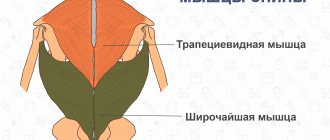
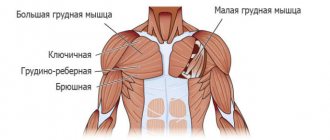
The back is a fragile, delicately balanced structure that can be easily damaged if not properly cared for. How to forget about pain and poor posture forever?
Anyone who has encountered spinal problems at least once will forever remember these painful sensations and dreams of strengthening their back muscles to avoid relapse. However, everyone needs to think about strengthening their back muscles.
Your back is your body's primary support structure. Together with the muscles and joints, it allows us to move, sit, stand, bend, and carry free weight. But the back is a fragile structure that can be easily damaged if you do not take care of strengthening it in advance. Knowing the basics of maintaining a healthy back, you can forever forget about pain and incorrect posture.
Back muscles and spine: a little anatomy
The spine is made up of 24 moving bones, the vertebrae, between which are cushion-like structures called discs that absorb shock.
The vertebrae and discs are supported by ligaments and muscles that keep the back straight in three balanced curves. When one of the components begins to hurt or gets injured, back pain and problems will almost certainly follow.
A healthy back is a balanced state of the muscles of the back and spine, when the cervical, thoracic and lumbar curves are aligned correctly (a state when the ears, shoulders and hips lie on the same line). Back health also depends on the flexibility and elasticity of the discs and good muscle condition, which can only be achieved by working on strengthening.
How to strengthen your back muscles
Exercise is an important part of strengthening, improving and maintaining normal back function. Regular exercise plays an important role in preventing back injuries and pain, and it has a beneficial effect not only on your back health, but also on your overall fitness level.
An example of a high-quality program would be the following training complex from Dmitry Yashankin:
Next, we will consider strengthening exercises in more detail, which will be useful both at home for independent training, and as a complement to the main program.
Please note: The exercises below are suggested for those who are not currently experiencing back pain. If you are worried about pain during physical activity, you need to adjust this complex according to your doctor’s recommendations, but under no circumstances should you continue exercising through pain.
Exercises to strengthen the back can be divided into the following three groups:
- Strength: repeated muscle contractions to the point of fatigue
- Stretching: slow static muscle stretching
- Aerobic: exercises that involve large muscle groups
All exercises should be performed slowly, without discomfort, to avoid injury. When doing strength exercises and stretching, remember to breathe in a natural manner: inhale at the moment of tension and peak load, exhale when relaxing.
Strength exercises for strong back muscles
Strength training is the best answer to the question “how to quickly strengthen your back muscles.” Such exercises help increase tone, strengthen the back muscles and improve muscle condition.
Developed abdominal and back muscles help stabilize the spine, making it easier to maintain posture and correctly perform movements that involve the back. Strong hips and leg muscles are also important for proper lifting technique and body mechanics.
You can easily strengthen your back muscles at home with the following exercises.
Upper press crunches
Lie with your back on the floor, place your arms along your body, bend your knees, press your pelvis so that there is no arch in your back or it is minimal. Raise your shoulders and head so that your shoulder blades lift off the floor. Hold for 5-10 seconds, repeat 10 times.
Twisting (crunches)
Oblique crunches
Like all abdominal exercises, oblique crunches are also great for strengthening your back. Lie with your back on the floor, raise your head and move your shoulders towards the opposite hip, stretch your arms forward. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times, then do the same number of times in the other direction.
Oblique crunches on a bench
Superman - body and leg lift
One of the best exercises for the back muscles without using weights. Lie face down, arms along your body. Tighten your buttocks and lift your head and shoulders as high off the floor as possible so that you feel like Superman above the floor. Hold for 5-10 seconds, repeat 10 times.
Exercise "Superman"
Various arm and leg raises
The technique is similar to the previous exercise. It involves opposite pairs of arms and legs.
Lie face down on the floor, place a rolled towel under your forehead, and stretch your arms above your head. Place a pillow under your pelvis and stomach. Keeping your right knee straight, lift your leg 3-5 cm from the floor and at the same time lift your left arm off the floor. Hold for 5 seconds. Do it with the other leg and arm. Repeat 10 times for each side.
This exercise can also be performed on a fitball (gymnastic ball) or from a standing position on all fours for greater activation of the stabilizer muscles.
Physical therapy exercises, physical therapy
If unpleasant pain symptoms appear, it is recommended to expand the complex through exercise therapy. Therapeutic exercises have long been considered an effective way to combat the symptoms of a spinal hernia at any stage of its manifestation.
Surgical intervention is used very rarely; the main approach in medical practice for treating and restoring the back is gymnastic exercises:
- Exercises for the spine and pain relief using the Bubnovsky method
- Sets of exercises for back and lower back pain
Physiotherapy for recovery
Physiotherapy is prescribed to the patient already at the second stage of treatment, when doctors allow him to gradually restore motor functions. Such procedures help restore muscles, bone tissue and nerves. During rehabilitation, the following methods are used:
- UHF is used to reduce pain, relieve swelling and improve blood circulation.
- Electrophoresis – helps to introduce medications into the body for better effect.
- Myostimulation is muscle contraction using electrical current pulses. Helps relieve stress, pain, and muscle tension.
- Paraffin-ozokerite sessions are the application of different types of energy to a diseased area of the body (in this case, thermal energy). The method helps improve muscle condition.
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart apparatus is a treatment method consisting of physical exercises necessary to strengthen muscle groups. Performing these exercises on a special device helps get rid of joint pain and normalizes blood circulation.
- Carboxytherapy is a treatment with carbon dioxide, one of the new methods of therapy, very effective for degenerative diseases of the joints and spine.
- Ural rays are used to destroy harmful microflora.
- Balneotherapy – treatment with mineral waters improves blood circulation and reduces muscle tension.
- Magnetic therapy – relieves pain and speeds up recovery.
Stretching and strengthening the back muscle corset
Adequate flexibility in the tissues around the spine and pelvis allows you to move easily using your back, prevents stress on your joints, and reduces the likelihood of injury.
Stretching and flexibility exercises also prepare muscles for physical activity. Stretching should be done before and after every intense workout to prevent muscle strain, soreness, and injury during the workout.
Perform the exercises at a slow pace, stretching as far as your fitness allows.
Lying hamstring stretch
You might be surprised, but this exercise will also help prepare your body for back-strengthening exercises. Lie on your back and bend your knees, lift one leg, supporting the back of your leg with your hands, try to straighten your knee, stretching the back of your thigh. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times. Do this for the other leg.
Dynamic hamstring stretch while lying on the floor
Pulling your knees to your chest
This exercise strengthens the back muscles well, relieving the load on the spinal erector muscles. Lie on the floor with your back relaxed and straight. Pull your knees to your chest until you feel a stretch in your lower back, do not make unnecessary movements. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 5 times.
Stretching while lying down
Back arch while standing
Stand straight with your hands on your waist. Bend back, arching your back as far as you can. Keep your balance. You should feel comfortable. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 5 times.
This movement is known in yoga as Anuvittasana Asana. In addition to strengthening your back, sleeping also opens up the front of your body. Strengthens the respiratory, cardiovascular and endocrine systems. Has a beneficial effect on the vestibular apparatus.
Recommended:
- Place your palms on your lower back, fingers down.
- Tighten your thighs and buttocks. Keep your knees together and press your feet into the floor.
- Keep your head straight or, if comfortable, tilt it back a little.
- When exiting the asana, do not relax your buttocks. As you exhale, slowly straighten your back, neck and then your head.
Quadriceps stretch
For balance, hold onto a support with one hand, bend your leg so that your foot touches your thigh. Take your foot with your hand and pull it with your buttock until you feel a stretch in the front of your thigh. This exercise can also be performed while standing on all fours.
Quadriceps stretch on all fours
Various arm and leg raises
Similar to the previous one, only here you use opposite pairs of arms and legs. Lie face down on the floor, place a rolled towel under your forehead, and stretch your arms above your head. Place a pillow under your pelvis and stomach. Keeping your right knee straight, lift your leg 3-5 cm from the floor and at the same time lift your left arm off the floor. Hold for 5 seconds. Do it with the other leg and arm. Repeat 10 times for each side.
Adequate flexibility in the tissues around the spine and pelvis allows you to move easily using your back, prevents stress on your joints, and reduces the likelihood of injury.
Stretching exercises also prepare your muscles for physical activity. Stretching should be done before and after every intense workout to prevent muscle strain, soreness, and injury during the workout.
Perform the exercises at a slow pace, stretching as far as your fitness allows.
Aerobic exercises to strengthen your back
Aerobic exercise strengthens your cardiovascular system, your heart and lungs, and improves your body's ability to use oxygen.
Such exercises increase energy levels, improve mood, accelerate metabolism, enhance metabolic processes in the body and promote fat burning.
Aerobic exercises that are helpful for strengthening your back muscles include:
- calm running
- skis
- robot on an ellipse
- a ride on the bicycle
- rowing
- dancing
- walks
It is advisable to always combine aerobic exercises with static exercises that continue them. For example, you can use different variations of the plank: classic, straight arms, side or reverse.
Side plank
Features of rehabilitation in children
Treatment of children with compression fractures is conservative. The first therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving the damaged areas, relieving pain and restoring impaired blood circulation.
A sick child's mobility is limited to prevent complications from developing. It is necessary to remain in an upright position to a minimum, avoid lifting weights and sudden movements.
Functional traction, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy and breathing exercises are prescribed. A little later, back massage and physical exercise are added, the action of which is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back, abs and shoulder girdle. The child is prescribed to wear a special corset and continue the recovery period of treatment.
Even such a serious diagnosis as a compression fracture is not always a death sentence. The situation can be corrected if you approach the issue of patient rehabilitation competently and responsibly. There are a huge number of techniques and procedures that will help restore damaged areas. It is only important to strictly follow all the doctor’s requirements in order to see the result.
Complete back workout
Elliptical training
- 5 minutes
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Exercise
Dynamic stretching of the back muscles
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: No
Stretch “Kitty”
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Lower Back Equipment: No
Stretching while lying down
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Lower Back Equipment: No
Stretching while sitting
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Lower Back Equipment: No
Throwing a medicine ball to the floor
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Medicine Ball
Standing lateral raises with dumbbells
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body part: Shoulders Equipment: Dumbbells
Reverse ring pull-ups
- 1 set of 20 reps
- Body Part: Middle Back Equipment: Other
Pull-ups with expander
- 1 set of 10 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Other
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
Tips for maintaining a healthy back
Do you want to keep your back healthy? Then remember these 10 useful tips that will help you maintain good posture and strengthen your back muscles:
- Watch your posture and always keep your back straight.
- Make sure you sit properly at your desk. Make sure the chair and table are the right height for you.
- If you have a sedentary job, try to get up more often during the working day, stretch your muscles after a long stay in one position.
- If you have to travel for a long time in a sitting position, use a special orthopedic seat or pillow.
- If you have to wear a backpack for a long time, do not overload it and choose models that support the spine.
- Carry and lift heavy objects carefully.
- Provide comfort for your neck and spine while you sleep.
- Perform exercises for the stabilizing region (back muscles and abdominal muscles), which will strengthen the muscular corset of the back.
- Maintain proper technique while performing physical exercises.
- To treat and prevent back diseases, seek help from a chiropractor.
Don't forget to constantly work your abdominal muscles as well. The time spent will never be wasted and the body will “say thank you.”
Exercise therapy for the spine
Therapeutic exercise perfectly helps to restore the muscles of the back and chest, which have time to atrophy during the period while a person is in a supine position. Exercise therapy also activates metabolic processes, accelerates bone tissue regeneration, and restores the nervous system.
The use of physical education helps prevent the development of the following complications:
- blood clot formation;
- tissue necrosis;
- digestive problems;
- development of neuropsychiatric or general asthenic syndrome.
At the very beginning, physical education helps maintain tone, and only later you can move on to building muscle mass.
Exercise therapy is prescribed in 85% of cases of injury, since it is almost the main component of the rehabilitation process. It is allowed to begin if a person has noted the following improvements in his condition:
- normalization of body temperature;
- the appearance of positive results of drug therapy;
- all vertebrae are compared, and casts, wires and other elements are removed.
Stages of exercise therapy
There are 4 stages of physical therapy that are used for spinal fractures.
First stage
Physical education in the first 7-10 days makes it possible to increase the patient’s vitality, improve the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and prevent loss of muscle endurance.
When carrying out exercise therapy, breathing and general developmental exercises are used, in which small and medium muscle groups, as well as joints, take part.
All movements should be performed lightly and alternately, since excessive muscle tension can lead to pain. You can lift your pelvis by focusing on your shoulder blades and feet. Classes are conducted individually and their duration should not exceed 15 minutes.
Second phase
The second stage helps to normalize the activity of internal organs and systems, as well as improve blood circulation in the damaged area, as this will have a positive effect on the recovery process and strengthens the muscles of the torso, pelvic and shoulder girdle.
A muscular corset is developed, exercises prepare a person for the subsequent expansion of motor activity. Exercises are carefully selected, the number of their repetitions is gradually increased, which allows for an increase in the total load.
After 2-3 weeks, the patient may be allowed to roll over onto his stomach. The patient must perform static and dynamic exercises that involve the arms, abs and back muscles.
To create the best conditions for correcting spinal deformities and strengthening the back muscles, patients should perform extension exercises.
Third stage
The third stage should help strengthen the muscles of the limbs, torso, and pelvic floor, and affect the coordination of movements and mobility of the spine. To increase physical activity, it is recommended to increase the duration and density of exercise, adding exercises with weights, resistance and isometric muscle tension to the complex.
A smooth transition to axial loads on the spine occurs due to the transition to exercises with the starting positions of “kneeling” and “standing on all fours”. The bed should be lowered during general developmental and special exercises.
Fourth stage
A set of exercises at the 4th stage develops the muscular system, walking skills and helps to form correct posture. It is important to increase the mobility of the spine to the state in which it was before the injury, to strengthen the muscular system so that you can perform any movements.
The exercises are performed lying down and standing, all this happens in the hospital, at the slightest manifestation of pain, the exercises should be stopped, after which the doctor should examine the patient and adjust the program.
Contraindications to physical therapy
Sometimes it is possible that the use of physical therapy needs to be postponed. This can happen due to the following points:
- the general condition of the patient is very serious;
- the temperature has risen;
- impaired sensitivity and motor activity in the limbs;
- constant pain that becomes stronger after performing the exercise;
- changes in blood pressure;
- weakness after performing the complex;
- intestinal diseases.