Causes and manifestations of NAFLD Diet for NAFLD Drug therapy for NAFLD Fatty hepatosis, or fatty liver, is a primary or secondary pathological syndrome characterized by excessive accumulation of fat in hepatocytes. This disorder, associated with an increased risk of developing cirrhosis, is a global problem of modern hepatology in particular and all medicine in general. Restoring the liver in obesity is a rather complex and lengthy process, which necessarily includes changing the diet to achieve significant improvement.
General rules
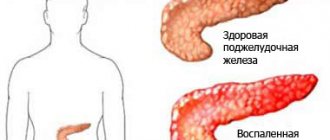
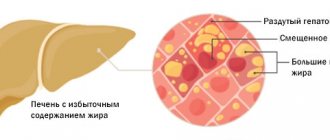
Fatty liver (fatty liver, fatty hepatosis, fatty infiltration, liver steatosis) is a morphological condition of the liver in which more than 5% of the total mass of the organ is fat, mainly triglycerides .
The morphological changes in the organ are based on various etiological factors, which can be divided into two main groups: alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver. And if the first is due to the systematic abuse of alcohol and the toxic effect of ethanol metabolism products ( acetaldehyde ), which cause a pronounced disturbance in fat metabolism and the accumulation of triglycerides inside the cytoplasm of the hepatocyte, then the second is due to many factors, the leading of which are overnutrition, arterial hypertension , fasting/rapid weight loss , insulin resistance , viral hepatitis B and C , genetic factors.
A potential danger with fatty infiltration of the liver is a high level of risk of developing fibrosis with transition to cirrhosis , since favorable conditions are created for the development of the inflammatory process, triggering the mechanism of morphological changes in the structure of hepatocytes and their death.
As a rule, fatty liver occurs asymptomatically or against the background of nonspecific complaints: general weakness, discomfort in the right hypochondrium. With severe fatty liver, the following may occur: skin itching, anorexia , dyspeptic disorders. Treatment and diet for fatty liver are aimed at normalizing biochemical parameters characteristic of the inflammatory process and slowing down/blocking the process of fibrogenesis .
If fatty degeneration develops against the background of overnutrition and the presence of abdominal-visceral obesity , the diet for fatty liver degeneration is primarily aimed at reducing body weight. To do this, the patient is prescribed a calorie-reduced diet with a high content of dietary fiber (vegetables/fruits) and foods with a low glycemic index.
Its selection is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account weight exceeding the physiological norm, age/gender, and level of physical activity. At the same time, the calorie content of the diet should not be reduced sharply, and even more so, fasting is unacceptable, since a rapid decrease in body weight is accompanied by the progression of fatty liver disease. On average, the calorie content of the daily diet should be in the range of 1600-2000 kcal/day, and the period of being on a hypocaloric diet should be at least 3 months.
However, it is important not to forget that nutrition aimed at losing weight must be combined with an increase in physical activity, which is especially important in cases of severe obesity and the presence of diabetes . It has been reliably proven that physical activity lasting 30-40 minutes, regardless of the type and nature of exercise, in combination with dietary nutrition, increases the sensitivity of insulin and contributes to a significantly significant normalization of biochemical parameters.
In case of fatty hepatosis against the background of physiologically normal body weight, nutrition should be aimed at sparing the liver and reducing the activity of the inflammatory process with a physiologically complete diet. This is achieved by regular meals, methods of culinary processing of foods and exclusion of a number of foods from the diet.
For this purpose, it is prohibited to consume fatty foods, especially refractory fats - margarine, solid fats of animal origin (lard, bacon), mayonnaise. Reduce/eliminate the consumption of foods high in cholesterol : egg yolks, fish caviar, fatty dairy products, fatty meats, offal, raw smoked sausages.
Products containing concentrates, preservatives and flavoring additives (long-term storage products) are not recommended - freeze-dried foods, dry juices, canned food, instant soups, confectionery products designed for a long shelf life, as well as products that have a pronounced irritating effect on the liver: smoked meats , seasonings, spices, vinegar, vegetables containing essential oils (garlic, sorrel, radishes, celery, onions, radishes), unripe berries and raw fruits (red currants, green apples, cranberries). The diet reduces the content of simple carbohydrates. Dishes prepared by frying or deep-frying are not allowed.
The liver is an organ whose uniqueness lies in its ability to potentially self-heal under favorable conditions. In this regard, it is recommended to increase the content of active substances in the diet that promote regeneration processes. A particularly pronounced hepaprotective effect is ensured by the combined intake of vitamin E , L-carnitine and phospholipids , which mutually enhance the effect of each of them.
At the same time, L-carnitine enhances the synthesis of its own phospholipids, which play an important role in the construction of hepatocyte , utilizes intracellular fat, accelerates cell repair processes, and tocopherol acetate ( vitamin E ) complements the hepatoprotective effect of essential phospholipids with an antioxidant effect (protects against oxidation) and is involved in processes of intracellular metabolism. Since it is almost impossible to obtain these ingredients with food in the optimal ratio, additional intake of the Gepagard Active dietary supplement is recommended.
Prohibited Products
During the treatment of fatty hepatosis, the following products from the usual diet are vetoed:
- Alcohol;
- Strong coffee, tea and cocoa;
- Meat broths, as they enhance the secretion of gastric juice;
- Fatty types of meat (pork, lamb, etc.);
- Fatty fish;
- Fresh white bread, muffins, pancakes, pancakes, etc.;
- Animal fats, namely: lard, margarine;
- Fatty sauces, for example, mayonnaise;
- Sausages, wieners and frankfurters;
- Smoked and overly salted meat;
- Pickles and canned foods;
- Fatty desserts: cakes and pastries;
- Hotter seasonings;
- Any concentrated food additives: store-bought seasonings containing flavor enhancers, “bouillon cubes”, etc.
Authorized Products
The diet for fatty liver should include:
- Well-baked dried/day-old white bread/crackers (if tolerated, black bread can also be used) without burnt crusts.
- Vegetable/weak meat broths and soups based on them with the addition of well-cooked cereals and vegetables. When preparing meat/fish broths, during the cooking process, drain the first broth and cook the meat/fish in a new portion of water until cooked.
- Dietary varieties of red meat (lean veal/beef), rabbit, chicken, turkey. Meat must be thoroughly cleaned of fat/tendons, and poultry from skin. Boiled meat can be further cooked.
- Low-fat fish (bream, pollock, pike perch, perch, hake, cod) in pieces or chopped, boiled, baked.
- Porridge, noodles and small pasta cooked in water. Allowed to be consumed in the form of casseroles with cottage cheese.
- Vegetables (cucumbers, cabbage - white, cauliflower, zucchini, beets, potatoes, carrots, pumpkin) raw and baked. You can add some garden herbs to salads.
- Low-fat fermented milk products, the consumption of which should be reduced or stopped when dyspeptic disorders occur.
- Sweet ripe berries/fruits: peaches, pears, apples, apricots, overripe bananas, strawberries, currants, kiwi, prunes, figs, persimmons, cherries, quinces, plums, pomegranates, watermelons, dates, dried apricots, raisins, blueberries. Grapes, as well as juices, compotes, jelly and jelly from them.
- In moderation: caramel, marmalade, jam, marshmallows, preserves, toffee.
- Refined/unrefined vegetable oil (corn, olive).
- Liquid up to 2 l. It is recommended to drink freshly prepared/diluted juices, herbal teas, rosehip infusion, and still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for fatty liver should exclude:
- Fatty poultry/fish, fatty meat, offal (liver, kidneys), cooking fats, fried foods, mayonnaise, smoked meats.
- Chocolate, confectionery, cream products (cakes, pastries), butter/puff pastry.
- Legumes, cabbage, if it causes bloating, okroshka/sauerkraut soup.
- Mushrooms, sorrel, garlic, radish, onion, spinach, radish
- Strong tea, coffee, cocoa.
- Juices from packages, carbonated drinks, alcohol.
- Pickled/salted foods, hot sauces, vinegar, mustard, horseradish, ketchup, pepper.
- Raw chicken eggs (soft-boiled, no more than three per week).
- Spicy cheese, whole milk. The consumption of fatty cottage cheese and yogurt, sweet cheeses, fermented baked milk, and sour cream is limited.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Products
What is prohibited
The list of prohibited products includes
- fried foods (disturb the digestion process),
- dishes with a large amount of animal fats and carbohydrates (contribute to the development of complications of the disease),
- irritating the gastric mucosa and increasing the production of gastric juice (activate the gastrointestinal tract, provoke excess formation of bile, which increases the load on the diseased liver).
In addition, it is necessary to avoid easily digestible carbohydrates, since they quickly turn into fats and are not stored in the liver as glycogen.
Products that cause increased gas formation and linger in the intestines for a long time, thereby “forcing” the liver to work in vain, should also be excluded.
What is allowed
All dishes that are indicated for fatty hepatosis should be boiled, baked or steamed.
This way, first of all, maximum sparing of the liver is ensured, and the load on the digestive tract is reduced. The process of absorption of nutrients in the intestines occurs faster, which does not force the pancreas and gallbladder to work beyond measure.
In addition, the list of permitted products includes those that contain large amounts of lipotropic (fat-dissolving) substances: methionine, inositol, lipoic acid, betaine, choline.
Lipotropic substances stimulate the synthesis of lecithin in the liver and promote the removal of fats from it. It is also recommended to consume fiber and pectins in large quantities (they require a long digestion time, create a feeling of satiety, which prevents overeating).
Vitamins
B1, B2, B6, B12, ascorbic acid.
List of prohibited and permitted foods for fatty hepatosis
| Product category | Prohibited for fatty hepatosis | Allowed for fatty hepatosis: |
| Beverages |
|
|
| Soups |
|
|
| Side dishes |
|
|
| Meat |
|
|
| Seafood |
|
|
| Bakery products |
|
|
| Dairy |
|
|
| Vegetables |
|
|
| Fruits |
|
|
| Eggs |
|
|
| Sauces and seasonings |
|
|
| Dessert |
|
|
| Fats | butter no more than 30 grams, refined vegetable oils, add to prepared dishes |
Reviews and results
As evidenced by the reviews of most patients, with fatty liver it is the diet that allows them to get rid of heaviness and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, constipation and bitterness in the mouth in a fairly short period. And, conversely, with fatty foods, pain in the right hypochondrium intensifies, which emphasizes the importance of proper nutrition.
- “... When examining my liver after suffering from hepatitis, I was diagnosed with fatty liver. I was very upset, but the doctor said that with the right diet, regression of the disease can be achieved within 6-12 months. Therefore, I very carefully chose everything that can be eaten if you have fatty liver and I do not violate this list. Indeed, only 3 months have passed since I have been on therapeutic nutrition, but I already feel good. There is little fat in my diet, mainly high quality unrefined vegetable oils (cold pressed) and butter. I eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, and also take hepaprotective drugs - phospholipids, milk thistle, artichoke, vitamins. I hope that by the specified date I will have restored my liver”;
- “... After fatty foods and heavy libations, I immediately begin to feel my liver. I went to the clinic. Diagnosis: fatty liver. I took care of my diet and went to the gym, as the doctor advised. I tolerate the diet easily, alternating lean boiled meat with fish, eating them with vegetables, and eating porridge separately. I try to cook food in a double boiler, conveniently and quickly.”