicitis.
Foods for gastritis with high acidity
- First meal. Soups are milk, cereal, pureed, with the addition of vegetables and pasta.
- Second courses. Lean meat without tendons, boiled or steamed, pureed and cut into small pieces. Low-fat fish, boiled and pureed. Jellied, weak jelly.
- Side dishes. Puréed vegetables and herbs, cereals, pasta, green peas.
- Sweet dishes. Ripe fruits and berries of non-acidic varieties, mousses, jams, jelly, honey.
- Dairy products. if tolerated - whole milk, cream, one-day yogurt, non-acidic mashed cottage cheese.
- Weak tea, rosehip infusion.
Mushrooms, white cabbage, onions and garlic, sorrel, spinach, turnips, rutabaga, and black bread are excluded from the menu. Peas, beans and beans, and citrus fruits are prohibited.
Nutrition should provide the body with all the necessary nutrients and energy, this is especially important if the stomach function is impaired. Particularly dangerous is an insufficient amount of protein with a complete amino acid composition. This problem can be solved with the help of a specialized food product - the protein mixture "DISO®" "Nutrimun". The product should be added to dietary dishes during their preparation, and Nutrimun can be used for both medicinal and preventive purposes.
General rules
Acidosis means a shift in the acid-base balance to the acidic side.
But this applies to tissues and environments that normally have a neutral environmental reaction of 7-7.35 (blood, tissues, lymph, internal environment of cells). This term does not apply to biological media that are initially acidic (for example, gastric juice) or slightly acidic (urine). To assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, the acidity value is determined, which consists of free hydrochloric acid and bound hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is produced by the parietal cells of the fundic glands of the stomach. A research method that allows you to determine acidity in the stomach and antrum is pH-metry . When performing daily pH measurements, even the daily rhythm of acid formation is determined. This allows for the most effective treatment - prescribing an acid-suppressing drug during the period of highest acidity.
What is dangerous about high stomach acidity? Normally, the process of acid formation is regulated and an increase in acidity turns on the mechanism of acid neutralization: the cells of the antrum of the stomach produce somatostatin , which blocks the secretion of hydrochloric acid. The cause of acid-related diseases is an imbalance in the mechanisms of acid production or acid neutralization, as well as poor nutrition and the presence of constant stress.
Against this background, with insufficient efficiency of the esophageal and pyloric sphincters, pathological gastroesophageal and duodenogastric reflux may occur, manifested by heartburn , belching and bitterness in the mouth. And with an imbalance between aggressive factors (with a high content of hydrochloric acid, pepsin , which represent acid-peptic factors) and protective factors (gastric mucus and duodenum, glycoproteins , bicarbonates , immunoglobulins , reparative activity of the mucosa, its good blood supply), inflammatory phenomena of the gastric mucosa occur . Increased acidity is a frequent companion to gastritis and peptic ulcers .
The secretion of hydrochloric acid and pepsin is regulated by the vagus nerve. And the mechanism of ulcer formation can be represented as follows: increased tone of the parasympathetic nervous system - gastric hypersecretion - formation of an ulcerative defect. Based on this, the opinion “No acid - no ulcer” was supported for a long time, but in recent decades, in connection with the discovery of Helicobacter pylori, the formulation became relevant: “No Helicobacter pylori - no ulcer.”
Therefore, treatment of peptic ulcer is aimed at the effects of two factors - acid-peptic, using drugs that reduce gastric acidity, and Helicobacter. The most powerful drugs that control stomach acid formation are proton pump inhibitors. Antacid drugs are still used, which reduce acidity by interacting with acid in the stomach cavity ( Almagel , Maalox , Taltsid , Rutacid phosphalugel ).
Nutritionists are also taking an approach based on the acidity of the stomach - the diet will depend entirely on this factor. Proper nutrition for high acidity is important, it is part of the healing process and is organized on the basis of Table No. 1 .
The purpose of therapeutic nutrition is to eliminate dyspeptic symptoms (heartburn, nausea, belching, flatulence), pain and improve food digestion. The diet is aimed at reducing gastric excitability and reducing the acid factor. Therefore, strong secretion stimulants (broths, mushrooms, coffee, carbonated drinks, smoked meats, alcohol) and mucosal irritants (condiments, spices, rough foods, rough vegetables, salty, spicy, pickled dishes) are excluded. The gentle regime includes fractional meals, which promotes good digestion and rapid absorption of food.
The degree of sparing and grinding of food depends on the severity of pain and dyspeptic syndromes, therefore the following types of diet can be prescribed:
- No. 1A - with severe exacerbation. It provides for maximum limitation of all effects on the stomach. Dishes are served only boiled, pureed and in a liquid state (slimy soups, porridges, pureed meats, jelly, compotes). Any vegetables and fruits are excluded.
- No. 1B - during the period of improvement. Dishes are also pureed, but their consistency is thicker. Vegetable purees from coarse vegetables, meat and fish soufflé are allowed.
- №1 - this is the main table, which is distinguished by a complete content of proteins, fats (limited animals) and carbohydrates (limited only simple carbohydrates) and moderate sparing of the stomach. It is used during the period of consolidation of treatment results and can be used for constant nutrition of patients.
In all cases, the diet for high stomach acidity involves the exclusion of foods that stimulate gastric secretion:
- meat, fish, mushroom broths, fermented milk products, sour drinks, coarse cereals and vegetables, tough meat with tendons;
- spicy, pickled, smoked and fried dishes;
- coffee, tea and alcohol;
- irritating foods: onions, garlic, peppers, spices, citrus juices, cranberries and other sour fruits and berries, tomatoes, turnips, radishes, ginger, chocolate;
- causing gas formation (legumes, fresh bread and pastries, kvass, drinks with gas, an abundance of sweets) and promoting the reflux of duodenal and gastric contents into the esophagus.
In all types of diet, the amount of animal fats is limited: fatty pork, cream, sour cream, lamb, goose and duck meat. It is not allowed to consume incompatible products that cause fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Dishes are prepared with the addition of vegetable oils and a small amount of high-quality butter. When preparing, steaming, stewing or baking (on the main table) is used. With increased acidity, it is important to follow a meal schedule and not overload the stomach with rich food, especially at night. The last meal is 3 hours before going to bed. Dry food, mono-diet and fasting are excluded. You also need to give up bad habits.
Special Purpose Products
- Honey has a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane and reduces the acidity of gastric juice. It can be consumed in small quantities.
- Cream and milk reduce gastric secretion. It is best to drink them before bed.
- Broccoli helps reduce the number of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which is one of the factors in the development of gastritis.
- Oatmeal and oatmeal jelly contain many vitamins and microelements, do not irritate the gastric mucosa, and help relieve nausea and heartburn.
You should not limit your diet to just these products. Nutrition should be as varied and balanced as possible, only then will it be healthy, and therefore optimal.
It will be useful to keep a food diary. By writing down what, when, how you ate and how your body reacted to it, you can quickly figure it out and create the optimal menu. If you follow your doctor’s recommendations as closely as possible, coping with the disease will be faster and easier.
With timely treatment, the patient will be able to get rid of gastritis and forget about painful symptoms. To prevent relapses, you should adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Chronic gastritis
Acute gastritis is an acute condition caused by a single influence of irritants (harmful microorganisms, poor-quality food, chemicals) on the gastric mucosa. An inflammatory process occurs. In this case, diet and drug treatment are indicated. If all rules are followed and effective treatment, acute gastritis will remain a thing of the past for the patient. Under the influence of certain factors (poor nutrition, chronic stress), periods of exacerbation become constant. This means that the process has become chronic.
There is usually a seasonality of exacerbations. Patients are admitted to the hospital with exacerbation in the fall and spring. This is due to decreased immunity during these months, the ability to resist bacteria is lower, which leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Chronic gastritis often worsens during a stressful situation. People who do not know how to adequately regulate their emotional state constantly experience stomach pain.
In order for a doctor to diagnose chronic gastritis, the patient must undergo a series of examinations:
- gastroscopy - examination of the esophagus and stomach using a special probe equipped with a camera;
- pH-metry – monitoring of stomach acidity for a day or more. The method allows you to detect inflammation and determine the nature of gastritis (hyperacid or hypoacid);
- examination of gastric juice, which is collected by a probe;
- respiratory test to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- biopsy of the gastric mucosa at the site of the pathological process to establish a more accurate diagnosis;
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray examination;
- blood test to look for antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms.
Acute gastritis usually does not lead to complications. This is a characteristic feature of a chronic process. Among the complications it is worth highlighting:
- anemia (develops due to chronic bleeding due to damage to the stomach wall);
- peptic ulcers;
- benign or malignant tumors.
Cancer may be indicated by changes in the usual course of chronic gastritis - a change in the location of pain and its nature. You should consult a doctor immediately if you have additional symptoms: black feces, pale skin, frequent dizziness and headaches, fainting, tachycardia, shortness of breath. This may indicate a complication of gastritis.
What's on the menu?
As part of diet No. 1, soups based on vegetable broth with the addition of vermicelli, rice, and various vegetables are welcomed. You can also season soups with cream or boiled egg. Fish and lean meats are allowed.
You should avoid rye bread, but you can replace it with dried bread or crackers. The diet also involves a complete rejection of puff pastry, fatty meats and canned food, salty cheeses, hot sauces and marinades. White cabbage, mushrooms, sorrel, spinach, onions, cucumbers, carbonated drinks, black coffee are contraindicated.
List of permitted products:
— Soups can be prepared from permitted pureed vegetables in carrot or potato broth. Milk soups made from pureed or well-cooked cereals (rolled oats, semolina, rice) with the addition of vermicelli and pureed vegetables and pureed soup from pre-cooked chicken or meat are allowed.
Article on the topic
In search of gastritis. What tests will help identify the disease? Meat and fish broths, mushroom and strong vegetable broths, cabbage soup, borscht, and okroshka are completely excluded.
— Bread and flour products are prohibited, but not completely. It is allowed to eat wheat bread made from premium and 1st grade flour, but only yesterday’s baked bread or dried bread. Sweet flour products include dry sponge cake, dry biscuits, well-baked savory buns, baked pies (with apples, boiled meat or fish and eggs, jam) and cheesecakes with cottage cheese.
Rye and any fresh bread, products made from butter and puff pastry are completely excluded.
— Meat and poultry can only be lean, without tendons and skin. Steamed and boiled dishes from beef, young lean lamb and trimmed pork, chicken, and turkey are allowed. Lean veal, chicken and rabbit can be eaten, but only boiled. Steamed cutlets, meatballs, quenelles, souffles, mashed potatoes, zrazy and beef stroganoff made from boiled meat are also allowed.
Fatty or stringy varieties of meat and poultry, canned food and smoked products are completely excluded.
- Fish - you can use low-fat types without skin, in pieces or in the form of cutlets. Fish can be boiled or steamed.
Fatty and salty types of fish, as well as canned fish, are completely excluded.
— Dairy products are allowed, in particular, you can drink milk, cream, non-acidic kefir, yogurt. Fresh non-acidic cottage cheese and sour cream (but in small quantities), baked cheesecakes, soufflé, lazy dumplings, puddings, and mild grated cheese are also allowed.
Dairy products with high acidity, sharp, salty cheeses are completely excluded.
— Eggs can be cooked soft-boiled or in the form of an omelet, 2-3 pieces per day.
Hard-boiled and fried eggs are completely excluded.
- Cereals - semolina, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal are allowed. Porridges are cooked in milk or water, semi-viscous and pureed. You can also prepare cutlets from ground cereals, boil vermicelli and finely chopped boiled pasta.
Millet, pearl barley, barley and corn cereals, all legumes and whole pasta are completely excluded.
Article on the topic
Stomach ulcer: how does it develop and what does it mean?
— Vegetables should be steamed or served pureed.
You can use potatoes, carrots, beets, cauliflower, and rarely green peas. You can use early pumpkin and zucchini in a non-grated form. Finely chopped dill can be added to soups. Tomatoes - only ripe, non-acidic and a maximum of 100 g. White cabbage, turnips, rutabaga, radishes, sorrel, spinach, onions, cucumbers, salted, pickled and pickled vegetables, mushrooms, canned vegetable snacks are completely excluded.
— Snacks are acceptable, but only boiled tongue, liver pate, doctor’s sausage, milk sausage, diet sausage, jellied fish in vegetable broth, sturgeon caviar, soaked low-fat herring and mincemeat, mild cheese, unsalted ham without fat.
All spicy and salty snacks, canned food, and smoked foods are completely excluded.
- Sweets . You can eat boiled and baked berries and fruits, purees, jelly, mousses, jellies, compotes, always pureed. You can also use butter cream, milk jelly, sugar, honey, non-sour jam, marshmallows and marshmallows.
Sour, insufficiently ripe, fiber-rich fruits and berries, unprocessed dried fruits, chocolate and ice cream are completely excluded.
— Sauces and spices . Moderate consumption of sour cream, fruit and milk-fruit sauces is allowed. Dill, parsley, vanillin, and cinnamon are allowed very limitedly.
Article on the topic
And what is useful is harmful? How can healthy foods be dangerous? Meat, fish, mushroom, tomato sauces, horseradish, mustard and pepper are completely excluded.
- Beverages . Weak tea, tea with milk, cream, weak cocoa and coffee with milk are allowed. Sweet juices from fruits and berries, as well as rosehip decoction.
Carbonated drinks, kvass, and black coffee are completely excluded.
— Fats and oils . You can - unsalted butter, premium quality cow's ghee, refined vegetable oils added to dishes.
All other fats are completely excluded.