Food, like clothing, has its own fashion trends. In the modern world, food trends change like gloves: white rice is replaced by brown rice; spaghetti - in no case made from flour, but from zucchini; no refined sugar - just muscovado. In the wake of all these trends, it was recently announced that yeast-free bread is a dietary and healthy alternative to yeast bread. The latter was presented in such an unsuitable light that all that remained was to exclude it from the daily diet, and when losing weight, not even think about it at all.
How true are these statements? Should we believe them and give up the fluffy loaf and soft loaf forever?
How to prepare
The name of the product speaks for itself: bread without yeast is made from flour and sourdough. It happens like this:
- in bunker dough-preparing units or batch dough mixing machines, sourdough is prepared from flour, water and bacteria (this is a multi-stage and multi-day process);
- the dough is kneaded in a special mechanism;
- the kneading process is carried out long and carefully so that the dough is saturated with air and is more fluffy;
- then it goes astray;
- unloaded into forms;
- goes to proof for a couple of hours (at 40°C and 85% humidity);
- usually baked at 230-250°C for half an hour to an hour (depending on the production technology used by a particular bakery plant).
The following ingredients can be used for production:
- leaven;
- flour (peeled rye, wheat, whole grain);
- seeds and nuts as flavoring additives;
- bran;
- salt, sugar (administered in the form of solutions);
- sunflower oil;
- dry wheat gluten;
- water.
However, each manufacturer has its own secret recipe. The following is used as a natural starter:
- whey;
- saccharified infusion of the carbohydrate-protein fraction of amaranth with hop cones;
- fruit purees;
- citric acid;
- a mixture of peeled rye flour, sugar, honey and water;
- hop mixture - a wort made from flour and malt.
The chemical composition of yeast-free bread is represented by such useful substances as:
- potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, manganese, copper, selenium, sodium;
- vitamins B1, B2, B9, PP;
- cellulose;
- mono- and disaccharides (digestible carbohydrates);
- glutamic acid (amino acid);
- Omega-9 fatty acids (oleic).
The lower the grade of flour, the richer and healthier its composition.
Step by step recipe
Consider the option of making unleavened bread using industrial sourdough (which is sold in stores).
Ingredients:
- 3 tbsp. l. sourdough;
- 350 ml water;
- 330 grams of rye flour;
- 1 tbsp. l. honey;
- 1 tbsp. l. dry kvass or honey;
- 1 tbsp. l. vegetable oil;
- 1 tsp. ground coriander;
- 1 tbsp. l. wheat or rye bran;
- 2 tsp. flax seeds;
- 1 tsp. salt.
Preparation:
- Get the starter out of the refrigerator in advance. Allow to warm to room temperature.
- Place the starter in a glass jar (500 ml), add 50 grams of flour and 70-75 ml of water, mix well.
- Cover the jar with a towel. Leave the starter for 3-4 hours at room temperature. During this time, its volume should increase 3-5 times.
- Select 100-120 grams of starter and put the rest in the refrigerator for the next culinary masterpiece.
- Add water (100 ml) and 50 grams of sifted rye flour to the starter. Mix thoroughly until lumps disappear. A glass jar is suitable for mixing the components of the dough.
- Leave the dough at room temperature for 3-4 hours, cover the jar with a towel.
- Brew malt with 50 ml of boiling water, let cool. Add honey and stir until completely dissolved.
- Add malt and honey to the dough. Mix well.
- Mix all ingredients, mix thoroughly. The flour must be sifted first. The dough can be kneaded by hand or with a wooden spoon.
- Prepare the mold - grease with vegetable oil. Pour out the dough and smooth the top with a damp brush or your hands. Cover the mold with a towel and leave for a couple of hours (to rise). The bread will be ready to bake when bubbles begin to appear on the surface.
- Sprinkle the surface of the bread with water and place in the oven for 15 minutes at 210°C. A container of water is placed on the lower level.
- Remove the container with water and bake the bread for another 15-20 minutes at 190°C.
- Then cover the bread with foil (to prevent a hard crust) and cook for another 20 minutes at 190°C.
- Let cool in the oven. The dish is ready.
Bread can also be prepared in a bread machine (according to the established cooking programs). The resulting product is not only soft and tasty, but also healthy.
You can make yeast-free bread with your own hands. The main thing is to follow all the cooking technology.
What is the difference between yeast-free bread and yeast bread?
Firstly, its effect on the body. It is believed that yeast-free bread is healthier because, unlike yeast bread, it does not disturb the intestinal microflora, is better absorbed and can be used in dietary nutrition, since it is lower in calories.
Secondly, properties. Yeast-free, for example, is stored longer and does not go stale, retaining maximum useful qualities. But yeast is more fluffy, softer and tastier.
Thirdly, the composition. It is believed that yeast-free food is richer in fiber and vitamins, since they are not spent on feeding yeast, which, as we know, are living organisms.
Recommendations
- Yeast-free bread is stored much longer than usual - the product can be eaten for even two weeks .
- When purchasing a bread product, make sure that it does not contain harmful food additives, preservatives, flavorings or chemicals. A good product should not contain soy.
- If you want to get as much benefit from the product as possible, choose bread with natural additives, such as seeds, bran or grains. This product is rich in vitamins and is very beneficial for the body.
Myths and truth
Until recently, the question of which bread is healthier: yeast-free or yeast-free bread did not raise any doubts. And even now most people will choose the first option. This point of view has been discussed and explained in detail above. However, recently more and more experts have disputed this point and claim that this was nothing more than a marketing ploy by the manufacturers. They provide quite compelling arguments as evidence.
Argument 1: sourdough also promotes fermentation
Compressed yeast is used to produce regular bread. They are created specifically to speed up the baking process, as they contribute to the rapid “ripening” of the dough. Having discovered the harmful properties of fermentation (allegedly it disrupts the intestinal microflora and impairs digestion), manufacturers hastened to announce this to consumers and began to produce yeast-free products based on sourdough. But the latter is a semi-finished bakery product obtained by fermenting a carbohydrate mixture (flour, water, sugar and honey) with lactic acid bacteria. That is, the fermentation process still occurs, which means that yeast fungi are also present there.
So when asked whether there is yeast-free bread, baking industry technologists will answer unequivocally: no! But there is such a dough. Everyone is familiar with its types: pancake, puff pastry and soda. However, the first one is intended for frying, which means it no longer fits into either proper or dietary nutrition. The second is prepared on the basis of oil, which gives it a high calorie content. Soda products often provoke heartburn and unpleasant belching, and also have many contraindications.
Argument 2: yeast is all around us
If you think that by refusing yeast dough, you have completely protected yourself from the harmful effects of this product, you are deeply mistaken. Yeast is present in the air, on the surface of fruits and vegetables, and one way or another they still end up in the digestive tract. In addition, everyone’s favorite drinks are prepared on their basis: kvass, wine, beer.
Argument 3: there is no yeast in the finished product
Any baked product is baked at high temperatures, at which living yeast fungi die, and in this state they cannot in any way affect the intestinal microflora.
Argument 4: there is no more fiber in yeast-free bread than in yeast bread
This is evidenced by recent research. The amount of fiber in a baked product depends on how much bran and grains it contains, but this has nothing to do with yeast microorganisms.
All these points become stumbling blocks for disputes. Manufacturers say one thing, scientists say another. There is no consensus and large-scale studies with conclusions, so you can only rely on such assumptions. But in any case, it’s strange to hear that yeast is so harmful to the body, because it is even sold in the form of a pharmaceutical preparation as a source of B vitamins. Moreover, they differ from their bakery counterparts only in the form of release and additional additives, but not in properties.
Which one can you eat?
As already mentioned, bread is baked from various cereals. Each type has its own distinctive characteristics. For example, pure wheat, made from premium flour, contains a lower concentration of nutrients than whole grain.
What bread is best to eat when losing weight? The following types are recommended:
- Yeast-free from various types of flour.
- Protein with the addition of eggs, cottage cheese, seeds and nuts. It is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Whole grain with a low glycemic index.
- Bread made from wholemeal flour, containing fiber necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Now on store shelves you can find a wide variety of breads: with the addition of bran, wheat germ, cereals, and nuts. Every person will be able to find the most delicious and healthy baked goods for themselves.
What you should pay attention to first of all is the calorie content, as well as the content of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. After all, to lose weight you need to count every day and maintain a deficit.
Black or white
A common dilemma for those losing weight: which bread to choose - black or white? Let's compare them.
| White | Black | |
| Calorie content | 260 | 202 |
| Nutrient content | essential amino acids; carbohydrates: gluten, starch; vitamins of groups B and E; micro-, macroelements, especially magnesium, phosphorus. | essential amino acids; carbohydrates: gluten, starch; vitamins of groups B and E; micro-, macroelements, especially magnesium, phosphorus; fiber, whole fibers. |
| Benefit | It supplies the body with energy, improves blood circulation, and strengthens the cardiovascular system. | Due to the large number of whole fibers, it improves peristalsis and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, it helps improve blood circulation and reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol. |
| Harm | Due to the small amount of whole fibers, it can negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. For the same reason, it gives a feeling of fullness for a short time. | Due to the large amount of fiber, black bread can cause gas formation and flatulence. Compared to wheat, it is absorbed worse. |
A completely healthy person can eat any type of bread, but in moderation. In all other cases, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Rye
Rye bread is made from a sourdough starter made from coarse rye flour. It contains a sufficiently large amount of nutrients, vitamins and minerals that benefit the body:
- is a source of fiber;
- gives a long-lasting feeling of fullness;
- normalizes hemoglobin levels, recommended for anemia;
- helps eliminate constipation;
- improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Rye bread goes well with lean meats, lettuce, mushrooms, and cheese. A good breakfast option is homemade ham and a slice of rye.
Borodinsky
Borodino bread is made from several types of flour, water, salt and yeast. Like other varieties, it is rich in vitamins, minerals and nutritional components that the body needs to function properly. Just like the previous option, it helps improve peristalsis and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Borodino bread can also be eaten for breakfast with cottage cheese, cheese, fermented milk products and lean meats. The main thing is to strictly maintain the serving size. Experts recommend eating no more than 30-50 grams daily. This is one small slice.
Yeast-free
Experts agree that bread that does not contain yeast is better absorbed by the body. It does not cause fermentation processes in the intestines, as a result, the likelihood of bloating, flatulence and other unpleasant symptoms after eating is reduced. But it also contains essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
It is worth noting that this variety contains fewer calories - only 177 per 100 grams. This is a huge plus for those losing weight who keep daily count.
With bran
Bran bread is also considered beneficial due to its dietary fiber content. They are not digested in the stomach and swell, providing a feeling of fullness for a long time.
Bran bread is usually made without adding yeast. Therefore, for those losing weight, this is a doubly good option. A person receives a sufficient amount of nutrients with a relatively low calorie content.
With buckwheat flour
Buckwheat bread is suitable for people who are gluten intolerant. It is prepared from ground buckwheat, sourdough and water. Dried fruits, nuts and honey are often added to it - this makes it tastier and more satisfying.
It is also allowed for use by children, since it is hypoallergenic, does not cause bloating or flatulence, and is easily digested by the body.
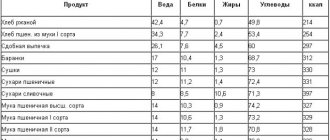
Calorie content
The calorie content of bread varies depending on the type. Here is an exact list with values per 100 grams in the table:
| Variety | Kcal | Squirrels | Fats | Carbohydrates |
| White | 260 | 8,2 | 2,1 | 50,3 |
| Gray or custard | 262 | 9,4 | 2,8 | 49,3 |
| Black "Borodinsky" | 202 | 6,9 | 1,3 | 40,9 |
| Rye | 250 | 13,0 | 3,0 | 40,0 |
| With bran | 227 | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 |
| With flaxseed | ||||
| With nuts and seeds | 302 | 10,5 | 10,1 | 43,3 |
| Corn | 266 | 6,7 | 7,1 | 43,5 |
| Rice | 310 | 6,0 | 1,3 | 69,0 |
| Pita | 277 | 9,1 | 1,1 | 56,8 |
As you can see, it is difficult to identify low-calorie bread; all values are approximately the same. Therefore, you can choose any bread, but try to give preference to healthy types, rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Benefits and harms
Why is it useful?
It is believed that the main benefit of yeast-free bread is to normalize digestion, due to the increased fiber content, which:
- cleanses the intestines and removes harmful substances and stagnant masses from it;
- stimulates peristalsis, which improves the absorption of the rest of the food several times;
- relieves intestinal disorders (flatulence, bloating).
Due to the fact that the body begins to absorb vitamins and microelements in full, the immune system is strengthened and the risk of developing infectious diseases is reduced.
Yeast-free bread also exhibits its beneficial properties in cases where there are contraindications to yeast bread. For example, with gastritis, ulcers and other serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, yeast causes heartburn. If you abuse it while breastfeeding, the baby will suffer from colic, bloating, and may develop diarrhea. But a yeast-free product will not cause such side effects if consumed in moderation.
It also turns out to be useful for diabetics, since it has a low glycemic index compared to other types of bakery products. For these people, almost all types of bread are prohibited, which has an extremely adverse effect on the body, which requires fiber. In this case, you can use this alternative. But do not forget that it is still a carbohydrate, so it is not recommended to get carried away with it. It would be better to consult a doctor about its use.
Why is it harmful?
Nuts and various seeds in unleavened bread can damage the thin walls of the intestines. Therefore, it is better to purchase it without such “surprises”. It can also worsen the condition with exacerbation of pancreatitis and gastric diseases (the same gastritis and ulcers mentioned above). Often, due to its too dense consistency, it scratches the throat, so doctors do not recommend eating it if you have a sore throat or problems with the vocal cords.
Harm and contraindications
Yeast-free bread is a safe product. However, in isolated situations, it can cause harm to health.
Side effects include:
- Dyspeptic disorders. The product activates the processes of putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines (if taken in excess), which leads to bloating, increased gas formation, and diarrhea.
- Infections. During the fermentation process, fungi of the genus Candida and some harmful bacteria can actively multiply in the sourdough. With impaired immunity, they can cause infections of the upper respiratory tract and digestive system.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. When eating unleavened bread on an empty stomach or in large quantities in its pure form, an exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer) is possible.
Homemade unleavened bread is not recommended for women during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is better to give preference to industrial options, since the starter culture at enterprises undergoes sanitary control.
Occasionally, such bread can cause harm to health. Most side effects are related to overeating.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
- has a natural composition: does not contain synthesized ingredients, dyes, preservatives, flavors;
- good for health;
- fits into dietary menus;
- easy to digest;
- long shelf life;
- recommended for baby food.
Minuses:
- unusual taste with sourness;
- there is no usual bread aroma;
- dense consistency, no fluffiness;
- damages gums due to dryness;
- not suitable for those who have dental problems;
- costs more than usual;
- It is difficult and time-consuming to cook at home.
Chemical composition and general benefits of yeast-free bread
The main advantage of such a product is the absence of yeast and negative effects on the digestive organs. It contains food cellulose in high concentration, which has a positive effect on the process of food digestion.
Composition and calorie content
The composition of baked goods without yeast includes components that provide beneficial qualities to the product.
Basic benefit of the product
The vitamin-mineral complex is represented by the following components:
- phosphorus (participates in protein synthesis);
- potassium (stimulates the work of the myocardium and brain);
- magnesium (promotes resistance of the nervous system to stress);
- iron (increases hemoglobin synthesis);
- zinc (promotes testosterone synthesis);
- calcium (part of bone tissue);
- fluoride (preserves the integrity of tooth enamel).
The vitamin complex is represented by vitamins A, E, and group B. Group B vitamins are not destroyed at high baking temperatures and are preserved in full. They affect metabolism, correct metabolic processes in the body, normalize hormonal levels and participate in the synthesis of hormones such as insulin and cortisol, testosterone and estrogen.
The benefits of yeast-free bread
Also, with the help of nicotinic acid, the cholesterol index in the blood is corrected, and with the help of folic acid, the production of hemoglobin increases. The calorie content of this baked goods is significantly lower than that of regular yeast baked goods. 100 g contains approximately 177 kcal. Protein compounds – 5.77 g, carbohydrates – 37.54 g, and fat – 0.51 g.
Beneficial features
The main benefit of baked goods made with natural leaven is the absence of baker's yeast.
Such baked goods have long been used for the prevention and treatment of pathologies of the digestive system.
Useful qualities of yeast-free baking:
- Easily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. After lunch, there is no feeling of heaviness in the stomach and no unpleasant symptoms in the intestines.
- Improves the functioning of all digestive organs due to the high content of coarse dietary fiber in the product. The dense crumb increases intestinal activity.
- The necessary balance of intestinal microflora is restored and the development of pathogenic microorganisms is prevented.
- Naturally leavened bread prevents the development of gas formation, bloating and flatulence. Bread with yeast promotes the accumulation of yeast bacteria in the intestinal sections, which lead to fermentation inside the organ and provoke an increased content of carbon dioxide in the intestinal sections, which causes the development of flatulence.
- Low sugar content. Regular bread contains a large amount of sugar to keep the yeast active, but baked goods without yeast contain virtually no sugar.
- These pastries can be prepared at home. You can add bran, seeds, spices, and dried fruits to it. And every time the bread will have a unique taste.
What does yeast-free bread provide?
Flaws
Yeast-free baked goods, despite their beneficial qualities, are still inferior to yeast baked goods in some respects. For example:
- Smaller product volume – with the same weight, the volume of a yeast loaf is almost twice as large as a yeast-free loaf. The buyer automatically chooses the product that seems larger to him.
- Absolutely different taste of baked goods. We are all accustomed to the aroma and taste of yeast baked goods, so not every person will like the taste of the new product.
- Hardness of bread. People who have problems with teeth and gums should avoid this product. But bread is not always hard and dense; there are quite soft varieties made with sourdough.
- Complex manufacturing technology that requires more time and production processes. First of all, you need to prepare the sourdough, and dough with sourdough takes much longer to prepare than with yeast. The production process of yeast dough is simple: yeast and baking powder are added to the flour and the bread is ready within an hour.
See also:
Rice flour - benefits and harms, what can be prepared