Prevention of overweight and obesity
In the world, by 2021, the number of obese people has reached 2 billion. Today, according to statistics from the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, more than half of the adult population of Russia (over 30 years old) suffers from excess body weight, and more than 20% from obesity.
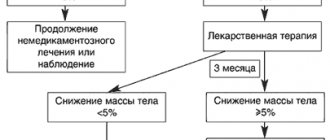
The main criterion that determines the level of deviation of a patient’s weight from the norm is considered to be the body mass index.
Formula: BMI = m/h 2 , where m is body weight (kg), h is height (m).
The World Health Organization defines overweight individuals as having a BMI ≥ 25, and obese individuals as having a BMI ≥ 30.
The root cause of the development of excess body weight is associated with an imbalance in which the caloric content of a person’s diet prevails over the real energy needs of his body.
The global increase in the incidence of obesity is due to the following factors: consumption of high-calorie, fatty (energy-dense) foods, as well as low physical activity. These factors, in fact, are decisive in the development of the disease and tend to increase. This is due to the development of urbanization, transport infrastructure, increased employment of the population, which does not require significant physical activity, a decrease in the availability of quality food, etc.
Obesity is the cause of the development of a number of diseases of various organs and systems of the body:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system: ischemic heart disease, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, etc.
- Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus - type II diabetes
- Degenerative joint changes: osteoarthritis
- Increased risk of developing cancer
The greatest threat to human health and life is the so-called abdominal obesity, in which excess fat is concentrated in the abdominal area. With this type of obesity, the patient is most at risk of developing the diseases listed above.
Rational control of body weight allows you to avoid obesity and significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular and other related diseases
Basic measures to prevent overweight and obesity
- Balance your diet. Exclude fatty foods: butter, lard, pork, smoked meats, mayonnaise, pasta, confectionery, wheat bread, cheese. Diversify your diet with vegetables and fruits. It is recommended to eat lean meat, poultry, bran bread, and a variety of cereals. Preference should be given to boiled and stewed food. Avoid fried foods.
- Food should be consumed slowly, chewing thoroughly. Also, you should not wash down your food with carbonated drinks, regardless of the calorie content of the latter. It has long been proven that “diet” cola, just like regular cola, helps increase appetite and eat more food.
- An alternative to cookies and sweets should be fruits or dried fruits.
- Workout. Running, swimming, fitness, hiking, badminton, tennis, football, etc.
- Consult a nutritionist to prescribe an individual nutrition plan to prevent excess body weight.
- Avoid factors that could potentially trigger eating large amounts of food. This could be: domestic quarrels, stress at work, frequent sitting in front of the TV, etc.
The population of East and Southeast Asia can be taken as an example of a healthy diet. The number of overweight people in this region is extremely small. And there are a number of explanations for this. 1) Asians have practically no bread, potatoes or pasta made from wheat flour in their diet; 2) the main side dish is rice or rice noodles; 3) traditional cutlery is chopsticks. This allows you to consume food most effectively - in small portions, and achieve satiety with a relatively smaller amount of food 4) In the culture of residents of China, Vietnam, Thailand and other countries in the region, it is not customary to eat on the go or while watching TV. Eating food is a separate process that Asians try not to combine with other activities. 5) Dessert as such is either absent or present in limited quantities. An alternative to desserts is fruit. 6) Small low-calorie portions of food 7) The basis of nutrition: soups, poultry, mushrooms, vegetables, seafood, pork and veal - in small quantities. 8) Approximate meal schedule: Breakfast (main meal) - 7-00, lunch - 12-00, light dinner – 19-00.
GBU RO "MEDICAL INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL CENTER"
OBESITY PREVENTION - HEALTHY LIFESTYLE
(memo for the population)
Obesity is a serious problem of our time. Obesity most often occurs as a complex metabolic disorder as a result of the influence of two main factors: overeating and insufficient physical activity.
Obesity significantly shortens a person's life due to complications - gallbladder diseases, diabetes, hypertension, early atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. Obesity in girls leads to premature puberty and, thereby, to short stature, which occurs as a result of premature “closure” of bone gaps and cessation of bone growth in length; in boys, it leads to delayed sexual development. Obesity is increasingly becoming a cause of decreased performance and disability, and this is facilitated by the person’s personal lifestyle.
The main cause of obesity is physical inactivity. Modern people experience minimal physical activity: today the average physical activity per city resident is 50 times lower compared to previous centuries. According to scientific research, due to insufficient physical activity, the incidence of obesity increases by 10% every 10 years. Insufficient physical activity is a risk factor for cardiovascular, endocrine and other socially significant diseases.
How to deal with physical inactivity?
- Study the energy expenditure of various activities.
In order to correctly select and calculate physical activity, to avoid physical inactivity and weight gain, you need to know the energy consumption for various types of activities; the energy consumption for various types of activities. So, sitting takes only 60 kcal/h, but walking takes 300 kcal/h, brisk walking and playing tennis consumes 400 kcal/h, swimming and cycling consumes about 500 kcal/h, sports games consume 600 kcal/h , and when climbing stairs and running slowly, 900 kcal/hour is consumed.
- Choose a physical activity that is adequate for your body, taking into account certain characteristics, your level of fitness, age and health status. The main thing is that specific tasks must be set to achieve certain goals. The exercise system should be developed by a doctor so as not to harm your health.
How to choose the type of load that suits you?
The chosen mode of physical activity must correspond to the level of fitness of the human body (respiratory and cardiovascular systems).
Test to determine the level of fitness of the cardiovascular system:
- Measure your heart rate at rest.
- Do 20 squats in 30 seconds.
- After 3 minutes, measure your pulse again and calculate the difference between the second and first results.
Result:
— good training – up to 5 hits;
— satisfactory - 5-10 strokes;
— low – more than 10 beats.
3. Regularly, 3-4 times a week, do physical exercise. Loads should be of low to medium intensity, but long-lasting. It is necessary to move actively: walk at least 10 hours a week. You can use daily training for 30–40 minutes, or 1–1.5 hours three times a week.
Result: regular moderate-intensity exercise consumes 150 kcal per day.
4. Practice systematically. Do exercises every day . Take the stairs instead of the elevator. Walk for 2-3 stops. Take 1.5–2 hour walks in the park several times a week. Exercise independently in the fresh air. Include walking, trail walking, race walking, skiing, swimming, running, exercising at home on an exercise bike or treadmill, etc.
Result: as you adapt and increase endurance, the loads gradually increase.
5 . Monitor your condition at the moment and over time under pulse control: normal – 12-24 beats per minute.
Result: a decrease in heart rate is a good indicator.
The optimal load is 85% of the maximum heart rate (MHR).
MHR = 220 - your age.
Moderate physical activity is safe and has a positive effect on the quality of life of practically healthy people.
Physical activity as a prevention of obesity is a reduction in the risk of overall death, a reduction in the risk of developing coronary artery disease and stroke, a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in bone loss, and therefore a reduction in the risk of developing osteoporosis, a decrease in blood glucose levels and cholesterol concentrations.
Types of physical activity:
— express - charging for the office;
- Nordic walking - burns energy almost one and a half times more than regular walking: about 90% of all muscles of the human body experience increased stress, and during normal walking - only 70%; relying on sticks reduces the load on the knee and hip joints, on the heel bones;
— recreational jogging;
- fitness for all ages:
Up to 30 years of age – metabolism is normal, calories are burned easily . The goal is to develop a habit of physical activity: strength training, dance programs, exercise bikes - 2-3 hours a week.
From 30 to 40 years old , the process of aging of bones and joints begins. The goal is to strengthen the muscle frame: do stretching exercises with dumbbells, expanders, and elastic bands.
From 40 to 50 years – hormonal disorders contribute to weight gain due to fat accumulation. Goal - strengthen muscles - stretching exercises - at least 1 hour weekly, swimming. For trained people – power aerobics; for the untrained – dancing, as well as walking ( normally 16 thousand steps per day at a fast pace).
From 50 to 60 years – the body rapidly loses fluid, which leads to loss of muscle mass up to 50% and destruction of joints. The goal is to exercise regularly, but for 15 minutes every day.
In order for the effect of physical education to be lasting, you need to make it your way of life!
To carry out its vital functions, the body needs energy, which it receives from food. If more energy is supplied than required, the excess energy is converted into fat and the person becomes fat. For the vast majority of obese people, the main cause of obesity is excess nutrition relative to energy expenditure. Obesity can be recognized by comparing body height and weight.
How to calculate your weight? It is necessary to calculate the body mass index. BMI = weight in kilograms / height (m) squared. Example: weight 73 kg, height 164 cm. BMI = 73/(1.64×1.64) = 27.14 Body mass index (BMI): BMI from 16 to 18 – underweight BMI from 18.5 to 25 – normal body weight BMI from 25 to 30 – overweight (pre-obesity) BMI from 30 to 35 – I degree of obesity BMI from 35 to 40 – II degree of obesity BMI from 40 or more – obesity degree III–IV
However, in people with developed muscles (for example, athletes), the BMI may be high, but the adipose tissue is not expressed. Therefore, at home, you can combine the determination of BMI with the measurement of waist circumference: for women this figure should be no more than 80 cm, for men - no more than 92 cm. Anything above these figures is a sign of overweight or obesity.
Follow the basic rules of nutrition:
- Eat small, frequent meals to prevent feelings of extreme hunger:
- avoid distractions while eating by watching TV or reading, eating hastily, on the go;
- minimize regular consumption of quickly digestible carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets, white bread, sugar);
- include fiber-rich foods in your daily diet;
- use unsweetened porridge with the addition of berries, dried fruits and flax seeds, bran, fermented milk products, vegetable oils; animal cartilage and meat and bone jellied meats;
- select the required ratio of proteins, carbohydrates and fats in the diet;
- consume a lot of fish, including it in the menu up to 3 times a week to saturate the body with polyunsaturated fatty acids as a preventative against deforming arthrosis of the knee and hip joints;
— Take advantage of the consultation of a therapist, endocrinologist, nutritionist and physical therapy doctor for examination, drawing up an individual weight loss program and general health improvement.
Increase your physical activity! Eat right! Save your health!
Nutrition for obesity
Path to page: Home For the population Disease prevention and healthy lifestyle Healthy lifestyle Nutrition for obesityNutrition for obesity
According to the World Health Organization, obesity is a growing threat to the health of the population in a huge number of countries, and the list is constantly growing. Obesity has become so widespread that it has overshadowed the problem of malnutrition among the population of underdeveloped countries and even infectious diseases, although previously the latter two points were considered the main threats to human health. Obesity began to be considered a disease because of its obvious negative impact on the health of almost all body systems. Obesity leads to increased blood pressure, the development of atherosclerosis and diabetes, heart and circulatory diseases, problems with joints and the spine, problems with hormonal levels and endocrine glands.
General principles and approaches to diet for obesity:
Pay attention to the frequency of meals and portion size. Most people have accustomed themselves to eating infrequently and plentifully. However, from the food we eat, the body takes only as much as it can take at one time. Some of the nutrients are used immediately, some are stored in the body in reserve in the form of fats around the internal organs, in the subcutaneous tissue and in the form of glycogen in the liver. Excess food forms unnecessary “deposits” in the intestines, which are involved in the processes of fermentation and decay, resulting in the formation of substances harmful to the body. Frequent split meals will help the body “process” nutrients better and “spend” the resulting calories faster. It is very important to control the portion size. The volume of one serving should be on average approximately 250 ml (the volume of a tea mug). Use the smallest plates you have for your meals. The sight of a full plate, even if it is small, accelerates the onset of the feeling of fullness in 60-70% of people. Gradual reduction in calories. It is advisable to calculate your individual daily calorie needs. Keep your diet within your desired baseline caloric intake or gradually reduce your caloric intake. At the Adult Health Center of Surgut City Clinical Clinic No. 1, they will help you calculate your daily caloric intake, taking into account the need to reduce body weight. It is better to “burn” fat with an active lifestyle than to starve yourself. A sharp reduction in calories or long-term abstinence from eating will not lead to stable results. Weight lost quickly is returned just as quickly, and sometimes with “additives.” In addition, sudden weight loss has a bad effect on the liver and can lead to neurotic disorders and menstrual irregularities. Don't try to lose weight quickly - try to lose weight for a long time. No diet will bring sustainable results unless you change your eating habits. The basis of a diet for obesity is a “healthy” diet, its principle is the dosed consumption of a variety of foods. There are general recommendations for a diet for obesity: Eat plenty of fiber-rich foods every day. These are fruits, vegetables, legumes, cereals. All these products are low in calories and rich in vitamins and minerals. Sweets, baked goods, fried foods are best excluded from the menu. Dishes made from fast carbohydrates and proteins are best combined with slow carbohydrates. For example, meat food with side dishes of vegetables and cereals. Dishes made from fast carbohydrates are best taken early in the day (in the morning), when metabolism is more intense. Eliminate animal fats. Replace them with healthy vegetable oils (olive, sesame). Be careful with hot, spicy and sour foods - do not overuse them, because they tend to stimulate the appetite. Don't forget that food should be varied. Then it will satisfy the body’s need for vitamins and microelements. Limit alcohol, as alcoholic drinks will add extra calories and no nutrients. Drink plenty of water to quench your thirst. Pure water contains 0 calories, and if you drink a glass of water 30 minutes before meals, you will feel fuller sooner. Remember that it is best to lose weight if you are obese under the supervision of a doctor. A specialist will be able to protect you from mistakes in your weight loss strategy and give advice when questions arise while following your diet. In addition, it will monitor in dynamics all the most important functions of your body.
Obesity is a disease that can be cured simply by adjusting your lifestyle. All you need is your desire and many of the problems that come with being overweight will bypass you.
At the Health Center for Adults in Surgut, they will help you determine your body mass index, the presence and severity of obesity, and determine the percentage of water, muscle and fat in the body. The specialist will calculate for you the daily calorie intake needed to lose weight, teach you how to use a calorie calculator, and give recommendations on proper nutrition. The Health Center runs a weight loss school. Information by phone: 56-21-70.
Prepared by: Head of the Health Center, O.A. Smirnova.
Correction of excess weight
Excess weight is almost always associated with two problems that prevent you from fully enjoying life:
- With the unpleasant prospect of chronic diseases;
- With self-doubt and dissatisfaction with your reflection in the mirror.
The great news is that even very moderate weight loss can reduce or prevent the development of problems associated with excess weight. Changing your diet and lifestyle, as well as increasing physical activity, can help you lose weight. It should be borne in mind that excess weight often does not “retreat” too quickly, despite maintaining a healthy lifestyle and even drug treatment. Plastic surgery can provide significant benefits in the fight against extra pounds:
- The ability to simultaneously and completely eliminate excess adipose tissue and at the same time lose several kilograms of weight at once;
- Get rid of cosmetic consequences and obesity (abdominal folds, stretch marks, sagging belly).
- Quickly achieve an excellent aesthetic result and the ability to maintain new figure contours, provided you follow a healthy lifestyle and moderation in diet.
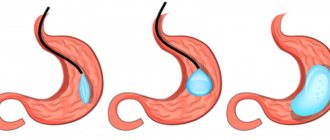
Surgeries that can help an overweight person get rid of this problem include:
- Various types of abdominoplasty (including removal of the fat “apron”, excess skin folds and fatty tissue on the sides, etc.)
- Liposuction is the removal of subcutaneous fat in various areas of the body, including the abdomen, hips and buttocks, sides and back, as well as the shoulder area, etc.