If you put sports nutrition products on a pedestal, then creatine will be among the most popular, namely among BCAA and essential amino acids, proteins and gainers. Why is creatine, or carboxylic acid, so popular and how does it affect the body?
What is creatine and how does it affect the body?
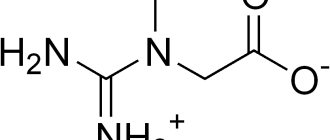
Creatine is a carboxylic acid that contains nitrogen. This chemical compound was discovered back in the nineteenth century! But then it was found in muscle tissue as an integral component of skeletal muscles, but this substance became a sports supplement not so long ago.
Creatine appeared as an anabolic agent in the 90s of the last century. Then scientists were able to prove that daily intake of the product creatine monohydrate contributed to an increase in creatine in muscles by almost a quarter in just five days. And, as you know, creatine is involved in energy metabolic processes, and it also has a positive effect on muscle contractility.
The human body constantly contains a supply of creatine, which is quite sufficient for life; this amount is approximately 150 grams. But for a person experiencing high physical activity, this amount is not enough and it is quickly consumed, which leads to overwork and degradation of the anabolic process. In other words, the muscles become exhausted and cannot work and develop effectively. It is in order to maintain a high level of the substance in the muscles that a creatine sports supplement is used.
Creatine. Harm or benefit?
This composition, like everything in our life, cannot be viewed solely from one side - black or white. Of course, the effectiveness of the composition has been proven theoretically and practically. But there may, under certain conditions, be some unpleasant aspects of the intake. As a rule, they come down to the side effects and actions of creatine.
Benefits of taking creatine
- Increase in strength characteristics, both explosive and long-term endurance.
- You can study the harms and benefits of creatine for a long time, but without this substance you can’t talk about effective growth of muscle mass. Yes, it does not directly cause an increase in muscle volume, but it ensures tissue performance, which leads to a positive result.
- Creatine promotes rapid recovery of the body after serious training and sports competitions. This occurs due to the binding of lactic acid.
- Creatine: benefits and harm to the body can be combined literally in one property. This substance perfectly retains water in the body, since it literally chemically binds to it. On the one hand, this is good because it promotes muscle growth and increased volume. In addition, during high and prolonged loads, this to some extent compensates for the removal of fluids through sweat. On the other hand, this leads to a slowdown in the breakdown of adipose tissue. If a person wants to lose weight or is losing weight before a competition, it is better to avoid creatine. It is important to understand that stopping creatine intake automatically eliminates both the positive and negative aspects of the issue. Athletes often actively eat creatine as a dietary supplement during the training and inter-competition periods, and stop taking it before a fight or performance.
- This composition, albeit indirectly, stimulates the production of testosterone and many other hormones important for the full development of the body, for example, growth.
- By the way, about growth. It is known that a chemical compound such as myostatin interferes with the growth and normal development of muscle mass. Creatine blocks this unpleasant effect. Experienced athletes from time to time are faced with offers of various offers of “myostatin blockers”. However, in practice they are ineffective, but creatine has proven itself in this regard exclusively on the positive side.
- Without going into complex chains and cause-and-effect relationships, this substance normalizes the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, reduces the likelihood of heart attack and stroke, and also calms the nervous system.
Why is a dietary supplement dangerous?
If we take into account all the known nutritional supplements that athletes use, creatine should probably be considered one of the safest. Firstly, all side effects are extremely rare and are not hazardous to health. Stopping the compound completely restores health and eliminates signs of side effects.
- There is an opinion that creatine can cause muscle cramps and spasmodic manifestations in the limbs. Any direct connection between taking the drug and such manifestations has not yet been clearly established. However, you need to be prepared for such manifestations. In this regard, creatine is not recommended for open water swimmers, for example, triathletes, cyclists and other categories of athletes in whom cramps are fraught with serious consequences. It is clear that for bodybuilders, weightlifters and boxers, spasms and cramps are unpleasant, but “not fatal.” In any case, this side effect is extremely rare and is determined purely individually upon administration.
- There is another unpleasant point that concerns physiology. We are talking about an upset stomach with all the ensuing consequences. This problem occurs quite rarely and can be solved by simply eliminating the supplement.
- In young people, dietary supplements can cause acne on the skin. This is due to a sharp increase in testosterone. Here you have to choose - beautiful skin or rapid muscle growth. At the same time, you can always refuse the composition, and the skin returns to normal very quickly.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that creatine is an extremely controversial drug. Its effectiveness when playing sports is undeniable, but you shouldn’t forget about side effects either. In general, the best solution in such a situation would be to consult with specialists on the advisability of taking creatine for you.
What foods contain creatine?
Creatine is found in a variety of foods. It is present in large quantities in fish and red meat (beef), as well as in pork. A small amount is found in fresh vegetables and fruits. The disadvantage of obtaining creatine in full from food is its sensitivity to high temperatures. That is, after baking the salmon in the oven, you can forget about creatine, and the same with pork. Of course, not the entire amount will be destroyed, but it’s not worth talking about the norm. For example, to replenish the daily dose of a substance, an athlete weighing 70 kg needs to consume one kilogram of beef.
Side effects
Side effects of using creatine may include:
The second most common side effect of creatine is gastrointestinal distress, which manifests itself as abdominal pain, nausea, flatulence and diarrhea.
- muscle cramps;
- dehydration;
- indigestion;
- diarrhea or nausea;
- acne or pimples (rarely detected).
If a person has any kidney disease, taking creatine supplements is prohibited because the kidneys cannot filter out the byproduct creatinine that is produced during the metabolic breakdown of creatine.
Although the supplement is generally accepted as legal and effective, the safety of long-term use has not been established clinically, and research in this area is ongoing. Some of them showed positive results. For example, a study conducted in May 2005 found that 200 patients who took 10 grams of creatine per day experienced no significant changes in health compared to those who took a placebo. Moreover, the patients took the supplement for 310 days, and their health status was constantly monitored.
Why is creatine needed in sports?
Creatine has many positive effects on the athlete’s body to achieve high athletic results, namely:
- Helps increase muscle strength and, accordingly, mass.
- Promotes the production of hormones involved in the anabolic process of the body.
- Increases training intensity.
- Helps reduce lactic acid levels after exercise and reduce muscle pain.
- Participates in central nervous system processes and strengthens the cardiovascular system.
History of discovery
Creatine was discovered in the 19th century as a component of skeletal muscle. Scientists were interested in the question of what this compound consists of. At the same time, combined molecules of creatine and phosphorus were found - phosphocreatine. Later, many studies were conducted, including on creatine as a dietary supplement. In the 20th century, researchers discovered that this substance helps increase muscle mass. In the 80s In the 20th century, it was established what creatine is needed for and how it affects the human body. Scientists have proven that consuming 20 grams of creatine over several days increases its concentration in muscles.
Types of creatine in sports nutrition
Today there are many types of creatine. It is available in tablets, capsules, powder, and also in effervescent tablets. There is no particular difference in the form; each athlete chooses a convenient form individually for himself.
Here are the three most popular and common types of creatine that athletes actively use.
Creatine monohydrate
It’s unlikely that anyone has not heard of creatine monohydrate, a classic supplement for bodybuilders and athletes of many sports. By the way, it is this form that is included in many sports nutrition supplements. More often than not, taking the supplement starts with a load. Monohydrate is better absorbed with glucose, namely grape juice.
Creatine hydrochloride
The newest creatine formula has such advantages and features as:
- Quick and complete dissolution in water.
- Does not require a loading phase like monohydrate.
- Does not retain water and allows you to gain quality mass.
- Fast absorption.
- No side effects.
Creatine citrate
This type of substance is creatine combined with lemon juice molecules. It is citric acid that is involved in the transformation of creatine into energy. According to the manufacturers, this form has a stronger effect on ATP production, increases endurance and energy reserves, and restores muscles as quickly as possible after heavy exercise.
When choosing a sports supplement, you should pay attention to the shape and size of the particles. The peculiarity is this: the smaller the particles, the faster the sports product is absorbed. Also a plus will be the additional content of fast carbohydrates. The presence of glucose in the composition allows you to consume creatine with water and not use juice, and such products are absorbed faster and better.
rules for taking creatine
There are two main ways to take creatine:
- With the loading and support phase. How to drink it: when loading for 5-7 days, the daily dose for an athlete is 20 grams. During the maintenance phase, take 2-5 grams of creatine per day for a month. Loading allows you to saturate your muscles with creatine in a short time, but this method of administration increases the risk of side effects.
- You can take creatine continuously in one dose, gradually accumulating it: 5 grams daily for up to 2 months. The absence of dosage jumps is safe for the body, but the peak of its effect is reached only after 3-4 weeks of use.
How to take: after training in combination with gainers, amino acids, protein drinks. If they are absent, drink at least a glass of water. On recovery days, the time of administration may be in the morning before breakfast.
Creighton University research has shown that adding carbohydrates to pure monohydrate improves strength training performance by 30%.
Do I need a break from taking it - yes. After the course you need to take a break for a month.
Do not exceed the dosage of creatine when taking
Side effects of creatine
One side effect of the drug that may occur when taking a sports supplement is water retention. In fact, many athletes are just waiting for this, since taking the supplement can quickly visually increase mass and muscle volume. Of course, this effect is insignificant and should not be compared with water retention from taking hormonal anabolic drugs. By the way, this water retention has a slightly different nature and does not affect blood pressure.
Individual intolerance to creatine, accompanied by indigestion, is also possible. To eliminate this side effect, simply reduce the dosage.
The effectiveness of creatine
Research and reviews from athletes indicate that with the right combination of creatine intake, strength training and a proper diet, you can increase from 2 to 5 kg of lean muscle mass within 30 days. This fact makes it one of the most popular sports supplements today.
The substance has an anti-inflammatory effect even in cases of serious and chronic inflammation, for example, arthritis. Exhibits an immune effect on the central nervous system (in case of ischemia).
Nutritional supplementation with creatine has been implicated in the treatment of muscle atrophy. Moreover, the supplement is being studied for its medicinal properties to suppress the growth of certain types of tumors in mammals. Based on the test results, it is suggested that creatine may have anti-cancer effects.
But you shouldn't abuse the substance. Increasing doses on your own may have negative consequences.
When doing bodybuilding, constantly maintaining a high intensity of training is very important, so creatine is simply necessary here.
Creatine for girls
Most studies of this type of sports nutrition have been conducted on men. But despite this, it has been scientifically proven that creatine monohydrate benefits both sexes in building a beautiful body.
It is much more difficult for women to build high-quality muscle mass than for men, due to less testosterone, the hormone responsible for muscle growth. Helping your body become strong, despite this factor, is possible with the use of creatine as a sports supplement.
Due to the fact that muscle mass increases, more calories are burned, because the larger the muscles, the more calories and energy they need. This helps girls in the process of losing weight and reducing the level of body fat.
Content
- 1 Creatine in bodybuilding 1.1 History of creatine
- 3.1 Increased strength
- 5.1 Creatine and children