The benefits and harms of flour
Complete exclusion of flour from the diet is not an advisable solution, since this product has many beneficial properties:
- has high nutritional value;
- contains a large amount of proteins, fiber, vitamins and minerals;
- improves mental activity;
- increases immunity;
- has a positive effect on the blood circulation process;
- accelerates metabolism in the body;
- prevents the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- reduces the likelihood of gallstones forming;
- has a positive effect on inflammatory processes, helping to reduce them at the initial stage;
- reduces symptoms of asthma and bronchitis.
Flour is considered a high-calorie product, so its main harm is associated with rapid weight gain. This applies primarily to wheat flour, which is used in baking and bakery products. Flour can also cause allergies, since some types contain gluten (many people suffer from intolerance to this protein).
Food calorie table
A calorie is a unit of energy found in almost all foods. Calorie content is a designation of the energy value of food, equal to the amount of energy received by the body after its complete absorption. The table of caloric content of foods per 100 grams includes a full range of energy sources necessary to support the vital functions of the body.
Thanks to simple calculations, we can calculate the number of calories needed for our diet. The table of caloric content of finished products helps to determine the proteins, carbohydrates, and fats contained in our diet. Their number corresponds to a number of factors:
technical process used by manufacturers,
recipe used in preparation,
weather conditions, when considering the calorie content of plant foods.
When performing calculations, the result will be averaged. To reduce the time spent counting calories, there are standard tables.
Types and varieties of flour
Flour is distributed according to several indicators:
- Type – determines the purpose of using flour. It can be bakery (rye and wheat flour from soft wheat, a mixture of different types of flour), confectionery and pasta flour (made from durum wheat).
- The type of flour is determined by the plant crop (mainly cereal plants) from which it was made. The most common flours are wheat, barley, rye, buckwheat, pea, rice and other types of flour.
- The grade is determined by the amount of flour that was obtained from 100 kg of grain raw materials. This means that the lower the grade of the product, the greater its yield.
The table below shows the existing varieties of wheat flour:
| Variety | Product Features |
| Krupchatka | Contains at least 30% gluten, has a grain size from 0.16 to 0.20 mm. Flour is white or creamy with a yellowish tint. It is added to the dough dough to give the product porosity. |
| Higher | Contains at least 28% gluten. The product is made from the core of the grain (without the outer shell). Premium flour is used to make most baked goods and is also added to sauces and creams. |
| First | Contains at least 30% gluten. It is used in the preparation of noodles, pies, savory buns, and pancakes. |
| Second | The flour turns out brown due to the fact that it contains a lot of the outer shell of wheat. |
| Whole wheat flour | The product is obtained by grinding unrefined grains. The flour particles are heterogeneous and large. Contains the highest amount of useful substances. |
What to cook with flour
You can prepare many different dishes from flour, but we decided to tell you about the simplest ones. You can easily prepare any of these dishes yourself; to do this, choose the flour you like and follow our recipes. Bon appetit!
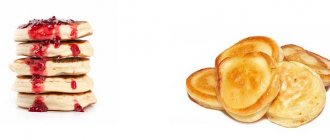
Pancakes
Calorie content: 227 kcal per 100 grams.
| Milk | 2.5 glasses |
| Flour | 1.5 cups |
| Eggs | 2 pcs. |
| Sugar | 1 tsp. |
| Salt | 0.5 tsp. |
| Vegetable oil | 3 tbsp. l. |
Cooking process:
- Mix milk, eggs, sugar and salt with a mixer.
- Add butter and continue beating with a mixer until smooth.
- Add flour and mix well.
- Fry in a frying pan with a little oil on both sides for 1-2 minutes.
- Ready! Serve with jam, condensed milk or sour cream!
Cupcakes
Calorie content: 300 kcal per 100 grams.
| Cocoa | 2 tbsp. l. |
| Milk | 5 tbsp. l. |
| Sugar | 4 tbsp. l. |
| Flour | 4 tbsp. l. |
| Baking powder | ¼ tbsp. l. |
| Vegetable oil | 3 tbsp. l. |
| Vanilla sugar | taste |
| Eggs | 1 PC. |
Cooking process:
- Beat egg, sugar and vanilla sugar with a fork.
- Add milk, butter and baking powder. Mix well.
- Gradually add flour and cocoa, stirring.
- Pour into molds and place in an oven preheated to 180 degrees.
- In 6-7 minutes the cupcakes are ready!
Flatbread
Calorie content: 226 kcal per 100 grams.
| Flour | 1 kg |
| Salt | 1 tbsp. l. |
| Yeast | 2 tbsp. l. |
| Water | 200 ml |
Cooking process:
- Sift the flour and prepare the yeast. To do this, mix the yeast with 2 tablespoons of flour and dilute in ½ cup of warm milk (or water). Place the finished mixture in a warm place and wait for it to rise.
- When the mixture rises, add the remaining water, salt and flour. Cover with a towel and let the dough rise.
- When the dough is ready, you need to grease it on both sides with oil and put it in the oven, tightly covering the top with something heavy (a frying pan, for example).
- Bake at 200 degrees for 10 minutes, then remove, turn over, cover with a frying pan and bake for another 10 minutes.
- Ready!
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of flour depends on the grain from which it was made.
It contains the following substances:
- proteins (gluten, proteins, albumins, glutelins, plolamins);
- amino acids (glutamine, leucine, proline);
- carbohydrates - such as starch, fiber, hemicellulose, polysaccharides, as well as small amounts of fructose and glucose;
- lipids;
- fatty acids (linoleic, oleic, linolenic);
- phosphoric and silicic acids;
- vitamins E, A, PP and group B;
- minerals (phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, potassium);
- trace elements (zinc, manganese, copper, iron);
- enzymes (proteinases, amylases, lipase and others).
Each type of flour has certain features of its composition, which are presented in the table below:
| Type of flour | Features of the composition |
| Rice | Gluten-free, rich in vegetable protein, lecithin and B vitamins. Helps cleanse the body of toxins and waste. |
| Oatmeal | Rich in mucous components that normalize the functioning of the digestive tract. The product does not contain gluten. Flour contains silicon, which is responsible for metabolic processes in the body. |
| Buckwheat | Contains a lot of copper and iron, which helps maintain normal hemoglobin levels in the blood. There is no gluten in flour. |
| Corn | Contains a lot of fiber, potassium, vitamins A, B and E, improves bone and connective tissue, normalizes the flow of bile. |
| Rye | Contains a large amount of lysine. The product contains 50% more magnesium and potassium than wheat flour. |
Oatmeal
It will allow you to withstand even the most restrictive diet, as it increases the production of the joy hormone - serotonin. It blocks hunger pangs and helps overcome stress, which is often the main cause of excess weight.
Distinctive features:
- refers to products with a low percentage of starch and gluten, which makes it even more useful for weight loss;
- At the same time, it contains a lot of fat, so you shouldn’t get carried away with dishes made from it;
- makes baked goods crumbly and airy.
Secrets of use: it is better to mix it with other types of flour in a ratio of 1:3. If you have a powerful blender at home, you don’t have to buy it separately: just grind regular oats into powder.
When preparing what dietary dishes can you use:
- pancakes;
- flatbreads;
- cookie;
- pancakes.
The amino acid composition of oatmeal resembles muscle protein, so it will be most useful for those who use not only diets, but also workouts to lose weight. Contains vitamins A, E, group B, microelements, dietary fiber, fiber.
Contents of the BZHU
BJU is the ratio of substances such as fats, carbohydrates and proteins in a product. Based on the calculation of this ratio, a diet and proper nutrition are compiled taking into account the needs of the body.
The main types of flour have the following ratio of BZHU (per 100 g):
- Wheat flour contains the most carbohydrates - 76%. In 2nd place are proteins – 10%, and in 3rd place are fats – 1%.
- Oatmeal contains 64% carbohydrates, 12.2% protein and 7.5% fat.
- Rye – 64% carbohydrates, 8.7% proteins, 1.7% fats.
- Rice contains 77.7% carbohydrates, 6.8% proteins, 0.8% fats.
- Corn – 71% carbohydrates, 8.2% protein and 1.9% fat.
- Buckwheat – 64% carbohydrates, 16.3% proteins and 3.5% fats.
- Barley flour contains 69.9% carbohydrates, 10.3% proteins, 1.1% fats.
- Soy flour contains only 24.2%, and the largest amount of proteins (of the presented types of flour) – 46.5%. Fats account for 11.2%.
- Pea flour contains 21.8% carbohydrates, 7.6% proteins, and is completely free of fat.
- Flaxseed flour contains the least amount of carbohydrates – 12.63%. The protein content is 31.94% and fat content is 12.41%.
Calories in seafood and fish
| Product | Quantity | Energy value (kcal) | Proteins (g) | Fat (g) | Carbohydrates (g) |
| Beluga fresh | 100 g | 147 | 21,0 | 0,7 | 0,0 |
| Dried roach | 100 g | 235 | 46,4 | 5,5 | 0,0 |
| Cold smoked roach | 100 g | 181 | 31,1 | 6,3 | 0,0 |
| Boiled pink salmon | 100 g | 168 | 22,9 | 7,8 | 0,0 |
| Fresh pink salmon | 100 g | 147 | 21,0 | 7,0 | 0,0 |
| Salted pink salmon | 100 g | 169 | 22,1 | 9,0 | 0,0 |
| Fried catfish | 100 g | 209 | 22,2 | 11,5 | 4,1 |
| Boiled catfish | 100 g | 114 | 15,5 | 5,8 | 0,0 |
| Granular pink salmon caviar | 100 g | 230 | 31,2 | 11,7 | 0,0 |
| Chum salmon caviar granular | 100 g | 251 | 31,6 | 13,8 | 0,0 |
| Sturgeon caviar granular | 100 g | 203 | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 |
| Sturgeon caviar | 100 g | 236 | 36,0 | 10,2 | 0,0 |
| Cod roe | 100 g | 115 | 24,0 | 0,2 | 0,0 |
| Boiled squid | 100 g | 110 | 18,0 | 4,2 | 0,0 |
| Fresh squid | 100 g | 74 | 18,0 | 0,3 | 0,0 |
| Hot smoked flounder | 100 g | 192 | 22,0 | 11,6 | 0,0 |
| Boiled flounder | 100 g | 103 | 18,3 | 3,3 | 0,0 |
| Fresh flounder | 100 g | 83 | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 |
| Boiled crucian carp | 100 g | 102 | 20,7 | 2,1 | 0,0 |
| Fresh crucian carp | 100 g | 87 | 17,7 | 1,8 | 0,0 |
| Boiled carp | 100 g | 102 | 16,0 | 3,7 | 2,0 |
| Salted chum salmon | 100 g | 184 | 24,3 | 9,6 | 0,0 |
| Spicy salted sprat | 100 g | 154 | 14,8 | 10,5 | 0,0 |
| Salted sprat | 100 g | 137 | 17,1 | 7,6 | 0,0 |
| Canned crabs | 100 g | 85 | 18,7 | 1,1 | 0,1 |
| Boiled crabs | 100 g | 96 | 16,0 | 3,6 | 0,0 |
| Canned shrimp | 100 g | 81 | 17,8 | 1,1 | 0,0 |
| Boiled shrimp | 100 g | 95 | 18,9 | 2,2 | 0,0 |
| Fresh shrimp | 100 g | 97 | 22,0 | 1,0 | 0,0 |
| Hot smoked bream | 100 g | 172 | 32,8 | 4,5 | 0,0 |
| Boiled bream | 100 g | 126 | 20,9 | 4,7 | 0,0 |
| Cold smoked bream | 100 g | 160 | 29,7 | 4,6 | 0,0 |
| Smoked salmon | 100 g | 162 | 21,5 | 8,4 | 0,0 |
| Salmon from the grill | 100 g | 283 | 20,7 | 22,3 | 0,6 |
| Salted salmon | 100 g | 269 | 21,0 | 20,5 | 0,0 |
| Boiled mackerel | 100 g | 124 | 22,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 |
| Boiled mussels | 100 g | 50 | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 |
| Boiled pollock | 100 g | 79 | 17,6 | 1,0 | 0,0 |
| Sea kale | 100 g | 5 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 0,0 |
| Boiled burbot | 100 g | 92 | 21,4 | 0,7 | 0,0 |
| Hot smoked sea bass | 100 g | 175 | 23,5 | 9,0 | 0,0 |
| Boiled sea bass | 100 g | 112 | 19,9 | 3,6 | 0,0 |
| Stewed sea bass | 100 g | 120 | 10,9 | 6,6 | 4,2 |
| Fried river perch | 100 g | 180 | 20,6 | 9,1 | 4,0 |
| Baked river perch | 100 g | 103 | 6,8 | 4,7 | 8,4 |
| Fried sturgeon | 100 g | 273 | 16,0 | 17,4 | 13,2 |
| Boiled sturgeon | 100 g | 179 | 17,7 | 12,0 | 0,0 |
| Octopus | 100 g | 73 | 18,2 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| Boiled halibut | 100 g | 216 | 14,0 | 17,8 | 0,0 |
| Cod liver | 100 g | 610 | 4,0 | 66,0 | 0,0 |
| Boiled sea crayfish | 100 g | 90 | 20,5 | 0,7 | 0,3 |
| Fresh sea crayfish (lobster, lobster) | 100 g | 89 | 18,8 | 1,3 | 0,5 |
| Boiled river crayfish | 100 g | 97 | 20,3 | 1,3 | 1,0 |
| Boiled sardine | 100 g | 178 | 20,1 | 10,8 | 0,0 |
| Sardines in oil | 100 g | 221 | 24,1 | 13,9 | 0,0 |
| Sevruga in tomato sauce | 100 g | 179 | 16,1 | 11,5 | 2,8 |
| Herring in vegetable oil | 100 g | 301 | 16,4 | 26,5 | 0,0 |
| Herring in sour cream | 100 g | 97 | 5,5 | 6,2 | 5,3 |
| Herring in tomato sauce | 100 g | 159 | 13,8 | 9,7 | 4,6 |
| Hot smoked herring | 100 g | 215 | 21,8 | 14,3 | 0,0 |
| Pickled herring | 100 g | 192 | 16,5 | 12,6 | 3,4 |
| Salted herring | 100 g | 217 | 19,8 | 15,4 | 0,0 |
| Smoked mackerel | 100 g | 221 | 20,7 | 15,5 | 0,0 |
| Boiled mackerel | 100 g | 211 | 19,6 | 14,7 | 0,0 |
| Mackerel, canned | 100 g | 258 | 16,4 | 21,4 | 0,0 |
| Catfish in tomato sauce | 100 g | 126 | 12,9 | 6,3 | 4,3 |
| Boiled catfish | 100 g | 196 | 18,4 | 13,6 | 0,0 |
| Horse mackerel in oil | 100 g | 309 | 15,6 | 27,4 | 0,0 |
| Horse mackerel in tomato sauce | 100 g | 110 | 14,8 | 2,3 | 7,3 |
| Fried horse mackerel | 100 g | 190 | 20,3 | 10,5 | 3,7 |
| Boiled horse mackerel | 100 g | 133 | 20,6 | 5,6 | 0,0 |
| Cold smoked horse mackerel | 100 g | 94 | 17,1 | 2,8 | 0,0 |
| Fresh sterlet | 100 g | 122 | 17,0 | 6,1 | 0,0 |
| Pike perch in tomato sauce | 100 g | 119 | 14,0 | 5,3 | 3,7 |
| Boiled pike perch | 100 g | 97 | 21,3 | 1,3 | 0,0 |
| Hot smoked cod | 100 g | 115 | 26,0 | 1,2 | 0,0 |
| Fried cod | 100 g | 111 | 23,0 | 0,1 | 0,0 |
| Baked cod | 100 g | 90 | 6,0 | 3,7 | 8,0 |
| Boiled cod | 100 g | 78 | 17,8 | 0,7 | 0,0 |
| Grilled cod | 100 g | 172 | 22,1 | 9,1 | 0,6 |
| Cold smoked cod | 100 g | 94 | 22,1 | 0,5 | 0,0 |
| Tuna in vegetable oil | 100 g | 190 | 27,1 | 9,0 | 0,0 |
| Tuna in its own juice | 100 g | 96 | 21,0 | 1,2 | 0,0 |
| Smoked eel | 100 g | 326 | 17,9 | 28,6 | 0,0 |
| Fresh oysters | 100 g | 95 | 14,0 | 0,3 | 6,0 |
| Trout | 100 g | 97 | 19,2 | 2,1 | 0,0 |
| Hamsa salted | 100 g | 166 | 21,2 | 9,0 | 0,0 |
| Boiled hake | 100 g | 95 | 18,5 | 2,3 | 0,0 |
| Sprats in vegetable oil | 100 g | 363 | 17,4 | 32,4 | 0,4 |
| Pike in tomato sauce | 100 g | 108 | 14,2 | 4,0 | 3,6 |
| Boiled pike | 100 g | 98 | 21,3 | 1,3 | 0,0 |
Calorie content per 100 g
The calorie content of different types of flour is presented in the table below:
| Type of flour | Calorie content (kcal per 100 g) |
| Wheat 2nd grade | 332 |
| Premium wheat | 350 |
| Rice | 321,1 |
| Oatmeal | 68 |
| Buckwheat | 367 |
| Corn | 370 |
| Soy | 391,7 |
| Rye | 298 |
| Barley | 325,2 |
| Linen | 287,8 |
| Pea | 118,4 |
Pumpkin
Pumpkin flour is low-calorie and beneficial for the body, therefore it is recommended as part of diets. It contains a lot of vitamins (C, A, B3, B9), microelements (potassium, manganese, iron, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, copper, zinc, selenium), omega-3 fatty acids.
Distinctive features:
- has a pleasant nutty taste;
- has an airy consistency;
- The baked goods turn out fluffy and tasty.
Secrets of use: goes well with.
When preparing what dietary dishes can you use:
- bakery products;
- protein shakes;
- salads and cereals;
- traditional side dishes.
In addition to the above, without fear of gaining extra pounds in diets, you can prepare dishes from the following types of flour:
- coconut;
- chickpea;
- barley;
- amaranth;
- soy;
- pea;
- chestnut;
- lentil
To independently determine the list of those varieties that will be most useful and effective for you, study the table below.
Table of nutritional value (BJU) and calorie content per 100 g of product
Based on the presented review and the table data, it is easy to decide which flour is better to use when losing weight: almond flour with a calorie content of 602 kcal or wheat-bran flour with 208 kcal. Now, while getting your figure and weight in order, you don’t have to give up golden brown pancakes and fluffy pancakes. Just let them not be nut, but rye or barley, for example. The choice is yours.
Whole grain wheat flour
rich in vitamins and minerals such as: vitamin B1 - 33.5%, vitamin B5 - 12.1%, vitamin B6 - 20.4%, vitamin B9 - 11%, vitamin PP - 24.8%, potassium - 14, 5%, magnesium - 34.3%, phosphorus - 44.6%, iron - 20%, manganese - 203.4%, copper - 41%, selenium - 112.4%, zinc - 21.7%
- Vitamin B1
is part of the most important enzymes of carbohydrate and energy metabolism, providing the body with energy and plastic substances, as well as the metabolism of branched amino acids. A lack of this vitamin leads to serious disorders of the nervous, digestive and cardiovascular systems. - Vitamin B5
is involved in protein, fat, carbohydrate metabolism, cholesterol metabolism, the synthesis of a number of hormones, hemoglobin, promotes the absorption of amino acids and sugars in the intestines, and supports the function of the adrenal cortex. A lack of pantothenic acid can lead to damage to the skin and mucous membranes. - Vitamin B6
is involved in maintaining the immune response, processes of inhibition and excitation in the central nervous system, in the transformation of amino acids, the metabolism of tryptophan, lipids and nucleic acids, promotes the normal formation of red blood cells, and maintaining normal levels of homocysteine in the blood. Insufficient intake of vitamin B6 is accompanied by decreased appetite, impaired skin condition, and the development of homocysteinemia and anemia. - Vitamin B9
as a coenzyme is involved in the metabolism of nucleic acids and amino acids. Folate deficiency leads to disruption of the synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, resulting in inhibition of cell growth and division, especially in rapidly proliferating tissues: bone marrow, intestinal epithelium, etc. Insufficient folate intake during pregnancy is one of the causes of prematurity, malnutrition, and congenital deformities and child development disorders. A strong relationship has been shown between folate and homocysteine levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease. - Vitamin PP
is involved in redox reactions of energy metabolism. Insufficient vitamin intake is accompanied by disruption of the normal condition of the skin, gastrointestinal tract and nervous system. - Potassium
is the main intracellular ion that takes part in the regulation of water, acid and electrolyte balance, and is involved in the processes of conducting nerve impulses and regulating blood pressure. - Magnesium
is involved in energy metabolism, the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, has a stabilizing effect on membranes, and is necessary to maintain the homeostasis of calcium, potassium and sodium. A lack of magnesium leads to hypomagnesemia, an increased risk of developing hypertension and heart disease. - Phosphorus
takes part in many physiological processes, including energy metabolism, regulates acid-base balance, is part of phospholipids, nucleotides and nucleic acids, and is necessary for the mineralization of bones and teeth. Deficiency leads to anorexia, anemia, and rickets. - Iron
is part of proteins with various functions, including enzymes. Participates in the transport of electrons and oxygen, ensures the occurrence of redox reactions and activation of peroxidation. Insufficient consumption leads to hypochromic anemia, myoglobin deficiency atony of skeletal muscles, increased fatigue, myocardiopathy, and atrophic gastritis. - Manganese
is involved in the formation of bone and connective tissue, and is part of enzymes involved in the metabolism of amino acids, carbohydrates, and catecholamines; necessary for the synthesis of cholesterol and nucleotides. Insufficient consumption is accompanied by slower growth, disturbances in the reproductive system, increased fragility of bone tissue, and disturbances in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. - Copper
is part of enzymes that have redox activity and are involved in the metabolism of iron, stimulates the absorption of proteins and carbohydrates. Participates in the processes of providing oxygen to the tissues of the human body. Deficiency is manifested by disturbances in the formation of the cardiovascular system and skeleton, and the development of connective tissue dysplasia. - Selenium
is an essential element of the antioxidant defense system of the human body, has an immunomodulatory effect, and is involved in the regulation of the action of thyroid hormones. Deficiency leads to Kashin-Beck disease (osteoarthritis with multiple deformities of the joints, spine and limbs), Keshan disease (endemic myocardiopathy), and hereditary thrombasthenia. - Zinc
is part of more than 300 enzymes and is involved in the processes of synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, nucleic acids and in the regulation of the expression of a number of genes. Insufficient consumption leads to anemia, secondary immunodeficiency, liver cirrhosis, sexual dysfunction, and the presence of fetal malformations. Research in recent years has revealed the ability of high doses of zinc to disrupt the absorption of copper and thereby contribute to the development of anemia.
more hide
You can see the complete directory of the most useful products in the application
The total calorie content of premium wheat flour per 100 grams is 335 kcal, including 100 g of product contains:
- proteins – 10.7 g (42 kcal);
- fat – 1.2 g (14 kcal);
- carbohydrates – 70 g (279 kcal).
The vitamin composition of wheat flour is represented by choline, vitamin PP, vitamins H, E, B9, B6, B5, B2, B1.
A special feature of premium wheat flour is that the particle diameter is less than 40 microns. There is almost no fiber in this product. High-grade flour is puffed, soft, but not useful for weight loss due to the large number of calories.
This product is the worst to remove from the body, significantly inhibiting the functioning of the intestines and digestive system.
To prepare flour dishes, it is important to know how much wheat flour fits in certain containers. So, 1 teaspoon contains 10 g of flour, one tablespoon contains 30 g of product, and 1 glass contains 155 g.
Good quality wheat flour is a fairly healthy product. With its balanced use, the body is saturated with all the necessary vitamins and minerals, and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized.
Wheat flour is an effective remedy for stimulating the formation of blood cells. If you refuse this product, the condition of the skin worsens and disruptions in the absorption of nutrients occur.
High-grade wheat flour is an indispensable component of most flour dishes. This product is used for preparing sweet flour desserts, pies, pancakes, as well as “serious” food - pasties, dumplings, pasta, bread.
What flour is suitable for the diet?
People who want to lose excess weight or have certain diseases or health problems follow a special diet. Based on the characteristics of the diet, the optimal type of flour is selected.
Weight loss
When losing weight, it is recommended to build a diet based on the ratio of fats, carbohydrates and proteins.
The following indicators are considered optimal:
- proteins – 40-50%;
- carbohydrates – 10-20%;
- fats – 30-40%.
Therefore, it is recommended to include dishes made from corn flour in your diet. It is rich in potassium, phosphorus, and contains a lot of fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol levels and speed up the process of losing excess weight. Corn flour also improves the microflora of the intestines and stomach, and has a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels.
The calorie content of different types of flour varies significantly
Rice flour has also proven itself well in dietary nutrition. It removes salts from the body and normalizes the digestion process due to the content of potassium, calcium and folic acid. It is also useful to consume buckwheat flour when losing weight. The slow sugars it contains satiate the body, satisfying the feeling of hunger for a long time.
Additionally, the product helps remove cholesterol from the body due to its selenium content. Oatmeal regulates fat metabolism in the body, cleanses it of toxins due to its fiber content. Also, when consuming the product, the body produces the substance serotonin, which is responsible for a person’s good mood.
On the diet, you are allowed to eat products made from several types of flour. For example, Borodino bread, which contains rye and wheat flour, helps fight excess weight, prevent the development of cancer and iron deficiency anemia.
Diabetes
The calorie content of different types of flour must be taken into account when creating a diet for people with diabetes. It is also necessary to take into account the glycemic index (the rate of breakdown of glucose that enters the blood after consuming the product) of flour. The optimal figure is up to 50 units.
Among the main types of flour, flaxseed flour has the lowest indicator - 35 units. Its use allows you to reduce the glycemic index (GI) of various dishes due to the low carbohydrate content.
The use of oatmeal is also allowed - its GI is 45 units. It has the ability to reduce blood glucose levels, improve liver function, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
If you have diabetes, you can also use rye flour. Its GI is 45 units. It is rich in magnesium, which is involved in the activation of many enzymes in the body, including the enzyme responsible for the production of insulin.
Buckwheat
- provokes severe allergic reactions;
- causes inflammation with further formation of edema and joint pain;
- and most importantly, it disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which forces the body to store everything that has not been digested in reserve in the form of fat depots.
Gluten is found in wheat, oatmeal, barley and rye. As a binding component, it forms dough of the required viscosity for baking. But it doesn’t contain it, which allows it to be used in diets.
Distinctive features:
- grey colour;
- specific taste;
- the dough turns out dense and steep;
- There is only one variety, but it is produced under different brands.
Secrets of use: for baking, it is better to mix it in equal proportions with wheat.
- pancakes;
- dumplings (provided they contain low-calorie poultry);
- bread;
- pies (preferably with vegetable filling).
Considering that buckwheat flour is hypoallergenic and also lowers blood sugar (which also promotes weight loss), it is not surprising that it is considered one of the healthiest. If you are going to go on a diet, it is better to choose this for delicious baked goods.
Daily volume of flour consumption on a diet
A person who does not have health problems, but wants to lose a few extra pounds, should consume up to 150 g of flour products per day. At the same time, a single serving containing flour products should not exceed 50 g.
Here are some tips to help you lose weight:
- Flour products are best consumed in the first half of the day.
- It is recommended to combine flour dishes with vegetables and dairy products.
- It is undesirable to simultaneously eat flour products along with cereals, fatty dairy products, and vegetables containing a lot of starch.
- The combined consumption of flour with sweet dishes, pickled and salted vegetables, as well as protein products is prohibited.
- Do not give up eating flour products - the substances they contain cannot be replaced with other food products.
What foods should you limit?
Both people suffering from diabetes and those who are losing weight should exclude high-grade wheat flour from their diet, since it contains a huge amount of starch and calories, which contribute to increased blood sugar levels and excess weight gain.
Calories, kcal:
Proteins, g:
Carbohydrates, g:
Flour is a food product obtained from cereal grains by grinding. Flour is produced from grains of various crops, most often wheat. There is also flour,... The latter varieties can be found not so often.
When making flour, the grain is first peeled from the shell and then ground. The central part of the grain contains carbohydrates. Gluten is the protein component of flour. Flour is a universal product that allows you to diversify the human diet and has wonderful capabilities for preparing delicious food. It is present in every home as a necessary product.
Wheat flour is made from grains, one of the most common cereal plants. Wheat flour is a powdery product with different grain sizes, white in color with shades of yellow or gray, depending on the degree of grinding. Wheat flour has a pleasant bready aroma, almost no taste.
Calorie content of wheat flour
The calorie content of wheat flour is 342 kcal per 100 grams of product.
Composition and beneficial properties of wheat flour
Wheat flour contains dietary fiber, which is most abundant in wholemeal flour and. Fiber helps normalize digestive processes and gently cleanse the walls of the intestines and stomach from waste and toxins. The product is carbohydrate, and can contain both simple carbohydrates () and complex ones (). Wheat flour is rich in calcium, which are responsible for the activity of the nervous system and improve the condition of the skin, hair and nails (calorizator). The product also contains minerals: necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
Harm of wheat flour
Wheat flour contains , so people with gluten intolerance need to replace wheat flour with gluten-free analogues. Wheat flour is a high-calorie product, excessive consumption of which can lead to gaining extra pounds.
Types and varieties of wheat flour
According to the degree of grinding, the following types of wheat flour are distinguished:
- Coarse
- flour is made from whole grains, including bran and cell membranes, the flour particles are quite large, and contain dietary fiber; - Fine grinding
- flour is produced only from the internal endosperm, the flour particles are small, the composition contains starch and gluten, and there is practically no fiber.
By grade, flour is divided into:
- Krupchatka
- small grains, produced from the endosperm of grains of special varieties of wheat, have a light cream color and high baking properties. Used for making rich pastries, Easter cakes, etc. - The highest grade
is very small white endosperm particles (powder), used in the production of baked goods and as a thickener in sauces; - The first grade
is small, finely ground particles, white with a yellowish tint, suitable for savory baking, preparing dough for noodles, dumplings and dumplings, sautéing, used mainly in the production of bread products; - The second grade
- particles of the grain shell are added to the endosperm particles, coarse flour with whiter larger particles of white color with a grayish or yellowish tint. Table varieties of white bread and savory pastries, gingerbreads, and cookies are baked from this flour; - Wallpaper
- consists of crushed grain, including the bran shell. The particles are large, heterogeneous in size, and contain the most protein and vitamins. It is used for the production of table varieties of bread that do not go stale for a long time.
For more information about flour, watch the video “Rye flour versus wheat flour” from the TV show “Live Healthy!”
Selection and storage of wheat flour
Depending on the goals and needs, different types of flour are chosen, but the selection rules are similar - the flour should flow freely, have no lumps, musty or moldy smell. Wheat flour should be stored in tightly closed glass or ceramic containers in a cool place, according to the expiration date indicated on the package.
Terms and conditions of flour storage
To get the maximum benefit from flour, it is necessary to store this product correctly.
Some recommendations will help with this:
- Favorable temperatures range from + 5 to + 18 0C.
- The ideal humidity level is no more than 60-70%. Its high level indoors can cause the development of fungus in the product.
- The formation of condensation should be avoided - it will cause the flour to become damp and mold may appear in it.
- The flour should not be exposed to direct sunlight - it is better to choose a shaded place (for example, a closed cabinet).
- The storage room should be dry and clean, free of foreign odors, since the wheat product tends to quickly absorb them.
- Do not allow changes in temperature and humidity, as the flour may deteriorate.
- The room where flour is stored must be periodically ventilated and cleaned to avoid the appearance of pests.
- After opening the bag, it is best to pour the flour into a glass or metal jar or box that closes tightly. You can also choose fabric or paper bags for storage.
- Storing flour in the refrigerator extends its shelf life.
- It is recommended to periodically inspect the flour - if insects are found, the flour should be sifted and left for listening.
- One of the ways to prevent insects and pests is to place 1-2 unpeeled cloves of garlic in flour.
- If you take flour in your hand and feel cold, this indicates increased moisture in the product. Therefore, it is recommended to dry the flour.
Its shelf life depends on the type of flour, which is presented in the table below:
| Type of flour | Shelf life (in months) |
| Wheat flour (highest grade) | 12 |
| Whole grain wheat | 6-8 |
| Rye | 4-6 |
| Corn (low-fat) | 3-6 |
| Soy (deodorized) | 12 |
| Buckwheat | 7 |
| Barley, rice | 6 |
| Pea | 8-10 |
When pouring flour from the original packaging, it is necessary to put a sticker on the container where it will be stored indicating the expiration date (indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging). After the end of the storage period, it is not recommended to use the product, as it loses its nutritional and quality properties.
Flour contains a large number of useful substances. This is a high-calorie product, but with the right choice of flour, you can create an optimal diet containing healthy flour products.
How to replace white wheat flour?
A beneficial solution for the daily menu of diabetics is the complete exclusion of the product, but often most patients are not capable of such sacrifices.
Different types of flour
An alternative in this case would be to replace wheat flour with healthy types:
- spelled;
- spelt;
- coarse buckwheat;
- bran;
- cereals;
- airy cookies and bread.
Instead of traditional white flour, it is recommended to purchase coarsely ground wallpaper, which is suitable for baking baked goods and unsweetened cookies.
Ingredients A glass of flour
1 faceted tbsp at risk = 195 ml 1 tbsp flour 105 g in 200 ml 1 tbsp flour 135 g in 250 ml
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “A glass of flour.”
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 312 kcal | 1684 kcal | 18.5% | 5.9% | 540 g |
| Squirrels | 11.5 g | 76 g | 15.1% | 4.8% | 661 g |
| Fats | 2.2 g | 56 g | 3.9% | 1.3% | 2545 g |
| Carbohydrates | 61.5 g | 219 g | 28.1% | 9% | 356 g |
| Alimentary fiber | 9.3 g | 20 g | 46.5% | 14.9% | 215 g |
| Water | 14 g | 2273 g | 0.6% | 0.2% | 16236 g |
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 2 mcg | 900 mcg | 0.2% | 0.1% | 45000 g |
| beta carotene | 0.01 mg | 5 mg | 0.2% | 0.1% | 50000 g |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.41 mg | 1.5 mg | 27.3% | 8.8% | 366 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.15 mg | 1.8 mg | 8.3% | 2.7% | 1200 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 80 mg | 500 mg | 16% | 5.1% | 625 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.9 mg | 5 mg | 18% | 5.8% | 556 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.55 mg | 2 mg | 27.5% | 8.8% | 364 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 40 mcg | 400 mcg | 10% | 3.2% | 1000 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 3.3 mg | 15 mg | 22% | 7.1% | 455 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 4 mcg | 50 mcg | 8% | 2.6% | 1250 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 7.8 mg | 20 mg | 39% | 12.5% | 256 g |
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 310 mg | 2500 mg | 12.4% | 4% | 806 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 39 mg | 1000 mg | 3.9% | 1.3% | 2564 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 94 mg | 400 mg | 23.5% | 7.5% | 426 g |
| Sodium, Na | 7 mg | 1300 mg | 0.5% | 0.2% | 18571 g |
| Sera, S | 98 mg | 1000 mg | 9.8% | 3.1% | 1020 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 336 mg | 800 mg | 42% | 13.5% | 238 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 24 mg | 2300 mg | 1% | 0.3% | 9583 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Iron, Fe | 4.7 mg | 18 mg | 26.1% | 8.4% | 383 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 4 mcg | 10 mcg | 40% | 12.8% | 250 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 2.46 mg | 2 mg | 123% | 39.4% | 81 g |
| Copper, Cu | 400 mcg | 1000 mcg | 40% | 12.8% | 250 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 22 mcg | 70 mcg | 31.4% | 10.1% | 318 g |
| Selenium, Se | 6 mcg | 55 mcg | 10.9% | 3.5% | 917 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 2 mg | 12 mg | 16.7% | 5.4% | 600 g |
The energy value of a glass of flour is 312 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
And a little about secrets.
The story of one of our readers, Inga Eremina:
I was especially depressed by my weight; at 41, I weighed as much as 3 sumo wrestlers combined, namely 92 kg. How to completely lose excess weight? How to cope with hormonal changes and obesity? But nothing disfigures or makes a person look younger than his figure.
But what can you do to lose weight? Laser liposuction surgery? I found out - no less than 5 thousand dollars. Hardware procedures - LPG massage, cavitation, RF lifting, myostimulation? A little more affordable - the course costs from 80 thousand rubles with a nutritionist consultant. You can, of course, try to run on a treadmill until you go crazy.
And when will you find time for all this? And it's still very expensive. Especially now. Therefore, I chose a different method for myself.
Source
Calorie content of rye flour
Rye flour, like wheat flour, has found wide use in traditional Russian cuisine, because bread was previously baked from it. It differs from wheat not only in composition, but also in its darker color, as well as lower gluten content, which affects the elasticity of the dough in finished products.
In addition, it is considered more healthy, and this is not only because of the relatively low calorie content of rye flour. A cereal product such as rye contains many vitamins and other useful substances that help regulate the functioning of the intestines and the body as a whole.
Finished products made from rye flour are not so dangerous for the figure. In addition, they help remove salts and harmful substances from the body. The calorie content of rye flour is usually about 298 kcal, so many diets allow you to consume a small amount of rye bread to replenish the need for valuable vitamins.