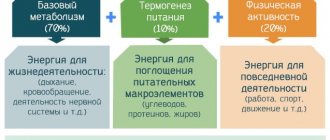
Health
Weight loss
Want to know your metabolic rate ? It's very simple: there are at least 3 proven methods that will clearly outline the state of your body. Each test can be done at home as often as you like.
Why is it important to know your metabolic rate? This indicator directly determines how quickly you will be able to lose weight and whether it is worth going on a diet at all (perhaps this is strictly contraindicated for you). Check right now to see if your metabolism is getting lazy.
Test No. 1. On oatmeal
To test this, cook a portion of oatmeal in water (200–250 g). Take the flakes for long cooking. Minute porridge in bags is not suitable: after processing, there is little useful fiber left in it, but harmful starch has been added.
It is also important to cook the oatmeal empty - without sugar, butter, salt, berries or jam. The porridge should be warm.
Eat the steamed cereal on an empty stomach, chewing thoroughly. After 10–15 minutes, listen to your body and evaluate the sensations.
About your energy
26.How many hours of night sleep do you need to feel normal?
- a) 8-9 hours 1 (P);
- b) from 4 to 6 hours 1 (N);
- c) 5-6 when I’m in shape, and when I’m tired 9-10 hours 1 (S);
- d) 7-8 hours 1 (D).
27.When are you most energetic?
- a) at the end of day 1 (P);
- b) all day 1 (N);
- c) after rest, after eating 1(SH);
- d) early in the morning 1 (G).
28.Do you have trouble falling asleep?
- a) very rarely 1 (P);
- b) often 1 (N);
- c) at times, sometimes 1 (Ш);
- d) sometimes, but several nights in a row 1 (D).
Test No. 2. Weight control
- Weigh yourself before bed. 2-3 hours before, do not eat, drink or exercise anything. Write down the result, labeling it A.
- Re-weigh immediately after waking up, mark the weight with the letter B.
- Subtract A from B. If the difference is 500 g , this indicates normal metabolism. If the indicator is less than normal or equal to zero (A equals B), your metabolism is slow.
There is no diet that suits everyone
For years, nutrition science has taken a generic, overly standardized approach to health and weight loss. This is why there is no one diet that suits everyone. There was all this hype about the Atkins diet, but Kelly, one of my The Biggest Loser contestants, only lost half a pound after a month of following the diet. Because I know that we are all different and need to diet according to our own body, I was able to train her so that she lost 25 kg in 3 months. We worked on it together during the show and she lost another 15kg after that.
Why?
Inherited genetics make each of us unique, from color to hair to the way our internal organs function. This uniqueness extends to how cells convert nutrients into energy. To learn how to get the most value for your calories, you need to understand your unique metabolic type. Once you do this, you can begin to create your new diet lifestyle around the foods that can help you achieve and maintain your ideal weight while optimizing physical energy, strength, and mental clarity.
Why determine your metabolism?
Metabolic Type is just a fancy name for figuring out how your body processes what you eat—in other words, what your body does with the three main nutrients in food: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Think of it as a stove: your body takes the food you eat and burns it with oxygen to turn the calories it contains into energy. This process is known as oxidation , and this is how carbohydrates from food are converted into glucose and released into the blood. When glucose enters the blood, the pancreas is signaled to secrete insulin to “clean” the blood of any sugar not used as energy by the body and transport it into cells where it will be stored as fat. The fact that we all oxidize nutrients from food in different ways is at the heart of why a certain diet works for one person and not for another. By learning more about how nutrients in food affect your body, you can avoid many pitfalls and seriously improve your health journey.
3 groups of oxidizing agents:
Although the severity may vary from one person to another, most people can be divided into the following 3 groups:
- fast oxidizers - slow oxidizers - balanced oxidizers
How do oxidizing agents work?
Fast oxidizers burn nutrients from food very quickly, as a result of which the resulting glucose enters the blood almost immediately. A sudden increase in blood sugar leads to a sharp release of large amounts of insulin in order to remove excess sugar, which is stored as fat in the cells.
The higher the carbohydrate content of your food, the more energy your body will have available right away, and the higher the chance that it will not be needed and will be stored as fat.
Insulin is a fast and effective blood purifier, and sudden rises and falls in sugar levels, as a result of rapid oxidation, lead to the manifestation of reactive hypoglycemia. As a fast oxidizer, foods high in carbohydrates cause weakness and cravings for sweets along with fat deposition.
Fast oxidizers should eat foods high in protein and fat to reduce the rate of oxidation and insulin release and to better maintain constant blood sugar and overall energy levels.
Slow oxidizers burn nutrients from food slowly and do not release glucose from carbohydrates into the blood quickly enough; this means that energy production and availability are delayed. Slow oxidizers should eat foods high in carbohydrates, as protein and fat slow the rate of oxidation and energy production even further.
Balanced oxidizing agents are exactly halfway between these two. They require food containing equal amounts of protein, fat and carbohydrates in order to optimally process, produce and use energy from food.
What happens in your blood every time you eat?
Now that we've defined the different types of metabolism, you might be wondering how you can find out what's going on in your blood every time you eat. Don't worry—there's a test you can take right now, and all you need is a pencil and paper.
The test consists of a series of detailed questions about everything from the type of food you eat to how dry your skin is. These questions cover such a wide range of physical manifestations because scientists now believe that metabolism, the way the body processes nutrients, is part of the central nervous system that controls a host of other functions in the body. Therefore, if you take a close look at some of your body's peripheral functions, they can shed light on your particular oxidative type and help determine your specific nutritional needs.
For each question, choose option A, B or C that best suits you.
You may not be able to answer the question right away. Take your time and think about the question. Take a few days, if necessary, to analyze how different foods affect your body and mood.
Don't answer questions based on how you feel you "should" eat. Be honest when answering about your preferences, inclinations and habits. Remember, the better you know yourself, the better your chances of achieving the results you strive for.
1. In the morning you: A. Don't have breakfast B. Eat something light (fruit, toast or cereal) C. Eat something substantial, heavy (eggs, bacon, steak, hash browns)
2. At the buffet you will choose: A. Lean meat (fish or chicken), vegetables and salad, various desserts. B. Something between A and C. C. Heavy fatty foods. For example, steak, ribs, pork chop, cheeses and creamy sauces.
3. Your appetite at lunch: A. Low. B. Normal. S. Strong.
4. Your appetite at dinner: A. Low B. Normal C. Strong
5. Caffeine affects you: A. Helps me concentrate B. Has no effect. S. Makes me anxious, or even causes nausea, nausea.
6. The type of food you like most (sugar is not given because everyone loves sugar when they are tired or exhausted. A. Fruits, bread, crackers. B. Both A and C C. Salty foods, cheeses, meat.
7. For dinner, do you prefer: A. Chicken or fish, salad, rice. B. No preference. Every day is different. C. “Heavy”, fatty foods - pasta, steaks, potatoes.
8. After dinner you: A. You need to eat something sweet. Q. You may or may not eat dessert. S. You don’t think about sweets, you prefer something salty, like popcorn.
9. Sweets that you prefer: A. Sugar candies like Skittles B. No preference. C. Ice cream or cheesecakes.
10. Fatty foods (meat, cheese) before bed: A. Prevents me from sleeping. B. Doesn't affect my sleep C. Improves my sleep
11. Carbohydrates, such as bread, crackers, before bed: A. Disturb my sleep. I sleep better if I eat light food Q. Doesn't affect me. S. Better than nothing. But I sleep better if I have a big dinner.
12. Sweets before bed: A. Doesn’t interfere with my sleep at all B. Sometimes they make me restless in bed. S. Keeps me up all night
13. How often do you eat every day? A. 2 or 3 times with snacks. B. 3 times and maybe 1 snack. C. 3 times with constant snacks.
14. Your attitude towards food: A. I often forget to eat. Q. I enjoy food and rarely forget to eat. S. I love food. This is the main part of my life.
15. When you skip a meal, you feel: A. Good B. Not as good as usual, but it doesn’t bother me that much C. Feel irritable, weak and tired.
16. How much do you like fatty foods? A. I don’t like it at all. B. Average C. I love it very much
17. When you eat a fruit salad for breakfast or lunch, you feel: A. Satisfied B. Normal, but I usually have a snack between meals. C. Unsatisfied and hungry
18. What type of food makes you feel exhausted? A. Fatty foods make me sleepy. Q. No food affects me like that. S. Fruits, sweets or confectionery make me active, and then a breakdown occurs.
19. The portions you eat are: A. Less than average B. Average, no more and no less than others. C. I eat large portions of food, usually larger than most people.
20. What do you think about potatoes? A. I don’t like potatoes B. I’m indifferent to them C. I love them.
21. Red meat makes you feel: A. tired B. Same as usual C. strong
22. Salad for lunch makes you: A. Full of energy and health B. Normal, but it’s not the best food for me C. Sleepy
23. What do you think about salt? A. Food is often too salty for me. B. I don’t care about salt C. I love salt and salt my food regularly
24. For a snack you will choose: A. I usually don’t snack. But if I do, it will be something sweet B. I can snack on anything C. I need snacks, I prefer meat, cheeses, eggs or nuts.
25. How do you feel about sour foods, such as pickles, lemon juice, vinegar? A. I really don’t like them B. I’m indifferent to them C. I like sour food.
26. When you just ate sweets, you: A. Sweets can satisfy my appetite B. I can only eat sweets, but that’s not enough C. I don’t feel full and often want more sweets.
27. When you eat only meat (bacon, sausage, ham, salmon) for breakfast, you: A. Become sleepy or irritable B. Always different C. Get full and not feel hungry until lunch
28. What would you like for dinner? A. Grilled fish, salad and rice B. A, or something from A and C C. Lamb chops, boiled carrots, baked potatoes
29. When you eat heavy or fatty foods, you: A. Become irritable B. It does not affect me C. It generally makes me calm and good-natured.
30. When you feel anxious, you: A. Eat fruits or vegetables B. Eat something to distract yourself C. Fatty foods make me calm.
31. You can concentrate better if you eat: A. Fruits and grains B. Usually nothing affects my concentration C. Meat and fatty foods.
32. You feel depressed when you eat: A. Fatty, heavy foods B. Food does not affect my mood C. Fruit, bread or sweets
33. You know your weight is increasing when you: A. Eat fatty foods B. Food does not affect my weight. I gain if I overeat C. Eat fruits and carbohydrates
34. What causes you insomnia? A. I rarely have insomnia from hunger B. I rarely have insomnia, but if it does, I need to eat something and I will fall asleep. S. It often happens to me that I wake up at night to eat something. If I eat before bed, I sleep well.
35. Your personality type: A. Calm, reserved, introvert. B. Not an introvert, not an extrovert. S. I am an extrovert.
36. Your emotional and physical state is better when you eat: A. Light protein foods (for example, egg whites), chicken, fish, fruits. B. Any healthy food C. Fatty foods
37. Do you prefer the climate: A. Warm or hot. V. I don't care. C. Cold climate.
38. Do you have problems with coughing or chest pain (pressure)? (if not, skip this question). S. Yes.
39. Does your skin ever get cracked or dandruff? (if not, skip this question). S. Yes.
40. Do you ever get dizzy? (if not, skip this question). S. Yes.
41. Your eyes are usually: A. Dry B. Normal C. Often watery
42. Your skin color: A. Very pale B. Normal color C. Pink or even red
43. Your nails: A. Thick B. Medium C. Thin
44. Do you have a gag reflex? A. Very rarely B. Normally C. Often
45. Do you ever get goose bumps? A. Often B. Sometimes C. Very rarely
46. You often have the following problems: A. Constipation B. There are no stomach problems C. Frustration (diarrhea)
47. If you are bitten by insects, what reaction do you have: A. Small B. Medium C. Strong
48. Your body type: A. Short and stocky B. Average A. Tall and thin
49. Your nose is usually: A. Dry B. Normal C. Wet
Calculation of test results
Count how many A, B and C you got after passing the test.
If the number of answers A is 5 or more more than B and C, then you have a slow metabolism
If the number of answers B exceeds A and C by 5 or more, or answers A, B and C do not exceed the other two types of answers by 5 or more, then you have a normal metabolism.
If the number of answers C exceeds A and B by 5 or more, then you have a fast metabolism.
Info: Jillian Michaels Winning by losing
More useful information:
How to speed up your metabolism?
You will also find a large amount of information on proper weight loss and a balanced diet in my project “Lose Weight in 12 Weeks”