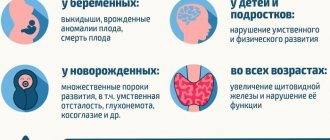
Characteristics and symptoms of anemia
Anemia is a condition in which there is a reduced content of red blood cells or hemoglobin in each individual red blood cell, measured per unit volume of blood. Hb levels decrease below the following limits:
- in children from six months to 6 years - 110 g/l;
- for schoolchildren 7-14 years old - 120 g/l;
- for women - 120 g/l;
- for men - 140 g/l
Symptoms of mild to moderate anemia (Hb value not lower than 70 g/l):
- skin - cold, pale, with a yellowish tint;
- spleen - enlarged;
- intestines - change in color of stool;
- muscles - flaccid, weakened;
- eyes - yellow tint;
- nervous system - fatigue, dizziness;
- circulatory system - low blood pressure;
- respiratory system - shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- heartbeat - rapid.
Symptoms of anemia.
With severe anemia (hemoglobin below 70 g/l), fainting, heart attacks, and chest pain are possible.
Against the background of reduced immunity, the risk of acute respiratory viral infections and tonsillitis increases.
Symptoms of anemia in older people
The symptoms of the disease are quite vague, they are often confused with other diseases characteristic of old age. Mainly hair and skin, intestines and stomach, nervous system and heart muscle are affected. If you rank the symptoms of low hemoglobin from the most common to the rarer, you get the following list:
- Paleness of the skin;
- Dizziness;
- Chronic fatigue, muscle weakness;
- Brittle, peeling nails;
- Dry skin;
- Slow hair growth, split ends;
- Sores and “jams” in the lip area.
Patients are also often bothered by tinnitus and rapid heartbeat. All of these symptoms cause serious discomfort. If in the initial stages an elderly person may not pay attention to the deterioration of well-being, then over time unpleasant sensations become constant companions. It is important not to waste time and start treatment in the early stages, when therapy is most effective.
Causes of the disease
Iron deficiency anemia develops for the following reasons:
- Processes in the gastrointestinal tract in which the function of iron absorption is impaired.
- Donation, blood loss after surgery, trauma.
- Siderosis (lung damage that develops when working with metal dust or shavings).
- Hormonal disorders, taking corrective medications.
- Chronic conditions associated with blood loss (enteritis, ulcerative colitis, uterine fibroids, peptic ulcer).
- Fasting, vegetarianism.
Medicines and food additives
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe iron supplements: tablets or solutions. “Adjusting nutrition is not enough even with moderate anemia, when the level of hemoglobin in the blood is below 90 g/l,” says Daria Kirillova. — Often such anemia accompanies other, more serious diseases, for example, oncology, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and female genital organs. Anemia often occurs as a complication during chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer.”
After consulting with your doctor, you can take a course of probiotic supplements.
The need to follow a diet
The purpose of therapeutic nutrition for anemia is to provide the body with the necessary amount of nutrients, vitamins, and nutrients. The diet contains enough iron required for Hb growth. It improves the quality of life, restores strength and strengthens the body's protective functions.
It is necessary to follow a diet to provide the body with the necessary substances.
Principles of diet planning
When developing a menu for people who suffer from IDA, adhere to the following rules:
- An increased amount of protein in the menu promotes good absorption of iron. The proportion of carbohydrates does not change, but fats decrease slightly.
- Inclusion of broths and soups in the menu. They stimulate gastric secretions and promote proper absorption of nutrients.
- Taking ferruginous mineral waters - “Darasun”, “Kuka”, “Polyustrovskaya”, etc. Drinking juices from pomegranate seeds, apples, grapefruit.
Authorized Products
The correct diet for anemia is based on the following products:
Lamb is an approved product.
- lamb, veal;
- beef and pork offal;
- seafood and sea fish;
- buckwheat, oatmeal, millet, barley groats;
- wholemeal bread;
- beets, tomatoes, eggplants, zucchini;
- dill, green onions;
- red and black berries;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- dark varieties of honey, bee bread, pollen;
- sunflower seeds, pumpkin;
- quinces, plums, peaches.
Sufficient amounts of vitamin C and folic acid promote better absorption of iron from food. To get them into the body, it is recommended to consume sea buckthorn, black currants, citrus fruits, and nuts. Milk and honey will help compensate for the lack of vitamin B12.
Prohibited Products
You should limit foods and drinks rich in calcium as much as possible: parsley, milk, chocolate, coffee, tea. Until your hemoglobin level normalizes, you should not frequently consume spinach, asparagus, rhubarb, and bran.
Coffee and chocolate should not be consumed if you are anemic.
Sources of iron
Leaders in iron content:
- Liver and red meat. 100 g of product contains 35% of the daily requirement of iron in heme form.
- Mussels. From 100 g of seafood you can get 13% of the daily requirement of a microelement.
- Quinoa. Inca cereal does not contain gluten, so it can be used in the diet of people suffering from celiac disease.
- Black beans. Includes maximum amounts of non-heme iron.
- Sugar cane molasses. In 1 tsp. The product contains almost 1 mg of iron.
How to increase low hemoglobin
To quickly restore Hb, you should consume:
- lean red meat and liver;
- red caviar;
- buckwheat porridge;
- pomegranate juice;
- honey with chopped dried apricots and nuts.
To increase low hemoglobin, you need to drink pomegranate juice.
Foods that interfere with iron absorption
To effectively correct the condition of IDA, exclude from the menu foods that contain oxalates that interfere with the absorption of iron:
- lard, margarine, bacon;
- smoked meats, fatty meats;
- brines, marinades;
- buns, pies;
- tea, coffee, lemonades;
- black grapes;
- green tea;
- artichoke;
- strong alcoholic drinks.
Fat interferes with iron absorption.
What should be excluded from the diet
And now about what food should not be in the diet for anemia. “Flour products (except whole grain bread) and baked goods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee, tea, sausages and smoked meats, pickles, lard, margarine - all these are undesirable products for people suffering from anemia,” says Daria Kirillova.
Try to cleanse your diet of all processed foods and minimize the amount of sugar. “Refined foods, fast food, and excess sweets contribute to the development of essential nutritional deficiencies,” says Rachel Link. “As a result, we suffer from fatigue, weight gain, as well as inflammatory bowel disease and candidiasis. With candidiasis, the normal pH balance is disrupted and the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract suffers. This, in turn, interferes with the normal absorption of nutrients. This is why candidiasis and anemia are linked, especially in women. To get rid of candidiasis, try eliminating all sugars from your menu for a while. Sweets are an ideal environment for harmful microorganisms.”
Here is a list of foods to avoid if you have low hemoglobin levels.
- Sugar.
- Processed grain.
- Dark chocolate. Although it is rich in iron, it also contains tannins, which interfere with iron absorption.
- Regular dairy products. Calcium binds to iron and can lead to poor absorption of the latter.
- Coffee and tea. Excessive consumption of these drinks can block iron absorption, so reduce the amount of coffee to one cup per day and tea to four cups.
Treatment table No. 11 for anemia
Diet No. 11 according to Pevzner is enriched with proteins, vitamins, and amino acids. It contains a sufficient amount of iron, folic acid, vitamins C and B12. The menu involves the use of foods that are involved in hematopoiesis and affect the absorption of iron. The total daily weight of products is about 3 kg, and the calorie content is 2900-3500 kcal.
Almost all foods are allowed for consumption, with the exception of some fats.
Chemical composition of the daily diet
The daily menu of the “Table No. 11” diet is based on the following principles:
- Protein content - 110-130 g. A large proportion of proteins (60%) comes from animal products.
- Amount of carbohydrates - 400-450 g.
- Fat consumption - 100-110 g. It is not allowed to consume cooking fats, lard, meat with a high content of refractory fats (duck, lamb).
It is not allowed to eat meat with a high content of refractory fats.
Rules for eating
The daily intake of products is usually divided into 4-6 doses.
Fractional nutrition promotes better absorption of vitamins and microelements, helps the body to normally perceive the high calorie content of the diet. The food temperature can be in the range from 15 to 40. During food preparation, all types of heat treatment are allowed, except for frying and smoking.
A prerequisite is to drink enough fluid (about 2.5 liters per day).
"Iron" fruits
The most famous iron-containing fruits are pomegranate and apple, but their high iron content is nothing more than a myth. In fact, the most iron is found in dried rose hips (28 mg), peach (4 mg), apricots and dried apricots (3.2 mg), prunes (3 mg), raisins (2.7 mg), persimmon (2.5 mg). ). Among the berries in terms of iron content, the leaders are viburnum (3.1 mg), raspberry (1.6 mg), black currant (1.3 mg) and strawberry (1.2 mg). Some vegetables also contain some iron. For example, in spinach (3.2 mg), sorrel (2 mg), parsley (1.8 mg), garlic (1.5 mg), beets (1.4 mg), carrots (1.2 mg), tomatoes (0.6 mg). Unfortunately, the absorption of iron from products of plant origin is low - only 1–5%.
Dietary rules for various types of anemia
The menu is developed by a nutritionist or hematologist, adjusting the menu depending on the type of anemia. For pathologies caused by iron deficiency, the menu includes foods high in vitamin C and Fe. If Hb is low due to a lack of vitamin B12, select foods that contain a lot of it (sardines, Atlantic mackerel, feta, salmon, lamb, cottage cheese, eggs).
For iron deficiency anemia
Fats interfere with the normal absorption of iron from food, so their daily intake is reduced to 80-90 g. Refractory fats are completely excluded. They are found in butter, lamb, duck, cream, cheese and curd products. Protein consumption is increased to 140 g.
For iron deficiency anemia, increase protein intake.
Calcium forms insoluble compounds with ferrum, which prevents its absorption. This can be avoided by timing the intake of calcium- and iron-rich foods. The menu includes foods rich in vitamin C.
For B12 deficiency anemia
If there is a lack of cyanocobalamin and the resulting changes in the biochemical composition of the blood, diet No. 11 is also prescribed. The emphasis is on dishes made from beef liver, kidneys, heart, fish and seafood. Additionally, they include foods containing folic acid, which promotes the absorption of vitamin B12.
These are asparagus, citrus fruits, nuts, watermelons, tomatoes, grain bread, avocados, cereals, cod liver.
For hemolytic anemia
With this form of pathology, the diet includes foods that contain substances to support the process of hematopoiesis. Adhering to the basic principles of diet No. 11, increase the proportion of the following components:
- Currants, milk, and rose hips will help compensate for the lack of cobalt.
- The source of manganese is greens.
- Zinc is found in mushrooms, cheese, and yeast.
- The lack of copper will be compensated by legumes: cereals, mushrooms.
For hemolytic anemia, you need to eat cheese and mushrooms.
For aplastic anemia
In case of pathology, it is necessary to support the process of hematopoiesis. The basis of the diet is table No. 11, including in the diet foods with a large proportion of cobalt, manganese, copper and zinc.
Diet therapy for intestinal stenosis (stricture)
Some patients with Crohn's disease may develop a complication over time - a narrowing of the intestinal lumen , called stricture or stenosis .
In ulcerative colitis, in the case of the development of cancer (adenocarcinoma) of the colon, the lumen of the intestinal tube may also be narrowed due to the tumor. Undoubtedly, the presence of a narrowing of the lumen of the intestinal tube requires limiting foods and dishes rich in dietary fiber. These foods include apples, tomato peels, pepper peels, green salad, cabbage, asparagus, spinach, beets, citrus fruits, whole grain products, nuts, seeds, mushrooms, grains, dried fruits, fruit peels and seeds, mushrooms, cucumbers, watermelon . If, despite the stricture, the patient consumes excessively fibrous foods, intestinal obstruction may develop. These complications can be prevented by avoiding fibrous foods and eating pureed foods.
In cases where the stenosis of the intestinal lumen is significant (often the lumen of the intestinal tube is only a few millimeters), at the stage of preparing the patient for a planned operation, it is possible to prescribe enteral mixtures in a volume that meets the daily needs of the body.
Enteral formulas are artificially created mixtures for therapeutic nutrition that provide the body with all the necessary nutrients. They can be dry or liquid (depending on the manufacturer and type), but even dry mixtures require dilution with water. Thus, the mixture enters the patient’s body in liquid form, minimizing the risk of developing intestinal obstruction and at the same time having high nutritional value.
After surgery to remove a section of intestine with a stricture, the diet is gradually expanded. Dietary recommendations are given taking into account the volume of the operation, the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition in the postoperative period.
Diet for anemia in children
In infants born from healthy mothers, anemia rarely occurs before the age of 1 year, since the absorption of iron from mother's milk is higher than from other products. If a blood test shows a decrease in Hb levels, a nursing mother should adjust her diet and include iron-rich foods in the menu.
A nursing mother needs to adjust her diet.
For anemia in children from one to 6 years of age, beef pates and offal, apple juices and purees, beets, fresh herbs, and sea fish are introduced into the diet. From the age of 4 you can try honey if you have no allergic reactions to bee products.
The child's diet should include meat, low-fat broths, sesame seeds, wholemeal bread, and cereal porridge. Drinks include apple and pomegranate juices, rosehip decoction with honey. During adolescence, children may consciously refuse meat.
Iron from plant foods is less absorbed, so Hb levels should be regularly monitored.
"Iron" leaders
The best sources of iron for humans are animal products - liver and meat. The absorption of such iron is 25–30%! The richest in iron are liver (20 mg), heart (6.2 mg), tongue (5 mg), rabbit meat (4.4 mg) and turkey (4 mg). Second place is occupied by dried mushrooms (35 mg) and brewer's yeast (18 mg). They are followed by seaweed (16 mg), cocoa (12.5 mg) and quail and chicken egg yolks (about 7.2 mg). The absorption of iron from these products is 10–15%. Special mention should be made about legumes and cereals. Beans (12 mg), peas (7 mg), buckwheat (7 mg), oatmeal (3.4 mg), millet (2.7 mg) and pearl barley (1.8 mg) are irreplaceable on the table of a person suffering from anemia.
Nutrition for anemia in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the intake of iron into the body of the expectant mother should be increased. Its daily share should cover the needs of the mother and fetus. The diet must include:
- cabbage - white, red, sea cabbage;
- low-fat fish;
- prunes;
- pumpkin seeds;
- lean red meat;
- blueberries, apples;
- dark honey.
You need to include cabbage in your diet.
Menu examples
The diet of people who adhere to the “Table No. 11” diet may contain many meat, lean, vegetarian and vegetable dishes. The large variety of foods available provides all the nutrients to support the body.
For anemia in older women and pregnant women
To build a therapeutic diet, you can follow this plan:
- Morning. Buckwheat porridge, dried fruits, pomegranate juice.
- Lunch. Cranberry juice jelly.
- Dinner. Salad (tomatoes, cucumbers, herbs and soft cheese), red borscht, boiled chicken breast. Berry juice.
- Afternoon snack. Cottage cheese casserole with candied fruits, yogurt without filler.
- Dinner. Stuffed eggplants. Tomato. Rose hip decoction.
- Dream Interpretation. Kefir or yogurt.
For anemia in older women and pregnant women, you should eat buckwheat porridge.
Juices can be alternated by squeezing them from apples, apricots, and peaches. For lunch and dinner you can cook steamed or baked fish and red meat. Honey, which should be consumed with tea, will bring benefits. The norm is 1 tsp. per day in the absence of diabetes and allergies to bee products.
For a week for children
Parents can prepare food for the child separately or eat according to the proposed menu with the whole family. An example menu is presented in the table:
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Dream Interpretation |
| Mon | Oatmeal with dried fruits, bread, apple compote | Orange | Pea soup with wheat croutons, baked sea bass fillet. Biscuits, cranberry juice | Cottage cheese casserole, apple juice | Mashed potatoes, beef cutlet, vegetable salad | Yogurt |
| VT | Buckwheat porridge with milk, sandwich with cheese, rosehip infusion | Banana | Cream of mushroom soup. Beef meatballs, buckwheat porridge, cabbage salad. Bread. Raspberry fruit drink | Pomegranate | Grated carrot salad with vegetable oil. Spaghetti with seafood | Rosehip infusion, biscuit |
| SR | Cheesecakes with sour cream and raisins, birch sap | Kiwi | Vegetable soup, tomato, beef liver pate, millet porridge | Cranberry jelly | Lentil puree, veal meatballs. Vegetable salad | Cocktail made from half a banana and milk |
| Thu | Muesli with dried fruits and nuts. Sea buckthorn infusion | Fruit salad of 1 apple, half a kiwi and an orange | Lentil soup. Bread. Spaghetti with stewed beef liver. Apple juice | Oatmeal cookies, berry juice or compote | Vegetable stew. Baked rabbit (fillet). Rose hip drink | Yogurt |
| PT | Nalistniki with beef liver. Rose hip drink | Green apple | Cream of broccoli soup. Bread, stewed potatoes with beef | Plums | Cucumber and tomato salad. Chicken souffle. Currant compote | Yogurt |
| SB | Sandwiches with cheese or boiled beef. Strawberry compote | Buckwheat bread | Ear. Bread. Mashed potatoes, fresh vegetable salad. Tomato juice | Apricots | Fish cutlets, baked cauliflower. Rose hip decoction | Milkshake |
| Sun | Pumpkin porridge in milk with dried apricots. Dried fruits compote | Some walnuts, peach | Buckwheat soup. Bread. Liver pancakes with potatoes. Berry juice | Grapefruit, oatmeal cookies | Chicken meatballs, pea puree. Cabbage salad. Rose hip decoction | Raspberry juice, blackcurrant jelly |
Order this menu:
Individual nutrition (Personal diet) from Performance Food
Rating: no ratings / 1 day: 3700 rubles
…
Order p-food.ru
Diet recipes
When compiling a diet, you should be guided by the list of permitted and prohibited foods.
Chicken and vegetable salad
Take 300 g of chicken fillet, 2 cucumbers and tomatoes, lettuce, green onions, olive oil - 2 tbsp. l. Wash and dry the breast, cut into pieces 2 cm thick. Fry in oil until golden brown. Cut cucumbers into slices, tomatoes into slices. Place lettuce leaves, vegetables and cooled meat on a plate. Season and sprinkle with green onions.
Chicken and vegetable salad has a very rich, pleasant taste.
Roast beef
Cut the peeled potatoes (500 g) into cubes, chop the onion, grate the carrots. Fry the onion until golden brown, add the carrots and simmer for about 4 minutes. Place the potatoes in a clay pot or glass baking tray. Add vegetable gravy to it. Cut the washed and dried beef (500 g) into small pieces. Send to vegetables, add salt and fill with hot water to the top. Bake in an oven preheated to 180°C for 45 minutes.
Cod in sour cream sauce
Cut the defrosted cod fillet (600 g) into pieces. Salt, pepper, roll in flour and fry in sunflower oil. Place on a napkin to absorb excess fat. Cut the onion into half rings and fry in the pan where the cod was cooked. Place the fish on the onion bed. Dissolve 5 tbsp in a bowl. l. sour cream, 400 ml water, 1 tbsp. l. flour. Add some salt and turmeric. Stir the sauce until smooth and pour it over the fish and onions. Cover with a lid and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes from the moment it boils.
Cod in sour cream sauce is a very tasty, tender dish.
Spaghetti with meatballs in tomato sauce
Prepare equal amounts of spaghetti and ground beef (300 g each), raw egg, onion, tomato paste and vegetable oil (3 tbsp each).
Before cooking, grate the onion. Add it along with the egg to the minced meat, salt and season to taste. Form meatballs and fry in a frying pan until golden brown. Dilute tomato paste in a glass of warm water, adding a pinch of sugar and salt. Place the meat balls in a saucepan, add the prepared tomato liquid and simmer for about 25 minutes over low heat. Boil the spaghetti and transfer to a dish. Place the meatballs and pour over the tomato sauce.
Oatmeal with dried fruits
Prepare 200 g of oatmeal, peeled and chopped apple, a handful of raisins, honey, cinnamon and butter. Pour boiling water over the washed raisins and leave for 5 minutes. Place oatmeal in a saucepan, add raisins and add water (2 cups). Bring to a boil, reduce heat and cook the porridge for about 10 minutes, stirring. Season with butter and place on a plate. Garnish with apple and sprinkle with cinnamon.
Oatmeal has a beneficial effect on digestion.
Stuffed eggplants
Pour 1 tsp of water overnight. sunflower seeds. In the morning, drain the water and dry the grains. Cut young eggplants (3 pieces) lengthwise, scoop out the pulp with a spoon and sprinkle it with salt. Leave for 10 minutes. Finely chop the pulp, sprinkle with chopped onion (1 piece) and simmer. After blanching, peel the tomatoes (4 pcs.) and cut into large cubes. Add tomatoes to eggplant pulp and onions, sprinkle with chopped herbs (except mint and basil). Simmer for 10 minutes. Remove from heat, add crumbled cheese (150 g) and seeds.
Fill eggplant boats with the mixture and place them on a greased baking sheet.
Bake in the oven at 180°C for 45 minutes. Serve sprinkled with mint and basil.
Duration of diet for anemia
The restoration of iron levels in the body of children and adults occurs gradually, so nutrition to increase hemoglobin is designed for a long period. Once a month, the patient donates blood, which allows the doctor to judge the effectiveness of therapy and adjust the treatment program.
Dietary food is designed for a long term.
The principles of the “Table No. 11” diet for anemia should be followed for at least 3 months. When the level of Hb in the blood is normalized, it is canceled, however, when creating a diet, it is recommended to rely on the acquired eating habits.
Traditional medicine recipes to combat anemia
Beetroot and carrot juice with honey.
You should squeeze juice from fresh beets (50 ml) and carrots (100 ml). Mix the liquids and add 1 tbsp. l. liquid honey. Use daily in the morning for 2 weeks. Vitamin drink. Extract juice from apples, pomegranate seeds, grapes, carrots and beets. Mix in equal proportions and drink immediately. You can sweeten the drink with fructose. The duration of the course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Product based on buckwheat and nuts. Grind 1 cup walnut kernels and 0.5 cup buckwheat to flour. Add 100 ml of light honey and stir. Use the mixture before meals 3 times a day, 1 tsp. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. You can repeat it in a month.
IBD and calcium deficiency
Calcium deficiency is often observed in patients with IBD. The cause of deficiency may be impaired absorption (due to inflammation and as a result of vitamin D deficiency), increased loss and/or insufficient intake of calcium from food due to dietary restrictions or decreased appetite.
Calcium deficiency is associated with a risk of bone fracture due to osteoporosis (i.e. decreased bone mineral density), which can even lead to disability. In patients with IBD, osteoporosis can be both a complication of the disease itself and an expected side effect when taking steroid hormones.
Products containing calcium are milk and its derivatives (the source of more than half of the amount of calcium consumed), cheeses, eggs, soy isolates, buckwheat and oatmeal, fish and fish caviar. The patient's intolerance to milk and milk-based products or their unreasonable exclusion from the diet creates the preconditions for calcium deficiency. This is especially significant during therapy with steroid hormones, which promote calcium loss in the urine. In these cases, the daily requirement for calcium increases to 1500-2000 mg per day.
According to Russian standards of physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population for healthy people is 1000 mg/day for men and women 18-60 years old, 1200 mg/day for people over 60 years old.
In order for the body to receive calcium in the required amount, it may be necessary to prescribe calcium supplements (necessarily in combination with vitamin D). Such drugs should be taken by all patients with IBD who take steroid hormones for more than 2 weeks. Calcium replacement therapy continues throughout the entire period of hormone treatment and is extended if necessary.
Consequences of not following the diet
By ignoring the recommendations of nutritionists, people with anemia can harm the body. Iron deficiency leads to chronic hypoxia of tissues and organs. Gradually, atrophy of the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive systems occurs. If anemia is left untreated, myodystrophy develops. Lack of Hb provokes the development of vascular and heart diseases, and leads to a decrease in immunity. The body becomes vulnerable to infections, there is constant weakness and drowsiness.
If the diet is not followed, there is constant weakness and drowsiness.
Comments from nutritionists
Lyudmila Smirnova, Professor, Head of the Department of Clinical Hematology and Transfusiology BelMAPO, Minsk: “The main source of iron for the human body is meat and fish.
The microelement is practically not absorbed from plant foods, so you cannot limit yourself to its consumption if it is necessary to increase hemoglobin. You should not combine fermented milk products and animal proteins, since calcium interferes with the absorption of iron.” Svetlana Fus, nutritionist, Kyiv: “If the diet does not give results, you should evaluate the food diary to understand whether there are competing products in one meal. For example, calcium/iron. With low acidity of gastric juice, iron is poorly absorbed from food. To check the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, you should contact a gastroenterologist.”
Vera Kodentsova, professor, leading researcher at the Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow: “Products No. 1 for iron deficiency anemia are beef liver and red meat. They contain B vitamins and iron in heme form, which is easily absorbed. Beef should be present in the diet every day, liver - 3 times a week.”
IBD and iron deficiency
Iron deficiency occurs in 60-80% of patients with IBD, and iron deficiency anemia occurs on average in 16% of outpatients and 64% of inpatients. The causes of iron deficiency and the development of iron deficiency anemia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are different: blood loss , decreased absorption of this microelement in the small intestine due to the inflammatory process, as well as insufficient intake due to dietary restrictions and poor appetite.
Healthy people absorb approximately 5-10% of the iron contained in food, and in conditions of iron deficiency - 10-20%. The absorption of iron from the intestines depends on the type of food: it is best absorbed from mammalian meat - 22%, from liver - 12-16%, from fish - 9-11%, while 2-3% of iron is absorbed from eggs and beans , from fruits – 3-4%, from rice and spinach – 1%. Oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel, legumes), tannins (blueberries, quince), phosphates and phytins (found in grains, legumes), strong tea and excess dietary fiber worsen the absorption of iron. Egg, soy, and milk proteins also reduce the absorption of iron from the gut. Organic acids (malic, citric, ascorbic) improve iron absorption. The optimal combination in one dose is of products containing heme iron (animal meat, poultry, liver, kidneys) and products rich in organic acids (rosehip decoction, blackcurrant, clarified juices, lemons, etc.).
Unfortunately, it is almost never possible to restore iron reserves in the body with diet alone, so patients are additionally prescribed iron supplements.
With low activity or remission of IBD, therapy for iron deficiency and mild iron deficiency anemia most often begins with oral iron supplements (tablets, capsules, dragees or liquid forms). Typically, these drugs are prescribed in a dose of 100-200 mg of iron per day (in terms of elemental iron), since the effectiveness does not increase with increasing dose, and the likelihood of side effects increases.
Iron therapy is considered effective when it leads to an increase in hemoglobin levels by 20 g/l or more within 4 weeks. After normalization of hemoglobin levels, iron supplements should be taken until the tissue depot of iron reserves is restored (controlled by determining the level of ferritin).
In case of high disease activity, intolerance or ineffectiveness of oral iron preparations (increase in hemoglobin, the use of parenteral forms of iron preparations (for intramuscular or intravenous administration) is recommended. In recent years, “bolus” intravenous iron preparations have become widespread, allowing the administration of a significant amount of iron in one infusion ( up to 500-1000 mg).
Reviews and results
Ivan, 42 years old, Yaroslavl: “After abdominal surgery, it took a long time to recover and ate sparingly.
As a result, hemoglobin dropped below 80 g/l. The doctor prescribed multivitamins, a preparation containing iron, and recommended table No. 11. I have been restoring hemoglobin for the third month, it has risen to 100 g/l. The menu includes pomegranate juice, honey with nuts and dried apricots, salmon caviar, meat pates, baked vegetables. However, it’s too early to talk about victory over anemia; you feel weak and drowsy.” Elizaveta, 29 years old, Yekaterinburg: “Because of uterine fibroids, I suffer from heavy and prolonged bleeding. Hemoglobin rarely rises above 100 g/l. The doctor knows about this, but does not refer her for myomectomy. I constantly have to keep table No. 11 and take courses of iron supplements. Red caviar, beef, and liver pate restore blood well. Since there is no time to cook during the week, the diet contains only salads and meat. For some this is meager, but I’m used to it.”
Nadezhda, 55 years old, Sretensk: “My granddaughter, a student, lives in a dormitory in Chita. Despite my support, he saves money and eats from hand to mouth, but still works part-time. It ended in a hungry faint. We went to the doctor, where it turned out that the girl’s hemoglobin was 75 g/l. She stayed with me for two weeks while on sick leave. I fed her dietary meat, cooked fruit drinks, made juices and porridge. My granddaughter felt better and returned to school.”
What is the human need for iron?
- The daily iron requirement for an adult is 1.5 -2 mg
- During pregnancy in the first trimester, the need increases to 2.5-3 mg
- in the second trimester - up to 3.5 - up to 5 mg
- in the third trimester - up to 6.5 - 7 mg
Fact
A typical diet provides 5 to 15 mg of essential iron per day, of which only about 1.5 to 2.5 mg is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. This amount is quite enough to ensure normal functioning of the body, taking into account the loss of iron through urine, sweat, bile and menstrual bleeding.
The intake of iron from food during the entire pregnancy with a normal diet is about 800 mg; the missing iron is replenished from reserve reserves in the depot.
But please note that replenishment of reserves from the depot is possible provided that the reserve reserves themselves are not depleted due to heavy and prolonged menstruation before pregnancy, subsequent pregnancies or bleeding during pregnancy. In addition, you should know that multiple pregnancies and long-term lactation also greatly deplete iron stores.
Restoration of iron reserves in the depot occurs within 4-5 years, so if you are planning a pregnancy before this period, the risk of developing anemia is much higher.