What is creatine?
Creatine is one of the most effective and popular nutritional supplements on the fitness market. This is all because of the many benefits it brings to athletes. Among the main benefits are, in particular, significantly improved performance, endurance and energy during intense physical activity. Creatine in the body quickly produces energy during exercise, so you can train harder. It is also known for its effect on muscle growth and strength. [1]
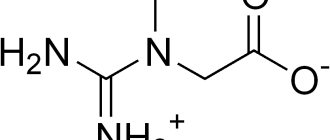
Creatine is an organic molecule that is formed from amino acids in the body . It is mainly produced in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys and pancreas. In the body, it is usually stored in the muscles, but it is also transported to the heart and brain. It contains high-energy phosphate groups in the form of phosphocreatine, which are transported into ADP (adenosine diphosphate). It is then converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the main energy carrier in the body. This role of creatine is especially important in conditions where the body requires large amounts of energy , such as when requiring physical or mental activity. [12]
Creatine is also found in some foods such as beef and fish . Athletes, however, tend to consume creatine in the form of dietary supplements, which serve to quickly and easily replenish the required amount of creatine. [1]
What is the best form of creatine to gain muscle mass?
Very often you can hear the opinion of creatine as a useless supplement that does not work at all. And not only in the gym, but also when used in boxing, weightlifting and rugby. But it is also often spoken of as a powerful assistant in achieving sports results. Some athletes use this sports supplement at those moments when progress in their indicators - strength, mass and other standards - stops!
Creatine comes in capsules, liquid and powder. Each of these forms is relevant in its own way.
- Liquid creatine is the most bioavailable form of creatine. It completely dissolves in water and, accordingly, begins to work faster than others.
- Creatine powder is convenient because it can be added to various sports nutrition products. For example, gainer, protein, pre-workout complex, amino acids and others. The disadvantage of this creatine is the preparation. To do this, the athlete needs to have a container in which the supplement must be mixed with water, a measuring spoon, and the product package itself. Of course, you can package creatine in portions, but it’s still inconvenient.
- Creatine capsules are the most convenient form. It is easy and quick to take regardless of conditions, even on public transport if necessary.
Creatine, its properties and benefits
The most important benefit of creatine is its ability to increase strength and performance during training . This benefit of creatine has been very well studied and the results only show the benefits of creatine as a supplement. By using creatine in combination with regular training, you can promote the growth of lean muscle mass . Creatine has also been tested in many studies for anaerobic athletic performance, with results showing improved performance. [3][4][5][6]
Creatine may theoretically affect cognitive performance . However, this fact has not been tested enough to fully confirm this property.
However, studies have shown a reduction in mental fatigue due to mental stress, sleep deprivation, or traumatic brain injury. At the same time, creatine may improve working memory , but probably only in people with very low creatine levels, such as vegetarians or older adults. [2]
Creatine has long been popular in the fitness community because it is an affordable and highly effective supplement . It is also suitable for beginners and professional athletes. However, there are different types of creatine available on the market, which can be confusing.
That's why we decided to present and explain them to you in the following lines.
Creatine and its types
Because creatine comes in several types, it can be difficult to choose the right type that will help you make your workouts more effective. Let's look at the most common types of creatine you may encounter when purchasing supplements.
Creatine monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is the most common type of creatine on the market. It is also the form that has been most scientifically researched and tested by experts in many studies. Essentially, this means that most of the scientific benefits of creatine are observed when consumed as the monohydrate.
Creatine monohydrate consists of a creatine molecule and a water molecule . However, various preparation methods are used in its production. If a water molecule is removed, it is creatine anhydrous . Removing water increases the amount of creatine in the product dose. Creatine anhydrous contains 100% creatine , while classic creatine monohydrate contains approximately 90% pure creatine. At the same time, the amount of creatine in the product affects the final cost of the dietary supplement.
Other types include micronized creatine or mechanically processed creatine, which has better water solubility . Theoretically, it is possible that better solubility of the product leads to faster absorption of the substance in the body , but this fact has not been sufficiently confirmed. [9]
Despite these slight differences in processing, each form of creatine monohydrate is likely to be equally effective at the same dose. Even 5-10g of creatine monohydrate can lead to increased performance, muscle endurance and muscle size. [10]
Creatine hydrochloride
Creatine hydrochloride (HCl) is convenient due to its good solubility in water . This form is the result of creatine binding to a hydrochloride molecule. One study confirmed that creatine hydrochloride is 38 times more soluble than creatine monohydrate. It is also believed that creatine HCl may be absorbed more efficiently into the body . This is why most supplements containing this type of creatine contain less than 1g of active ingredient per dose. This is a significantly smaller portion compared to creatine monohydrate, which is typically consumed in 5 gram doses. [10]
Unfortunately, there is not enough research to confirm this effect in humans. also a lack of research examining the differences in the effects of creatine HCl and creatine monohydrate. However, this does not mean that creatine HCl is not effective. Conversely, it is suitable for people who have stomach problems from creatine monohydrate. These side effects are much less common when consuming creatine hydrochloride . [11] [12]
Kre-Alkalyn – buffered creatine monohydrate
Kre-Alkalyn or buffered creatine monohydrate is a form of creatine that contains a slightly alkaline powder, such as bicarbonate. Manufacturers claim that its addition creates an alkaline compound that can reduce the breakdown of creatine in the stomach and improve its absorption into muscles . Kre-Alkalyn is sold alone or as a pre-workout stimulant.
Currently, only one study evaluates the effectiveness of this form of creatine. This is a study conducted in 2012 that showed similar performance improvements between different testing groups. The first group received 5 g of creatine monohydrate for 28 days , another group consumed an equivalent dose of Kre-Alkalyn, and the third group received a low dose of 1.5 g of Kre-Alkalyn daily. Groups receiving 5 gram doses began testing after a 7-day saturation phase using 5 grams of creatine 4 times daily. [13]
As a result, all groups significantly improved their muscle mass , body fat percentage, and strength in their legs and arms. Even the group that received lower doses and did not go through the saturation phase achieved comparable values . However, it is important to note that the subjects who took creatine monohydrate had an increased muscle creatine content of 50.4% after 28 days, while the group receiving Kre-Alkalyn only had an increase of 27.3%. [13]
This means that you will see the same results if you consume Kre-Alkaline and creatine monohydrate. However, when using Kre-Alkalyne, a lower dose seems to be sufficient and you do not need a saturation phase. [14]
Creatine magnesium chelate
Creatine magnesium chelate is another form of creatine that is produced by binding magnesium to the creatine molecule. Its properties were examined in one study in which experts compared bench press strength and performance among athletes divided into 3 groups. The first group received creatine monohydrate, the second group received magnesium chelate with creatine, and the third group received placebo. Both groups that consumed creatine improved their scores more than placebo. It follows that creatine magnesium chelate is effective , and no less effective than creatine monohydrate. [15]
Another study conducted in 2003 found that creatine magnesium chelate could improve performance without the addition of water , which is usually made with creatine. This would be especially helpful for athletes trying to maintain a low weight . In the meantime, however, we must treat this with caution because this fact has only been confirmed by one study and more in-depth research is needed. [16]
Creatine ethyl ester
Creatine ethyl ester is enriched with an organic component – ethyl ester. Some manufacturers claim that it is better absorbed and has a longer half-life than regular creatine monohydrate because it dissolves more easily in fat. Unlike the other types of creatine discussed in this article, ethyl ester is not a favorite . In different studies, the results of its effectiveness do not agree.
One study found that 7 weeks of consuming creatine ethyl ester resulted in a lower muscle-to-blood ratio of creatine than creatine monohydrate. In addition, its use may result in increased plasma creatinine Generally, creatinine is eliminated from the body as waste, but is not good for the kidneys, so the use of creatine ethyl ester is not recommended . [18]
Creatine citrate
It is produced by combining creatine with organic citric acid , which is found in citrus fruits and is often used as a natural flavoring in dietary supplements. However, a 2007 study by the International Society of Sports Nutrition found no significant difference in the absorption of creatine citrate compared to creatine monohydrate. However, creatine citrate is more soluble in water, but this is not a reason to believe that it is also more efficiently absorbed in the human body. [19]
Creatine malate
Creatine malate is bound to malic acid , another organic acid commonly found in fruits. Malic acid alone can improve endurance performance , which is why manufacturers have begun combining it with creatine. [10]
Creatine malate has been tested in several studies indicating that it improves anaerobic production in runners and judokas. However, no study has been conducted comparing creatine maleine monohydrate and placebo. Like creatine citrate, creatine malate is more easily soluble in water. [20]
Creatine nitrate
Creatine nitrate is one of the newer forms of creatine . Manufacturers claim that by binding a creatine molecule to a nitrate molecule, athletes will need a lower dose than creatine monohydrate. But let's look at the research results.
Research conducted in 2021 showed the effect of creatine nitrate on improving performance . However, the results did not confirm any significant differences between the groups of subjects receiving creatine nitrate, creatine monohydrate, or low-dose creatine nitrate. However, all of these groups achieved much better results than the placebo group. [17]
Creatine gluconate
This is creatine, which is bound by a glucose molecule . There is a theory that creatine gluconate is absorbed more efficiently because it is combined with carbohydrates enriched with insulin. However, no studies have yet been published to test this theory. [24]
Creatine pyruvate
Creatine pyruvate is produced by binding pyruvic acid and is a very interesting combination between the individual forms of creatine. However, research on its effectiveness is rather mixed. One study found that it had a better effect on endurance than creatine citrate (which is an effective form of creatine), but another study found that it did not improve endurance at all . [21] [22]
Some studies have also confirmed that, compared to creatine monohydrate, creatine pyruvate results in higher blood creatine levels . This may mean less creatine in the muscles, which is ultimately not effective. Therefore, this study concluded that creatine pyruvate is unlikely to be more bioavailable than creatine monohydrate. [23]
Creatine Alfacetoglutarate
It is also known as creatine AKG , which is made from alpha-ketoglutaric acid and creatine. Theories state that alpha-ketoglutarate, as a precursor to glutamine, is better absorbed in the intestine . It also serves to prevent stomach problems and diarrhea that plague some athletes when they consume creatine. In addition, users of AKG creatine claim that it is absorbed more efficiently and results in higher creatine concentrations in the muscles than monohydrate. However, there is currently not enough evidence from relevant research to support these theories. [10]
Multi-component creatine
Multi-component creatine combines several types of creatine in one product. It combines the benefits and properties of different types of creatine into one blend. For example, it can contain 7 types of creatine per product, such as our Crea7in. Physically active people and athletes will appreciate its benefits , such as faster absorption, muscle growth, more energy and better results. If you can't decide between different types of creatine, try multi-ingredient creatine.
The best creatine powder
When exposing your body to excessive physical activity, do not underestimate the importance of creatine. Taking dietary supplements with this component supplies muscle tissue with energy. We have selected only safe, quickly absorbed drugs for athletes, allowing them to withstand stress and increase training productivity. Let's start the review with 4 nominees in powder form.
Maxler 100% Golden Creatine
The first creatine for men is presented by the German-American sports nutrition brand Maxler. This is a dietary supplement based on highly purified creatine monohydrate.
The powder helps the athlete build muscle mass by enhancing anabolism, making it easier to recover after physical activity. The powdery 100% micronized form of the active component is characterized by a high rate of dissolution in water and absorption by tissues.
The product “Golden Creatine 100%” is available in 300 g cans with a measuring spoon. Purpose – increasing strength indicators. There are 2 powder options to choose from - with a neutral or watermelon flavor.
There are restrictions on the use of dietary supplements - these are disorders of water-salt metabolism, pregnancy, lactation, kidney disease, liver disease, gastrointestinal tract, as well as age under 18 years. The course is allowed along with protein, simple carbohydrates, amino acids.
Advantages:
- Easy dissolution;
- Fast absorption;
- Increased endurance, strength indicators;
- Pronounced effect;
- Nothing extra inside the composition;
- Price.
Flaws:
- Bitter taste;
- Fast consumption.
One serving is 5 g of powder, which contains 5000 mg of the active ingredient. This is the daily requirement, it can be swallowed with water, or taken as a solution. The optimal time is the post-training period or in the morning.
Ultimate Nutrition 100% Micronized Creatine Monohydrate
The following sports nutrition creatine is offered by the American brand “Ultimate Nutrition”. The powder structure of the active substance promotes rapid absorption by the digestive organs and entry into muscle fiber tissue. There are no additional ingredients here, just creatine.
An invigorating effect, a charge of energy is felt 15 minutes after taking the required dosage. The line includes 2 varieties of dietary supplements - a vacuum jar made of food-safe plastic “Creatine Monohydrate from Ultimate Nutrition” with a volume of 300 g, “Ultimate Nutrition Creatine Monohydrate” 1000 g.
Regular use guarantees not only an increase in anaerobic endurance, but also a gain of muscle mass, subject to parallel training. For better absorption, the manufacturer recommends combined use with carbohydrates. The resulting solution is tasteless.
Advantages:
- High bioavailability of micronized powder;
- Quick effect;
- Different jar volumes;
- A good boost to muscle growth;
- High quality;
- On sale everywhere.
Flaws:
- Tastelessness;
- Causes intense thirst.
If you don’t like drinking tasteless powder diluted with water, you can add it to a protein shake or gainers. Daily dosage – 5 g. In case of overdose, negative reactions from the digestive system may occur.
Be First Micronized Creatine Monohydrate Powder
The next creatine for weight gain is offered by the Russian brand “Be First”. Compared to classic dietary supplements, this one is characterized by smaller crystal size, improved solubility and rate of absorption by the gastrointestinal tract.
The active formula includes only one active ingredient - creatine monohydrate, designed to supply muscle cells with energy for their contraction. Increasing the reserves of this substance increases the energy potential of the muscles and endurance during intense training.
Creatine “creatine micronized” prevents the release of lactic acid, relieves inflammation of muscle tissue, and has a pronounced restorative effect. Support for the secretion of anabolic hormones - somatotropin, testosterone - was also noted.
Advantages:
- Safe effective formula;
- Compliance with international standards;
- Various flavors to choose from;
- Increase in strength indicators;
- Lowering cholesterol;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws:
- Dye, flavor;
- Fast consumption.
There are 2 can formats to choose from - unflavored with a substance dosage of 5500 mg, and with a taste of 5270 mg. You can take the powder in two ways - with a loading phase, 3-4 servings per day, without a loading phase, one serving per day.
Geneticlab Nutrition Creatine Powder
The latest dietary supplement in powder form from the Russian brand of special nutrition in sports is intended to reach a new level of training intensity.
One dosage of 5 g of powder contains the optimal amount of creatine monohydrate - the “fuel” resource of working muscles. The main advantage of this nominee is the price.
The effect develops gradually with regular use due to its cumulative properties. The active ingredient also neutralizes acids that occur during physical activity, which can reduce muscle fatigue.
The powder can be diluted with a protein shake, so its effectiveness will only increase. It has no smell or taste, which indicates the absence of flavoring. One can contains 300 g of product - this is approximately 60 servings.
Advantages:
- Efficiency;
- Reduced fatigue from training;
- Increase in body weight;
- Safe composition;
- Increased performance;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws:
- Diuretic effect;
- It feels bitter.
To take 200 ml of water, mix with 2 measuring spoons of 5 g of powder. Shake the solution well before use. The product has no contraindications other than pregnancy, lactation, and minors.
Creatine, its safety, method of application and dosage
Most of the myths that are spread about creatine are untrue . However, creatine has had a reputation for years since it was banned in many countries as a carcinogen. However, since 2004, creatine has been approved in all countries, and it is not on the list of dangerous additives. However, even today, some people mistake it for a dangerous substance that harms the kidneys. However, none of this is true, and many studies have confirmed this . Other than minor digestive problems caused by excessive creatine consumption, there are no other risks of consumption. [7] [8]
The correct use of creatine is 5 g per day . Higher doses of creatine (up to 10 g per day) may be beneficial for people with large muscle mass and high levels of athletic activity. Athletes are recommended to use creatine before and after exercise . On non-training , you can take it at any time of the day . Remember that creatine does not work when used short term. It must be consumed correctly and regularly. [12]
If you take creatine without enough water , you may experience stomach cramps. Diarrhea and nausea occur if you consume too much creatine. In this case, reduce the dose and spread it throughout the day , and take creatine with food and liquids .