What is metabolism
Metabolism is the chemical process of converting nutritional components that enter the body along with food. In other words, the body breaks down food into small particles and creates molecules from them. The functioning of all organs is impossible without the presence of such energy.
There are two main types of metabolism:
- Anabolism is a complex of chemical processes through which new tissues and cells are formed in the body.
- Catabolism is a set of processes that destroy complex elements into simple ones.
What will we talk about
Unfamiliar words, incomprehensible to some people, are simply translated: basic metabolism. Everyone should know what it is.
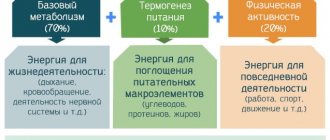
I propose to memorize it as an equation of life: for any process in our body - respiration, cell repair, enzyme production, the breakdown of proteins into amino acids, the combination of amino acids into new proteins, the breakdown of long molecules of polysaccharides into glucose, the functioning of brain cells, the work of the heart muscle, the burning of fat and pr.pr.pr. — we need energy, those same kilocalories that we are so afraid of.
70% of all calories that food provides goes to this basal metabolism, and we use only thirty for physical activity.
Metabolic rate
Metabolic rate is the amount of energy required by the body to carry out full activities.
This indicator comes in several types:
- The minimum speed, which is present only at moments when the body is at rest.
- The person is at rest, but does not sleep, but also does not overload himself with excessive loads. This type processes approximately fifty to seventy percent of the calories that are consumed and burned by the body daily.
- The thermic effect of food refers to the calories that the body needs to digest food.
- The thermic effect of sports activity is those calories that are broken down during exercise.
- There is another thermogenesis, during which resources are spent on moderate physical activity.
“The Theory of Relativity” in our life
So, the formulas are approximate, the numbers are not exact, the tables are relative. We have only purely empirical data that cannot be used in practice without modification. What to do? How to understand your level? Act logically.
The best coach is a professional athlete. The best theorist is a practicing doctor.
There are medical standards for daily consumption for adults:
- 1200 kilocalories is the absolute minimum, followed by exhaustion (this value should be taken as the starting point in calculating your basal metabolism);
- 2000 kcal - for a bedridden patient;
- at least 2300-2500 - for a person leading a less active lifestyle;
- from 3000 - for heavy physical activity.
I have made an online calorie intake calculator for you:
Other calculators are here.
Factors affecting metabolism
Diet
Metabolism is mainly affected by:
- Age. The best metabolic rates are present in the human body at the age of twenty. After this age, they deteriorate by two to three percent every decade.
- Hormonal background. All processes that occur inside the body directly depend on its condition. Thus, if a person suffers from disruptions in the functioning of the hormonal system, this can negatively affect the rate of absorption of substances.
- Diet. If a person consumes excessive amounts of fatty, fried, smoked and other unhealthy foods, this negatively affects the quality of digestion. In addition, regular diets and hunger have a similar effect on these processes.
- Water mode. Without fluid, none of the processes occurring inside the body is possible. With excessive or insufficient water intake, the body is not able to fully function. It is recommended to drink two to two and a half liters of fluid per day.
- Lifestyle. The rate of food absorption is directly affected by the amount of physical activity: the more of it, the better the food is digested.
Read
About nettle tincture with vodka and its use
Genetic predisposition plays an important role. However, if metabolism is slowed down solely due to heredity, then it will not be possible to correct it.
Physical activity
This is the most variable component, responsible for 10-30% of the calories you burn each day and is directly related to the mobility of your lifestyle.
Since we have already figured out the calculation of metabolism, now all you have to do is find out your physical activity quotient in order to calculate how much energy you spend daily.
Again, according to British scientists who sifted through a mountain of literature on the topic of energy expenditure, the following numbers best reflect the different levels of physical activity of the population:
- 1,49 – sedentary lifestyle (for example, sedentary work without exercise);
- 1,63 – an average active lifestyle (for example, sedentary work (or one that does not require serious physical activity) + irregular sports or regular but light-intensity training;
- 1,78 – a more active lifestyle - energy-intensive work or regular training of medium-high intensity 3-5 times a week;
- > 2 – a very active lifestyle, which is usually observed among professional athletes and soldiers during preparation for combat missions.
Example
So, our average Masha works in an office, sometimes runs in the park and goes to yoga, so we multiply her basal metabolism of 1253 kcal by a factor of 1.63 and get 2042 kcal - approximately this amount of energy in general Masha spends daily.
As for losing weight, nutritionists advise losing weight by no more than 0.5 kg per week by reducing energy intake by 500 kcal per day. In Masha’s case, this means a safe, but rather meager diet of 1540 kcal, so in her case it is better to increase energy expenditure through sports.
It is noteworthy that in order to lead a more active lifestyle with a coefficient of 1.78, Masha only needs to walk half an hour longer a day at an average pace.
Symptoms of impaired metabolism
Bloating
The following signs may indicate metabolic problems:
- excess weight, which you cannot get rid of either through diets, physical exercise, or other similar methods;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- low body temperature;
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- allergic reactions;
- acquired intolerance to certain foods;
- insomnia or disruptions in sleep patterns;
- feeling of anxiety;
- lethargy;
- regular colds;
- constipation;
- reduced concentration level;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- heartburn;
- increased irritability;
- nails become brittle and stop growing.
Test No. 1. On oatmeal
To test this, cook a portion of oatmeal in water (200–250 g). Take the flakes for long cooking. Minute porridge in bags is not suitable: after processing, there is little useful fiber left in it, but harmful starch has been added.
It is also important to cook the oatmeal empty - without sugar, butter, salt, berries or jam. The porridge should be warm.
Eat the steamed cereal on an empty stomach, chewing thoroughly. After 10–15 minutes, listen to your body and evaluate the sensations.
Signs of a healthy metabolism
If a person has no problems with uncontrolled gain or loss of kilograms of weight, it means that the body absorbs the incoming substances well.
A good exchange can be called one that digests food neither in an accelerated nor in a slow manner.
The fact that the metabolic level is within optimal limits is indicated by:
- stable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- there are no rashes on the face;
- hair is in good condition;
- Feeling tired is rare.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
What is metabolism?
Scientifically speaking, metabolism is the chain of chemical transformations of nutrients from our diet from the moment they enter the stomach to the moment they are excreted from the body. Simply put, Metabolism is the process of converting food into energy.
In this case, metabolism is divided into two interrelated processes that occur simultaneously and continuously.
Anabolism is the process of creating more complex chemical elements from a number of simple organic substances. For this process, the body expends a certain amount of its energy.
Catabolism is the process of breaking down organic substances with the release of clean energy and breakdown products that must be eliminated from the body.
Thus, the energy released during catabolism many times covers the energy spent on anabolic processes. This is exactly what a person needs to live. The energy needed by a person is calculated as follows: the minimum energy consumption in a state of complete rest is taken into account, with the exclusion of all internal and external influences within 12 hours after eating. This is our minimum. It is enough to breathe and support the functioning of all internal organs. But in reality, a person requires much more energy, because he moves, and muscle tension consumes much more energy than all organs and systems combined. There is also a designation for our energy - these are kilocalories (kcal) or kilojoules (kJ). Even when your body is at rest (you are sleeping), it needs energy, for example: for breathing, blood circulation, cell repair (renovation). The number of calories required to perform these vital body functions is called the basal metabolic rate.
What does metabolism depend on?
The basal metabolism of an adult is approximately 1 kcal per 1 kg of body weight for 1 hour. The continuous metabolic processes occurring in all cells of all tissues of the human body proceed more slowly or more intensely depending on in which organ and in which tissue it occurs. For example, the most intensive exchange occurs in the tissue of the gray matter of the brain, muscles and organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but the slowest - in bone mass and fat cells. Therefore, people with well-developed muscles require much more energy (10-15%) than “loose” fat people.
Indicators of the intensity of metabolic processes may also vary for other reasons.
- Depending on age, height and weight, gender, health status of all organs. In women, for example, metabolism is slower than in men by about 5-6%, because They have less muscle mass and more fat tissue. For example, a woman weighing 60 kg requires less energy than a man of the same weight.
- From nutrition and from the intensity of physical activity,
- From external influences on the body (climate, etc.).
- From the presence or absence of nervous stress.
- From the health and functioning of the endocrine glands.
- Whether a person is healthy or sick (for example, a fever requires a lot of energy).
- Age also affects the metabolic process - on average, they slow down by 7-10% for every 10 years of life, which is associated with a decrease in the activity of the body as a whole, starting with cellular processes and ending with the work of all organs, as well as a decrease in muscle mass.
Metabolism and excess weight
As we have already said, metabolic processes in adipose tissue proceed slowly - their speed is 3 times lower than the speed in muscle tissue. This means that one gram of our fat consumes approximately 30% less energy than one gram of the so-called. “lean mass” of the body (muscles, all organs, brain and nervous tissue, bones and all fluids). Therefore, obese people need less energy, and the whole problem is that it is the latter who eat more than they would need and move less, which ultimately contributes to additional deposition of adipose tissue. The fact is that excess calories from food of any type, be it fats, carbohydrates, proteins or alcohol, lead to the deposition of fat reserves.
- The fat itself “works” the fastest in this direction; it almost immediately goes into our fat layer.
- Carbohydrates are broken down into so-called. simple sugars, and they enter tissues to replenish energy deficiency. If there is no such deficiency, then they are also stored in reserve, converted into glycogen, and from it into fat.
- With proteins, things are a little more complicated. They break down into amino acids involved in the formation and renewal of tissues. Excess proteins are converted into glucose, and its excess (if not in demand) is again converted into fat. Thus, food that is so necessary for a person, such as protein, if consumed in excess, can serve us very badly.
- If we drink alcohol, its calories are used as a source of energy. Meanwhile, all the food eaten during the day will transfer its calories as unnecessary... that’s right, again into fat!
Thus, adipose tissue is the “depot” where all our unspent energy is deposited, and this “depot” is not at all passive. It is an active endocrinological organ that secretes the hormone leptin. It, in turn, also affects the accumulation of fat in the body, as well as the functioning of the entire endocrine system. Metabolic processes are disrupted unnoticed by humans, and the level of production of fat-accumulating hormones, such as insulin, increases. Obesity is progressing, and most often the most dangerous obesity is progressing - the so-called. abdominal, when fat is deposited not only under the skin, but also in the abdominal cavity, “clinging” to the organs and interfering with their work. If the waist circumference is higher than 80 cm in women and 94 cm in men, this means that obesity of this type is already present, metabolism is reduced, and the risk of developing further metabolic disorders is high, which leads, if no measures are taken, to the development of the so-called. metabolic syndrome.
It should be remembered that all metabolic changes begin with obesity. That is why doctors fight it so fiercely. And if you see that your weight and waist size are more than normal, do not hesitate to take care of yourself.
How to increase metabolism and reduce excess weight
How metabolic syndrome is determined
by the presence of a combination of obesity and two of the following factors:
- increased blood pressure more than 130/85;
- an increase in blood triglyceride levels of more than 1.7 mmol/l (atherosclerosis)
- decrease in the level of high-density lipoproteins (good cholesterol, which protects blood vessels from atherosclerotic plaques) by more than 1 mmol/l in men and 1.2 mmol/l in women
- an increase in blood sugar level (diabetes may not exist, but it may occur) of more than 5.6 mmol/l.
- Limit energy-intensive foods, primarily fats and simple carbohydrates. Leave lean protein products (meat, eggs, milk) and fiber (vegetables, fruits) - they help increase metabolic processes and sharply reduce carbohydrates in any form (they slow down metabolism).
- Muscular work helps increase basal metabolism. More energy is consumed, less fat is deposited, or it is not deposited at all.
- In combination with proper nutrition, an increase in physical activity leads to the breakdown of adipose tissue. Slowly and reluctantly, our “depot” gives up its precious reserves to be converted into energy.
Remember that neither high blood pressure nor elevated cholesterol and blood sugar levels, if your weight and waist size are normal, are signs of metabolic syndrome. In the case of existing abdominal obesity and at least two of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome listed above, it is best to consult a doctor, since the patient is most often no longer able to lose weight, much less normalize blood pressure and blood levels on his own.
Interesting on the topic:
Common myths about metabolism
TOP 20 foods that burn fat and regulate metabolism
How to change a slow metabolism
In order to speed up a slow metabolism, it is necessary to review your diet. It is worth including products that contain fiber (porridge, hard pasta) and proteins (fermented milk, dairy products, chicken, eggs). Eating citrus fruits of any kind will be beneficial: lemons, oranges, tangerines, grapefruits, etc.
Fractional meals
It is better to eat according to the fractional system. That is, eat food five to six times a day, but in reduced portions. It is recommended to eat at approximately the same time, since over time the body gets used to the regime and begins to better absorb food at a certain time of the day.
It is necessary to drink enough water. You need to take at least two, but no more than three liters per day. You can dilute the intake of liquids with the help of compotes, decoctions based on medicinal plants, freshly prepared juices, green tea, and fruit drinks. It is not advisable to add sugar to drinks, but the use of sweetener substitutes is acceptable.
Read
Various diets: menu for 14 days
It is necessary to devote sufficient time to sleep and rest. At night, a person should sleep at least seven to eight hours. It is useful to regularly be in the fresh air, taking leisurely walks. Physical activity is a prerequisite, without which it is unlikely that you will be able to speed up your metabolism. However, it is not worth tormenting the body with excessive stress. An organism exhausted by sports will begin to consume energy from its own resources, which not only will not help speed up metabolism, but will also slow it down even more.
It is necessary to build and stick to a daily routine. It is recommended to go to bed no later than ten in the evening, and wake up around eight or nine in the morning. It is advisable to have dinner three to four hours before going to bed. You will have to give up late-night snacks.
Quitting alcohol
It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks. Smoking has a detrimental effect on metabolism, so you should give up cigarettes. However, if quitting smoking right away is too difficult, you are allowed to smoke no more than two or three pieces a day.
If a person wants to speed up metabolism with the help of special drugs, it is necessary to consult a relevant doctor. Self-medication can lead to deterioration of health and the development of some side effects.
To avoid being healthy and helpless
Important! WHO recommends not limiting yourself to aerobic exercise, but be sure to do exercises for joints, balance and strength at least 2 times a week.
The fact is that life expectancy —the performance of the cardiovascular, endocrine and immune systems—depends on general activity (and on calorie consumption). But the quality of life depends on the condition of the joints and muscles, as well as on brain activity.
Everyone wants to live to be a hundred years old, but no one wants to be old and helpless. Medicine and social institutions are now shifting their focus from life expectancy to its quality.
Just 20 years ago, only 25% of the population lived to age 75. Now this is the general norm. In countries with high life expectancy (for example, Japan), according to forecasts, by 2025, one in nine residents will exceed the age limit of 90 years. And preserving their ability to at least self-care is already a matter of political importance, so that 90-year-old elders with more or less healthy hearts do not lie in bed with arthrosis and osteoporosis, drawing a significant army of young people from the economy to the position of caregivers.
Therefore, WHO is gradually shifting its emphasis and making the priority no longer the number of years lived, but the quality of life and level of independence in old age. Naturally, in this situation, not only the intensity, but also the form of the loads becomes of fundamental importance.
How to calculate metabolic rate for men
Let's consider how to determine the metabolism of men. The procedure consists of several stages:
- Set height in centimeters. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) depends on height: the taller the person, the faster the metabolism.
- Set body weight in kilograms. The amount of energy consumed directly depends on a person’s weight. That is, the larger the person, the more energy the body needs to carry out full-fledged activities.
There is a special equation for installation. Its formula is: basal metabolic rate = 66 + (13.8 times weight in kilograms) + (5 times height in centimeters) - (6.8 times age).
Basal Metabolism Formula
Determination of female metabolism
Almost all women watch their figure. That is why they often ask the question: what kind of metabolism do I have? You can find out by analogy with the male method.
Read
Smecta or Enterosgel: which is better to choose
First you need to set your height in centimeters and weight in kilograms. Female version of the equation: BSM = 655 + (9.6 times body weight in kilograms) + (1.8 times height in centimeters) - (4.7 times age). In both cases, speed is measured in one unit - kilocalories.
What is moderate for one, intense for another
For example, we have two girlfriends: Tanya and Manya. Tanya weighs 50 kg with a height of 165 cm, and Manya weighs 65 kg with the same height. Let Tanya be 30 years old, and Manya 32. And so they decided to jog together in the morning.
Tanya's basal metabolism (according to the Muffin formula):
665 + (9.6 x 50) + (1.8 x 165) - (4.7 x 30) = 1300 kcal/day, or 54 kcal/hour.
Basal Metabolism Mani:
665 + (9.6 x 65) + (1.8 x 165) - (4.7 x 32) = 1435 kcal/day, or 60 kcal/hour.
This means that in order to spend 3 METs, Tanya needs to burn 162 kcal in an hour, and Manya needs to burn 180. Let’s say they ate an apple each in the morning (90 kcal). Tanya's overconsumption will be small, but Manya's 2/3 of calories will already be leaving the body's reserve reserves.
Naturally, she will feel more exhausted, her heart will begin to pump blood more intensely, because it is necessary to redistribute resources urgently, the pulse, accordingly, will increase more than that of her friend, the pores will open to drain excess fluid from the intercellular space - and Manya on the subjective level will feel that her loads were intense, and Tannins were moderate.
Although from a purely formal point of view, both were moderate - only 3 MET. When Manya loses weight to Tanya’s condition, their subjective perception will most likely also become similar.
Advertising