Description and benefits of omega-3
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- organic compounds, in the structure of which, in addition to single (in other words, “saturated”) bonds, there are also double bonds between carbon atoms. The most famous representatives of this class - eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) - can be formed during the transformation of essential alpha-linolenic acid - due to the body’s inability to synthesize it, it must be supplied with food or in the form of dietary supplements.
- Omega-3 and the nervous system
Remarkable and very important from the point of view of growth and normal development is the fact that DHA predominates in the gray matter of the brain. Despite the fact that this acid is also contained in breast milk, the baby’s needs for it (especially in the first months of life) are very high.
Considering that during the last trimester, the formation of omega-3 reserves is very active - these polyunsaturated acids, penetrating the placental barrier, regulating and selectively (as when issuing a visa) passing certain molecules through the blood from the mother to the child and vice versa, have a powerful stimulating effect. influence on the formation of the Central nervous system. That is why for prematurely born children it is recommended to consider additional intake of essential omega-3 PUFAs.
In addition, after birth, these compounds continue to exhibit multiple effects across a very broad spectrum. So, for example, in the course of a study, British scientists discovered the positive effect of omega-3 in the treatment of ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) - at least 40% of children had a higher concentration and concentration, and young schoolchildren significantly improved their abilities to reading and writing.
- Omega-3 and vision
Docosahexaenoic acid occupies a leading position among phospholipids in the cell membranes of retinal photoreceptors. In addition, DHA is also involved in the process of regeneration of visual pigment (that is, its restoration).
In addition, polyunsaturated fatty acids in the retina have a protective effect, protecting its delicate structure from reactive oxygen species, inflammatory mediators and various signaling molecules involved in inflammatory processes.
Study
: Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 family in the prevention of diseases in adults and children: the view of a clinical pharmacologist
- Omega-3 and the cardiovascular system
Numerous studies by scientists show that taking omega-3 PUFAs is associated with a reduced risk of heart pathologies. In particular, this is achieved by reducing the level of triglycerides (due to increased oxidation of fatty acids included in their composition in the liver, as well as inhibition of lipogenesis in general) and increasing the concentration of high-density lipoproteins (HDL - anti-atherogenic), as well as by inhibiting aggregation platelets (that is, their connection with each other and the subsequent formation of a “plug” at the site of damage).
The American Heart Association emphasizes that taking 4 grams per day of prescription medications containing omega-3 PUFAs reduces high triglyceride levels. However, doctors emphasize: first of all, it is necessary to exclude other causes of their increase: such as hypothyroidism and/or type 2 diabetes.
Study
: Prescription omega-3 fatty acid medications effectively lower high triglycerides
In addition, taking DHA (4 g/day) was accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure - thus, scientists came to the conclusion that omega-3 fatty acids can also affect the endothelium (inner lining) of blood vessels.
In addition, omega-3 fatty acids, when included in the phospholipid layer of cell membranes, are able to change their fluidity, as well as control the transmission of signals through them.
These organic compounds, by regulating the function of membrane channels (sodium and calcium), prevent the development of lethal arrhythmias.
Omega-3 PUFAs can, instead of arachidonic acid (omega-6 PUFAs), act as a substrate (raw material) for the action of an enzyme such as cyclooxygenase. As a result, much weaker reaction products are formed instead of pro-inflammatory molecules.
Study
: Cardioprotective mechanism of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- Omega-3 and skeletal muscle
Studies note that consuming omega-3 PUFAs prevents the breakdown of muscle proteins, a function associated specifically with the action of EPA.
Thus, supplementing the diet of 45 exercise volunteers with 2 grams of omega-3 for 90 days was associated with significant improvements in muscle fiber strength and neuromuscular transmission. It is believed that these results are achieved by increasing the sensitivity of muscle tissue to a neurotransmitter such as acetylcholine, which takes part in the synapse and thereby stimulates muscle contraction.
In addition, some data indicate the ability of omega-3 to activate the formation of new mitochondria due to increased expression of certain mitochondrial factors and proteins.
Considering that skeletal muscles are insulin-dependent tissues (that is, through the action of this hormone, glucose from the blood enters their cells), any dysfunction in the implementation and regulation of this process leads to insulin resistance - a key stage in the path of type 2 diabetes. With the development of this pathology, there is a decrease in the absorption of glucose by muscles, a decrease in the synthesis of glycogen (acting as a reserve reserve of carbohydrates), a violation of the oxidation of fatty acids and, accordingly, an increase in their pool.
Rodents fed a high-fat diet but supplemented with fish oil had less impaired glucose tolerance than those fed a high-fat diet. In addition, they, although to a lesser extent than the control group of rodents on a normal, balanced diet, showed a decrease in intracellular lipids and some types of ceramides (markers of lipid-induced insulin resistance).
Study
: Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Skeletal Muscle Health
Benefits and harms
The main function of PUFAs is to maintain the functioning of cell membranes, myelin sheaths of organs, transmembrane ion channels, and connective tissue. Once in the body, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids are integrated into the phospholipid layer of cells, improving their functional properties (enzymatic activity, membrane viscosity, permeability, electrical excitability).
Other beneficial properties of PUFAs:
- suppress the synthesis of lipoproteins and triglycerides in hepatocytes, regulating fat metabolism (hypolipidemic effect);
- impart “fluidity” to the cell membrane, preventing heart rhythm disturbances (antiarrhythmogenic effect);
- regulate the content of serotonin in the brain (antidepressant effect);
- increase the sensitivity of receptors to insulin, preventing the development of insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes);
- dissolve exogenous deposits on the walls of blood vessels (hypocholesterolemic effect);
- normalize hormonal levels, improving the course of premenstrual and menopausal syndromes (estrogenic effect);
- potentiate the synthesis of substances (prostaglandins) that suppress autoimmune, atopic and inflammatory processes in the body (anti-inflammatory effect);
- reduce platelet aggregation, which leads to an improvement in blood rheological parameters (antiplatelet effect);
- participate in the construction of the myelin sheaths of the brain (as a structural element), improving attentiveness, memory, psychomotor coordination;
- regulate vascular tone of capillaries, normalizing blood pressure (hypotensive effect);
- prevent the penetration of foreign agents into the body;
- reduce the synthesis of inflammatory mediators (due to integration into the phospholipid layer of cells);
- improve the functional condition of nails, skin, hair;
- participate in the metabolism of B vitamins (thiamine and pyridoxine).
Vitamin F is not synthesized by intestinal microflora, so it must be supplied to the body daily with food or vitamin-mineral complexes.
Signs of Omega-3 PUFA Deficiency
- Low weight in a newborn baby
— this statement was based on a study of 12 thousand Danish children.
- Premature birth
- were associated with a decrease in the concentration of docosahexaenoic acid in the child’s blood.
- Decreased visual acuity
— in addition to the previously mentioned mechanisms of action of omega-3 fatty acids, their inhibitory effect on apoptosis (self-programmed death) of retinal epithelial cells is also noted.
- Cognitive impairment
— in particular, are accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of tissue hormones such as neuroprotectin D, in the synthesis of which DHA is involved. This biologically active compound inhibits the apoptosis of nerve cells by activating a complex cascade of signaling processes and thereby suppresses the development of inflammation.
In addition, docosahexaenoic acid itself directly inhibits the formation of pro-inflammatory molecules - in particular, in the hippocampus - one of the most important structures of the brain involved in the mechanisms of transition of short-term memory to long-term memory, as well as in the formation of emotions.
- ADHD
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, accompanied by impaired ability to concentrate, impulsive behavior, lack of self-control and self-control.
- Mental and behavioral disorders
- are associated with accelerated atrophy (under conditions of omega-3 PUFA deficiency) of the gray matter of the brain (in particular, in the area of the following structures: the hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, prefrontal and temporal cortex), as well as with a violation of the integrity of the white matter.
Thus, in rodents unable to accumulate DHA, behavioral abnormalities, the development of a depression-like state, and an increase in heart rate were observed.
- Dyslipidemia
(increased levels of cholesterol and/or triglycerides in the blood, decreased HDL) and increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
A 30-year study of several thousand American scientists showed that eating fish (at least 2 times a week) significantly reduced the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
- Skin diseases
. Omega-3 PUFAs are used not only in aesthetic medicine as a prevention and treatment of skin aging (due to their activation of the formation of the main protein of connective tissue - collagen), but are also actively used in dermatology in the treatment of acne, atopic dermatitis and even psoriasis.
Interestingly, in an autoimmune disease like psoriasis, which causes red patches, omega-3 metabolites are also found in these plaques - these are thought to be converted into much weaker inflammatory molecules than, say, omega-6.
We recommend
“Psychology of stress: types, stages, ways of dealing with it” Read more
Daily requirement
The daily intake of PUFAs varies in the range of 10 – 15 grams.
Considering that essential fats compete in the body, the optimal ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 lipids is 6:1. Otherwise, the synthesis of triglycerides is disrupted. The physiological need for omega-6 is 8–10 grams per day, for omega-3 it does not exceed 1–2 grams.
The amount of polyunsaturated acids in the diet should be increased in the following cases:
- during intense sports (physical labor);
- during periods of pregnancy and lactation;
- for autoimmune diseases, pancreatic dysfunction (diabetes), skin rashes, prostatitis;
- in old age (55 – 85 years) and childhood (0 – 12 years);
- when living in the northern regions;
- in the cold season.
Interestingly, deficiency of omega-6 lipids in the human body is extremely rare, in contrast to omega 3 PUFAs. Let's consider how deficiency of lipids of the latter group manifests itself.
Signs of a lack of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in the daily menu:
- dry skin, including exacerbation of psoriasis and eczema;
- lack of coordination;
- blurred vision;
- growth retardation (in children);
- decreased cognitive function, including learning ability;
- weakness in the body;
- numbness or tingling of the extremities;
- increased blood pressure;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- mood swings;
- acne;
- craving for alcoholic beverages;
- depressive states;
- peeling of nails;
- hair loss.
Long-term deficiency of essential lipids leads to the occurrence of autoimmune diseases, thrombosis, nervous disorders, and cardiovascular pathologies. In severe cases, mental disorders develop.
However, excessive intake of polyunsaturated fats, in particular omega-6, against the background of low intake of omega-3, leads to increased development of inflammatory processes, narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, increased risk of developing systemic diseases, oncology, diabetes mellitus, stroke, coronary insufficiency, depressive states. Therefore, strictly control the amount of PUFAs you consume per day.
Absorption of omega-3 PUFAs
As previously mentioned, both eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids can be formed in the body from their common precursor - the essential alpha-linolenic acid, excellent sources of which are:
- Linseed oil.
- Walnuts.
- Hemp oil.
- Mustard oil.
- Milk thistle oil.
The conversion of alpha-linolenic acid to EPA and DHA occurs through complex biochemical reactions, including the elongation of the carbon chain and the addition of a double bond. Two important genes are actively involved in these processes: FADS1 and FADS2. In the presence of their polymorphism, accelerated, more efficient transformation can be observed.
The influence of sex hormones on the processes of transformation of alpha-linolenic acid is also interesting - for example, estrogens increase its conversion.
Omega-3, like all fatty acids, is included in the processes of breakdown and absorption in the small intestine. So, first, under the action of specific pancreatic enzymes, they are released from food components. In addition, the condition for the occurrence of this process will be the normal outflow of bile - a secretion formed by liver cells and acting not only as an emulsifier, but also activating all pancreatic enzymes.
So before adding omega-3 PUFA supplements to your diet, make sure your digestive system is healthy. If necessary, you may consider taking herbal enzymes or their animal counterparts, as well as bile flow stimulants. It is also important to diagnose the gallbladder for the presence of stones in its body or in the liver/bile ducts.
Omega-3 absorption occurs on the villi of intestinal epithelial cells - here they are delivered through special transport machines - micelles, into which they are included with the help of bile acids.
Are there side effects from eating Omega-3 foods?
Omega-3s are considered safe and effective when taken up to 20 grams at a time, but some people experience mild side effects when taking omega-3 fish oil supplements. Some side effects that may occur from taking fish oil include:
- "Fishy burps" or a fishy taste in the mouth (this is by far the biggest complaint, but it shouldn't happen if you're taking a high-quality supplement)
- Stomach pain or nausea
- Problems going to the toilet (diarrhea)
- Risks of excessive bleeding if you take more than 3 mg Omega-3 per day
- Allergic reactions
- Changes in blood sugar (or complications from diabetes medications)
Although most people do not experience any side effects when they eat plenty of Omega-3 foods and take supplements daily, talk to your doctor about side effects you experience when taking larger doses than recommended. The only thing you need to remember is that you should not take omega-3 fish oil supplements if you are allergic to most types of fish, as there is a high risk of a serious reaction.
Source
Causes of omega-3 PUFA deficiency
- Insufficient consumption of oily fish
- perhaps one of the most common causes of omega-3 fatty acid deficiency. So, say, in the USA, according to statistics, the average person eats less than 13 grams of fish per day - for comparison: the recommended minimum is 40 grams.
In addition, the modern Western diet is rich in their antagonists - omega-6 with pronounced pro-inflammatory properties.
Add salmon, salmon, herring, trout and tuna to your diet - they are richest in these fatty acids.
- Impaired flow of bile (cholestasis)
- another common problem leading to a lack of fat-soluble compounds (vitamins and acids). Bile is an emulsifier of fats. In addition, it is she who activates pancreatic enzymes.
The following medications are recommended:
- Plant enzymes or enzymes of animal origin - when exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is detected.
- Phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid that can be taken on an ongoing basis. Part of the components of bile and cell membranes.
- If methylation is impaired (necessary, in the context of these pathologies, for the formation of phospholipids), use supplements containing methyl group donors (S-adenosylmethionine, trimethylglycine, methylcobalamin).
- If the outflow of bile is impaired, a doctor may consider using animal bile (only if there is no damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract).
- Ursodeoxycholic acid is a non-toxic bile acid with anti-inflammatory, litholytic effects. Used in the treatment of cholestasis and cholelithiasis.
- Malabsorption
- this is a question about the intestines and the integrity of its epithelial cover. A decrease in the number of villi, on which the process of splitting and then absorption also occurs, leads to indigestibility of nutrients.
- Genetics
— in particular, polymorphisms in genes involved in the conversion of alpha-linolenic acid to EPA and DHA.
- Mitochondrial dysfunction.
Mitochondria are the furnaces where fatty acid oxidation occurs. There are many reasons for their damage. One of the most common, perhaps, is taking antibiotics - and this is not surprising: after all, our little power plants were once bacteria that successfully formed partnerships with other cells.
In addition, say, proton pump blockers (“Omez”), used to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the treatment of gastritis and gastric and duodenal ulcers, will also affect mitochondria outside the digestive tract.
As a rule, disturbances in the functioning of mitochondria will occur in the presence of metabolic syndrome - its diagnosis takes into account body mass index, waist size, as well as the following indicators:
- Insulin.
- Glucose.
- Triglycerides.
- HDL (high density lipoprotein).
- LDL (low density lipoprotein).
- Cholesterol.
Note
: dosage - 10-15 mg/kg body weight. Take at night.
We recommend
“Physiology of digestion: stages, organs, enzymes” Read more
You can also take a test for organic acids in your urine - in particular, monitor the level of:
- Succinate.
- Aconitata.
- Fumarata.
- Citrate.
- Isocitrate.
- 2-oxoglutarate.
Note
: the Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix - that is why determining the concentration of the acids involved in it will be indicative.
If mitochondrial function is impaired, it is recommended to consider taking the following dietary supplements:
- L-carnitine - transports fatty acids from the cytoplasm into the mitochondrial matrix.
- Magnesium.
- Coenzyme Q10.
- Alpha lipoic acid.
- B vitamins.
- antioxidants that protect lipids from oxidation by free radicals.
Dietary supplements containing polyunsaturated fatty acids[edit | edit code]
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, contained in some dietary supplements and also in food products, play an important role in regulating and maintaining optimal levels of the immune and cardiovascular systems, as well as pro-oxidant-antioxidant homeostasis in the athlete’s body. The following are the ratios of different polyunsaturated long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) in some products recommended for use as sports nutrition products.
Included in Energomax Reishi Omega-3
includes omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as alpha-linolenic acid (from flaxseed oil) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosohexaenoic acid (DHA) from cold-water fish oil.
The action of DD is based on the biological effects of PUFAs, which form the basis of cell membranes, ensuring their flexibility, fluidity and the necessary permeability; regulate the flow of substances into the cell and prevent the penetration of foreign organisms and compounds; significantly influence all processes occurring in cells, since they are one of the main high-energy molecules in nature. PUFAs are part of the membranes of the cells of the gray matter of the brain and the retina of the eye, provide nerve transmission between neurons of the brain; improve the absorption of calcium and magnesium by cells, ensuring the transport of these minerals through membranes; reduce the level of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
Indications for use of "Energomax Reishi Omega-3": chronic fatigue syndrome, allergies, depression, anxiety, insomnia, attention disorder and/or hyperactivity, to strengthen the cardiovascular system, prevent arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis, to reduce cholesterol levels, triacyl- glycerols and increasing the level of high-density lipoproteins, increasing potency and libido, improving skin condition, preventing anemic conditions. In addition, polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega-3 series are necessary in the following situations: functional disorders of the central nervous system, accompanied by a decrease in the level of mental energy and intellectual functions, a state of chronic fatigue, rehabilitation after acute cerebrovascular accidents; bone fractures, trophic ulcers. In sports practice, at all stages of preparation, it is used to prevent overtraining, dysbiosis resulting from irrational irregular nutrition and inadequate pharmacological support, and to strengthen the musculoskeletal system subject to high loads.
The method of application and dosage are determined based on needs and loads and range from 1 to 3 capsules 3 times a day. Dosage for daily preventive use - 1 capsule 3 times a day. You should not take excess amounts of DD; it is advisable to supplement with vitamin E.
Special instructions: use for diabetes is carried out under medical supervision; Due to the presence of a choleretic effect, it is not recommended for acute cholecystitis.
Flaxseed oil "Organic Flax Seed Oil" is a high-tech mixture of unsaturated omega acids of plant origin, an encapsulated cold-pressed product of fresh flaxseed, created using nanotechnology. Compensates for unbalanced diet, improves metabolism and utilization of adipose tissue during training, and has a positive effect on the immune system. A long course is recommended 2 times a year - 3 months each (winter - summer). Take 2-3 capsules 1 time per day with meals. Available in a package of 180 capsules containing 1000 mg of flaxseed oil.
Source:
Omega-3 fatty acid intake standards
ISSFAL (International Society for the study of Fatty Acids and Lipids) recommends that adults take at least 500 mg/day of the EPA+DHA combination.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations gives wider ranges of values, in particular dividing the population by age groups:
- 0-6 months: DHA (0.1-0.18% E, where E is energy).
- 6-24 months: DHA (10-12 mg/kg body weight).
- 2-4 years: EPA + DHA (100-150 mg).
- 4-6 years: EPA + DHA (150-200 mg).
- 6-10 years: EPA + DHA (200-250 mg).
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding: 0.3 g/day.
Study
: GOED recommendations for EPA and DHA
Many studies also note that taking omega-3 PUFAs during pregnancy significantly reduces the risk of premature birth - in particular, this was noted when supplementing with them (at a concentration of 2.7 g) from the 20th week. This effect is believed to be associated with their influence on muscle tissue (which includes the middle layer of the uterine cavity - the myometrium) through the regulation of calcium channels.
The American Heart Association advises women with heart disease to eat fatty fish at least twice a week, and to consider taking capsules containing 850-1000 mg EPA + DHA, and for patients with high blood triglyceride levels, 2-4 grams of omega-3 PUFAs per day.
Study
: Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Women: Comments on the AHA Guideline: Evidence-Based Guidelines
PUFAs during pregnancy
Polyunsaturated lipids are the most important nutrients for expectant mothers, as they reduce the risk of premature birth and alleviate the manifestations of toxicosis. In addition, the elements are “responsible” for the formation of the peripheral nervous system in the growing embryo. Considering that fats make up 70% of the retina and 30–40% of brain lipids, vitamin F controls the ontogenesis of the visual apparatus and brain in the developing fetus.
During pregnancy, the mother “gives” 2.5 grams of PUFAs to the child, so the daily need for essential fats doubles. The daily requirement of vitamin F for pregnant women is 15 grams (omega-3 – 2 grams, omega-6 – 13 grams).
Other effects of taking PUFAs during pregnancy:
- They potentiate the release of prostaglandins and eicosanoids, which improve the child’s immune status.
- Participate in the mechanisms of building the cardiovascular system of the embryo.
- “Control” the proper formation, maturation and functioning of the placenta (metabolism and blood supply).
- Prolongs pregnancy.
- Prevents the development of toxicosis in the third trimester (gestosis).
- Prevents the development of thrombophilic disorders, and as a consequence, placental insufficiency.
- Reduces the likelihood of developing postpartum depression by 50%.
- Increases the tolerance of the birth act by the embryo.
To replenish the daily requirement for fats, flaxseed or camelina oil, nuts, fish, vegetables, and fruits are introduced into the daily menu. However, a balanced diet, in 90% of cases, does not cover the daily requirement of the substance. Therefore, it is advisable for expectant mothers to use biologically active complexes, which include omega-3 acids.
Consider the list of drugs containing essential fats:
- Premium Omega-3 fish oil (Madre Labs, USA). 1 capsule contains 180 milligrams of eicosapentaenoic acid, 120 milligrams of docosahexaenoic acid and 1000 milligrams of fish oil.
- Rx Omega-3 Factors (Natural Factors, USA). The drug contains fish oil (1170 milligrams in 1 tablet) and a concentrate of polyunsaturated fats ω-3 (600 milligrams in 1 capsule).
- Novomegin (Art-life, Russia). The biocomplex consists of a concentrate of omega-3 polyunsaturated lipids (150 milligrams per 1 capsule), flaxseed oil (200 milligrams per tablet), lipoic acid, vitamin E, dihydroquercetin, organic selenium.
- Prenatal DHA (Nordic Naturals, USA). Organic tablets include: eicosapentaenoic acid (102.5 milligrams), docosahexaenoic acid (220 milligrams), cholecalciferol (200 IU), fish oil (500 milligrams).
- Omega-3 (Solgar, USA). The dietary supplement contains a concentrate of polyunsaturated fats extracted from the muscles of cold-water fish of the northern seas. 1 capsule of the drug contains 900 milligrams of omega-3, 1500 milligrams of fish oil.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To normalize the psycho-emotional background of a woman during pregnancy, along with taking these complexes, it is advisable to drink 15 milliliters of flaxseed oil per day.
TOP 20 foods high in omega-3
| The product's name | EPA g/kg wet weight | DHA g/kg wet weight |
| 1. Sardine | 6.6 | 19 |
| 2. Herring | 8.5 | 8.3 |
| 3. Salmon | 6.2 | 5.8 |
| 4. Rainbow trout | 0.9 | 3.1 |
| 5. Sockeye Salmon | 0.8 | 1.9 |
| 6. Capelin | 3.6 | 5.7 |
| 7. Eel | 1.6 | 2.2 |
| 8. Horse mackerel | 1.64 | 5.86 |
| 9. Perch | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| 10. Pike perch | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| 11. Tilapia | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 12. Pollock | 1.0 | 2.4 |
| 13. Cod | 0.6 | 1.5 |
| 14. Hake | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| 15. Flounder | 1.8 | 1.1 |
| 16. Tench | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| 17. Pike | 0.3 | 1 |
| 18. Bream | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 19. Crucian carp | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| 20. Mullet | 0.46 | 0.08 |
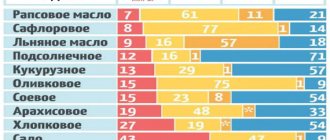
Content of polyunsaturated fatty acids in products
Table of the percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids in food.
| Product | Content |
| Grape seed oil | 69.90 g |
| Flaxseed oil | 67.85 g |
| Walnut oil | 63.30 g |
| Poppy oil | 62.40 g |
| Wheat germ oil | 61.70 g |
| Soybean oil | 57.74 g |
| Corn oil | 54.68 g |
| Cottonseed oil | 51.90 g |
| Walnut | 47.17 g |
| Mayonnaise | 44.69 g |
| Butternut | 42.74 g |
| Sesame oil | 41.70 g |
| Oat oil | 40.87 g |
| Salmon oil raw | 40.32 g |
| Hemp seed | 38.10 g |
| Black Walnut | 36.44 g |
| Rice bran oil | 35.00 g |
| Pine nut without shell | 34.07 g |
| Roasted sunflower seeds (hulled) | 32.88 g |
| Peanut butter | 32.00 g |
| Raw sardine fat | 31.87 g |
| Apricot oil | 29.30 g |
| Flaxseed | 28.73 g |
| Poppy seeds | 28.57 g |
| Canola oil | 28.14 g |
| Margarine | 26.74 g |
| Unroasted sesame | 25.49 g |
| Brazilian nut | 24.40 g |
| Chia seeds | 23.67 g |
| Sunflower seeds, peeled | 23.14 g |
| Turkey fat, raw | 23.10 g |
| Cod liver oil, raw | 22.54 g |
| Pecan | 21.61 g |
| Mustard oil | 21.23 g |
| Roasted sesame | 21.04 g |
| Peeled pumpkin seeds | 20.98 g |
| Raw chicken fat | 20.90 g |
| Beechnut | 20.09 g |
| Almond oil | 17.40 g |
| Corn chips (nachos) without salt | 17.09 g |
| Sesame flour | 16.26 g |
| Raw herring fat | 15.60 g |
| Peanuts raw | 15.56 g |
| Fresh pistachios | 14.38 g |
| Avocado oil | 13.49 g |
| Roasted pistachios (no salt) | 13.35 g |
| Roasted salted pistachios | 13.35 g |
| Roasted almonds | 12.96 g |
| Duck fat raw | 12.90 g |
| Safflower oil | 12.82 g |
| Peanut paste | 12.54 g |
| Fresh almonds | 12.33 g |
| Onion rings | 12.15 g |
| Soy flour | 11.66 g |
| Soybeans, mature, dry | 11.26 g |
| Pork fat (pork fat), raw | 11.20 g |
| Raw goose fat | 11.00 g |
| Potato chips without salt | 10.94 g |
| Raw turkey skin | 10.92 g |
| Rendered pork lard (lard) | 10.54 g |
| Olive oil | 10.52 g |
| Pork lard (without layer) raw | 10.35 g |
| Chicken egg yolk in powder form | 10.32 g |
| Hazelnut oil | 10.20 g |
| Mustard seeds ground mustard | 10.09 g |
| Roasted peanuts | 9.77 g |
| Palm oil | 9.30 g |
| Halva | 8.48 g |
| Cracker | 8.47 g |
| Roasted hazelnuts | 8.46 g |
| Raw pork cheek | 8.11 g |
| Ground dry chili pepper | 8.01 g |
| Fresh hazelnuts | 7.92 g |
| Cashew raw | 7.85 g |
| Roasted cashews | 7.84 g |
| Dry baked muesli (granola), crispy, with honey | 7.81 g |
| Raw lamb fat | 7.80 g |
| Paprika spice, powder form | 7.77 g |
| Walnut drank | 7.61 g |
| Unheated rice bran | 7.46 g |
| Raw pork fat | 7.28 g |
| Boiled chicken skin | 6.96 g |
| Peanut flour | 6.92 g |
| Raw chicken skin | 6.81 g |
| Salted mackerel | 6.21 g |
| Chicken back raw, meat with skin | 6.14 g |
| Multigrain crispbread | 5.98 g |
| Pork lard (with layer) raw | 5.65 g |
| Tortilla | 5.50 g |
| Fried onions | 5.47 g |
| Smoked sausage | 5.30 g |
| Shea butter (karite) | 5.20 g |
| Canned sardine in oil | 5.15 g |
| Boiled soybeans (ripe) | 5.06 g |
| Fried chicken wings | 4.95 g |
| Salami | 4.90 g |
| Fried potato | 4.70 g |
| Chocolate cupcake with chocolate icing | 4.62 g |
| Boiled sausage | 4.59 g |
| Fermented tofu cheese (fuyu) | 4.52 g |
| Caramel popcorn | 4.48 g |
| Pepperoni sausage | 4.46 g |
| Marjoram spice powder | 4.41 g |
| Nutmeg spice, ground | 4.39 g |
| Baked mackerel | 4.30 g |
| Tempe | 4.30 g |
| Raw egg yolk | 4.20 g |
| Raw beef fat | 4.00 g |
| Cooked chicken back (meat with skin) | 4.00 g |
| Mars chocolate bar (almond) | 3.98 g |
| Raw pork ribs (ribs) | 3.95 g |
| Cooked pork tail | 3.94 g |
| Sausages | 3.93 g |
| Donuts | 3.92 g |
| Sunflower oil | 3.80 g |
| Fresh sprouted soybeans | 3.78 g |
| Raw goose meat | 3.76 g |
| Celery seeds | 3.72 g |
| Fried shark meat | 3.70 g |
| Dried tarragon | 3.70 g |
| Butter | 3.69 g |
| Raw pork tail | 3.68 g |
| Sponge cake layers for cake | 3.63 g |
| Cloves (spice) seasoning powder | 3.61 g |
| Baked chicken wings | 3.59 g |
| Chicken wings, boiled or stewed | 3.58 g |
| Caramel | 3.48 g |
| Raw chicken thighs, meat with skin | 3.47 g |
| Blood sausage | 3.46 g |
| Fried chicken thighs (meat with skin) | 3.41 g |
| Caviar, red or black, cooked (heat-treated) | 3.40 g |
| Chicken legs (legs) raw, meat with skin | 3.35 g |
| Raw mackerel | 3.35 g |
| Fried chicken legs (meat with skin) | 3.33 g |
| Oat flour | 3.33 g |
| Quinoa grains dry | 3.29 g |
| Jeera cumin seeds | 3.28 g |
| Cumin seeds | 3.27 g |
| Dried mint | 3.26 g |
| Baked salmon | 3.26 g |
| Fried chicken egg | 3.25 g |
| Chicken thighs, boiled or stewed (meat with skin) | 3.25 g |
| Fried chicken drumstick (meat with skin) | 3.23 g |
| Fresh green soybeans | 3.20 g |
| Liver pate | 3.16 g |
| Anise seeds | 3.15 g |
| Dried parsley | 3.12 g |
| Doctor's sausage | 3.12 g |
| Hot chili peppers dried in the sun | 3.08 g |
| Milk sausages | 3.02 g |
| Snickers chocolate bar | 3.01 g |
| Boiled green soybeans | 3.01 g |
| Cacao butter | 3.00 g |
| Baked chicken thighs (meat with skin) | 2.99 g |
| Chickpea flour | 2.98 g |
| Cooked chicken feet | 2.98 g |
| Smoked herring | 2.92 g |
| Fried croaker | 2.92 g |
| Boiled or stewed chicken legs (meat with skin) | 2.87 g |
| Chinook salmon raw | 2.80 g |
| Dry amaranth groats (seeds) | 2.78 g |
| Unheated oat bran | 2.77 g |
| Chocolate cake layers | 2.76 g |
| Baked herring | 2.74 g |
| Dry chickpeas | 2.73 g |
| Egg omelette | 2.71 g |
| Raw chicken hearts | 2.71 g |
| Soy protein powder | 2.70 g |
| Baked chinook salmon | 2.66 g |
| Dry soy tofu cheese | 2.66 g |
| Caviar, red or black, raw | 2.66 g |
| Millet flour | 2.62 g |
| Canned anchovies (in oil) | 2.56 g |
| Oatmeal cookies | 2.54 g |
| Raw salmon | 2.54 g |
| Dry oatmeal oatmeal | 2.54 g |
| Baked goose | 2.52 g |
| Raw chicken wings | 2.50 g |
| Paratha flatbread | 2.48 g |
| Raw pork pancreas | 2.48 g |
| Lupine (lupine beans) dry | 2.44 g |
| Pork knuckle, raw shank | 2.41 g |
| Cooked bear meat | 2.40 g |
| Chicken drumstick, stewed or boiled (meat with skin) | 2.38 g |
| Ground allspice | 2.36 g |
| Dried rosemary | 2.34 g |
| Salted popcorn | 2.32 g |
| Beef brain fried | 2.31 g |
| Dry oat flakes (instant) | 2.30 g |
| Cooked chicken hearts | 2.30 g |
| Bay leaf | 2.29 g |
| Baked omul | 2.27 g |
| Skinless chicken thighs, boiled or stewed | 2.24 g |
| Unheated wheat bran | 2.21 g |
| Stewed turkey liver | 2.17 g |
| Dry corn kernels | 2.16 g |
| Raw pork ham and rump | 2.16 g |
| Edamame cooked | 2.16 g |
| Turkey heart raw | 2.15 g |
| Fried chicken | 2.15 g |
| Cooked squid (fried) | 2.14 g |
| Millet dry millet groats | 2.13 g |
| Herring raw | 2.13 g |
| Roasted turkey (meat and skin of the whole carcass) | 2.12 g |
| Naan flatbread Indian wheat flatbread | 2.10 g |
| Bread crackers | 2.09 g |
| Baked chicken drumstick (meat with skin) | 2.08 g |
| Dried spirulina (in powder form) | 2.08 g |
| Saffron spice | 2.07 g |
| Breadcrumbs | 2.06 g |
| Raw pork carbonate | 2.05 g |
| Boiled or stewed turkey neck | 2.04 g |
| Pork pancreas, cooked | 2.03 g |
| Reveler seeds | 2.02 g |
| Coho salmon raw | 1.99 g |
| Chicken liver stewed or boiled | 1.99 g |
| Chicken drumstick (without skin) fried | 1.97 g |
| Raw chicken drumstick, meat with skin | 1.97 g |
| Chicken breast raw, skin on | 1.96 g |
| Marshmallows in chocolate | 1.94 g |
| Boiled pork tongue | 1.93 g |
| Baked trout | 1.92 g |
| Raw chicken egg | 1.91 g |
| Raw minced pork, 20% fat | 1.91 g |
| Popcorn without salt | 1.90 g |
| Multigrain bread | 1.87 g |
| Cooked minced pork (20% fat) | 1.87 g |
| Baked chicken legs (meat with skin) | 1.86 g |
| Milkfish (hanos) raw | 1.84 g |
| Baked carp | 1.84 g |
| Cooked turkey heart | 1.83 g |
| Avocado fresh | 1.82 g |
| Dried openwork chervil | 1.80 g |
| Raw pork tongue | 1.78 g |
| Ground sage | 1.76 g |
| Rice bran bread | 1.76 g |
| White whole grain corn flour | 1.76 g |
| Yellow whole grain corn flour | 1.76 g |
| Coriander seeds | 1.75 g |
| Hot Dog | 1.74 g |
| Gruyère cheese | 1.73 g |
| White corn flour (masa) | 1.72 g |
| Oat bread | 1.70 g |
| Coconut oil | 1.70 g |
| Oat bran bread | 1.69 g |
| Fennel seeds | 1.69 g |
| Baked chicken | 1.69 g |
| Turkey liver raw | 1.68 g |
| Powdered egg replacers | 1.68 g |
| Salted herring | 1.68 g |
| Abalone cooked | 1.68 g |
| Raw goose egg | 1.67 g |
| Baked turkey thigh (fillet) | 1.66 g |
| Turkey egg raw | 1.66 g |
| Cheese Fontina | 1.65 g |
| Canned horse mackerel | 1.65 g |
| Hard tofu cheese (linen) | 1.65 g |
| Soy Protein (Isolate) Powder | 1.65 g |
| Anchovies raw | 1.64 g |
| White wheat bread | 1.62 g |
| Raw pig ears | 1.61 g |
| Cheesecake | 1.60 g |
| Babassu oil | 1.60 g |
| Pork neck (neck) raw | 1.60 g |
| Whole grain wheat bread | 1.59 g |
| Beef brain raw | 1.59 g |
| Cooked rabbit meat | 1.56 g |
| Dry sorghum grains | 1.56 g |
| Boiled pork legs | 1.54 g |
| Boiled or stewed chicken | 1.54 g |
| Sweet yeast dough buns | 1.53 g |
| Raw minced chicken | 1.51 g |
| French fries | 1.50 g |
| Macadamia nut | 1.50 g |
| Trout raw | 1.50 g |
| Roasted macadamia nut | 1.50 g |
| Duck (duck meat) baked (meat without skin) | 1.49 g |
| Cream cheese | 1.48 g |
| Turkey neck raw | 1.48 g |
| Pork brain cooked | 1.47 g |
| Chicken back (without skin) raw | 1.47 g |
| Raw turkey, meat and skin of the whole carcass | 1.47 g |
| Raw carp | 1.43 g |
| Pig brain, raw | 1.43 g |
| Cheddar cheese | 1.42 g |
| Hamburger (McDonald's) | 1.42 g |
| Yellowtail (lacedra) raw | 1.42 g |
| Boiled chicken egg (hard-boiled) | 1.41 g |
| Whole grain sorghum flour | 1.40 g |
| Dry muesli (with dried fruits and nuts) | 1.39 g |
| Milk chocolate | 1.38 g |
| Chicken drumstick (without skin), stewed or boiled | 1.37 g |
| Oregano oregano, dried | 1.37 g |
| Baked swordfish | 1.37 g |
| Baked river perch | 1.36 g |
| Stewed turkey gizzards | 1.36 g |
| Beaver meat cooked | 1.35 g |
| Swiss cheese | 1.34 g |
| Raw pork loin | 1.34 g |
| Dry egg noodles | 1.33 g |
| Baked sockeye salmon | 1.33 g |
| Raw quail egg | 1.32 g |
| Roquefort cheese | 1.32 g |
| Canned green olives | 1.31 g |
| Chicken liver raw | 1.31 g |
| Boiled or stewed pork heart | 1.30 g |
| Cooked stewed pork | 1.29 g |
| Fried cooked pork | 1.28 g |
| Baked coho salmon | 1.27 g |
| Fried chicken liver | 1.27 g |
| Spelled cereal in dry form | 1.26 g |
| Dark chocolate (70-85% cocoa) | 1.26 g |
| Milk Protein Supplement Powder | 1.24 g |
| Raw duck egg | 1.22 g |
| Dark chocolate (60-69% cocoa) | 1.22 g |
| Pretzels without salt | 1.22 g |
| Pork intestines cooked | 1.22 g |
| Baked or smoked eel | 1.21 g |
| Boiled mussels | 1.21 g |
| French green beans fresh | 1.21 g |
| Shark meat raw | 1.20 g |
| Soy milk | 1.19 g |
| Dried thyme | 1.19 g |
| Mexican Cotija cheese | 1.19 g |
| Cooked pheasant | 1.19 g |
| Raw pheasant meat | 1.18 g |
| Baked pork loin | 1.17 g |
| Whole grain flour (wheat) | 1.17 g |
| Boiled chickpeas | 1.16 g |
| Baked chum salmon | 1.15 g |
| Boiled pig ears | 1.15 g |
| Raw swordfish | 1.15 g |
| Boiled beef kidneys | 1.14 g |
| Lentils (red or pink), dry | 1.14 g |
| Dry whole wheat noodles | 1.14 g |
| Fried smelt | 1.14 g |
| Raw pork heart | 1.12 g |
| Raw sockeye salmon | 1.12 g |
| Beef liver, stewed or fried | 1.11 g |
| Dry barley groats | 1.11 g |
| Cheese Queso Fresco | 1.11 g |
| Dark chocolate (45-59% cocoa) | 1.09 g |
| Raw pork feet | 1.09 g |
| Baked catfish | 1.08 g |
| Raw rabbit meat | 1.08 g |
| Quinoa boiled in water | 1.08 g |
| Dry teff cereal | 1.07 g |
| Fresh grape leaves | 1.07 g |
| Raw river perch | 1.06 g |
| Pork liver fried or stewed | 1.05 g |
Excess omega-3 PUFAs
In the realities of the modern world, when omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids usually predominate in the diet, and most patients have problems with the outflow of bile, which are accompanied by bending of the gallbladder neck, helminthic infestation or stones, it is quite difficult to achieve an excess of omega-3 .
We recommend
“How to avoid vitamin B12 deficiency and what foods to take for this?” More details
However, like any biologically active compound, omega-3 PUFAs must be taken strictly according to the instructions. Moreover, it must be taken into account that they, although to a much lesser extent, are capable of forming pro-inflammatory molecules (as in the case of the previously described psoriasis).
In addition, their use in individuals with low platelets should be strictly supervised by nutritionists and physicians, as omega-3 PUFAs can further reduce blood clotting.
Beneficial properties of saturated fatty acids, their effect on the body
Saturated fatty acids are considered to be the most harmful.
But if you consider that breast milk is saturated with these acids in large quantities (in particular, lauric acid), it means that the consumption of fatty acids is inherent in nature. And this is of great importance for human life. You just need to know which foods are best to eat. And you can get plenty of such benefits from fats! Animal fats are the richest source of energy for humans. In addition, it is an indispensable component in the structure of cell membranes, as well as a participant in the important process of hormone synthesis. Only due to the presence of saturated fatty acids does the successful absorption of vitamins A, D, E, K and many microelements occur.
Proper consumption of saturated fatty acids helps improve potency, regulates and normalizes the menstrual cycle. Optimal consumption of fatty foods prolongs and improves the functioning of internal organs.
Interaction with other elements
It is very important for saturated fatty acids to have interaction with essential elements. These are vitamins that belong to the class of fat-soluble.
The first and most important on this list is vitamin A. It is found in carrots, persimmons, bell peppers, liver, sea buckthorn, and egg yolks. Thanks to him - healthy skin, luxurious hair, strong nails.
Vitamin D is also an important element, which helps prevent rickets.
Signs of a lack of EFAs in the body
- disruption of the nervous system;
- insufficient body weight;
- deterioration of the condition of nails, hair, skin;
- hormonal imbalance;
- infertility.
Signs of excess saturated fatty acids in the body:
- significant excess body weight;
- atherosclerosis;
- development of diabetes;
- increased blood pressure, cardiac dysfunction;
- formation of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
Factors influencing the content of EFAs in the body
Not consuming EFAs puts increased stress on the body because it has to look for substitutes from other food sources to synthesize fats. Therefore, the consumption of EFAs is an important factor in the presence of saturated fats in the body.
Selection, storage and preparation of foods containing saturated fatty acids
Following a few simple rules when selecting, storing and preparing foods will help keep saturated fatty acids healthy.
- 1 If you do not have increased energy expenditure, when choosing food products it is better to give preference to those in which the saturated fat content is low. This will enable the body to better absorb them. If you have foods high in saturated fatty acids, then you should simply limit yourself to small amounts.
- 2 Storage of fats will be long-term if moisture, high temperature, and light do not enter them. Otherwise, saturated fatty acids change their structure, which leads to deterioration in the quality of the product.
- 3 How to properly prepare foods with EFAs? Culinary processing of foods rich in saturated fats involves grilling, roasting, stewing and boiling. It is better not to fry. This leads to an increase in calorie content of food and reduces its beneficial properties.
If you are not going to engage in heavy physical labor, and you do not have any special indications for increasing the amount of EFAs, it is still better to slightly limit the consumption of animal fats in your food. Nutritionists recommend trimming excess fat from meat before cooking it.
Saturated fatty acids for beauty and health
Proper consumption of saturated fatty acids will make you look healthy and attractive. Gorgeous hair, strong nails, good vision, healthy skin - all these are integral indicators of a sufficient amount of fat in the body.
It is important to remember that EFA is energy that should be expended in order to avoid the formation of unnecessary “reserves”. Saturated fatty acids are an essential component of a healthy and beautiful body!
Attention! The information is for informational purposes only and is not intended to make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. Always consult a specialized doctor!
Tatyana Eliseeva chief editor of the Food+ project
Ask a Question
Rating:
10
/10
Votes: 2
Usefulness of material 10
Reliability of information 0
Formatting of Article 10
Including fats in the diet
The main preferred sources of fat for forming a diet and recommended consumption amounts are presented in the infographic above.
| When frying in oil, it is important to consider the stability of the oil when heated (table in the section “Issues of eating fats”), since not all of them are stable when heated. If possible, it is better to minimize this type of frying. |
Choose cooking methods such as stewing in water, steaming, baking in the oven, or grilling. Remove fat that forms during cooking of meat and fish.
When including foods such as commercial baked goods (cookies, donuts, muffins, cakes, pizza dough), packaged snacks (crackers, microwave popcorn, chips), fried foods (french fries, fried chicken, chicken nuggets, breaded fish ), sweets, it is important to remember that they most likely contain trans fats that are harmful to the body.
Preference should be given to low-processed fats (for example, butter rather than margarine), because In the process of technological processing and long-term (or incorrect) temperature treatment at home, most of the beneficial properties of the product are lost, only its energy value is retained.
Dietary fats must be fresh, as they quickly oxidize and accumulate harmful compounds.