This article will help you calculate your personal physical activity quotient.
The physical activity ratio ( PAL or PAL ) measures a person's activity level. To lose weight, it is necessary to assess our energy needs and thus formulate the right nutrition and exercise plan. Read in another article on our website how you can build an athletic figure with the help of nutrition . How to calculate the PAL ? What is the relationship between total and basal metabolic rate and physical activity rate? Find answers to these questions below.
What is physical activity ratio?
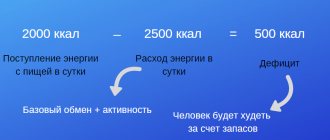
Physical activity coefficient is a value equal to the ratio of a person’s energy expenditure during activity to expenditure at rest (the value of basal energy metabolism).
The value of the physical activity coefficient is always higher than one and can vary from 1.4 to 2.4. Values of 2.4-4.5 and higher can be observed in athletes during intense training or competitions and are temporary, periodic in nature.
Values below 1.4 (in the range of 1.2-1.3) occur when a person is bedridden due to age or illness, but even in this case, to determine the energy value of the diet, it is necessary to take into account the damage factor, temperature factor, the presence of protein-energy deficiency.
Physical activity coefficient is a value showing the ratio of a person’s energy expenditure during activity to energy expenditure at rest.
How to determine the physical activity ratio?
To determine the coefficient of physical activity, there are tables that show the coefficient of each type of physical activity per unit of time.
The problem is that throughout the day, different types of activities continuously replace each other. How can you find out your coefficient?
To do this, with varying degrees of error, you can use the data given below.
| Occupation | kfa |
| REST | |
| Dream | 1,0 |
| Rest sitting, reading | 1,4 |
| Rest standing | 1,8 |
| Personal hygiene | 2,2 |
| Fishing | 3,5 |
| Dancing (waltz) | 3,7 |
| Taking a shower | 4,2 |
| Dancing (energetic) | 10 |
| BRAINWORK | |
| Mental work while lying down without moving | 1,03 |
| Reading | 1,4 |
| Paperwork | 1,6 |
| Counting on a calculator | 1,6 |
| Mental work while sitting | 1,7 |
| Conversation while sitting | 1,7 |
| School lessons | 1,7 |
| Violin playing (professional) | 1,7 |
| Listening to a lecture | 1,8 |
| Drawing while standing | 1,8 |
| Computer work | 1,8 |
| Playing chess without a board | 1,8 |
| Drawing | 1,8 |
| Working on a typewriter | 1,9 |
| Conversation while standing | 1,9 |
| Reading aloud | 1,9 |
| Playing the orchestra trumpet while sitting | 1,9 |
| Report standing | 2,0 |
| Typing | 2,2 |
| Playing the violin (amateur) | 2,3 |
| Giving a speech, teaching while sitting | 2,4 |
| Working in the laboratory while standing | 2,6 |
| Reading a lecture | 3,3 |
| HOMEWORK | |
| Eating | 1,6 |
| Washing dishes | 2,2 |
| Light (cooking, sweeping the floor, washing dishes, setting the table, removing dust) | 2,4 |
| Housework (average) | 3,5 |
| Wash by hand | 3,8 |
| Light work (making beds, cleaning rooms, polishing floors, washing windows) | 3,9 |
| Heavy work (beating carpets, mopping floors, polishing furniture) | 4,5 |
| WORK IN INDUSTRY | |
| Fitting and assembly work | 2,0 |
| Distribution works | 2,2 |
| Turning and grinding work | 2,4 |
| Turning and milling work | 2,5 |
| Working on a grinding machine | 2,6 |
| Semi-automatic welding | 2,7 |
| Manual welding | 2,9 |
| Work of a chemist operator | 3,1 |
| Miner working on a combine | 3,1 |
| Ancillary work | 3,1 |
| Plumbing | 3,2 |
| Boring works | 3,3 |
| Manual electric welding | 3,4 |
| Painter's work | 3,4 |
| Molding work | 3,5 |
| Slinging works | 3,5 |
| Machine tool production | 3,6 |
| Working at a chemical plant | 3,7 |
| Tractor driver's work | 3,7 |
| Assembly of flat sections | 3,8 |
| Plasterer work | 4,2 |
| Spray painting | 4,2 |
| Work in a rolling shop | 4,5 |
| Working with a jackhammer | 4,7 |
| Carpenter's work | 5,3 |
| Cleaning weld seams | 5,4 |
| Concrete worker's work | 5,8 |
| Blacksmithing | 5,9 |
| Fly saw maintenance | 5,9 |
| Bricklayer's work | 6,5 |
| Work at a metallurgical plant | 7,4 |
| Slag removal work | 10 |
| WORK IN THE MINING INDUSTRY | |
| Mining jobs (average) | 6,2 |
| Mechanical drilling of oil wells: | |
| Driller job | 2,5 |
| Job of 1st assistant driller | 3,0 |
| Job of 2nd assistant driller | 3,7 |
| Job of 3rd assistant driller | 3,9 |
| Auxiliary work when drilling oil wells: | |
| Driller job | 2,9 |
| Job of 1st assistant driller | 3,7 |
| Job of 2nd assistant driller | 3,7 |
| Job of 3rd assistant driller | 3,8 |
| Lowering and raising the drill string: | |
| Driller job | 2,9 |
| Job of 1st assistant driller | 3,8 |
| Job of 2nd assistant driller | 4,0 |
| Job of 3rd assistant driller | 3,1 |
| Oil well support | |
| Driller job | 3,1 |
| Job of 1st assistant driller | 3,6 |
| Job of 2nd assistant driller | 4,6 |
| Job of 3rd assistant driller | 3,9 |
| Working with an excavator | 6,2 |
| Coal or ore excavation | 6,5 |
| Loading coal | 7,2 |
| Working with a pick and shovel | 8,7 |
| Moving trolleys | 9,5 |
| WORK IN THE WOOD PROCESSING INDUSTRY | |
| Working on a grinding machine | 3,4 |
| Carpenter's work | 3,5 |
| Work in a furniture factory | 3,6 |
| Turning works | 3,6 |
| Feeding sawdust slabs into a thickness planer | 3,9 |
| Working on a circular saw | 4,0 |
| Receiving sawdust slabs from a thickness planer | 4,1 |
| Mechanical firewood sawing | 4,4 |
| Package | 4,4 |
| Plywood sorting | 4,8 |
| Working on woodworking machines | 5,9 |
| Excavation | 7,0 |
| Manual wood cutting | 7,3 |
| Wood chopping | 8,4 |
| Tree cutting | 8,6 |
| Timber felling | 8,9 |
| Planing with a plane | 9,1 |
| AGRICULTURAL WORK | |
| Operator work on an automated irrigation system machine | 1,5 |
| Manual post-cleaning of beet roots | 2,0 |
| Refueling equipment | 2,2 |
| Operation of the chaff stacker | 2,2 |
| Machine milking | 2,2 |
| Sowing, cultivation | 2,3 |
| Preparing for machine milking | 2,3 |
| Potato picking | 2,4 |
| Milking with partially mechanized labor | 2,4 |
| Digging beets | 2,4 |
| Work of a sorter on an automated line | 2,6 |
| Planting potatoes | 2,6 |
| Manual milking with non-mechanized labor | 2,6 |
| Clearing nodes from the ground | 2,7 |
| Lubrication of components | 2,7 |
| Collecting and laying eggs | 2,8 |
| Cleaning milking areas | 2,8 |
| Washing milking machines | 2,9 |
| Working with a scraper | 2,9 |
| Combine operator work | 3,0 |
| Inspection and culling of birds | 3,1 |
| Cleaning of poultry farm premises | 3,1 |
| Work of a sorter | 3,4 |
| Washing and cleaning poultry farm equipment | 3,4 |
| Work of the planter | 3,5 |
| Picking tomatoes | 3,5 |
| Combine harvester repair | 3,6 |
| Loosening the earth with a rake | 3,7 |
| Delivery of feed in trolleys | 3,8 |
| Watering the bird | 3,9 |
| Land surveying work | 4,0 |
| Filling with seeds and fertilizers | 4,2 |
| Laying feed with partially mechanized labor | 4,3 |
| Pulling beets out of the ground | 4,4 |
| Mechanized agriculture (average) | 4,5 |
| Harvesting cabbage to the edge of the field | 4,5 |
| Planting | 4,6 |
| Operation of a straw stacker on a combine harvester | 4,7 |
| Engine starting | 4,7 |
| Feeding the bird | 4,8 |
| Laying feed for cows during non-mechanized labor | 4,8 |
| Loading bags | 4,9 |
| Loosening the soil | 5,0 |
| Watering the beds | 5,0 |
| Garden work, weeding | 5,3 |
| Traditional agriculture (average) | 5,9 |
| Harvesting vegetables in the field | 6,1 |
| Plowing on horseback | 6,2 |
| Winnowing by hand | 6,4 |
| Removing bird droppings | 6,4 |
| Plowing | 6,6 |
| Knitting sheaves | 7,4 |
| Digging the earth with a shovel | 7,8 |
| Operating a manual grain sorting machine | 8,0 |
| Mowing with a scythe | 10 |
| SERVICE WORK | |
| Watch repair | 1,5 |
| Mechanized tailoring and clothing repair | 1,5 |
| Repair of household appliances | 1,5 |
| Shoe repair | 2,0 |
| Tailor's work | 2,1 |
| Electrician's work | 2,1 |
| Repair carpenter work | 2,3 |
| Radio assembly | 2,5 |
| Tailoring | 2,6 |
| Sewing shoes | 2,7 |
| Elevator repairman work | 3,2 |
| Laundry work | 3,7 |
| Working in the canteen | 3,7 |
| WORK IN THE FAR NORTH | |
| Transfer to the fishing spot and back by boat with a motor | 1,6 |
| Working with a seine | 3,7 |
| Pulling a seine with fish | 4,8 |
| Hunting for sea animals | 5,2 |
| Loading and unloading carcasses | 5,8 |
| Skin dressing | 5,9 |
| Towing sea animal carcasses | 6,1 |
| Drilling holes for ice fishing | 6,1 |
| Sleigh control | 6,2 |
| Traveling to the fishing spot and back by boat without a motor | 6,3 |
| Boat rowing | 6,3 |
| Cutting up sea animal carcasses | 9,2 |
| IN THE HOSPITAL | |
| Doctor's work (office appointment) | 2,2 |
| Laboratory assistant's work | 2,2 |
| Moving in a chair on wheels | 2,4 |
| Surgeon's work | 2,6 |
| Nurse job | 2,9 |
| The work of an orderly | 3,7 |
| Using a bedpan | 4,7 |
| Walking on crutches | 8,0 |
| OTHER ACTIVITIES | |
| The work of a navigator, radio operator | 1,4 |
| Helmsman's work | 1,5 |
| Storekeeper job | 1,6 |
| The work of a navigator-mechanic | 1,7 |
| Driving a car | 1,8 |
| Hairdresser's work | 2,2 |
| Airplane control | 2,2 |
| Motor mechanic's work | 2,4 |
| The work of a steering mechanic | 2,5 |
| Working in a bakery | 2,5 |
| Mechanic's work | 2,6 |
| Binding works | 2,7 |
| The work of a conductor on a ship | 2,8 |
| Working at a brewery | 3,0 |
| Sailor's work | 3,3 |
| Motor mechanic work on a high-speed boat | 3,3 |
| Driving a locomotive | 3,4 |
| Driving a motorcycle | 3,6 |
| Carwash | 3,7 |
| Truck driver job | 3,9 |
| Fireman's work on a locomotive | 5,2 |
| Mail delivery | 5,4 |
| Forester's work | 5,8 |
| SPORTS ACTIVITIES | |
| Walking very slow | 2,2 |
| Walking slow, walking | 2,7 |
| Billiards | 2,4 |
| Walking 3 km/h | 3,3 |
| Walking 4.2 km/h | 4,6 |
| Walking 5.3 km/h | 5,8 |
| Walking 6 km/h | 6,7 |
| Walking 7 km/h | 7,8 |
| Walking 8 km/h | 9,0 |
| Walking on a snowy road 6 km/h | 7,6 |
| Walking on a snowy road 8 km/h | 10 |
| Walking on sand 4.8 km/h | 6,2 |
| Walking 2 km/h from the mountain | 2,3 |
| Walking 2 km/h uphill | 18 |
| Running to attack | 6,5 |
| Running 8 km/h | 8,8 |
| Running 12 km/h | 10 |
| Running 15 km/h | 13 |
| Running 18 km/h | 17 |
| Running 20 km/h | 40 |
| Running 24 km/h | 90 |
| 100 m sprint | 50 |
| 30m sprint | 100 |
| Skis 8 km/h | 13 |
| Skis 12 km/h | 15 |
| Skis 14 km/h | 18 |
| Ski competitions | 21 |
| Ice skating (recreation) | 3,3 |
| Speed skating training | 9,5 |
| Skating 12 km/h | 8,2 |
| Skating 20 km/h | 14 |
| Speed skating competition | 27 |
| Cycling 9 km/h | 3,5 |
| Cycling 10 km/h | 3,8 |
| Cycling 15 km/h | 5,4 |
| Cycling 20 km/h | 8,3 |
| Cycling 21 km/h | 8,6 |
| Cycling 30 km/h | 13 |
| Horse riding at a walk | 3,0 |
| Horse riding at trot | 7,4 |
| Horse riding gallop | 9,1 |
| Bathing | 3,4 |
| Swimming (training) | 9,0 |
| Swimming in cold water | 12 |
| Swimming 0.6 km/h | 3,2 |
| Swimming 0.9 km/h | 3,7 |
| Swimming 1.2 km/h | 4,7 |
| Swimming 3 km/h | 13 |
| Swimming 3.2 km/h | 14 |
| Swimming 3.6 km/h | 22 |
| Swimming 4.2 km/h | 28 |
| Boating | 3,0 |
| Shooting exercises | 3,3 |
| Descending the stairs | 3,4 |
| Archery | |
| Baseball | 4,2 |
| Playing golf | 4,8 |
| Table tennis | 4,9 |
| Morning exercises | 5,3 |
| Badminton | 5,9 |
| Cricket | 6,0 |
| Gymnastics (warm-up) | 6,1 |
| Aerobics (medium intensity) | 6,2 |
| Weightlifting | 6,3 |
| Uphill 15 degrees, 2 km/h | 6,9 |
| Digging trenches | 7,4 |
| Football | 7,7 |
| Tennis | 7,7 |
| Volleyball | 7,9 |
| Aerobics (high intensity) | 8,0 |
| Rowing free | 8,2 |
| Fencing | 8,9 |
| Mountaineering | 8,9 |
| Climbing stairs | 8,9 |
| Motorball | 9,4 |
| Struggle | 11 |
| Handball | 12 |
| Ski slalom (training) | 12 |
| Rugby | 13 |
| Basketball | 13 |
| Boxing | 14 |
| Figure skating competition | 16 |
| Swimming competition | 18 |
| Judo | 21 |
| Rowing competition | 24 |
| Cycling track competition | 24 |
| Ice hockey | 26 |
| Ski slalom (competition) | 34 |
| One powerful jerk | 300 |
| ELEMENTARY MOVEMENTS | |
| Flexion at the wrist joints | 1,2 |
| Abductions in the wrist joints | 1,4 |
| Circular movements in the wrist joints | 1,3 |
| Elbow flexion | 1,4 |
| Rotations at the elbow joints | 1,3 |
| Shoulder flexion | 1,8 |
| Abductions in the shoulder joints | 1,7 |
| Rotations in the shoulder joints | 1,2 |
| Circular movements in the shoulder joints | 2,1 |
| Leads in the cervical joints | 1,2 |
| Rotations in the neck joints | 1,2 |
| Circular movements in the neck joints | 1,5 |
| Lumbar flexion | 1,8 |
| Abductions in the lower back | 1,4 |
| Lumbar twists | 1,4 |
| Circular movements in the lower back | 2,0 |
| Ankle flexion | 1,7 |
| Abductions in the ankle joints | 1,5 |
| Rotations at the ankle joints | 1,3 |
| Circular movements in the ankle joints | 1,6 |
| Knee flexion | 1,7 |
| Rotations in the knee joints | 1,8 |
| Hip flexion | 2,4 |
| Abductions in the hip joints | 2,4 |
| Rotations in the hip joints | 1,7 |
| Circular movements in the hip joints | 2,8 |
| Flexion in all joints | 2,2 |
| Leads in all joints | 1,7 |
| Rotations in all joints | 2,0 |
| Circular movements | 2,2 |
| NORMALIZED PHYSICAL WORK | |
| Pushing a trolley, speed 3.6 km/h, force 11.6 kgf | 7,0 |
| Pushing a trolley, speed 3.6 km/h, force 16.1 kgf | 9,5 |
| Trolley traction, speed 3.6 km/h, force 11.6 kgf | 7,7 |
| Trolley traction, speed 3.6 km/h, force 16.1 kgf | 9,8 |
| Work as a cleaver (2 kg), 35 beats/min | 9,6 |
| Ax work (cutting), 34 beats/min | 3,4 |
| Ax work (cutting), 51 beats/min | 4,2 |
| File work, 42 movements per minute | 1,8 |
| File work, 60 strokes per minute | 2,3 |
| File work, 80 strokes per minute | 3,8 |
| Hammer work (4.4 kg), 15 beats/min | 6,6 |
| Hammer work (10.6 kg), 15 beats/min | 7,4 |
| Sawing with a two-handed saw, 60 double strokes per minute | 10 |
| Shovel work (sand, 3 kg): | |
| Throw length 1 m, 15 throws per minute to a height of 0.5 m | 5,7 |
| Throw length 1 m, 12 throws per minute to a height of 1 m | 6,0 |
| Throw length 1 m, 12 throws per minute to a height of 1.5 m | 7,2 |
| Throw length 1 m, 12 throws per minute to a height of 2 m | 8,1 |
| Throw length 2 m, 12 throws per minute to a height of 0.5 m | 6,5 |
| Throw length 2 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 1 m | 7,1 |
| Throw length 2 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 1.5 m | 8,1 |
| Throw length 2 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 2 m | 9,0 |
| Throw length 3 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 1 m | 8,0 |
| Throw length 3 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 1.5 m | 8,6 |
| Throw length 3 m, 10 throws per minute to a height of 2 m | 9,4 |
* according to data calculated by Yuri Georgievich Garin
^ Back to top
The benefits of active recreation
Active rest is the continuation of intense physical activity with a change in its type. This form of leisure is preferable for people whose work activities involve limited physical activity.
The stricter these restrictions are, the more a person needs active rest, which is, essentially, compensation for forced immobility during the working day.
On a note:
People whose work limits physical activity during the day need an active form of rest.
Of course, active recreation cannot always replace passive recreation (for example, reading books or doing creative work is a useful and necessary form of recreation). But you may well prefer walking or doing yoga to watching “endless” TV series or “deep immersion” in social networks.
On a note:
If you want to watch a movie, go to the cinema.
Just go, outline a walking route of 2-3 kilometers and walk them before and after the session. The ability to walk for a long time and quickly is determined not only by physical fitness, but also by appropriate equipment, and in order for your walk to be useful and enjoyable, you first need comfortable shoes.
If the weather is not conducive to walking, then you can start cleaning - this will increase energy costs by 60%. Working in the garden or playing outdoor games with children gives an even greater effect.
Age groups
Children and teenagers (6-17 years old)
Children and adolescents should get at least 60 minutes of physical activity per day . The majority of these 60 minutes should include moderate- to vigorous-intensity , as well as vigorous-intensity exercise at least 3 days a week .
| The main physical activities of this age group include games, competitions, sports, trips, physical education classes and family activities. |
Children and adolescents are often active in short bursts rather than for long periods, and these short bursts of activity should add up to the minimum amount of physical activity required.
Physical activities for children and adolescents should be developmentally appropriate, interesting, fun and varied, and most importantly, the more, the better. A child’s active lifestyle contributes to the full development of the cardiovascular system and muscle-bone frame.
Adults (from 18 to 64 years old)
Minimum physical activity for adults involves:
- 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week . That is, at least 30 minutes a day must be devoted to movement.
- 2 times a week, to maintain the muscle frame and bones, it is necessary to perform strength training for all major muscle groups.
OR
- 75 minutes per week of high-intensity cardio and 2 times a week strength training for all major muscle groups.
| It is important to remember that for full effect all exercises must be performed for at least 10 minutes. |
However, there is no reason to limit yourself to this load. Research shows that increasing moderate-intensity exercise to 300 minutes per week or 150 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity exercise will produce additional benefits on health and well-being.
Although there are no official recommendations, the American College of Sports Medicine also recommends adding and performing stretching exercises 2-3 times per week and motor skills training (called functional training, which focuses on balance, agility, posture and coordination). exercise 20-30 minutes a day.
Elderly people (65 years and older)
For people in this age category, it is advisable to increase cardio load to 5 hours per week at moderate intensity . You should also add coordination and stretching exercises to your cardio and strength training.