Anorexia is a mental illness, the main symptom of which is an eating disorder, characterized by an inadequate assessment of one’s appearance, a pathological desire to lose weight, a panicky fear of being overweight and a distorted attitude towards food.
Although cases of anorexia have been described for a very long time, their number has been growing rapidly in the last couple of decades. This disease is most common among teenage girls aged 14-18 years; among teenage boys, the disease is 10 times less common.
Signs of developing anorexia
- constant preoccupation with one's weight and appearance;
- reluctance to eat at a common table;
- constant dissatisfaction with the achieved result, although the weight loss was greater than planned;
- distorted perception of one’s appearance: even with severe emaciation, the teenager sees himself as fat;
- non-recognition of illness;
- depression;
- fatigue, irritability;
- cessation of menstruation in girls;
- alternating periods of aversion to food with bouts of bulimia;
- calorie counting, constant weighing;
- mirror symptom: constantly looking for figure flaws in front of the mirror.
In the case of bulimia, a person first experiences extreme hunger and cannot stop eating, and then experiences feelings of guilt and self-loathing, causing vomiting.
The disease begins to develop in adolescence because rapid changes occur in the body, hormonal changes, which indicate the need to soon enter adulthood:
- accept your sexuality
- adapt to new relationships and demands of society.
Such a morbid interest of a girl or boy in his body means that mentally he (she) is not ready for these life tasks. The inability to adequately adapt to reality shifts to dissatisfaction with one's body . The teenager says to himself and everyone around him: if only I were thin and looked normal, then everything would be fine with me. And if you don’t notice this problem in time, you can waste precious time. Because while a teenager is focused on his appearance, he loses his position in other areas: he abandons his studies, narrows his social circle, etc.
In addition, an unbalanced and extremely poor diet after some time begins to affect the nervous and hormonal systems, which aggravates the condition of increased fatigue, anxiety and depression.
Anorexia nervosa in children and adolescents
The first signs of the disease are dissatisfaction with one’s own body, increased interest in ways to lose weight. Ideas about beauty, health, and attractiveness are changing. The child begins to admire famous personalities, movie heroes who have a thin, fragile physique. The idea of excess weight and ugliness is just emerging. Thoughts are carefully hidden from others. As the patient develops, the body changes; physiological transformations occur during adolescence, often accompanied by an increase in body fat. This becomes a trigger for taking action.
The teenager tries to discreetly skip meals and is fanatically involved in sports that promote weight loss. At the initial stage, there is a desire to hide the desire to lose weight from adults, gradually behavior becomes oppositional and negative: refusals to eat become more frequent, with persuasion and reproaches from parents, outbursts of irritability arise, and conflicts are provoked. The child shows more and more selectivity in food, often creating his own “diet”. First of all, exclude foods high in fats and carbohydrates from the diet. The menu is dominated by vegetables, fruits, and low-fat dairy products. To reduce the feeling of hunger, the patient begins to smoke, drink a lot of fluids (drink water, coffee, teas), and take medications that reduce appetite.
Constant emotional tension, depression, dysphoria (embarrassment), dissatisfaction with oneself manifests itself, and fears are formed. In some adolescents, periods of depression are replaced by hypomania - general activity and mood increase, and with emotional uplift, behavioral control decreases. Disinhibition of drives is manifested by bouts of gluttony, after which self-accusation, self-abasement develops, and sometimes vomiting is provoked. In the somatic sphere, symptoms of asthenia (weakness, dizziness) and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (heartburn, nausea, pain in the stomach) predominate.
After losing weight by a third or more, the weight loss process slows down. The body is exhausted, which is manifested by hypo- or adynamia (decreased motor activity), high fatigue, feeling tired, dizziness, fainting, and decreased critical thinking function. The teenager continues to refuse to eat food and is unable to assess his thinness and his own health. An overvalued/delusional thought about the imperfection of the body persists. Dehydration of the body develops, the skin becomes pale, dry, epigastric pain becomes more frequent, and in girls menstruation is disrupted or stops. The function of digesting food is gradually lost, each meal causes a feeling of heaviness, nausea, heartburn, pain, and prolonged constipation.
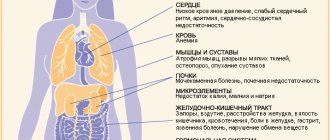
Consequences of anorexia for the body
- changes in hormonal levels (the function of the thyroid gland is disrupted, the formation of sex hormones), which leads to menstrual irregularities and osteoporosis (destruction of bone tissue);
- the number of heart contractions decreases;
- blood pressure decreases;
- the electrolyte composition of the blood changes - the potassium content drops, which causes a disturbance in the rhythm of cardiac activity that is life-threatening;
- increased serum cholesterol levels;
- decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood;
- development of anemia;
- damage to tooth enamel;
- weight loss (up to 40–50%);
- disruption of the digestive tract (bloating, constipation);
- brittleness of hair and nails;
- memory loss, slow thinking;
- headaches, dizziness;
- frequent fainting.
If left untreated
Anorexia in children must be treated. Otherwise the following will occur:
- hormonal imbalances;
- avitaminosis;
- calcium deficiency leading to frequent fractures;
- severe nervous system disorders;
- disturbances in the activity of the heart;
- tendency to caries, premature loosening and loss of teeth.
Without receiving the necessary nutrients on a regular basis, the body loses its ability to function normally. Subsequently, it is not always possible to eliminate all the negative consequences of childhood anorexia. Some chronic pathologies remain with the patient for life. Therefore, it is so important to enlist the support of a psychotherapist at the first signs of a mental disorder.
In Moscow, you can get treatment for anorexia by contacting the doctors at the Leto mental health center. Just call 8(969)060-93-93 and tell us what happened. Leto doctors will definitely help you.
You suspect your child has anorexia. What to do?
Due to their severe consequences, eating disorders such as anorexia and bulimia are life-threatening and require immediate professional help.
Treatment requires psychotherapy with the obligatory, at least at the first stage, use of medication prescribed by a psychiatrist. Therefore, if you notice at least a few of the above signs in your child, be sure to contact a psychologist and (or) psychiatrist .
Unfortunately, statistics indicate that a third of patients return to obsessions with weight control and nutrition. And the decisive factor is the time of contacting a specialist.
The sooner help is provided, the greater the chance of a complete cure for the disease!
What is the disease
Very often, articles on the topic of eating disorders are illustrated with an unusual picture. It shows a thin girl looking in the mirror. Her reflection does not correspond to reality - in it we see clear signs of obesity.
This is exactly what happens in reality - anorexics think they are fat, even if they are underweight. At the same time, it is impossible to convince patients that they are thin.
To lose weight, patients deliberately refuse food and fast. They starve themselves of the most severe diets, as a result of which they literally “melt” before our eyes. The difficulty is that with such behavior the food instinct is disrupted. It gets to the point where a gag reflex occurs in response to eating even a small portion of food.
Children with anorexia do not experience the urge to eat. Their greatest value is the thought of soon acquiring an ideal figure. According to statistics, the peak incidence occurs at the age of 13-15 years. Twenty percent of cases end in suicide.
Teenage anorexia: how to notice in time and how to help
– Anorexia in a broad sense is a disorder of eating behavior in the direction of a decrease in appetite and the amount of food consumed, not directly related to a violation of one’s attitude towards oneself. Anorexia nervosa is a common mental disorder in teenagers. It is based on a person’s desire to change himself, his physical self, most often to lose weight.
– Who is most likely to experience anorexia?
– Those for whom appearance has an extremely valuable meaning, that is, one that lies at the center of all human experiences. Naturally, such interest in one’s physical self is characteristic primarily of adolescents and young adults. Adolescents are in a special risk zone when they have left childhood, but have not yet reached adulthood, and this is why they are “stormy.”
Nowadays, anorexia also occurs in boys, but 90% of cases still occur in girls. They are disturbed when their appearance, in their opinion, does not correspond to standards.
– How can you tell if something is wrong with your child?
– We need to pay attention if a previously unusual attitude towards oneself and towards food manifests itself. There is a special interest in diets; the topic of losing weight and special exercises for this takes center stage in conversations. Moreover, these conversations become emotionally charged. Vulnerability also appears; any opinion causes a disproportionate, excessive reaction, which manifests itself both in expression and in the duration of processing of the message. A person literally gets stuck on this. Children or teenagers begin to feel ashamed of themselves, cover up what they think are problematic areas: sit down in a certain way, buy different clothes.
Help is almost always needed when a teenager begins to regard his peculiarity as a defect and becomes obsessed with this idea.
– Who should I contact in such a situation?
– First, see a pediatrician or therapist, depending on age. You need to report changes in eating behavior. The doctor will assess whether there is weight deficiency, metabolic disorders, or changes in the blood count. Girls who diet often develop problems with the menstrual cycle, so sometimes consultations with more specialized specialists are required. The pediatrician will point this out if necessary.
You can immediately contact a psychiatrist. Precisely to a psychiatrist, and not to a psychologist or psychotherapist. This is important to determine whether a person has a mental disorder and, if found, to begin treatment immediately.
– My daughter faced the problem you are talking about. She is 16 years old, she has begun to develop as a girl, she is quickly gaining excess weight and has a lot of complexes because of this. She has become irritable and cries a lot. What do you recommend?
- I will give advice to my mother. First of all, treat your daughter with understanding. She should see the person approaching her not as a person who rejects her experiences, but as someone who sympathizes with her and tries to understand.
On a behavioral level, demonstrate to the girl that her experiences are not a trifle. In any case, there are experiences, they are significant for a person, no matter what caused them. If you don't support your daughter and downplay her problems, you will only alienate her from you.
You need to say: “I see that this worries you a lot.” Remember the phrase, this is a universal formula that helps in solving many problems of adolescents.
Second: you must give a careful message that this is not necessarily a disease, it can be an age-related stage. But do not say directly that this happens to almost everyone at this age, that all girls begin to perceive themselves this way, otherwise there is a risk that the child will perceive this as a denial of the problem. Say that you are not sure, but you have read that this happens, you need help and there are specialists who can help. This will set you up for a positive perception of help.
Then you need to ask: “How will you feel if we turn to specialists?” If a child says that he wants to go to a psychologist and not a psychiatrist, you need to agree even to this incorrect order of help, but first you need to talk to the psychologist so that he can also recommend a doctor.
We must accept as much as possible from the child. All his options for help, all his problems, then he will join in the interaction and the treatment will be successful. No matter what ridiculous arguments a teenager may give in your opinion, they need to be understood and accepted without any buts. This is universal advice. The rest will be decided by the specialist individually.
– How should you behave with a teenager so that obsessive thoughts about changing himself do not enter his head?
– I would advise everyone to initially be thoughtful and careful about value judgments regarding appearance. Sometimes even the family doesn’t notice it. A father can say to his daughter: “Well, you’re overfed! Daughter, you need to lose weight.” And if this is still supported by the mother and grandmother, then the teenager comes to understand that he is rejected based on his physical appearance by the entire family.
Teachers can also get involved here and say: “You are now a well-fed generation. Look how well-fed everyone is.”
If this exists, there is an urgent need to rebuild communication in the family and school. Even if the words do not lead to anorexia, they will definitely hurt children and adolescents and cause psychological trauma.
In general, you need to avoid making value judgments regarding children, teenagers, and everyone around you. Be careful with your tongue! It is important to strengthen a person’s self-esteem by celebrating the merits of his actions. Look at the example. The boy cleaned the apartment. You can say: “What a great fellow you are! You're so good!" That is, you will appreciate his personality. Or you can say, “I’m so pleased! I feel like you tried really hard and the apartment looks different.”
In this case, the person will evaluate himself. And he will not become dependent on the opinions of others. It is very important.
Note actions and actions that please you, notice at least this in your children.
It’s also good when children approach adolescence with certain interests in life. Then they have more resources to cope with different situations. The less developed a child is as a person, the more susceptible he is to external influence.
For preschoolers (4-7 years old)
Anorexia is often diagnosed in preschool children, since at 5-6 years the psyche is already more or less formed, the child has adapted to society, and begins to understand a lot about relationships between people. And here any stress suffered can cause an eating disorder.
Causes
These could be:
- conflicts with someone from the environment (peer neighbor, brother or sister, stepfather);
- unfavorable family environment;
- visiting a kindergarten where relationships with other children or the teacher do not develop;
- parental divorce;
- severe fright (dog attacked, fell from a height, etc.);
- death of a family member;
- fear of school;
- physical or sexual violence.
Symptoms
Along with refusal to eat and weight loss, preschoolers may experience:
- insomnia;
- hyperexcitability or, conversely, lethargy;
- dizziness;
- isolation, development of acquired autism;
- constipation;
- skin itching;
- urinary incontinence.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out within the framework of psychotherapy. Commonly prescribed pediatric sedatives include:
- soothing pharmaceutical teas: Calm down, Bayu-bai, Evening fairy tale;
- weakly brewed infusions for the night: linden blossom, mint, lemon balm, valerian, lavender, motherwort;
- Persen is a completely herbal preparation;
- Citral is more powerful, contains magnesium sulfate and sodium bromide;
- Glycine;
- Magne B-6 - mineral and vitamin complex;
- potent tranquilizers (Sibazon, Phenazepam, Elenium) are prescribed to correct a clearly defined disorder exclusively by prescription and under the supervision of a physician.
A child with anorexia needs support, do not instill in him a feeling of guilt, as this will have the opposite effect.
Children suffering from anorexia, first of all, need to feel that they are loved. Usually, family psychotherapy courses are prescribed for treatment, where both parents are invited. The preschooler’s recovery depends only on them.
Treatment of childhood anorexia
At TsIRPP, you can undergo outpatient and inpatient treatment for childhood anorexia, depending on the patient’s health status at the time of contacting the clinic. We offer:
- an individual approach to solving problems with childhood feeding disorders;
- application of methods of treatment and identification of the causes of the disease that are recognized as effective and safe in the world community;
- a better approach through collaboration with the Linehan Institute, an international academy for eating disorders, where our therapists receive additional training and supervision;
- progressive treatment methods that involve the involvement of relatives;
- drawing up an individual menu taking into account food preferences for each patient;
- treatment services in the intensive care unit if the child is in serious condition;
- participation in family intensives, communication with a psychotherapist via Skype to exclude relapses of childhood anorexia.
Anorexia in adolescents and toddlers is often associated with weight loss, so the first goal of treatment is to address symptoms of malnutrition. At this stage, treatment methods such as frequent fractional and parenteral nutrition and maximum rest in bed are used.
When weight gain is noted, you can begin to address the issue of food perception for children. With the help of a psychologist, psychotherapist or psychiatrist, the fight against the psychological manifestations of anorexia begins. To do this, cognitive behavioral therapy is carried out for up to six months, which allows you to change distorted children's ideas about food and get rid of anger and anxiety.
Family therapy plays an important role in treatment. It is important to find problems in the relationship between parents and child that could provoke the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease in childhood
Diagnosis of childhood nervous diseases is complicated by denial and silence of the reasons for refusing food. Therefore, if the baby can communicate, then treatment begins with a conversation. Parents are also interviewed to look for behavioral problems, changes in weight and appearance.
The process uses special questionnaires to detect eating disorders. You can conduct tests with your child to determine self-esteem and emotional state. Popular methods SMIL, Dembo-Rubinstein and others.
To treat the disorder, you need to rule out other causes of the problem. Especially if symptoms appear in young children. It is almost impossible to establish full contact with them, so the survey is carried out only with parents, test data and the general clinical picture are taken into account.
Also, treatment of childhood anorexia includes general laboratory tests, including blood and urine tests, hormone tests, and checking the condition of the kidneys and liver. To understand the causes of poor appetite, the gastrointestinal tract is examined using instrumental methods.
A child psychiatrist must exclude the early development of schizophrenia or other serious mental disorders, against the background of which anorexia may develop as one of the symptoms. To do this, the specialist checks thinking functions and other features.