Everyone who improves their physical fitness has a priority exercise. Usually for girls it’s working the abs and buttocks, for men it’s working the biceps and shoulders. Back training is often given secondary importance: it is not visible under clothes. However, it is the back that is the core that shapes the figure. The latissimus muscles, called the “wings,” play an important role in this. Let's look at how to pump them up in the gym and at home.
- Latissimus dorsi muscle: anatomical information
- How to pump up your “wings” at home: training the latissimus dorsi muscles at home
- Pull-ups on the horizontal bar will help pump up your “wings”
- Video: pull-up exercise technique for pumping up “wings”
- Pushups
- Dumbbell rows
- Bent-over dumbbell row
- Latissimus muscle training in the gym
- Bent-over barbell row
- Video: bent over barbell row technique
- Pullover
- T-bar row
- Latissimus muscle training: secrets of effectiveness
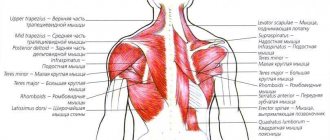
Anatomy and structure of the latissimus dorsi muscles
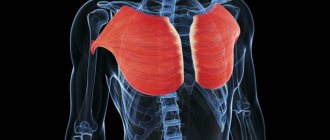
The latissimus muscle is a superficial layer of the lower and partly the middle part of the back. It has a triangular shape. In sports, the term wings is often used for these back muscles, which is also related to the shape of the lats. They are considered one of the largest muscles in the body. The upper bundles have a lateral fiber direction and are partially covered by the trapezius muscle. The lower beams are directed obliquely, upward and to the side.
If you look at the photo of the latissimus dorsi muscles, you will see that it originates from:
- 5-6 lower thoracic vertebrae.
- 4 lower ribs.
- All sacral and lumbar vertebrae.
- Superficial layer of the thoracolumbar fascia.
- Sacral crest.
- Posterior part of the outer lip of the iliac crest.
The muscle is attached to the crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus.
The direction of the muscle fibers is different, so exercises for the wings of the back should be selected taking into account the anatomical features. The upper beams have a predominantly horizontal orientation, and the lower beams have a diagonal direction.
Training principles for a wide back
The back muscles are usually divided into three parts:
- The top is formed mainly by trapezoids.
- The middle part is the most massive part, represented by the widest.
- Lumbar region.
Many movements involve the upper and middle parts. Therefore, there is no need to work on each area separately. The lower back is usually worked with general movements (like deadlifts), as well as focused ones with the help of hyperextensions.
If we consider a wide back in men as the goal of training, then the main emphasis should be on the latissimus muscles. However, it should be remembered that training cannot influence only the width or thickness. The shape of each person's muscles is determined by genetics. With the help of physical activity, you can increase the muscle in volume, from which it will not grow in width, but increase in size, depending on its shape.
Therefore, any attempts to purposefully expand the back beyond one’s genetic potential will not be successful; it is simply impossible. This means that any specialized exercises for the width of the back will reduce the overall effectiveness of the training.
In order for a muscle to grow, it is enough to give it a systematic load with progression, choosing the most effective movements. This is the secret of how to pump up a wide back.
Basic rules for back training:
- Train the group once a week, allowing 4-5 days for full recovery.
- Prioritize your back in splits (for example, in the classic chest/back version).
- Focus on exercises that engage as many muscle fibers as possible (that is, basic and compound movements).
- Remember the main rule for maintaining the effectiveness of the exercise - your back should be straight.
- Learns to tense the latissimus muscles (an important element in increasing the efficiency of movements).
You should also provide a powerful stretch to the muscles. In order to make the back wider and fully utilize the lats, taking into account their functions, the movements must involve shoulder work (the rear deltoid is primarily responsible for this). The indicator is the shoulder blades; at the top point in most exercises they should converge, at the bottom point they should diverge, with a slight drop in the shoulder (this will give the desired stretch). Whether you're doing wide back exercises at home or at the gym, you almost always end up doing some stretching at the end of the session.
Workout Features
Although training the latissimus dorsi muscles is quite simple and requires only an understanding of the basic functions to maximize effectiveness, many athletes neglect the basic rules. This reduces the overall benefit of exercise and slows progression. To pump up the latissimus dorsi muscles, it is recommended to follow a number of basic rules that are related to the specifics and characteristics of the group:
- When performing traction movements, it is necessary to prevent swaying of the body (in exercises, “swinging” of the body is allowed no more than 10 degrees. This contributes to better stretching of the muscle at the peak point).
- When performing exercises for the latissimus dorsi muscles, it is necessary to exclude the use of hands as much as possible (use them only to support the weight).
- The ability to focus on the group being worked on is important. The ability to contract your lats even at rest is the first step towards increasing the effectiveness of your training.
- Movements are performed only in full amplitude (with the exception of some exercises and techniques, for example, static dynamics).
- To pump the latissimus dorsi muscles, you need to work with heavy weights and high load intensity.
The back lends itself well to high-volume training. You can perform at least 10 failure sets of lat exercises, and the average work range per workout can range from 13 to 25 sets without the risk of overtraining.
The main thing is to be able to concentrate the load so that in back exercises in the gym the latissimus muscles take on the main load.
Back exercises without equipment
Back exercises without equipment demonstrate equally high-quality results, despite the fact that the athlete trains without weights. This is the best option for people who do not have dumbbells at home, but want to work hard on their figure.
However, even if you have dumbbells, we recommend performing the proposed back exercises without equipment for a more effective and comprehensive workout of the back muscles. In addition, the exercises presented below strengthen the spine and improve your back health.
You can perform back exercises without equipment in the second round after exercises with dumbbells or on a separate day. The lesson plan is suggested below.
Abduction of hands to the buttocks
What are the benefits : This is an optimal and simple back exercise without equipment, which works the latissimus muscles and has a beneficial effect on strengthening the shoulder muscles. This is the optimal element of back training for beginner athletes, as it is absolutely safe and at the same time very effective.
How to do it : Lie on your stomach on a gymnastic mat, then stretch your upper and lower limbs lengthwise. Alternately, begin to move your hands to your hips, performing short pauses at the peak point. Take your time, making sure to thoroughly work your back and shoulders. The wider the swing, the greater the load.
Hyperextension lying on stomach
What are the benefits : Exercise for the back at home puts an emphasis on the lumbar region, and also helps strengthen the muscles that support the spinal column. This is another element that is optimal for beginners. The exercise helps correct posture, straightens the back and opens the thoracic spine.
How to do it : Take a lying position with your stomach down on a gymnastic mat, then bring your palms together at the back of your head, straightening your elbows in opposite directions. Now lift your body up, relying solely on the strength of the lumbar muscles. Pause at the top to feel maximum tension.
"Butterfly"
What are the benefits : A back exercise without equipment is aimed at working the latissimus muscle. Often used as a warm-up before doing pull-ups on the horizontal bar. The rear and front deltoids take no less part in the work, which helps strengthen the shoulders and make them more prominent.
How to do it : Lying on your stomach, stretch your arms forward, then lift them off the floor. Also raise the top of the case slightly. Now move your upper limbs to your hips through your sides, briefly fixing the position at peak amplitude. The legs do not come off the floor, but advanced practitioners can lift their hips synchronously with the movement of their arms. This will complicate the exercise, but will help pump up the buttocks and back of the thigh.
"Butterfly" with arm curls
What are the benefits : This variation of the exercise relieves some of the tension from the shoulder muscles, focusing on the work of the latissimus muscle. The posterior bundle of deltoids is still involved in the work, but it is less tense than in the classic “butterfly”. Additionally, the rhomboid muscles are involved in the process.
How to do it : Lie on your stomach on a gymnastics mat and slightly raise your upper body. Stretch your arms in front of you, and then begin to pull yourself back, as if you were pulling yourself up on a horizontal bar (this will make it easier to master the technique). Press your feet to the floor so as not to create additional stress on the muscles of the lumbar region.
"Superman"
What are the benefits : The at-home element of back training is one of the most effective, using the spinal erector muscles, buttocks, hamstrings, stabilizers and deltoids. This is a great exercise for both beginners and advanced, as Superman is extremely effective.
How to do it : Lying on your stomach, lift your head off the floor. Stretch your lower and upper limbs lengthwise, then begin to simultaneously lift them 10 cm from the floor, making second delays at peak amplitude. After it, the arms and legs return back.
"Swimmer"
What are the benefits : The presented back exercise without equipment ensures an even load on all muscle groups of the back, and also has a beneficial effect on the development of flexibility of the spinal column. In addition, the training element improves coordination of movements, due to which it is often used in rehabilitation practice.
How to do it : Lying on your stomach, stretch your upper and lower limbs lengthwise. Your task is to alternately raise opposite arms and legs as if you were swimming. Do not make the amplitude too wide so as not to overload the lower back.
Raising arms apart while lying on your stomach
What are the benefits : The presented exercise emphasizes the load in the area of the posterior bundles of the deltoid muscles, strengthens the rhomboid muscles, and also promotes the development of the trapezius. In addition to developing strength characteristics, the exercise straightens your posture, helping to make your shoulders more prominent.
How to do it : Lying on your stomach, spread your arms so that your body assumes a T-shape position. Palms face down. Lift your head slightly off the floor. After this, lift your upper limbs until you feel tension in the back of the deltoids. This simple exercise is also great for working on your posture.
Superman in plank
What are the benefits : This is a complicated variation of the classic hand plank exercise, which loads the back, legs, and also increases the overall endurance of the athlete. During the work process, the abs and stabilizing muscles play an important role. This is an excellent exercise for developing coordination of movements and a very effective element for athletes who want to get rid of excess subcutaneous fat, tighten their stomach and all muscles in general.
How to perform : The execution system is extremely simple, since from a prone position (hand planks), you need to raise opposite arms and legs, while maintaining the position of the torso with the limbs standing on the floor. When mastering the technique, take your time, trying to carefully work through the full amplitude of the exercise.
Plank + front kicks
What is the benefit : Since the plank is an exercise for developing the athlete’s static strength, the muscles of the entire body are under tension. Particular stress is placed on the back and abdominal muscles. These areas maintain a static position of the torso during work. The extra punches will help you stretch your lats and also strengthen your shoulder muscles.
How to do it : To begin, take the classic plank position while standing on your elbows. With your gaze directed in front of you, begin to perform alternating strikes in front of you with each hand in turn. With your arm extended, pause briefly to make the exercise slightly more difficult.
Circular arm swings in plank
What are the benefits : An exercise for the back at home perfectly works the latissimus muscle, loads the deltoids, and also strengthens the entire body as a whole, since the work is done from an emphasis while lying in a static position. The muscles of the back and abdomen are constantly under tension, due to which not only the strength indicators, but also the endurance of the athlete increase.
How to do it : Taking a classic position while lying on outstretched arms, begin to perform circular rotations of one arm, the other arm remains the supporting one. Take your time, trying to make the amplitude of the circular swings as wide as possible. Since during rotation the body is supported on three points of support, it is necessary to carefully monitor your posture, avoiding strong deflections of the back.
Reverse plank pelvic lift
What are the benefits : This is another exercise that puts an accentuated load on the muscles of the lumbar region. In addition, the gluteal muscles are involved in the work, the triceps of the arms and abs are strengthened. The presented training element will be especially useful for people with weak back and lower back muscles.
How to do it : Sitting on the floor, rest your arms on it and slightly move your body back. After this, begin to raise your pelvis until your body and legs form an even, straight line. You need to pause at the peak point to fix the position and feel the tension of the working muscles. Take your time, the pace of the exercise is average.
Hand to toe row from plank position
What are the benefits : Not only the back muscles, but also the arms, abs and legs take part in the work process. Get ready to give your entire body a good workout. This is a complex exercise that is optimally used during fat-burning training. Due to its high complexity, it is recommended for experienced athletes who already have a strong physical base.
How to do it : Having assumed the position of a classic prone position, you need to alternately touch the toes of opposite legs with your hands (left hand to right leg and vice versa). During the movement, the pelvis rises, but the back does not slouch, maintaining a natural deflection. The weight of the torso at its peak amplitude is held at three points, which additionally forces the stabilizing muscles to work.
Body rotations with arm raises from plank position
What are the benefits : This is an excellent exercise for strengthening the thoracolumbar fascia, serratus externus, and oblique abdominal muscles. The latissimus muscle, rear deltoids, and buttocks are also involved in the work. Since the work is done from the plank, such turns increase the overall endurance of the athlete.
How to do it : Assuming a plank position on your elbows, rotate your body so that it is perpendicular to the floor in a side position. At the same time, raise your hand up, then fix the position for a second and return back.
Top 4 exercises for the latissimus muscles for the gym and at home
In sports, there are 4 main types of exercises for the latissimus dorsi muscles with dumbbells, barbells and other equipment. Each type has many variations of execution that allow you to change the nature of the load to avoid muscle adaptation. These 4 exercises are fully enough to pump up your lats.
Pull-ups
Ultimate and basic movement for working out the entire group. It is deservedly considered the best exercise for the latissimus dorsi muscles. If you have a weak level of physical fitness, you can perform it with the support of rubber bands (or use lightweight techniques, such as horizontal pull-ups).
Technique:
- Hang from the horizontal bar, holding the handles (or bar) with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Begin to pull your body up using your back muscles (at the top point, your arms and shoulders are more involved in the work).
- As soon as your chin crosses the line of the bar, pause and return to the starting position.
- At the lowest point, it is important not to spread your shoulder blades or relax your shoulders, as this can increase the risk of injury.
- Use the grip that allows you to make the movement cleanly and without jerking (with greater development of the biceps, when the triceps becomes a limiting factor, you can master the technique with a reverse grip).
Read more about pull-ups for back muscles →
Bent-over row
It can be used in different variations, but the specificity of the exercise is the same. For variety, you can alternate options:
- Bent-over row with a barbell.
- Alternately with dumbbells with emphasis on the bench..
- Together with dumbbells.
- With rubber band/expander.
- With bottom block.
- In the Smith machine.
- The technique for each exercise will be different, but in all movements it is important to perform the pull using the back , not the arms (the arms only engage when bringing the weight to the body).
- also important to exclude any inertia . Unlike other types of rods, the body must be fixed.
Vertical block thrust
Although this movement is often called a “pull-up replacement,” it is actually incredibly effective. Taking into account the fact that a huge part of athletes (and almost all beginners) cannot do full pull-ups, working with the upper block becomes one of the best among all exercise machines for the latissimus dorsi muscles.
Technique:
- Take the (long) handle with a wide grip and lower yourself onto the seat. The back should be straight, the elbows should be pulled straight to the sides (for the correct position of the shoulder and arm).
- Start pulling the handle towards you without changing the position of your body. The pull is carried out to the upper chest.
- To avoid damaging your nose or face, your head can be pulled back when lowering the handle (no more than 2-3 cm).
- Pause at the bottom and return to the starting position.
Read more about vertical block traction →
Horizontal rods
The peculiarity of these movements for pumping the latissimus dorsi muscles lies in the position of the body. In the lever pull, it is securely fixed and any swinging is excluded - the load will fall on the target muscle. In block deadlifts, on the contrary, it is recommended to swing the body a little, in the range of 10 degrees. This allows for a better stretch of the lats while abducting the handle.
Technique for performing horizontal traction (in a block):
- Sit on the bench and grab the handle so that the cable is taut in the starting position.
- Begin to pull the handle towards your lower abdomen, straightening your shoulders in parallel.
- Pause and return the handle to the starting position (bend your shoulders forward a little to stretch the muscles).
In the exercise, it is important to avoid rocking the body, rounding the back, and pulling with the arms and shoulders.
Exercises for home
In most cases, exercises performed at home for the latissimus dorsi muscles will be a replacement or alternative to movements from the gym:
- Pull-ups - there is nothing to replace them at home; they are performed only with a horizontal bar.
- Horizontal pull-ups – TRX loops, gymnastic rings.
- Vertical traction – in the presence of a horizontal bar and a harness (which will provide tension and the required load).
- Bent-over rows - using dumbbells, a tourniquet, a sandbag, or even a bottle of water or sand (the movement technique does not change).
- Horizontal traction - only with a tourniquet.
These options allow you to completely replace all movements and efficiently work out the lats without losing efficiency.
What about deadlifts?
Separately, it is worth noting the deadlift. This is a technically complex exercise for the latissimus dorsi muscles for men, which is very popular. It is a mistake to use it to load the lats, because the upper back does most of the work. The lats are loaded primarily in the lower part.
Home workouts without special equipment
If you don’t have any additional equipment in your arsenal, but you want to get yourself in order, you shouldn’t despair, it’s enough to show a little ingenuity and perform basic exercises technically correctly.
To begin with, you can simply do push-ups from the floor. There are a lot of variations of this exercise, with the help of which you can regulate which muscle group needs to be directed more load. If you need to work on the latissimus muscles, then you should opt for push-ups with a wide support with your hands.
To begin with, you can simply do push-ups from the floor
Hyperextension provides an excellent load on the lumbar region and longus muscle. To perform it, you can use a bed, a sofa, a bench, or a large sports ball (fitball). Its essence lies in the fact that it is necessary to fix the legs, while the body does not lie on the surface, but seems to hang over the edge parallel to the floor. From this position, you need to lower your torso down and raise your top, maybe a little higher than the level of your legs, bending at the lower back. You can change position, fix your arms and perform up and down movements with your legs.
The “bridge” exercise, known since childhood, pumps and stretches the back muscles well. Beginners perform it from a lying position, focusing on the feet and palms. At the same time, the body rises, arching its back. It is enough to do 2-3 approaches, increasing by one every month. More experienced athletes do it from a standing position, bending backward until the arms raised above the head rest on the floor with the palms.
The “bridge” exercise, known since childhood, pumps and stretches the back muscles well.
You can do chest rows with one arm at home. For support, use any hard surface of suitable height (bench, coffee table), and dumbbells can be replaced with cans of water.
The main thing is to perform the exercises technically correctly. Most of them are done with a perfectly straight back, when only the natural deflection is maintained in the lower back. It is important to monitor this very carefully to prevent injury.
Broadest program
- Warm up – 5 minutes.
- Pull-ups – 5* to failure.
- Bent-over barbell row – 4*8.
- Horizontal thrust in the block – 4*10.
- Bent-over dumbbell row – 4*10.
- Lever rod (alternately with each hand) – 4*10.
- Muscle stretching.
Who needs to pump up their back and why?
To pump up a sculpted back, you need to work with deep and superficial muscles.
It is customary to distinguish between deep and superficial muscles.
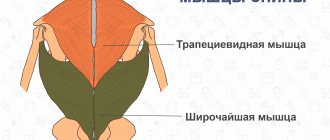
The deep or longitudinal muscles include the transverse spinalis - 3 groups of muscles that ensure the stability of the spine and its movement. Extensors are considered to be trained. The rest participate in the exercises, but cannot act as targets. This also includes the rhomboid and trapezius muscles - the wing. They are responsible for the movement of the scapula and the position of the neck.
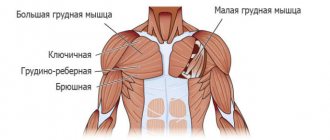
Superficial muscles are called the latissimus - the largest muscle of the back, the quadratus muscle, which is responsible for the work of the lower back, the large round muscle and the posterior bundle of deltas. They provide posture, stable position of the body in space and the actual movement of the body.
The back muscles are the base of the body. Any athlete needs to develop them, regardless of gender, level and training goals. The reasons are as follows:
- The latissimus and other muscles of the back are a large group. Pumping provides a serious increase in the athlete’s muscle mass.
- The back is involved in most basic exercises. Without a strong lower and mid-back, training your butt, chest, and abs becomes difficult.
- Developed spinal muscles are the key to normal functioning of the spine. Posture, flexibility, ease of movement - all this depends on the muscles, since they move the spine, and not vice versa.
- The V-shaped silhouette and thin waist at the back are created by the widest.
- The spinal frame supports the position of the spine when walking. No problems with hip joints and knees are guaranteed.
- Along with the lumbar and upper back, the arms are also pumped - triceps, biceps, brachialis. Working with a kettlebell and a barbell is a great option for working on your grip.
To pump up various back muscles, just basic exercises are not enough. Deltas, trapezoids, and diamonds need to be worked on additionally. This is especially important for people engaged in sedentary work. In this position, the muscles that hold the shoulder blades and neck are subjected to too much stress, enter a state of hypertonicity and cause headaches and discomfort in the upper back.
Exercises for the lower back muscles
It is better to leave this group of exercises for the end of the lesson. By strengthening the lumbar muscles, the risk of spinal problems is reduced.
Exercises with weights
Deadlift
This exercise works almost all the muscles in your back and is essential for increasing muscle mass.
- I.p. – standing in front of an empty bar, your legs should be placed slightly narrower than your shoulders, your feet parallel to each other. Keep your back straight and your pelvis pushed back, which creates a natural arch in your lower back. Make sure your back is not round.
- Next, tilt your body slightly forward, pushing your pelvis back. If you did everything correctly, your shoulders will be slightly in front of your shin line. The knees will be slightly bent. The tilt should be made at an angle of 40-45º.
- Squat down to grab the bar with your palms facing you. Make sure your body remains motionless. The shoulders should move along a vertical axis.
- Slowly straighten your legs, and only then straighten your back. When you stand up straight, your shoulder blades should be squeezed together.
- Then start lowering the bar. First, bend your back 40-45º, then your legs.
Do 10-15 repetitions for 3-4 sets.
Deadlift
Before you begin this exercise, make sure you have a good stretch in your lower back and back of your thighs. The main technical points of this exercise are the same as in a regular deadlift.
- I.p. – standing, feet shoulder-width apart, toes under the barbell.
- Do a squat and grab the barbell with the following grip: one hand on top, the other on bottom. The grip should be shoulder width apart.
- The back should be straight. When the bar is above your knees, sharply straighten your legs. Make sure your chest and shoulders are back. Maintain a stable position.
Perform 10-12 repetitions of 3-4 sets.
Sumo deadlift
This deadlift is similar to the classic version, but there are important differences. One of them is that leg stretching is important for this exercise. Also, the feet need to be turned 45º degrees, and the legs should be set quite wide.
- Place your feet wider than your shoulders. Consider your height: the taller you are, the wider your feet should be. The lower back should have a natural arch due to the pelvis moving back. Keep your head straight.
- Do a deep squat with your body slightly bent. Take the bar with a close grip.
- You must lift the barbell using your leg muscles. When your legs are completely straight, straighten your body and squeeze your shoulder blades together.
- There should be no breaks between the work of the legs and lower back; all movements are smooth and measured.
Do 15-20 repetitions for 3-4 sets. Gradually increase the weight.
Forward bends using a barbell
This exercise is the most effective for training the lower back:
- Feet shoulder width apart. Take a barbell with a wide grip, place it on your trapezius and stand straight.
- I.p. – stand up straight, bend your back slightly at the lower back. The lower back muscles should be tense, and your legs should be slightly bent at the knees.
- While inhaling deeply, slowly lean forward while moving your pelvis back.
- When the body is parallel to the floor, take the position.
Perform 10-12 inclines in 3-4 sets.
How to pump up the back muscles along the spine. How to strengthen your spine?
Below are the basic rules for strengthening the spine at home, which should be followed systematically and with full dedication.
Lifestyle changes. In fact, strengthening your spine starts with your lifestyle and daily habits. All this together is very important: gait, posture, sitting at the computer, etc. All bad habits can affect the condition of the spine, so you should get rid of them.
3 habits for a healthy spine!
- Walk more! With regular walks, you increase not only the blood circulation of the spine itself, but also of all the muscles surrounding it, and also stretch the ligaments and tendons.
- Keep your back straight! With incorrect posture, the risks of developing osteochondrosis and back pain increase. Therefore, you must always maintain your posture and all the natural curves of the spine.
- Short breaks from the computer! Take a break every hour for 5-10 minutes, this is the minimum that will help you get rid of overstrain and fatigue of your back muscles and ligaments.
Do exercises to strengthen your spine. The muscles of the spine are the only support for it, without which it is simply not able to withstand the load and remain healthy. Therefore, it is so important to train the muscles of the spine: tone, strength, elasticity and blood circulation. If you train regularly and correctly (at least 15-20 minutes a day), your muscles will become stronger and more resilient, and your spine will receive a powerful frame. They will take on the load, which will relieve tension from the spine. Below are exercises to strengthen all parts of the spine at home.
Massage . To strengthen and maintain the spine, it is recommended to conduct back and neck massage courses in 5-10 sessions. If this is not possible, then at least do self-massage.
Proper and balanced nutrition. What we eat goes into our body and into all tissues, so the spine is no exception. It gets everything you eat (nutrients and vitamins). If you eat unhealthy food that is poor in vitamins and minerals, then your spine will receive only toxins and “empty” substances. But if your diet is balanced with all nutrients (proteins, fats and carbohydrates), vitamins, fiber and microelements, then the spine and all surrounding tissues receive full support. Therefore, try to eat more natural and natural foods, reduce your consumption of processed foods, preservatives and dyes. Try to replace harmful products with healthy analogues.
To consolidate the material, you can look at this
- Swim and dive more - this will strengthen and improve the condition of the spine as a whole.
- Use special orthopedic insoles and corsets.
- Drink healthy teas to strengthen the spine: rose hips, rowan and hawthorn.
Is it possible to train effectively at home?
The answer is clear: of course yes! Home exercises for the back have repeatedly proven their effectiveness. Undoubtedly, it would be incorrect to draw a parallel between even the most intense home workout and training in the gym, however, if we talk about achieving an effect and a visible result, then back exercises at home will definitely give it.
For what reason does training outside the gym not give the same significant results? It's all about the scales: constantly increasing the working weight, the load of which falls on the muscle group, is the key to progression and growth. In everyday conditions, it is almost impossible to ensure the availability of different-sized free weights suitable for use in training. But it is worth emphasizing once again that very large weights are necessary for trainees with an experience of regular training of 2 years or more, so pumping up your back at home at the start of the path to a beautiful and powerful back is more than realistic.