This table of calories and content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and water contains the most complete number of products. The nutritional value and nutritional value of all products is indicated per 100 grams of product. But let me remind you that it is best to look at the energy value of products on their packaging; use the table only if it is not possible to find out the calorie content from the product packaging. Knowing the calorie content of foods is necessary in order to correctly count calories for weight loss (you can read about this in our article How to correctly count calories to lose weight).
Caloric content of products is given in raw form, unless otherwise noted. For example, you need to take into account that if buckwheat in its raw form has a calorie content of 329 kcal, then when cooked, the calorie content will decrease. For example, if you add 300 grams of water to 100 grams of cereal, the calorie content of the finished dish will be only 82 kcal.
To quickly search for a product in the table, press CTRL + F at the same time, and in the search window that appears, enter the product name.
Milk and dairy products
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Brynza | 52,0 | 17,9 | 20,1 | 0,0 | 260 |
| Yogurt 1.5% fat | 88,0 | 5,0 | 1,5 | 3,5 | 51 |
| Kefir 0% fat | 91,4 | 3,0 | 0,1 | 3,8 | 30 |
| Kefir 3.2% fat content | 88,3 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,1 | 59 |
| Milk 3.2% fat | 88,5 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,7 | 58 |
| Whole milk powder | 4,0 | 25,6 | 25,0 | 39,4 | 475 |
| Condensed milk with sugar | 26,5 | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 315 |
| Curdled milk | 88,4 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,1 | 58 |
| Ryazhenka | 85,3 | 3,0 | 6,0 | 4,1 | 85 |
| Cream 10% | 82,2 | 3,0 | 10,0 | 4,0 | 118 |
| Cream 20% | 72,9 | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,6 | 205 |
| Sour cream 10% | 82,7 | 3,0 | 10,0 | 2,9 | 116 |
| Sour cream 20% | 72,7 | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| Special cheeses and curd mass | 41,0 | 7,1 | 23,0 | 27,5 | 340 |
| Russian cheese | 40,0 | 23,4 | 30,0 | 0,0 | 371 |
| Dutch cheese | 38,8 | 26,8 | 27,3 | 0,0 | 361 |
| Swiss cheese | 36,4 | 24,9 | 31,8 | 0,0 | 396 |
| Poshekhonsky cheese | 41,0 | 26,0 | 26,5 | 0,0 | 334 |
| Processed cheese | 55,0 | 24,0 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 226 |
| Fat cottage cheese | 64,7 | 14,0 | 18,0 | 1,3 | 226 |
| Cottage cheese 9% fat | 71,0 | 16,7 | 9,0 | 1,3 | 156 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 77,7 | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,5 | 86 |
The role of protein in weight loss
When losing weight, it is important to follow a complete protein diet:
- The digestion of protein requires more energy expenditure than the digestion of carbohydrates and fats.
- Internal (endogenous) nutrition with protein deficiency occurs to a greater extent due to muscle tissue.
Protein for weight loss:
- regulates blood glucose levels, protects against sudden spikes in insulin;
- helps to gain a feeling of satiety, reduces appetite;
- accelerates metabolism, increases metabolism;
- supports muscle mass.
When losing weight, proteins of animal and plant origin should be consumed in approximately equal proportions; animals can even make up up to 60–70%; they are better absorbed and reduce appetite.
Meat should be of dietary grades:
- lean beef;
- chicken breasts;
- rabbit meat.
If possible, the diet should be supplemented with seafood. In addition to protein, they contain vitamins, trace elements and minerals.
Seafood for weight loss:
- squid meat;
- shrimp and crabs;
- tuna fillet.
Plant foods contain fiber, vitamins and promote better protein absorption.
Plant-based protein products for weight loss:
- legumes and nuts;
- buckwheat, oats;
- broccoli, spinach;
- avocado, peach;
- dried fruits;
Low-fat lactic fermentation products will complement the protein part of the diet:
- kefir (0–1%);
- dry cottage cheese;
- hard cheeses;
- sour cream (10%).
The essence of a healthy diet is the variety and nutritional value of food. The protein intake rates in the tables are recommended. A nutritionist will help you create a more accurate list of products.
Article design: Anna Vinnitskaya
Bakery products, flour
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Rye bread | 42,4 | 4,7 | 0,7 | 49,8 | 214 |
| Wheat bread from grade I flour | 34,3 | 7,7 | 2,4 | 53,4 | 254 |
| Butter pastries | 26,1 | 7,6 | 4,5 | 60,0 | 297 |
| Baranki | 17,0 | 10,4 | 1,3 | 68,7 | 312 |
| Drying | 12,0 | 11,0 | 1,3 | 73,0 | 330 |
| Wheat crackers | 12,0 | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,4 | 331 |
| Cream crackers | 8,0 | 8,5 | 10,6 | 71,3 | 397 |
| Premium wheat flour | 14,0 | 10,3 | 0,9 | 74,2 | 327 |
| Wheat flour, grade I | 14,0 | 10,6 | 1,3 | 73,2 | 329 |
| Wheat flour, grade II | 14,0 | 11,7 | 1,8 | 70,8 | 328 |
| Rye flour | 14,0 | 6,9 | 1,1 | 76,9 | 326 |
Cereals
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Buckwheat core | 14,0 | 12,6 | 2,6 | 68,0 | 329 |
| Buckwheat done | 14,0 | 9,5 | 1,9 | 72,2 | 326 |
| Manna | 14,0 | 11,3 | 0,7 | 73,3 | 326 |
| Oatmeal | 12,0 | 11,9 | 5,8 | 65,4 | 345 |
| Pearl barley | 14,0 | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 324 |
| Millet | 14,0 | 12,0 | 2,9 | 69,3 | 334 |
| Rice | 14,0 | 7,0 | 0,6 | 73,7 | 323 |
| Wheat “Poltavskaya” | 14,0 | 12,7 | 1,1 | 70,6 | 325 |
| Oatmeal | 10,0 | 12,2 | 5,8 | 68,3 | 357 |
| Barley | 14,0 | 10,4 | 1,3 | 71,7 | 322 |
| Hercules | 12,0 | 13,1 | 6,2 | 65,7 | 355 |
| Corn | 14,0 | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 325 |
Vegetables
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Eggplant | 91,0 | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,5 | 24 |
| Swede | 87,5 | 1,2 | 0,1 | 8,1 | 37 |
| Green peas | 80,0 | 5,0 | 0,2 | 13,3 | 72 |
| Zucchini | 93,0 | 0,6 | 0,3 | 5,7 | 27 |
| White cabbage | 90,0 | 1,8 | – | 5,4 | 28 |
| Red cabbage | 90,0 | 1,8 | – | 6,1 | 31 |
| Cauliflower | 90,9 | 2,5 | – | 4,9 | 29 |
| Potato | 76,0 | 2,0 | 0,1 | 19,7 | 83 |
| Green onion (feather) | 92,5 | 1,3 | – | 4,3 | 22 |
| Leek | 87,0 | 3,0 | – | 7,3 | 40 |
| Bulb onions | 86,0 | 1,7 | – | 9,5 | 43 |
| Red carrots | 88,5 | 1,3 | 0,1 | 7,0 | 33 |
| Ground cucumbers | 95,0 | 0,8 | – | 3,0 | 15 |
| Greenhouse cucumbers | 96,5 | 0,7 | – | 1,8 | 10 |
| Sweet green pepper | 92,0 | 1,3 | – | 4,7 | 23 |
| Sweet red pepper | 91,0 | 1,3 | – | 5,7 | 27 |
| Parsley (greens) | 85,0 | 3,7 | – | 8,1 | 45 |
| Parsley (root) | 85,0 | 1,5 | – | 11,0 | 47 |
| Rhubarb (petiole) | 94,5 | 0,7 | – | 2,9 | 16 |
| Radish | 93,0 | 1,2 | – | 4,1 | 20 |
| Radish | 88,6 | 1,9 | – | 7,0 | 34 |
| Turnip | 90,5 | 1,5 | – | 5,9 | 28 |
| Salad | 95,0 | 1,5 | – | 2,2 | 14 |
| Beet | 86,5 | 1,7 | – | 10,8 | 48 |
| Tomatoes (ground) | 93,5 | 0,6 | – | 4,2 | 19 |
| Tomatoes (greenhouse) | 94,6 | 0,6 | – | 2,9 | 14 |
| Green beans (pod) | 90,0 | 4,0 | – | 4,3 | 32 |
| Horseradish | 77,0 | 2,5 | – | 16,3 | 71 |
| Cheremsha | 89,0 | 2,4 | – | 6,5 | 34 |
| Garlic | 70,0 | 6,5 | – | 21,2 | 106 |
| Spinach | 91,2 | 2,9 | – | 2,3 | 21 |
| Sorrel | 90,0 | 1,5 | – | 5,3 | 28 |
Recipes and calorie content of popular dishes with turkey meat
Skinless white meat is an excellent food source for people following any low-fat or salt-free diet
. Protein is filling and also slows down digestion, thereby making you feel full long after eating. Turkey is easier for the body to digest than other types of meat, making it a good choice for people who have digestive problems.
In addition, the same protein is involved in building and maintaining muscle mass. Therefore, bodybuilders and simply those who decide to improve their body often use turkey in their diet.
Pasta with turkey and broccoli
- 300 g pasta;
- 2 cups of inflorescences;
- 3 tbsp. l. ;
- 400 g minced turkey;
- 2 cloves;
- 1 tsp. seeds;
- 1/2 tsp. ground red pepper;
- kosher salt.
Cook the pasta and add the broccoli at the last minute. Drain the water and return the pasta and broccoli to the pan. Meanwhile, heat the oil. Add the turkey, fennel seeds, garlic and red pepper and cook until the stuffing is browned and season with salt. Stir turkey mixture into pasta and broccoli. Serve with Parmesan.
Calorie content – 143 kcal/100 g.
Turkey Fried Rice
- 3/4 cup brown;
- 2 tbsp. l. canola oils;
- 200 g minced turkey;
- 1 tbsp. l. chopped garlic;
- 1 tbsp. l. chopped;
- 4 green feathers;
- 1 cup peas;
- 1/4 ;
- 2 tbsp. l. rice vinegar.
Cook the rice. Heat oil in a large frying pan. Add the turkey, garlic, ginger and half the green onions and cook, breaking up the meat with a spoon, until browned, 3 to 5 minutes. Add rice, peas, carrots, vinegar and stir for 2-3 minutes.
Calorie content – 152 kcal/100 g.
Turkey and taco salad
- 1 tbsp. l. olive oil;
- 400 g minced turkey;
- kosher salt and pepper;
- 20 g salsa sauce;
- 2 tbsp. l. sour cream;
- 1 head of Romaine lettuce;
- 1 bag of corn chips;
- 50 g from a jar;
- 1, cut into cubes;
- 1 cup shredded Cheddar cheese.
Heat the oil. Add turkey, salt and pepper. Cook, breaking up the meat with a spoon for 5-6 minutes. Drain off excess liquid. Stir in ½ salsa. In a small bowl, combine sour cream and remaining salsa. Tear the lettuce leaves, break the chips a little and mix with the beans, avocado, minced meat and cheese in a bowl. Serve with dressing.
Calorie content – 180 kcal/100 g.
Turkey cutlets
- 500 g minced white meat;
- 1 onion;
- 150 ml;
- 1/4 white;
Soak white bread in water. Mix minced meat, egg, finely chopped onion and salt. Mix all ingredients, form small cutlets and fry on both sides.
Calorie content - 89.57 kcal/100 g.
Light Turkey Soup
- 500 g turkey;
- 1/2 medium head of cabbage;
- carrot;
- bulb;
- peas.
Cut turkey and potatoes into cubes. Cut the cabbage into strips. Place carrots, onions, and turkey into boiling water. After 20 minutes, add potatoes and peas. Cover with a lid and cook for about 10 minutes more. Add the cabbage, cover again and turn off the gas.
Calorie content – 57 kcal/100 g.
Fruits and berries
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Apricots | 86,0 | 0,9 | – | 10,5 | 46 |
| Quince | 87,5 | 0,6 | – | 8,9 | 38 |
| Cherry plum | 89,0 | 0,2 | – | 7,4 | 34 |
| A pineapple | 86,0 | 0,4 | – | 11,8 | 48 |
| Bananas | 74,0 | 1,5 | – | 22,4 | 91 |
| Cherry | 85,5 | 0,8 | – | 11,3 | 49 |
| Pomegranate | 85,0 | 0,9 | – | 11,8 | 52 |
| Pear | 87,5 | 0,4 | – | 10,7 | 42 |
| Figs | 83,0 | 0,7 | – | 13,9 | 56 |
| Dogwood | 85,0 | 1,0 | – | 9,7 | 45 |
| Peaches | 86,5 | 0,9 | – | 10,4 | 44 |
| Rowan garden | 81,0 | 1,4 | – | 12,5 | 58 |
| Rowan chokeberry | 80,5 | 1,5 | – | 12,0 | 54 |
| Garden plum | 87,0 | 0,8 | – | 9,9 | 43 |
| Dates | 20,0 | 2,5 | – | 72,1 | 281 |
| Persimmon | 81,5 | 0,5 | – | 15,9 | 62 |
| Cherries | 85,0 | 1,1 | – | 12,3 | 52 |
| Mulberry | 82,7 | 0,7 | – | 12,7 | 53 |
| Apples | 86,5 | 0,4 | – | 11,3 | 46 |
| Orange | 87,5 | 0,9 | – | 8,4 | 38 |
| Grapefruit | 89,0 | 0,9 | – | 7,3 | 35 |
| Lemon | 87,7 | 0,9 | – | 3,6 | 31 |
| Mandarin | 88,5 | 0,8 | – | 8,6 | 38 |
| Cowberry | 87,0 | 0,7 | – | 8,6 | 40 |
| Grape | 80,2 | 0,4 | – | 17,5 | 69 |
| Blueberry | 88,2 | 1,0 | – | 7,7 | 37 |
| Blackberry | 88,0 | 2,0 | – | 5,3 | 33 |
| Strawberries | 84,5 | 1,8 | – | 8,1 | 41 |
| Cranberry | 89,5 | 0,5 | – | 4,8 | 28 |
| Gooseberry | 85,0 | 0,7 | – | 9,9 | 44 |
| Raspberries | 87,0 | 0,8 | – | 9,0 | 41 |
| Cloudberry | 83,3 | 0,8 | – | 6,8 | 31 |
| Sea buckthorn | 75,0 | 0,9 | – | 5,5 | 30 |
| White currant | 86,0 | 0,3 | – | 8,7 | 39 |
| Red currants | 85,4 | 0,6 | – | 8,0 | 38 |
| Black currant | 85,0 | 1,0 | – | 8,0 | 40 |
| Blueberry | 86,5 | 1,1 | – | 8,6 | 40 |
| Fresh rosehip | 66,0 | 1,6 | – | 24,0 | 101 |
| Dried rose hips | 14,0 | 4,0 | – | 60,0 | 253 |
Daily protein intake
Since the body is not able to independently synthesize some of the amino acids that make up protein, a person needs to get it from food. There are generally accepted protein intake standards for adults and children.
For children
The daily intake of foods containing large amounts of protein for children is several times higher than for an adult. This is due to the fact that the body is in a process of constant growth and continuous change.
The table below shows daily values by age:
| Age | Protein intake rate g/day |
| 0-3 months | 10,5 |
| 3-6 months | 17,2 |
| 6-12 months | 29,5 |
| 1-1.5 years | 48 |
| 1.5-2 years | 53 |
| 2-4 years | 63 |
| 4-6 years | 72 |
| 6-10 years | 80 |
| 10-13 years | 96 |
| 13-17 years old (boys) | 106 |
| 13-17 years old (girls) | 93 |
To understand how much protein a particular child needs, you can use the values below:
- Children aged 1 to 3 years need 4 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight.
- From 3 to 7 years - 3.5 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight.
- From 7 to 10 years - 3 g of protein per 1 kg.
- Children over 10 years old need 2.5 g of protein per 1 kg of weight.
For adults
Average daily intakes for adults are:
- 120 g for men;
- 90 g for women.
For more accurate data, you can take into account the following standards, depending on lifestyle:
- A sedentary lifestyle requires 1.2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight.
- Active lifestyle - 1.6 g of protein per 1 kg.
- With regular physical activity, you need to consume 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight.
During pregnancy, the body's need for protein increases sharply. It becomes necessary not only for the mother, but also for the continuously developing fetus. 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight is the required amount of protein for a pregnant woman, which is maintained during the period of breastfeeding, since some of the substances absorbed by the mother are transferred to the baby with breast milk.
Dried fruits
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Dried apricots | 18,0 | 5,0 | – | 67,5 | 278 |
| Dried apricots | 20,2 | 5,2 | – | 65,9 | 272 |
| Raisins with pit | 19,0 | 1,8 | – | 70,9 | 276 |
| Raisins sultanas | 18,0 | 2,3 | – | 71,2 | 279 |
| Cherry | 18,0 | 1,5 | – | 73,0 | 292 |
| Pear | 24,0 | 2,3 | – | 62,1 | 246 |
| Peaches | 18,0 | 3,0 | – | 68,5 | 275 |
| Prunes | 25,0 | 2,3 | – | 65,6 | 264 |
| Apples | 20,0 | 3,2 | – | 68,0 | 273 |
What is contained in cottage cheese
To answer this question you need to thoroughly understand the product. It is obtained from sour milk. During heat treatment, the curdled milk is divided into whey and white curd mass - this is what needs to be collected and squeezed out. It has a pleasant delicate consistency and excellent taste with a slight sourness.
It occupies a leading position in its composition, which includes: phosphorus, vitamins (A, B, C), calcium, and a large amount of protein. The product does not lose its beneficial properties after heat treatment, therefore it is very popular in cooking. You can use it to make casseroles and cheesecakes, dumplings, cakes and other confectionery products.
Protein consists of a chain of amino acids and is an organic substance. Not a single living organism is able to exist without it, because with its help the cells and tissues of organs are built. In Greek, “protos” means “first,” and protein becomes the primary element for any life activity.
Protein compounds are also part of hormones and enzymes. Hemoglobin, whose function is to provide oxygen to the blood, is, in principle, also a protein.
The human cellular structure contains thousands of different proteins, each of which includes 20 amino acids of various types of sequences. These chains create a specific load of protein compounds.
The high protein content in cottage cheese and its fast breakdown chain make the product universal for instant and effective recovery after the training process.
Protein is also known as casein - it is rich in calcium and amino acids, without which the body cannot fully function:
- lysine – ensures tissue growth and repair, promotes the production of antibodies, hormones and important enzymes;
- methionine – is the “building material” of cells;
- tryptophan – when it enters the body, it is converted into serotonin, which has a positive effect on the emotional state. With low levels of the amino acid, depression, insomnia, decreased attention levels and migraines are observed.
If protein is a building material, then carbohydrates are a source of energy. Both elements are necessary for full functioning.
We recommend reading: Lying calf flexion
It should be noted that no matter how many grams of protein there are in cottage cheese, carbohydrates are also present in it one way or another, but they are much smaller. Therefore, the question “what is cottage cheese: protein or carbohydrate?” should not arise. A large amount of protein allows carbohydrates to be better absorbed, speeding up metabolism (carbohydrate metabolism). In this fermented milk product, the ratio of macroelements can be considered ideal.
Legumes
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Beans | 83,0 | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,3 | 58 |
| Peas | 14,0 | 23,0 | 1,6 | 57,7 | 323 |
| Whole peas | 14,0 | 23,0 | 1,2 | 53,3 | 303 |
| Soybeans | 12,0 | 34,9 | 17,3 | 26,5 | 395 |
| Beans | 14,0 | 22,3 | 1,7 | 54,5 | 309 |
| Lentils | 14,0 | 24,8 | 1,1 | 53,7 | 310 |
Eggs
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Chicken egg | 74,0 | 12,7 | 11,5 | 0,7 | 157 |
| Egg powder | 6,8 | 45 | 37,3 | 7,1 | 542 |
| Protein powder | 12,1 | 73,3 | 1,8 | 7 | 336 |
| Dry yolk | 5,4 | 34,2 | 52,2 | 4,4 | 623 |
| Quail egg | 73,3 | 11,9 | 13,1 | 0,6 | 168 |
Fish and seafood
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Gobies | 70,8 | 12,8 | 8,1 | 5,2 | 145 |
| Pink salmon | 70,5 | 21 | 7 | 0 | 147 |
| Flounder | 79,5 | 16,1 | 2,6 | 0 | 88 |
| crucian carp | 78,9 | 17,7 | 1,8 | 0 | 87 |
| Carp | 79.1 | 16 | 3.6 | 0 | 96 |
| Chum salmon | 71.3 | 22 | 5.6 | 0 | 138 |
| Smelt | 79.8 | 15.5 | 3.2 | 0 | 91 |
| Icy | 81.8 | 15.5 | 1.4 | 0 | 75 |
| Bream | 77.7 | 17.1 | 4.1 | 0 | 105 |
| Salmon | 62.9 | 20.8 | 15.1 | 0 | 219 |
| Macrurus | 85 | 13.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 60 |
| Lamprey | 75 | 14.7 | 11.9 | 0 | 166 |
| Pollock | 80.1 | 15.9 | 0.7 | 0 | 70 |
| capelin | 75 | 13.4 | 11.5 | 0 | 157 |
| Navaga | 81.1 | 16.1 | 1 | 0 | 73 |
| Burbot | 79.3 | 18.8 | 0.6 | 0 | 81 |
| Marbled notothenia | 73.4 | 14.8 | 10.7 | 0 | 156 |
| Sea bass | 75.4 | 17.6 | 5.2 | 0 | 117 |
| River perch | 79.2 | 18.5 | 0.9 | 0 | 82 |
| Sturgeon | 71.4 | 16.4 | 10.9 | 0 | 164 |
| Halibut | 76.9 | 18.9 | 3 | 0 | 103 |
| Blue whiting | 81.3 | 16.1 | 0.9 | 0 | 72 |
| Saber fish | 75.2 | 20.3 | 3.2 | 0 | 110 |
| Caspian fisherman | 77 | 19.2 | 2.4 | 0 | 98 |
| Carp | 75.3 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 0 | 121 |
| Large saury | 59.8 | 18.6 | 20.8 | 0 | 262 |
| Small saury | 71.3 | 20.4 | 0.8 | 0 | 143 |
| Salaka | 75.4 | 17.3 | 5.6 | 0 | 121 |
| Herring | 62.7 | 17.7 | 19.5 | 0 | 242 |
| Whitefish | 72.3 | 19 | 7.5 | 0 | 144 |
| Mackerel | 71.8 | 18 | 9 | 0 | 153 |
| Som | 75 | 16.8 | 8.5 | 0 | 144 |
| Horse mackerel | 74.9 | 18.5 | 5 | 0 | 119 |
| Sterlet | 74.9 | 17 | 6.1 | 0 | 320 |
| Zander | 78.9 | 19 | 0.8 | 0 | 83 |
| Cod | 80.7 | 17.5 | 0.6 | 0 | 75 |
| Tuna | 74 | 22,7 | 0,7 | 0 | 96 |
| coal fish | 71.5 | 13.2 | 11.6 | 0 | 158 |
| Sea eel | 77.5 | 19.1 | 1.9 | 0 | 94 |
| Acne | 53.5 | 14.5 | 30.5 | 0 | 333 |
| Hake | 79.9 | 16.6 | 2.2 | 0 | 86 |
| Pike | 70.4 | 18.8 | 0.7 | 0 | 82 |
| Ide | 80.1 | 18.2 | 0.3 | 0 | 117 |
| Far Eastern shrimp | 64,8 | 28,7 | 1,2 | 0 | 134 |
| Cod liver | 26,4 | 4,2 | 65,7 | 0 | 613 |
| Squid | 80,3 | 18 | 0,3 | 0 | 75 |
| Crab | 81,5 | 16 | 0,5 | 0 | 69 |
| Shrimp | 77,5 | 18 | 0,8 | 0 | 83 |
| Sea kale | 88 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 3,0 | 5 |
| Pasta “Ocean” | 72,2 | 18,9 | 6,8 | 0 | 137 |
| Trepang | 89,4 | 7,3 | 0,6 | 0 | 35 |
Why is protein needed in the human diet? Role and functions of proteins
Protein is an organic substance consisting of amino acids connected to each other in a chain. It is the main component of the diet of all living beings. The human body is not able to independently synthesize all the necessary amino acids. For this reason, it is important to eat foods daily that will help fill the gap.
The main ones are listed in the table:
| Product group | Product name | Protein content g/100 g |
| Legumes | White beans | 25 |
| Red lentils | 24,2 | |
| Chickpeas | 20 | |
| Cereals | Wild rice | 14 |
| Quinoa | 14 | |
| Couscous | 12,8 | |
| Nuts | Cashew | 25,4 |
| Almond | 18,6 | |
| Hazelnut | 16,1 | |
| Fish and seafood | Tuna | 24,4 |
| Shrimps | 20,6 | |
| Salmon | 20 | |
| Dairy | Cheese | 29 |
| Cottage cheese | 18 | |
| Meat | Veal | 23 |
| Beef | 23 | |
| Turkey | 23 |
Since protein is the main component of the cells of a living organism, it performs functions that affect all human systems:
- Catalytic - the function of proteins called enzymes, thanks to which metabolism and energy occur. It consists in accelerating the breakdown and synthesis of complex molecules. Therefore, a sufficient amount of this substance in the diet helps to avoid digestive problems.
- Structural. Protein is involved in the formation and maintenance of cell shape. Proteins of the intercellular substance are also responsible for this function, the most famous of which are collagen and elastin. They maintain skin elasticity and organ youth.
- Protective. Liver enzyme proteins accelerate the process of removing various toxic substances from the body. Lysozymes and interferons provide immune protection for the body. Keratin serves to maintain mechanical protection.
- Regulatory. Hormone proteins are responsible for transmitting information within cells and regulate slow processes occurring in the body. Receptor proteins are responsible for intracellular processes, helping to activate them.
- Signal. Proteins facilitate the transmission of signals between cells, tissues and organisms. This function is responsible for skeletal growth, satiety, blood sugar levels and other important processes.
- Transport. Promotes the transfer of substances from one cell to another.
- Spare. Some proteins are stored by the body as a reserve source of energy or as an additional source of amino acids, which are later converted into substances that regulate metabolism.
- Receptor. Responsible for the perception by cells of signals coming from the external environment, as well as from other cells.
- Motor. Responsible for the movements of the body, as well as the movement of cells within it.
Protein-rich foods, the table of which is given in the article, are important to include in your daily diet. Healthy hair, nails, skin, strong muscles, properly functioning internal organs and metabolism, correct functioning of the digestive system are factors that depend on a sufficient amount of protein.
Caviar
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Chum salmon granular | 46,9 | 31,6 | 13,8 | 0 | 251 |
| Bream punch | 58 | 24,7 | 4,8 | 0 | 142 |
| Pollock punch | 63,2 | 28,4 | 1,9 | 0 | 131 |
| Sturgeon granular | 58 | 28,9 | 9,7 | 0 | 203 |
| Sturgeon punch | 39,5 | 36 | 10,2 | 0 | 123 |
Fats, margarine, butter
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Rendered lamb or beef fat | 0,3 | 0 | 99,7 | 0 | 897 |
| Pork bacon (without skin) | 5,7 | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0 | 816 |
| Milk margarine | 15,9 | 0,3 | 82,3 | 1 | 746 |
| Sandwich margarine | 15,8 | 0,5 | 82 | 1,2 | 744 |
| Mayonnaise | 25 | 3,1 | 67 | 2,6 | 627 |
| Vegetable oil | 0,1 | 0 | 99,9 | 0 | 899 |
| Butter | 15,8 | 0,6 | 82,5 | 0,9 | 748 |
| Ghee | 1 | 0,3 | 98 | 0,6 | 887 |
Meat, poultry
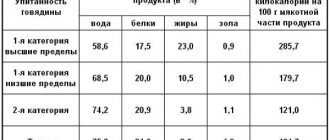
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Mutton | 67,6 | 16,3 | 15,3 | 0,0 | 203 |
| Beef | 67,7 | 18,9 | 12,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| horsemeat | 72,5 | 20,2 | 7,0 | 0,0 | 143 |
| Rabbit | 65,3 | 20,7 | 12,9 | 0,0 | 199 |
| Pork lean | 54,8 | 16,4 | 27,8 | 0,0 | 316 |
| Pork is fatty | 38,7 | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| Veal | 78,0 | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| Lamb Kidneys | 79,7 | 13,6 | 2,5 | 0,0 | 77 |
| Lamb Liver | 71,2 | 18,7 | 2,9 | 0,0 | 101 |
| Lamb Heart | 78,5 | 13,5 | 2,5 | 0,0 | 82 |
| Beef Brains | 78,9 | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| Beef liver | 72,9 | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| Beef Kidneys | 82,7 | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| Beef Udder | 72,6 | 12,3 | 13,7 | 0,0 | 173 |
| Beef Heart | 79,0 | 15,0 | 3,0 | 0,0 | 87 |
| Beef Tongue | 71,2 | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| Pork kidneys | 80,1 | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| Pork liver | 71,4 | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| Pig heart | 78,0 | 15,1 | 3,2 | 0,0 | 89 |
| Pig tongue | 66,1 | 14,2 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 208 |
| Geese | 49,7 | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
| Turkey | 64,5 | 21,6 | 12,0 | 0,8 | 197 |
| Chickens | 68,9 | 20,8 | 8,8 | 0,6 | 165 |
| Chickens | 71,3 | 18,7 | 7,8 | 0,4 | 156 |
| Ducks | 51,5 | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
Sausages
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Boiled sausage Diabetic | 62,4 | 12,1 | 22,8 | 0 | 254 |
| Boiled sausage Dietary | 71,6 | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0 | 170 |
| Boiled sausage Doctorskaya | 60,8 | 13,7 | 22,8 | 0 | 260 |
| Boiled sausage Lyubitelskaya | 57,0 | 12,2 | 28,0 | 0 | 301 |
| Boiled sausage Milk | 62,8 | 11,7 | 22,8 | 0 | 252 |
| Boiled sausage Separate | 64,8 | 10,1 | 20,1 | 1,8 | 228 |
| Boiled veal sausage | 55,0 | 12,5 | 29,6 | 0 | 316 |
| Pork sausages | 53,7 | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| Dairy sausages | 60,0 | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0 | 277 |
| Russian sausages | 66,2 | 12,0 | 19,1 | 0 | 220 |
| Pork sausages | 54,8 | 11,8 | 30,8 | 0 | 324 |
| Boiled-smoked Amateur | 39,1 | 17,3 | 39,0 | 0 | 420 |
| Boiled-smoked Cervelat | 39,6 | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0 | 360 |
| Semi-smoked Krakow | 34,6 | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0 | 466 |
| Semi-smoked Minsk | 52,0 | 23,0 | 17,4 | 2,7 | 259 |
| Semi-smoked Poltavskaya | 39,8 | 16,4 | 39,0 | 0 | 417 |
| Semi-smoked Ukrainian | 44,4 | 16,5 | 34,4 | 0 | 376 |
| Raw smoked Amateur | 25,2 | 20,9 | 47,8 | 0 | 514 |
| Raw smoked Moscow | 27,6 | 24,8 | 41,5 | 0 | 473 |
Proteins in products TABLE. Bioavailability and how they are absorbed
How to correctly calculate proteins in food? This video will be useful for those who monitor their diet and take care of their health. This will help you, when looking at a plate of food, visually determine exactly how much protein is there.
Whether you prefer animal or plant-based protein sources, keep the following in mind: The amount of protein you need to consume depends on the quality of the protein. Let's learn right now about the biological value of protein and the digestibility coefficient of different types of proteins.
Biological value of protein
On average, the average person needs 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight. For athletes, children and older people, the norms are slightly different. Biological value (BC) is a parameter that determines how efficiently the body can use nutrients. This value depends on the amino acid composition of the protein and the degree of its digestibility.
In other words, BC shows how quickly and efficiently the body can use consumed protein. Now on your screen is a table of protein digestibility in foods. I will voice it for those who are watching on a small smartphone screen.
| Products | Protein digestibility |
| Eggs | 96% |
| Milk serum | 96% |
| Kefir, milk (2.5%), hard cheese (26%), cottage cheese (bold) | 95% |
| Meat: beef (breast), rabbit, lamb, chicken (breast) | 90% |
| Carp, squid, pike, tuna, herring, salmon | 90% |
| Mushrooms (white) | 70% |
| Peas | 70% |
| Pork meat (tenderloin) | 65% |
| Buckwheat | 60% |
Another table compares the value of proteins from food and sports nutrition.
| Protein source | Biological value |
| Whey isolate | 159% |
| Whey concentrate | 104% |
| Eggs (whole) | 96% |
| Chicken/turkey | 90% |
| Casein (dietary supplement) | 77% |
| Soy Protein (Dietary Supplement) | 74% |
The high biological value of whey isolate and whey concentrate is due in part to the fact that they are produced in powder form. Accordingly, the body spends a minimum of energy on breaking down such protein into amino acids. And another table with another approach, assessing the quality of proteins.
The coefficient is estimated by the content of digested protein after passing through the small and large intestine. This test is the most modern way to assess protein quality. The table shows protein sources that are rated based on protein digestibility and amino acid content.
| Coefficient (%) | Protein quality | |
| Whole milk powder | 143 | High |
| Milk protein concentrate | 118 | High |
| Whole milk | 114 | High |
| Hard boiled eggs | 113 | High |
| Beef | 111 | High |
| Whey isolate | 109 | High |
| Chicken breast | 108 | High |
| Whey concentrate | 98,3 | good |
| Pea protein | 91,5 | good |
| Soy protein | 90 | good |
| Chickpeas | 83 | good |
| Rice (boiled) | 59 | Low |
| Almond | 40 | Low |
| Cornflakes | 10 | Low |
How to apply the data from these tables in practice.
Let's find out how much protein we get by consuming 100 g of chicken breast. Let's look at several cooking options as an example. As we see, each cooking method has a different effect on the final amount of protein in meat. Boiled breast contains the most protein. We will take this as an example.
| Cooking method | Proteins, g |
| Raw | 23,6 |
| Boiled | 27,6 |
| For a couple | 23,6 |
| Fried | 25,2 |
| Baked | 24,8 |
| Grill | 19 |
| Smoked | 18 |
So, 100 grams of smoked fillet contains approximately 27 grams of protein. Previously, we learned that the biological value of chicken meat is 90%. That is, 10% is not absorbed. Subtract 10 percent from 27 g. As a result, from 100 grams of boiled chicken fillet, you will get approximately 24 grams of protein. Of course, these are just mathematical calculations. In reality, the protein will most likely be absorbed even less. This is individual for everyone and depends on the health of the gastrointestinal tract. This also needs to be taken into account when choosing your diet.
What about plant-based proteins? Let's count. 100 grams of dry buckwheat contains approximately 13 grams of protein. The biological value of this cereal in terms of proteins is only 60%. That is, in fact, 100 grams of buckwheat contains only 8 grams of protein. That's why getting protein from cereals, chickpeas and peas is not as easy as it seems.
What conclusions can be drawn from this?
1. If you are in a restaurant and are trying to purely visually estimate how much protein is in a serving, then now you know that 100 grams of chicken breast does not contain 100 grams of protein, but 24. At the same time, how much of these 24 grams will actually be absorbed, you do not know . You also now know that 100 grams of buckwheat porridge contains only 8 g of protein.
2. It is preferable to replenish your daily protein intake from protein products that have high biological activity, as well as a high amino acid ratio. Why? At a minimum, it is more economical, because protein products are the most expensive compared to fats and carbohydrates. The less protein product is required, the more profitable it is from an economic point of view. It is also healthier for your gastrointestinal tract. It makes a difference how you get the proteins you need, for example 50 grams per day. Or you will need to eat 200 grams of chicken breast, or eat a kilogram of buckwheat. And this is dry weight, after cooking it will be twice as much in volume. No digestive system can withstand such loads.
3. If you cannot get the proteins you need from foods, then the normal solution would be to add protein from sports nutrition to your diet. For example, instead of just one snack, make yourself a protein smoothie or protein shake. At the same time, the sports nutrition industry has advanced and you can find what you need for yourself. There are plant proteins and animal proteins from organic milk and everything you like. If we talk about me, what do I use? Then, taking into account my needs and lifestyle, and I lead an active lifestyle, I do athletics 6 times a week. I replenish my proteins like this: a few eggs for breakfast, a piece of fish or turkey for lunch, a protein shake for a snack, fish or cheesecakes for dinner. Like this.
Health Academy
Canned meat and smoked meats
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Beef stew | 63,0 | 16,8 | 18,3 | 0 | 232 |
| Tourist breakfast (beef) | 66,9 | 20,5 | 10,4 | 0 | 176 |
| Tourist breakfast (pork) | 65,6 | 16,9 | 15,4 | 0 | 206 |
| Sausage mince | 63,2 | 15,2 | 15,7 | 2,8 | 213 |
| Pork stew | 51,1 | 14,9 | 32,2 | 0 | 349 |
| Raw smoked brisket | 21,0 | 7,6 | 66,8 | 0 | 632 |
| Raw smoked loin | 37,3 | 10,5 | 47,2 | 0 | 467 |
| Ham | 53,5 | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0 | 279 |
Mushrooms
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| White fresh | 89,9 | 3,2 | 0,7 | 1,6 | 25 |
| White dried | 13,0 | 27,6 | 6,8 | 10,0 | 209 |
| Fresh boletus | 91,6 | 2,3 | 0,9 | 3,7 | 31 |
| Fresh boletuses | 91,1 | 3,3 | 0,5 | 3,4 | 31 |
| Fresh russula | 83,0 | 1,7 | 0,3 | 1,4 | 17 |
Proteins in plant foods
The protein content in plant foods largely depends not on the type of specific plant, but on which part of the plant is used for food. For example, fruits and seeds (from nuts to beans), as well as grains (including cereals and all kinds of flour) contain much more protein than plant stems (broccoli, lettuce) and roots (potatoes).
Fresh vegetables, fruits and berries contain a minimal amount of protein, since the basis of their mass is water, carbohydrates and plant fiber (dietary fiber). Separately, we note that potatoes, just like other vegetables, contain no more than 2-3 g of protein per 100 g - in fact, a large plate of mashed potatoes contains less protein than one chicken egg.
| The product's name | Protein content per 100 g | Approximate level of protein absorption |
| Soy protein | 30 – 50 g | 90 – 95% |
| Dried mushrooms | 20 – 30 g | 70 – 80% |
| Beans | 20 – 25 g | 65 – 70% |
| Lentils | 20 – 25 g | 65 – 70% |
| Dry peas | 20 – 22 g | 65 – 70% |
| Various nuts | 10 – 25 g | 65 – 70% |
| Potato | 2 – 3 g | 65 – 70% |
| Vegetables and fruits | 2 – 3 g | 65 – 70% |
| Fresh mushrooms | 1 – 3 g | 65 – 70% |
| Berries | 1 – 2 g | 65 – 70% |
Protein content in cereals
Let us remember that the vast majority of cereals are processed products of cereal crops (primarily wheat, rice, corn, barley and oats). Various flours are also made from cereals (wheat, rye and others). The exceptions are buckwheat and quinoa, which are essentially flower seeds - and these pseudocereals contain more protein.
Nuts
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Hazelnut | 4,8 | 16,1 | 66,9 | 9,9 | 704 |
| Almond | 4 | 18,6 | 57,7 | 13,6 | 645 |
| Walnut | 5 | 13,8 | 61,3 | 10,2 | 648 |
| Peanut | 10 | 26,3 | 45,2 | 9,7 | 548 |
| sunflower seed | 8 | 20,7 | 52,9 | 5 | 578 |
High Protein Foods for Vegetarians
Vegetarian food includes only products of plant origin. Protein balance is the most important factor in a vegetarian diet.
Plant-based foods high in protein:
- legumes - beans, peas, lentils;
- nuts and seeds;
- soy products;
- mushrooms (tubular);
- broccoli, spinach;
- fruits - avocado, banana, peach;
- cereals (rice and cereals)
- dried fruits.
Advantages:
- contain fiber, which improves digestion, slows down the breakdown of sugars, and reduces cholesterol levels;
- a low-calorie vegetarian diet is absorbed faster by the digestive system;
- contain vitamins and minerals.
Flaws:
- large volumes of food - the amount of protein in plants is incomparably small.
- high price;
- vegetable protein is not considered complete, for example, beans do not contain methionine, and rice does not contain lysine.
Protein content in legumes:
| Product | Protein content, g |
| soybeans | 34,9 |
| lentils | 24,8 |
| beans | 22,3 |
| peas | 23 |
Protein in food: table in ascending order (nuts and seeds):
| Product | Protein content, g |
| peanut | 26,3 |
| sunflower seed | 20,7 |
| almond | 18,6 |
| hazelnut | 16,1 |
| Walnut | 13,8 |
Protein content in mushrooms:
| Product | Protein content, g |
| white dried | 27,6 |
| white fresh | 3,2 |
| fresh boletus | 3,3 |
| boletus fresh | 2,3 |
| boletus | 2,1 |
| lamellar (honey mushrooms, russula) | 1,7 |
Protein content in dried fruits:
| Product | Protein content, g |
| dried apricots | 5,2 |
| dried apricots | 5 |
| apples | 3,2 |
| peaches | 3 |
| raisin | 2,3 |
| pear | 2,3 |
| prunes | 2,3 |
| cherry | 1,5 |
Examples of combinations to replenish amino acids:
- peanut butter rice;
- rice and beans;
- cereals with legumes;
Sweets
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Honey | 17,2 | 0,8 | 0 | 80,3 | 308 |
| Fruit dragee | 7 | 3,7 | 10,2 | 73,1 | 384 |
| Marshmallow | 20 | 0,8 | 0 | 78,3 | 299 |
| Iris | 6,5 | 3,3 | 7,5 | 81,8 | 387 |
| Marmalade | 21 | 0 | 0,1 | 77,7 | 296 |
| Caramel (average) | 4,4 | 0 | 0,1 | 77,7 | 296 |
| Chocolate coated candies | 7,9 | 2,9 | 10,7 | 76,6 | 396 |
| Paste | 18 | 0,5 | 0 | 80,4 | 305 |
| Sugar | 0,2 | 0,3 | 0 | 99,5 | 374 |
| Tahini halva | 3,9 | 12,7 | 29,9 | 50,6 | 510 |
| Sunflower halva | 2,9 | 11,6 | 29,7 | 54 | 516 |
| Dark chocolate | 0,8 | 5,4 | 35,3 | 52,6 | 540 |
| Milk chocolate | 0,9 | 6,9 | 35,7 | 52,4 | 547 |
Protein for weight loss
During the active process of losing weight, that is, during a period of negative energy balance, proteins supplied with food are the protection of the body's own proteins from excessive catabolism (the decomposition process in which energy is released into the body). This process accompanies the weight loss regimen. As a result of reduced energy consumption, body tissue proteins serve as a substitute, an alternative source of energy. The loss of body proteins also negatively affects the weakening of the immune system.
Confectionery
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calorie content, kcal per 100 g |
| Waffles with fruit fillings | 12 | 3,2 | 2,8 | 80,1 | 342 |
| Waffles with fat-containing fillings | 1 | 3,4 | 30,2 | 64,7 | 530 |
| Puff pastry with cream | 9 | 5,4 | 38,6 | 46,4 | 544 |
| Puff pastry with apple | 13 | 5,7 | 25,6 | 52,7 | 454 |
| Sponge cake with fruit filling | 4,7 | 9,3 | 84,4 | 344 | |
| Gingerbread | 14,5 | 4,8 | 2,8 | 77,7 | 336 |
| Sponge cake with fruit filling | 25 | 4,7 | 20 | 49,8 | 386 |
| Almond cake | 9,3 | 6,6 | 35,8 | 46,8 | 524 |
We tried to make this table of calorie content and nutritional supplements as complete as possible and included many products in it. If you find any inaccuracies or errors, or have questions, please write in the comments.
Turkey fried, boiled, baked
The energy value may vary depending on what kind of meat is chosen (red or white), as well as on the method of heat treatment. This should be taken into account when dieting. Boiled turkey fillet has the lowest calorie content - about 130 kcal, and steamed turkey fillet - only 90 kcal. Stewing and baking are also the best ways to prepare meat when creating a healthy diet (120 and 160 kcal, respectively).
Fried turkey with a calorie content of 165 kcal can be included in the menu when losing weight, but in small quantities.
Nutritionists advise making poultry cutlets, quenelles and zraza, since the value of the finished dish does not exceed 150 kcal. White poultry meat without skin is an excellent source of energy for active people: digestion slows down and the feeling of fullness remains for a long time. Compare with from our publication.