Our modern lifestyle puts a lot of stress on our backs. We spend a lot of time on computers and smartphones. Also, driving a car, carrying huge bags of groceries, and many other factors that significantly overload the back muscles. That's why it's so important to train and keep her in shape.
In this article, you will discover the 13 best basic women's back exercises to recreate that elegant and impeccable posture and sculpt a strong and beautiful back. They can be performed both at home and in the gym, so you will no longer be able to avoid training.
A little about your back
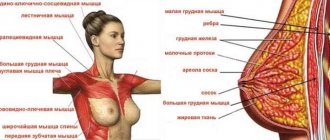
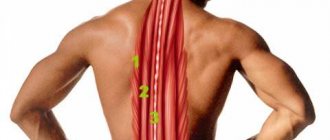
There are many large muscle groups in the back. The trapezius sits at the top, forming a diamond shape between your shoulders and the middle of your spine. Your rhomboids are located in the middle of your upper back, connecting the deltoids.
The largest muscles of the back are the latissimus, which cover the outer sides of the body and form that beautiful V of muscles. The lower back muscles, known as the erector spinae muscles, run on either side of the spine. Maintaining a strong and reliable spine will solve all the problems that may arise in the lumbar region, which are typical for many women. They also help improve your balance and coordination.
Strengthening and toning all areas of your back will not only give you a tight, firm, and stable spinal column. It will also lift your breasts, promoting the blossoming of your femininity.
A set of physical exercises to correct posture.
A set of physical exercises to correct posture.
Compiled by: Titareva Evgenia Vladimirovna.
Posture correction.
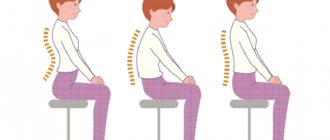
Correct posture is characterized by: straight position of the torso and head;
expanded chest; shoulders laid back, at the same level; moderate natural curves of the spine, legs fully straightened at the hip and knee joints, shoulder blades adjacent to the chest, located at the same height, stomach tucked. Correct posture.
The physiological curves of the spine are moderately expressed. The child holds his head and torso straight, his shoulders are at the same level and slightly turned, his stomach is tucked in, his legs are straight.
Most children, due to general functional weakness, hypotonic state of muscles and ligaments, low level of development of physical qualities and coordination abilities, have a wide variety of postural disorders, including all of its most typical forms.
Typical posture disorders.
1. Sluggish posture. The head is lowered, the chest and back are flattened, the shoulders are brought together, the legs are slightly bent. 2. Slouching. The head is pushed forward, the shoulders are strongly brought forward, the stomach is protruded. 3. Lordosis. Excessive deflection of the lumbar spine. 4. Scoliosis. Lateral curvature of the spine. Shoulder girdle asymmetry
To determine the type of postural disorder, a table is provided that lists all the signs of postural deviations from the norm. Often, poor posture is combined with flat feet, foot deformity, and clubfoot, which negatively affects the position of the pelvis and spine. Many mentally retarded schoolchildren have baggy posture, awkward movements, and a tense and unsteady gait. There are children with obvious paresis or paralysis of individual muscle groups. Children, as a rule, have an idea of correct posture and can demonstrate it quite accurately, especially against a vertical wall, but they immediately violate it when performing physical exercises, in everyday movements, walking, sitting at a desk. When correcting posture in younger schoolchildren with mental retardation, it is necessary to be guided by the following provisions. 1. The formation of posture is based on the harmonious development of the strength of the muscles of the back, abdominals, upper and lower extremities, the ability to differentiate muscle-joint sensations, the position of individual parts of the body in space, the ability to tense and relax muscles at rest and in motion. 2. It is necessary to use all types of adaptive physical education and all possible forms of physical education and health activities: morning hygienic gymnastics, physical education breaks, outdoor games, additional extracurricular and extracurricular activities, walks in the fresh air, swimming, hardening, etc. 3. On the part of parents it is necessary everyday attention to the child’s posture, creating conditions for its formation: adequate hygienic and physiological requirements for clothing, furniture, lighting, sleeping positions, sitting, standing, etc. 4. Correction of posture, on the one hand, includes a broad complex effect a wide variety of exercises for all muscle groups, on the other hand, the specific impact of purposefully selected exercises to compensate for violations of a certain type of posture.
Item no.
Exercises
Corrective focus
1.
"Kitty." From a standing position on all fours - lowering and raising the head with bending in the lumbar region, followed by extension in the thoracic and lumbar spine
Flexibility of the spine, strengthening of the muscular corset, coordination of movements of the head and torso, vestibular stability
2.
"Ring". From a kneeling position, hands on the waist - bending, bending back until your head touches the floor. Carried out with insurance
Spinal flexibility, abdominal stretching, back strengthening, vestibular stability, symmetry of movements
3.
"Vanka-Vstanka." From a sitting position with your knees bent as much as possible, pressed to your chest and clasped with your arms, roll back and return to the starting position without using your hands
Strengthening the muscles of the trunk, coordination of movements, differentiation of muscle sensations, orientation in space
4.
"Bird". From a sitting position on the floor, legs apart, arms to the sides (fix correct posture) - bend forward until your hands touch your toes, maintaining the position of your head, torso and arms
Flexibility of the lumbar spine, stretching of the back muscles, symmetry of movements, control over the position of body parts in space
5.
"Snake". From a lying position on your stomach, legs together, arms at shoulder level, palms forward - slowly straightening your arms and raising your head, bend as much as possible in the thoracic and lumbar regions, throwing your head back
Flexibility of the spine, stretching of the chest and abdominal muscles, control of force and timing characteristics of movement, resistance to vestibular irritation
6.
"Boat". From a lying position on your stomach, hands behind your back, raise your head, chest, legs, fix the pose, sway “on a boat”
Flexibility of the spine, static strength of the muscles of the shoulder girdle, back and abdomen
7.
"Swimmer". From a position lying on your chest - move your arms, as in breaststroke swimming on your chest, gradually increasing the amplitude and tempo of movements, without touching the floor with your hands
Strengthening the muscles of the trunk, coordination and symmetry of movements, differentiation of spatial and temporal characteristics of movement
8.
"Fish" From a lying position on your stomach, hands on your forearms on the floor, fingers forward - slowly straightening your arms, raise your head, bend in all parts of the spine and touch your feet, bent at the knees, to your head
Flexibility of the spine, stretching of the chest and abdominal muscles, strengthening of the torso muscles
9.
"Candle". From a lying position on your back, hands behind your head - first bend your knees, and then straighten them to a vertical position relative to the floor, fix the pose and slowly lower it to the starting position
Abdominal muscle strength, coordination of movements, spatial orientation, regulation of range of motion
10.
"Bike". From a lying position on your back, arms along the body and raising your legs to a vertical position - imitation of the movements of a cyclist, first slowly, with gradual acceleration
Strength of the abdominal muscles, coordination and rhythm of movements, differentiation of the tempo of movements
11.
"Arrow". From a lying position on the right side, the right arm is extended upward, the left one rests on the floor at shoulder level - abducting the left leg upward. The same - on the left side with the right leg abducted
Strengthening the lateral muscles of the torso, abdomen and legs, coordination of movements
12.
"Pendulum". From the starting position lying on your back, arms to the sides - raise your legs 900 and, without spreading them, lower them to your right, lift them up again and lower them to your left, without lifting your shoulders from the floor
Strengthening the abdominal muscles and lateral muscles of the body, coordination of movements, orientation in space, volitional effort
3 exercises for advanced women
Exercise #11: Dumbbell Pullover
Muscles involved:
- Primary: latissimus dorsi
- Secondary: deltoid muscle
Technique:
- Lie face up, bend your knees and hold a dumbbell between your palms. Extend your arms straight above your head.
- Without bending your arms, walk them back until the weight touches the floor behind you. This position works your lats.
- Also, without bending your arms, return the weight to the starting position, working the muscles of your upper back. Keep your abs tense throughout the movement.
Exercise No. 12: Lat Pulldown
The lat pulldown is an exercise performed on a machine that can be found in any gym. This exercise is the opposite movement of pull-ups. And as we all know, pull-ups are the best exercise for the back. However, it is very complex. The lat pulldown is a very good transition movement.
Muscles involved:
- Primary: latissimus dorsi
- Secondary: trapezoid
Technique:
- Stand in front of the machine. Sit on the seat and grasp the block with both hands. Your grip should be slightly wider than shoulder width.
- Place your knees under a pillow to support your upper body.
- Maintaining a neutral spine (allowing a slight arch in your back), lower your shoulder blades down and squeeze them together. Keep your chest lifted throughout the movement. Your elbows should fall down and to the sides, while looking at the floor. Pause in the down position.
- Slowly return to the starting position, feeling the full stretch in your back muscles.
Exercise No. 13: Straight Arm Pulldown
In this exercise you will use the same machine as in the previous one.
Muscles involved:
- Primary: latissimus dorsi
- Secondary: trapezoid
Technique:
- Stand shoulder-width apart, approximately arm's length from the machine. Grasp the block at shoulder level with your palms facing down. Your arms should be straight, but not rigidly motionless. Maintain a neutral spine.
- Lower your shoulder blades and squeeze them together, tensing your abs. Keeping your arms straight, pull the block toward the front of your thighs.
- Hold the bottom position for a few seconds and then slowly return to the starting position.
Back workout (first round – with dumbbells)
Exercises with your own weight are effective at first, but gradually the need for weight training arises. Training with dumbbells helps increase muscular endurance, overcome plateaus and improve progress.
The first round of our workout includes back strengthening exercises with dumbbells. At home, you can use water bottles instead of dumbbells.
How to do strength training with dumbbells on the back for girls:
- For a complete strength training on the back. Perform each exercise 10-12 repetitions for 3-4 sets. Rest 30-60 seconds between sets, 2-3 minutes between exercises.
- For a short strength workout on the back. Perform each exercise for 15 repetitions, one after the other. Rest 15-30 seconds between exercises.
- For circular strength training on the back. Perform exercises according to the scheme 40 seconds work / 20 seconds rest. You can repeat the workout in 2 laps.
Before training, we recommend performing a joint warm-up.
Dumbbell row with elbows raised
How to do it: Take the equipment in your hands, stand and place your feet shoulder-width apart, take a stable position with your heels supported. Bend your knees slightly, lean forward, and lower your arms freely down. Pull the dumbbells to your chest, spreading your elbows out to the sides and bringing them above your shoulders. Return to the starting point. Start the pulling movement by contracting the back muscles.
Benefits of the exercise: Working on the latissimus dorsi, posterior deltas, trapezius, teres minor, teres major, and infraspinatus muscles. The posture straightens, and the shoulders straighten and open. The upper spine is stabilized.
"Good morning" with dumbbells on shoulders
How to do it: Stay standing in a stable position with your heels supported, the dumbbells over your shoulders, and your elbows out to the sides. Bend your knees slightly. Begin to simultaneously tilt your body forward and move your pelvis back. Do not throw your head and neck back, but keep a slight arch in your lower back. As soon as you lower your top to parallel to the floor, return to the starting position by pushing your pelvis slightly forward.
Benefits of the exercise: Strengthening and strengthening the lower back muscles with back extensors. This stabilizes the spine and improves posture. Although “good morning” is included in the back workout, the load also affects the hips and buttocks, which is no less important for girls.
One-arm dumbbell row for back
How to do it: Leave the support on one leg, move the other slightly back, slightly bend your knees and lean forward. Fix a slight bend in the lower back, without abduction of the pelvis. Place one hand on your supporting thigh, and with the other take a dumbbell and lower it freely down. Perform a deadlift - move clearly along the body, with the dumbbell at chest level at the end point. Lower it back down.
Benefits of the exercise: Accented work on the latissimus dorsi muscles, part of the load is taken by the rear deltoids, trapezius, rhomboid muscles, biceps and spinal extensors. Posture improves and the waist visually narrows.
Bent-over dumbbell raises
How to do it: Go into a classic stance, place your feet at shoulder length, find a clear position. Take the inventory in your hands. Bend your knees a little, lean forward, but not reaching parallel with the floor. Leave a slight curve in your lower back. Place your arms in front of you and clasp your hands together. Swing to the sides to shoulder level. Return to the start of the movement and repeat.
Benefit of the exercise: Uniform pumping of the posterior deltoid with the infraspinatus, teres minor and major, trapezius muscles. The diamond-shaped fascicles are also used in strength exercises for the back, as they bring the shoulder blades together.
Lifting opposite arms and legs while lying down
How to do it: Move to a lying position on your stomach, stretch into a line - legs together, arms extended forward. Take light dumbbells in your palms, but you can do this without weights. At the same time, raise your right leg and left arm, without lifting your body from the floor, just slightly your head. Lower, then switch sides.
Benefits of the exercise: Targeted load on the quadratus muscle in the lumbar area, spinal erectors. Posture improves and the muscle corset is strengthened. This strength exercise for the back also works the buttocks, legs and shoulder girdle. Lifting is useful for preparing the body for serious exercise.
Don't forget to work on your core for a healthy spine:
- Core muscles: 30 effective exercises
- Top 10 Planks for a Flat Stomach: Core Workout
Getting rid of back fat
Now you have a large set of exercises to work your entire back. But what about those fat folds and rolls that form under your bra? Will these exercises get rid of this?
Yes, but while maintaining a calorie deficit in the diet.
Stored fat will not simply disappear when you perform the targeted exercises listed above. However, if you combine our exercises with regular cardio exercises, you will burn fat from all parts of the body, including your back. A healthy, balanced diet is also necessary to ensure that the calories entering your body are used for energy rather than stored as fat.
Jogging, cycling and using an elliptical machine are good choices if you need to shed extra pounds. However, to burn fat faster, you should consider doing a HIIT workout.
HIIT involves performing hard, fast exercises for a short period of time, followed by even shorter periods of rest. For example, you can do HIIT on a stationary bike. First, do a two-minute warm-up, then move up to your maximum speed for 30 seconds and select the highest level of resistance you can handle. Then give yourself 20 seconds to recover. Now do a second such sprint for 30 seconds. Repeat this cycle 6-8 times.