General rules of the Montignac glycemic index diet
The diet is based on the calculation of the glycemic index (GI), the calorie content of foods is not taken into account. This allows you to lose weight without feeling hungry, and the results of the diet last for a long time.
The glycemic index is a parameter characterizing a product based on its effect on the concentration of sugar in the blood. Easily digestible foods can quickly increase the level of glucose, which is the main supplier of energy for the body.
Due to rapid digestion, the feeling of fullness does not last long. As a result, the body requires a new portion of food without using up the incoming energy reserves.
When an excess of glucose arrives, after metabolism, it is converted into reserves “for future use”, in the form of fat deposits. Difficult to digest food, after consumption, gradually saturates the body with energy, there is no sharp increase in glucose levels, and the feeling of fullness persists for a long time.
As a result, if there is a need to increase energy expenditure, the body is forced to spend its own reserves.
When drawing up a menu for a week, with a diet based on GI, it is necessary that the total index value be in the range from 60 to 180 units per day.
To do this, foods with a low GI content (up to 55) are included in the diet. Less commonly used with an average value (56-69). And foods with a high GI index (more than 70) are excluded from the diet.
When following a diet, it is additionally recommended:
- Mandatory intake of water (without gases and additional additives) is at least 2 liters. This allows you to cleanse the body of toxins and prevents you from experiencing a false feeling of hunger. Pure water better saturates the body with the necessary moisture.
- It is prohibited to combine carbohydrate-containing foods with high-fat dishes. Their interaction will reduce the effectiveness of the diet.
- During the day it is necessary to consume vegetables and fruits up to 5 times, while it is advisable to exclude sweet fruits from the diet or they should be present in small quantities.
The glycemic index diet involves eating unsweetened fruits and vegetables. - Dishes should be prepared by boiling, stewing or baking. Frying is excluded.
- It is forbidden to starve; a lack of glucose and nutrients can lead to a malfunction of the body.
- There should be an interval of at least 3 hours between meals. But no later than 3 hours before going to bed.
With a correctly composed menu and following the instructions, weight loss and improved well-being are noted from the 1st week. Before starting the transition to nutrition according to the GI, it is necessary to conduct an examination or consult a therapist for the presence of contraindications.
Effectiveness of the glycemic diet
The glycemic index diet is one of the most effective, because following the rules of dietary nutrition will make it easy to lose excess weight, benefit the body, and even cope with certain diseases. Among the advantages of switching to certain product groups are:
- it’s easy to cope with 2-3 extra kilos in a week (the result is not stunning, but the slow burning of fat deposits ensures that excess weight does not return as soon as possible after completing the diet);
- in case of diabetes mellitus, continuing the diet will significantly improve your overall health; consuming foods with a low glycemic index will help maintain normal sugar levels;
- active consumption of healthy carbohydrates will allow the body to not feel hunger for a long period, maintain efficiency and energy;
- the amount of bad cholesterol in the blood is effectively reduced, the risk of plaque formation on the walls of blood vessels disappears;
- The functioning of the cardiovascular system is normalized, the risk of developing heart disease and pressure surges is reduced.
Another advantage of eating foods with a low glycemic index is that there is practically no risk of breakdowns, since the consumption of carbohydrates blocks the increase in appetite and the feeling of hunger. Continuing the diet, it is allowed to consume protein foods and fats, which will affect general well-being, the functioning of major organs, and the condition of the digestive tract.
Pros and cons of the diet
The glycemic index diet has its advantages and disadvantages, which must also be taken into account when switching to a new diet.
The benefits of a diet taking into account GI foods:
- Reduces the concentration of glucose in the blood, which helps prevent diabetes. And also there are no sudden increases in sugar, this is important for people who already have type 2 diabetes.
- Due to the reduction of excess weight, the functioning of internal organs is normalized, including the stabilization of intestinal function and the functioning of the heart. This in turn is characterized by an improvement in general condition.
- Restoring the functioning of the body starts the process of strengthening the immune system. Accumulated toxins and impurities are removed.
- A decrease in adipose tissue is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of “bad” cholesterol. Which improves the elasticity and patency of blood vessels.
- This food is suitable for women carrying a child and the elderly.
- The achieved result lasts for a long time. Since the diet normalizes the metabolic process in the body.
- There is no need to starve, which spoils the digestive tract and suppresses the psychological state.
- Snacks are allowed, but only with low GI foods.
- There is no particular craving for “harmful” dishes and products, thanks to the saturation of the body with necessary substances.
- There are no time restrictions; you can use a diet taking into account the GI for a long time. There are no side effects observed.
This positive reaction of the body is observed when all the rules of the GI diet are observed. Small deviations may distort the results.
Disadvantages of nutrition according to GI:
- Instead of counting calories, you need to consider the GI amount of each food.
- Will not allow you to quickly lose weight. You can lose no more than 7 kg in a month (without physical activity or counting calories). By playing sports and taking into account the caloric content of food, you can reduce your weight by up to 10 kg. But improvement in well-being occurs from the first days.
- It has a small list of contraindications (discussed below).
Additionally, the disadvantages include the practical refusal of alcoholic beverages and the exclusion of familiar everyday dishes. People who are slightly overweight do not experience significant changes.
The essence of the hypoglycemic diet
Before making nutritional corrections, eliminating foods that are dangerous for your figure, and introducing healthy dishes, it is recommended to understand the features of a diet with a low glycemic index. Each product has its own GI, which should be taken into account when creating a fat-burning diet.
Some foods, once ingested, cause a sharp increase in blood sugar. The consequences are easy to predict - lipolysis is blocked, which results in the deposition of fat reserves, and energy production slows down significantly. Products containing high levels of bad carbohydrates provoke rapid weight gain and are not recommended in the diet.
The next group of products, characterized by a slight effect on sugar levels, is characterized by a low glycemic index. The amount of insulin is not enough to negatively affect lipolysis. Fat deposits are not formed - the resulting food is evenly distributed and used for energy production. Good carbohydrates are useful in losing weight; foods with a low glycemic index are often used in fat-burning diets.
To effectively cope with fat deposits, it is recommended to introduce into the diet only foods that have a low GI, having an index of up to 35. The average level is in the range of 40–50. High - from 60, usually the table of weight loss products whose glycemic index exceeds this norm includes sweets, dishes rich in animal fats. Nutritionists warn that it is better to cross out these ingredients from the menu, otherwise getting rid of excess weight will be problematic, and the diet will end in a lack of results.
Contraindications to the diet
Nutrition according to the glycemic index has no direct contraindications, but there are conditional prohibitions that require consultation with a specialist:
- acute gastrointestinal diseases (stomach ulcer, pancreatitis, gastritis) and other pathologies that require individual dietary nutrition;
- During the period of bearing a child and when breastfeeding, it is necessary to take into account the nutritional value. When compiling a menu, you need a complete composition of all useful nutrients for the child;
- children under 3 years of age, adolescents during puberty and old age after 60 years. During this period, proper nutrition is also necessary. It is recommended to prepare the first menu together with a nutritionist, taking into account the age-related needs of the body;
- mental disorders (depression, disorders);
- renal or heart failure;
- severe wear and tear of the vascular system with a predisposition to thrombosis.
If you have diabetes, it is necessary to take into account the severity of the disease.
Adopting a GI diet on your own can have negative consequences.
Prohibitions on the glycemic diet
Despite the fact that the low-glycemic diet is considered one of the most gentle, there are many prohibitions that should be the reason for abandoning this weight loss technique. Active consumption of carbohydrate-rich foods can result in serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart and changes in blood composition, so studying contraindications is mandatory.
The glycemic index diet is not recommended in a number of cases, including:
- serious disorders of the digestive organs (gastritis, ulcers);
- pathologies of blood vessels (thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, tendency to form blood clots);
- disorders of the nervous system, disorders, depression, breakdowns, sleep problems;
- heart failure;
- chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- problems with the kidneys and genitourinary organs.
During pregnancy or lactation, you should also not get carried away with consuming carbohydrates. A glycemic diet and refusal of certain foods can affect the development of the fetus and cause disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs of a baby who consumes breast milk.
The last prohibition is age. For teenagers and older people, it is better to use more gentle diets for body correction than glycemic nutrition. It is recommended to combine different food groups - a lack of insulin threatens serious health consequences.
Authorized Products
The glycemic index diet is based on the separate consumption of fat and carbohydrates.
The main diet consists of products with a GI content of less than 55 units; per day should not exceed 180 units.
A brief overview of permitted products taking into account the GI:
Glycemic index with an indicator of 55 units:
- canned corn;
- tomato ketchup;
- juice from light grape varieties;
- sushi;
- shortcrust pastry cookies;
- wholemeal spaghetti;
- margarine and processed cheeses.
Glycemic index with an indicator of 50 units:
- natural juices from pineapple, cranberry and apple, without sugar;
- orange, kiwi and mango;
- natural coffee without added cream and sugar;
- egg and omelet (with low-fat milk);
- boiled brown rice;
- steamed meat and fish cutlets;
- fried beef liver.
Glycemic index with an indicator of 44-40 units:
- dry wines and champagne;
- juice from grapefruit, orange or carrots;
- coconut, cranberry;
- canned green peas, eggplant caviar;
- bread products made from whole grain flour and pasta made from durum flour;
- buckwheat grain;
- crab sticks;
- dried prunes and dried apricots.
Glycemic index with an indicator of 35-30 units:
- fresh green peas, beans and sour apples;
- vermicelli and instant noodles;
- sesame seeds;
- fresh plum, quince nectarine;
- apricot, tangerine and passion fruit;
- yogurt and cottage cheese with zero fat content;
- soy sauce and soy milk;
- white meat chicken;
- boiled sausages;
- dried fruit compote without sugar;
- fresh tomato juice;
- garlic, beets and tomato;
- blueberries, lingonberries;
- bitter chocolate.
Glycemic index with an indicator of 25-15 units:
- red berries (raspberries, strawberries, cherries);
- pumpkin seeds, soy flour;
- kefir;
- seaweed;
- eggplant, zucchini, cucumber;
- lemon;
- different varieties of fresh cabbage;
- cashew nuts;
- celery, asparagus, ginger.
Glycemic index with an indicator of 10-5 units:
- green pepper, avocado;
- sunflower seeds;
- greens (dill, parsley, lettuce);
- vanillin and cinnamon;
- boiled shrimp without salt;
- hard cheeses.
Depending on the method of preparation and storage of products, the GI indicator changes; this is important to take into account when creating a menu of ready-made dishes. When boiling, baking and chopping, the GI level increases. Therefore, it is recommended to create a diet for the first month together with a nutritionist.
Product Lists
We will not provide complete lists of permitted and prohibited products here, as they are too long. You will find them in special tables. They have three sections:
- Products with a low glycemic index (less than 35), which are allowed as part of such fasting, form the basis of his diet.
- Foods with an average GI (40-55), which can be eaten in small quantities no more than once a day.
- Foods with a high GI (more than 60) that need to be completely excluded from the diet.
Below are approximate lists that, even before working with the table, will orient you on what menu you can create and what kind of sacrifices you will have to make.
Important note. Please note that the list is for raw foods. After heat treatment, their glycemic index changes significantly, most often upward, and in such situations the product moves from permitted to prohibited. Example: GI of raw celery root = 15, and GI of boiled celery = 85.
Allowed:
- Diet for knee arthritis. What foods are good and what are bad for arthrosis?
- fruits, dried fruits, berries: apricot, avocado, quince, orange, green banana, pomegranate, grapefruit, pear, lemon, tangerine, nectarine, peach, plum, apple, dried apricots, figs, goji, strawberries, raspberries, red and black currants, cherries, blueberries;
- all nuts (including coconut) and seeds;
- vegetables, greens: eggplant, broccoli, zucchini, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, carrots, cucumber, peppers, tomatoes, radishes, lettuce, beets, beans, garlic, onions, rhubarb, celery, asparagus, spinach, sorrel;
- peas, chickpeas, lentils;
- cereals: pearl barley, sprouted wheat, egg;
- sweets: creamy ice cream with fructose, dark chocolate;
- dairy products (with a minimum percentage of fat): feta cheese, plain yogurt, kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, cream, most cheeses, cottage cheese;
- eggs;
- lean meat and fish, seafood;
- soy vermicelli, nut and soy flour, Essene bread;
- drinks: alcohol (except beer), coffee, tea, tomato juice.
Prohibited:
- fruits: papaya, melon, watermelon;
- raisin;
- vegetables: rutabaga, corn, pumpkin;
- cereals: white rice, wheat, millet;
- sweets: chocolate bars, glucose, honey, ice cream, sugar, waffles, cookies, jam and jams with sugar;
- dairy products: curd cheese, condensed milk;
- wheat and rice bread, baguette, crackers, dumplings, wheat flour, lasagna, donuts, crackers, croutons, rolls, bagels;
- drinks: beer, soda, protein shakes.
Moderate consumption:
- fruits: pineapple, persimmon, mango, kiwi, grapes, ripe banana;
- dried fruits: prunes, dates;
- berries: cranberries, lingonberries;
- beans;
- cereals: buckwheat, red and wild rice, basmati, oats, semolina;
- sweets: maple syrup, lactose;
- dairy products: yogurt with additives, sour cream, processed cheese, feta;
- sushi;
- buckwheat pancakes, whole grain pasta, whole grain rye bread, al dente spaghetti, ravioli, pizza, buckwheat flour;
- fruit and vegetable juices.
Fully or partially limited products
When creating a menu, you need to exclude products with a GI content above 70 and minimize the consumption of products with a GI of 56-69 units.
Table of foods with medium and high GI content:
| 56-69 | 70 or more |
| With GI 69: premium and 1st grade wheat flour. | With GI 110: beer and other drinks made with malt or yeast. |
With GI 65:
| With GI 100:
|
With GI 60:
| With GI 95-90:
|
With GI 85-80:
| |
With GI 75-70:
|
Additionally, the use of salt in dishes is limited. It can increase appetite and also cause swelling.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VHnL76sdTag
Nutrition for type 2 diabetes mellitus
In most cases, the main cause of the disease is obesity. Therefore, diet for type 2 diabetes is the first and main component of treatment and prevention of complications. With its help, it will be possible to normalize sugar levels and control weight, thereby preventing the occurrence of unwanted changes and deterioration of the condition.
All patients need to independently monitor their blood glucose levels daily using household glucometers, and if they consistently receive high levels, immediately contact their doctor.
If a patient is diagnosed with a non-insulin-dependent form of the disease, mild or moderate, and his weight is within the normal range, he is prescribed basic diet No. 9 with a daily calorie content of up to 2500 kcal. In such situations, you can consume no more than 275-300 g of complex carbohydrates per day from various sources.
In the presence of obesity, it is necessary not only to maintain glucose levels within normal limits, but also to reduce weight, since its excess negatively affects the effectiveness of treatment and the well-being of patients. Therefore, in such cases, patients are prescribed the so-called reduced diet No. 9, which is characterized by a reduced calorie content due to an even greater limitation of the permissible amount of complex carbohydrates consumed daily. In this case, the endocrinologist individually calculates this norm based on the degree of obesity. Therefore, in different cases, patients may be allowed to consume from 100 to 225 g of carbohydrates, and the total caloric content of the diet should not exceed 1700 kcal per day.
What not to do
So, with type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to completely exclude from the diet foods containing so-called fast carbohydrates, i.e. those that are broken down into glucose and absorbed into the blood within 15 minutes. They quickly give a boost of energy, but do not create a feeling of fullness, so after eating them, hunger returns very quickly. These include:
- sugar;
- honey;
- confectionery, classic pastries;
- ice cream, chocolate;
- marmalade, jam, marmalade, preserves;
- sweet vegetables, fruits, berries (grapes, bananas, dates, pineapple, persimmons, dried fruits);
- white bread, loaf;
- semolina;
- smoked meats, fatty foods;
- mayonnaise;
- fast food, snacks.
Special recipes have been created for diabetics, including approved products for baking.
Diet No. 9 does not require complete refusal, but recommends reducing the amount consumed as much as possible:
- potatoes;
- beets;
- corn;
- carrots;
- soy products;
- pasta;
- of bread.
If you are obese, you will need to completely avoid all foods high in fat:
- butter and vegetable oil, spreads;
- sour cream, fatty cheeses, cottage cheese, cream;
- lard, fatty meat and fish, chicken with skin;
- nuts, seeds;
- alcohol, etc.
In such situations, it is recommended to replace these foods with vegetables that have a beneficial effect on carbohydrate metabolism. These are leafy greens, eggplants, cucumbers, turnips, cauliflower, pumpkin, zucchini, radishes, etc.
You should definitely try to completely avoid foods with a lot of fat, in particular canned food, meat processing products, and store-bought sauces. They are replaced with boiled or stewed dietary meat (chicken, rabbit, turkey, low-fat yogurt without additives).
What is possible
Carbohydrates are an essential part of the daily diet, and they must be present on the menu for diabetes, but only in acceptable quantities. Patients are allowed to eat only foods with slowly absorbed carbohydrates and a high content of dietary fiber. This:
- vegetables;
- coarse bread, whole grain, with bran;
- whole grain cereals (8-10 tbsp), with the exception of refined rice.
Since sugar in any form is prohibited for diabetics, its substitutes that do not contain glucose were specially created. Many of them are many times sweeter than sugar and can be used in minimal quantities. Modern sweeteners include: xylitol, stevia, sorbitol, fructose. But studies have shown that some of them can have a negative effect on the body. Stevia is considered the safest sweetener today. It is obtained from natural raw materials, and its sweetness is 10-30 times higher than sugar (depending on the form of release: grass powder or an extract called stevioside).
It is important for patients to know the glycemic index of foods. Today there are special tables that help you navigate your choice and correctly calculate the permissible consumption rate. For diabetes, preference should be given to foods with a GI of less than 55 (apples, cucumbers, cherries, broccoli, lettuce, milk, cauliflower, etc.). They break down slowly and practically do not lead to an increase in blood sugar levels. You can eat up to 200 g of such products per meal, but preferably together with protein foods.
Heat treatment increases GI.
Allowed to use:
- potatoes (no more than 200 g per day);
- dishes with meat and vegetable broth;
- lean varieties of meat and fish (chicken, turkey, pollock, pike, hake);
- lentils;
- low-fat fermented milk and dairy products, cheeses with a fat content of less than 30%;
- eggs (3-4 per week, but not more than 1 per day);
- vegetable oil (no more than 1 tbsp per day);
- special candies, waffles, breads for diabetics.
When preparing homemade compotes, sweeteners are added instead of sugar.
Diet duration
A diet based on the glycemic index of foods consists of 3 main stages. Each of them lasts depending on the physical condition of the body and psychological characteristics.
On average, each stage takes 2 weeks, but the last one can last indefinitely, in order to constantly maintain normal weight.
At the same time, it is recommended to take tests once a year to monitor the condition of the body and the performance of organs. If changes are detected, consultation with a therapist and nutritionist is necessary with possible adjustment of the diet or its cancellation.
Diet stages
For sustainable weight loss, the standard GI diet consists of 3 stages (skipping 1 of them will affect the final result). In the Montignac method, the 1st point is missing.
Features of each stage of the diet:
- First stage. It is allowed to eat foods with a GI content below 40 units. When eating food with a low GI, the body will be forced to spend the energy accumulated by the body, since the food will lack the necessary energy. At this stage, active burning of excess fat occurs. Nutritionists do not recommend staying longer than 2 weeks at the initial stage. This can harm the body's functioning due to lack of energy and nutrients. The average duration is 1-3 weeks.
- Middle stage. The menu includes products with a GI of up to 40 - main dishes. Sometimes it is allowed to eat dishes with a GI content of 55 units. The duration of this stage does not have large time restrictions. It lasts until the weight drops to the desired values. Fat burning will occur more slowly and smoothly.
- The final stage. Prepared meals should contain no more than 69 GI units, but sometimes high-glycemic foods are allowed. At this stage it is necessary to consolidate and stabilize the achieved result. The duration of the stage is the period of the initial and middle stages together. If you skip it, there is a high probability of quickly returning the lost kilograms. Often the last stage of a GI diet lasts a lifetime.
Diet features
The diet for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus has some differences that patients should understand. Regarding nutrition for insulin-dependent diabetes, in which patients receive lifelong replacement therapy in the form of regular insulin injections, doctors in different countries look at the need to limit simple carbohydrates differently.
Foreign endocrinologists believe that it is not necessary to reduce the amount of their consumption in type 1 diabetes with properly selected insulin therapy. Domestic doctors believe that this is fraught with undesirable consequences and insist on the need to limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates, but not completely abandon them, as in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. With type 2 diabetes mellitus, such disputes are not appropriate, since with it, consuming sugar can lead to disastrous consequences, which is not questioned in any country.
In addition, people with type 1 diabetes should be able to count bread units (BU), and people with type 2 diabetes should be able to determine the glycemic index (GI). Nutrition should be structured in such a way that these daily diet indicators meet the developed standards.
Therefore, today, patients with diabetes mellitus are prescribed the so-called diet No. 9 in various modifications, the differences between which are insignificant. The endocrinologist determines which table is most suitable for a particular patient, based on test results and the person’s condition.
In general, diet No. 9 is designed in such a way as to normalize carbohydrate metabolism by reducing the amount of simple carbohydrates consumed and, accordingly, reducing blood glucose levels. As a result, it is possible to bring the amount of sugar in the blood to normal, preventing the development of possible lipid metabolism disorders and complications of the disease.
Diet No. 9 involves a complete rejection of simple carbohydrates while consuming no more than 300 g of complex carbohydrates daily while maintaining the amount of protein food within the physiological norm.
What results can you achieve in a month of diet?
A diet according to the glycemic index allows you to lose weight for a long time, provided that all points are followed. At the initial stage, weight loss will be from 1.5 to 2.5 kg per week.
At the middle stage, weight loss will already be from 0.7 to 1.5 kg per week.
Depending on the body’s metabolism and how often foods with an average GI were consumed, at the middle stage, weight loss in a month can be 5-7 kg, in 3 months up to 15-16 kg.
Choosing the right products
Since the glycemic diet is part of the life of a person with diabetes, it is necessary to learn how to calculate the GI.
You need to know that the glycemic index always also depends on the quality and methods of heat treatment of food. It is important to always take this fact into account when planning a diet for a diabetic.
The highest indicator was assigned to glucose, its value is 100.
Food products can have a glycemic index:
- low – food with an index below 40;
- average – from 40 to 70;
- high – over 70.
The glycemic index diet provides for an individual approach and adherence to the regimen; the menu can be compiled based on the patient’s preferences and financial capabilities.
For simplicity, nutritionists suggest using tips. So, you can eat fruits in unlimited quantities:
Exotic fruits are prohibited, ranging from kiwi to pineapples; melons and grapes are recommended to be consumed in moderation.
Everything is much simpler with vegetables; only corn is not recommended, as well as boiled beets and carrots. Other vegetables can be eaten in any quantity, but within reason. If a person loves potatoes, if you have diabetes, it is better not to overdo it with overcooked, baked potatoes. Ideally, they eat young potatoes; they contain resistant starch, which reduces glucose and has a positive effect on microflora and intestinal functioning.
Diabetics should not eat polished rice; it is replaced with brown rice. Pasta must be selected only from durum wheat varieties and consumed cold.
A one hundred percent useless product for diabetes is white bread, you should discard it, it should be made from wholemeal flour.
Diet menu by glycemic index (GI) for a week
Depending on the characteristics of the body and the desire to quickly lose excess fat, the composition of the menu may change.
The following is a classic nutrition plan for 7 days:
| Days | Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| 1st | Porridge prepared with low-fat milk from whole grain oatmeal | An apple, preferably green varieties, and walnuts. | Boiled, white, chicken meat with tomato. Grapefruit juice | Medium fat kefir | Buckwheat porridge with water and orange |
| 2nd | Crispbread with milk | Pear | Cucumber and cabbage salad (without oil) and boiled fish. Not strong tea without sugar | Drinking yogurt (without additives) | Stewed cabbage with carrots and green peas with a piece of beef |
| 3rd | Instant oatmeal with milk, you can add some nuts | Grapefruit and croutons (no oil or hot spices) | Cucumber salad, no oil. Steamed rice and boiled fish. Grape juice | Low fat kefir | White meat chicken (boiled) with apricots |
| 4th | Buckwheat porridge with added milk | Cucumber and tomato salad, without oil | Boiled oatmeal with fish (also boiled) and an apple. Not strong tea | Drinking yogurt | Boiled chicken meat. Additionally, you can drink 150 ml of milk |
| 5th | Whole grain oatmeal with water. Apple. You can drink 150 ml of kefir | Milk up to 200 ml | Cucumber salad, no oil. Boiled buckwheat with baked chicken. Grapefruit juice | Peanuts and pear | Boiled beans and baked fish |
| 6th | Milk or kefir with crackers (no butter or spices) | Walnuts | Cucumber salad, no oil. Buckwheat porridge. Not strong tea | Drinking yogurt | Boiled vegetables and steamed cutlets |
| 7th | Oatmeal water porridge with fruit salad | Drinking yogurt | Rice porridge, boiled white chicken meat and baked cabbage. Grape juice | Baked apple | Cabbage and cucumber salad, no oil. Boiled or baked fish. |
Portion sizes should not exceed 200 g. If you feel very hungry, in the evening, it is allowed to consume low-fat yogurt 1 hour before bedtime. If desired, fruits can be replaced according to the GI. During the day, do not forget to drink more clean water.
Nutrition for gestational diabetes
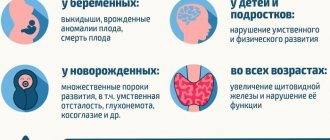
Pregnant women with a genetic predisposition to developing diabetes may experience the development of so-called gestational diabetes at 20-24 weeks. It occurs against the background of hereditary reduced sensitivity of tissues to inulin, which increases under the influence of hormones produced during pregnancy in increased quantities: estrogen, prolactin, cortisol. They are able to block insulin and cause an increase in blood sugar levels.
Often after childbirth, carbohydrate metabolism gradually returns to normal as hormonal levels normalize. But still, if the basic principles of nutrition and diet are not followed, there is not only a risk of maintaining diabetes mellitus, but also the development of complications that can lead to premature birth, pyelonephritis in the mother, pathologies of the fundus, as well as complications during childbirth. It is for the purpose of timely detection of gestational diabetes during pregnancy that blood glucose levels are regularly tested, and if hyperglycemia is detected, a diet is prescribed.
In such situations, women are recommended to:
- completely eliminate simple carbohydrates from the diet (the same sugar, confectionery, chocolate, pastries, white and brown bread, bananas, grapes, juices, dried fruits, etc.);
- limit your intake of complex carbohydrates to the amounts recommended by your doctor;
- devote most of the daily diet to vegetables and unsweetened fruits;
- Avoid eating fatty foods, fried foods, processed foods, a variety of sausages, and smoked foods;
- when choosing a method of preparing food, give preference to baking, stewing, and steaming;
- eat in small portions, preferably every 2 hours, highlighting 3 main meals (breakfast, lunch and dinner), as well as 2 additional ones (second breakfast, afternoon snack);
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water.
Pregnant women with gestational diabetes are advised to measure their blood sugar levels after each meal.
All these recommendations are also relevant for the postpartum period. In any case, in the first months of a baby’s life, a woman who is breastfeeding is forced to follow a hypoallergenic diet and give up fried, fatty foods. The same diet will help eliminate gestational diabetes and avoid its transition to a chronic disorder of carbohydrate metabolism within 2-3 months after childbirth. If, after this period of time, the blood glucose level does not normalize, the woman needs to contact an endocrinologist to undergo an examination and develop treatment tactics.
Low Glycemic Index Recipes
The glycemic index diet is based not only on low GI foods, but also on ready-made meals with a low index.
Frequently used recipes:
- Chicken stew with mushrooms. Cut the chicken fillet and onion (preferably into large pieces), fry with a little oil. After frying for 5 minutes, add chopped mushrooms. After 5 minutes, add salt, water (just enough to cover the contents of the pan) and a little pepper. Cook for 15-25 minutes. Depends on the size of the pieces of meat.
- A fresh vegetable salad. Tear greens and lettuce leaves with your hands. Cut tomatoes and cucumbers into medium sizes. Season with olive oil and mustard. You can add a little salt.
- Fresh cabbage soup. For the broth, boil 250-300 g of lean meat. Chop the onion, tomato, carrot and green bell pepper and fry with a small amount of oil. Add chopped cabbage to the prepared broth, and after 5 minutes add potatoes. After 10 minutes, season the soup with cooked roast and bay leaf. Cook for 5-7 minutes. If the potatoes or cabbage are slightly undercooked. This only reduces the GI of the dish. But if the ingredients are very undercooked, then you need to cook for another 5 minutes.
- Baked chicken breast. The breast is cut into strips and marinated in a marinade (soy sauce - 50 ml; sesame oil - 10 ml; rice vinegar - 15 ml). If desired, you can add 50 ml olive oil to the sauce. The meat is infused for 30 minutes. Fry with a small amount of oil. As a side dish, you can boil peeled potatoes or bake cabbage.
- Fresh fish soup. Boil pollock and pink salmon tail for 20 minutes. Next, the fish is removed from the broth and cleaned of bones. For frying, onions and carrots and tomatoes are used. Add fish meat and buckwheat to the strained broth and fry after 15 minutes. Before turning off, add the raw egg, salt and peppercorns. Let the soup brew for 5 minutes.
When using spices, it is necessary to take into account that they can also increase the GI of the prepared dish.
Therefore, it is recommended to use them to a minimum. The larger the ingredients are cut, the less the index will increase. It is important that the dish is tasty, otherwise the feeling of fullness will come for a short time.
Possible side effects of the diet
If the menu is correctly drawn up, taking into account the GI and existing contraindications, an adverse reaction develops extremely rarely.
With a protracted initial stage and severe restrictions in the middle, the following side effects may develop:
- violation of stool and its frequency;
- a large amount of fiber and a small amount of fat and oil can cause bloating;
- changes in the condition of the skin, peeling, dryness, increased irritability, manifested by inflammatory reactions on the skin;
- headaches, slight loss of strength due to changes in diet and energy intake;
- with a lack of fatty foods, the functioning of the liver and gall bladder may deteriorate, which will feel bitter in the mouth;
- temporary decrease in metabolism in the body, initially this may be expressed by a slight increase in body weight;
- if the menu is drawn up incorrectly, the functioning of the joints may deteriorate, which will be accompanied by pain;
- rare, but the condition of the scalp may change. Hair may fall out and become dull.
If you have these side effects, it is recommended to immediately seek advice from a therapist and nutritionist. Nutrition will be adjusted.
Common diet mistakes
People trying to change their weight through diet, especially beginners, often make common, classic mistakes:
- for rapid weight loss, the quantity and quality of food consumed is sharply reduced, which only leads to a disorder in the functioning of organs;
- when a diet takes into account the GI, frequent fasting days are added, which also harms the condition of the body;
- it is not taken into account that during heat treatment and strong grinding of products, the GI can increase by more than 2 times;
- low consumption of clean water;
- exclusion of breakfast, which disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- use of additional products (teas, dietary supplements) for weight loss;
- lack or, conversely, excessive use of physical activity.
Lack of sleep and excess nervousness, due to slow weight loss, also negatively affect the final result. When following a diet, it is recommended not to focus on nutrition and lead a normal lifestyle. The weight will come off faster.
Dietary nutrition helps normalize weight and body functioning. A menu compiled according to the glycemic index allows you to achieve the desired results, which last for a long time due to the normalization of the metabolic process in the body.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oksana Grivina