The essence of the diet
The principle of losing weight on a calorie diet is that during the day the body should receive fewer calories than it burns. Thus, energy will begin to be wasted from fat deposits.
This method is considered the safest, since the kilograms will disappear slowly.
“Nothing tastes better than feeling thin” Kate Moss
What are proteins for?
Proteins are nutrients essential for cell growth and repair and for the proper functioning of the body. They are located in muscles, bones, skin, hair and tissues.
Proteins are made up of amino acids, 20 of which we need for proper and healthy functioning. The body can synthesize half of them on its own, but 9 are essential amino acids. That is, they can be obtained exclusively from food.
Proteins are also:
- full-fledged
- defective
Complete ones include those that contain all the essential amino acids. As a rule, they are part of animal products (meat, eggs, dairy products, etc.).
Proteins that lack at least one of the essential amino acids are considered incomplete. Examples include vegetables, fruits, cereals, grains, nuts, etc.
Content of complete and incomplete proteins in products
Because proteins are complex molecules, the body takes longer to break them down. As a result, they are a much slower and longer lasting source of energy than carbohydrates. In general, the body uses proteins as extra fuel when it doesn't get enough calories from other nutrients or fats stored in the body. When protein is consumed in excess, the body stores its components as fat.
It is believed that adults need to consume about 60 grams of protein per day (0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight). But this figure varies depending on goals and age. For example, those who want to build muscle mass should consume more of it. Children can also exceed the norm, as they grow and need more building materials for the body.
Calorie calculation
The opinions of nutritionists on this issue are divided: some are convinced that the calculation is individual for each person, others offer average options.
By formulas
The most common weight loss options are based on the number of calories per day, which depend on the height, weight and age of the person wishing to lose weight. There are several formulas for calculating optimal calorie content:
Option #1
(1.8 • height, cm) + 655 + (9.6 • weight, kg) – (4.7 • age, years)
The resulting figure is the amount of energy required to maintain the body's systems.
The second stage of calculations will be to determine the physical activity coefficient. You can determine it by assessing your lifestyle:
- Passive lifestyle (sedentary) – 1.2
- Low-intensity activity (physical exercise 1-2 times a week, walking) – 1.4
- Moderate level activity (exertion more than 3 times a week) – 1.5
- High-level activity (work on the legs, systematic sports) – 1.7
- Excessive activity (heavy daily long-term exercise) – 1.9
The number after the first stage is multiplied by the selected coefficient.
The result obtained is weight stability. In order for weight to begin to decrease, you need to subtract another 400-500 kcal.
Option No. 2
30 • (height, cm – 105)
The resulting number is to save weight. To reduce it, we take away another 300-600 kcal, depending on the activity of our lifestyle.
On average
Weight loss methods from this group do not imply individual calculations, but consist of following a diet of a certain calorie content.
These include diets of 800, 1000, 1200 calories per day and other options.
Food nutrition table
The main rule of a balanced diet: the composition of the product is more important than its calorie content. Thus, the energy value of a cheeseburger and a fish steak with buckwheat and stewed zucchini is the same, but these products have different effects on the body. A cheeseburger contains large quantities of flour and butter, so it contains a high amount of calories and fat, which is harmful to the body.
| № | Product name | Weight, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal |
| Total: | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total per 100 grams: | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Enter the product name and click the "Add" button
Clear
Table of KBJU of some products.
| Product | Calorie content per 100 g | Proteins per 100 g | Fats per 100 g | Carbohydrates per 100 g |
| Boiled egg | 144 | 12,7 | 10,7 | 0,8 |
| Rice | 330 | 7 | 1 | 77,3 |
| Buckwheat | 335 | 12,6 | 3,3 | 68 |
| Oatmeal | 303 | 11 | 6,1 | 65,4 |
| Hard cheese | 352 | 26 | 26,8 | 0,6 |
| Milk | 64 | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 |
| Kefir | 30 | 3 | 0,05 | 3,8 |
| Sour cream | 115 | 3 | 10 | 2,9 |
| Banana | 89 | 1,5 | 0,1 | 21,8 |
| Watermelon | 38 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 10,9 |
| Apple | 45 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 11,8 |
| Strawberry | 36 | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,2 |
| Cabbage | 27 | 1,8 | 0,1 | 6,8 |
| Corn | 101 | 3,5 | 2,8 | 15,6 |
| Potato | 80 | 2 | 0,4 | 18,1 |
| Tomatoes | 23 | 1,1 | 0,2 | 5 |
| Cucumber | 14 | 0,8 | 0,1 | 3,8 |
| Cod | 81 | 17,1 | 1,1 | 0,6 |
| Pink salmon | 147 | 20,8 | 6,8 | 0,5 |
| Tuna | 115 | 22,5 | 2,6 | 0,3 |
| Beef liver | 125 | 18,8 | 4,2 | 3,4 |
| Pork | 209 | 20,5 | 11,5 | 0,04 |
| Chicken | 175 | 21,3 | 9,7 | 1,3 |
| Beef | 193 | 20,4 | 12,7 | 0,5 |
| Peanut | 551 | 26,3 | 45,2 | 9,9 |
| Pasta | 337 | 10,4 | 1,1 | 74,9 |
| Wheat bread | 231 | 8,1 | 1,4 | 45,6 |
| Black bread | 207 | 6,8 | 1,3 | 41,8 |
| Mushrooms | 20 | 1,6 | 1,1 | 2,2 |
| Honey | 314 | 0, | 0 | 80,3 |
| Sugar | 379 | 0 | 0 | 99,8 |
| Coffee | 2 | 0,2 | 0 | 0,3 |
| Sausage | 431 | 17 | 40,3 | 2,1 |
| Sausages | 256 | 11,2 | 23,9 | 2,3 |
| Pancakes | 206 | 6,1 | 8,4 | 27,9 |
| Dumplings | 265 | 11,5 | 14 | 25,8 |
| Pizza | 260 | 9,3 | 13,4 | 24,7 |
| Bouillon | 32 | 3,2 | 1,6 | 1,4 |
| Raisin | 262 | 1,8 | 0 | 72,2 |
| Dates | 271 | 2,5 | 0 | 72,1 |
What is possible and what is not
A low-calorie diet is not strict regarding the names of products. But still there are both more and less suitable foods.
Recommended Products
Ideally, the diet should include:
- Buckwheat and pearl barley porridge
- Lean meat, poultry and fish
- Cutlets, steamed meatballs
- Egg white
- Mushrooms
- Vegetable soups with light broth
- Rye bread, bran bread or wholemeal bread
- Vegetables, raw or steamed
- Low calorie fruits (apples, oranges, etc.)
- Unsweetened tea, coffee, fresh
- Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, cheeses)
Unwanted Products
If you wish, you can create your own diet and count calories. But it is important to remember that there are prohibited foods. If there are any, then the weight loss process will be slowed down. Among these:
- Preservation and salinity
- Smoked meats
- Sausages
- Fatty meat, poultry and fish
- Potatoes in any form
- Egg yolk
- Nuts
- Pasta
- Baking
- White bread
- Margarine, butter
- Cocoa
- High-calorie fruits and dried fruits
- Sweets (except marshmallows and marmalade)
- Sauces
You can create a menu by combining products taking into account their energy value and portion size.
Calorie content of individual products
For the convenience of calculating acceptable food combinations, you can use the table of caloric content of permitted foods.
Calorie content is indicated for the product in its raw form.
Calorie content of dishes
It is impossible to create a high-quality menu for every day without knowing the calorie content of already prepared dishes.
Calorie table for ready meals:
On a note. For convenience, it is better to print the tables and keep them for quick access.
Building a relationship with food: how to create a menu for the day. About BZHU in simple language
A healthy and proper diet is a diet that contains enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates. We have already said that food is fuel for our body.
Today we will figure out how to improve the quality of this fuel and why it is needed.
Today we will learn what to eat during the day to feel good and stay healthy.
What is BJU?
An abbreviation for proteins, fats and carbohydrates. In some places you can find KBJU - the same thing, only with calories. Each component has its own role, so it is important to be able to find a balance.
Tested from personal experience: the side effect of maintaining such a balance is beautiful skin without rashes, a healthy complexion and shiny hair.
If you maintain the balance of KBJU, you will notice clear skin, shiny hair and a great mood
What is the function of protein?
Protein “builds” our muscles; in addition, our organs and tissues are made of protein.
For those involved in sports or fitness, protein is essential for building muscle mass and building that famous athlete's body.
High-protein foods reduce cravings for sweets, strengthen the immune system, and increase bone strength
People who are not so concerned about pumping up muscles will be interested to know that high-protein foods reduce sugar cravings, strengthen the immune system, increase bone strength, and your nails will say “thank you.”
In addition, protein absorption is a very energy-intensive process. In order to compensate for the costs, the body has to use our fat layer. Protein is also a transporter for vitamins, microelements, minerals and fatty acids entering our body.
Protein deficiency slows down metabolic processes and the rate of weight loss.
A lot of protein is found not only in meat and eggs, but also in beans and lentils.
Why do we need fats?
Many people who have gone through all sorts of diets are afraid of fat like fire, and completely in vain. The function of fats is to provide thermoregulation of the body.
Once upon a time, thick hair on our skin was responsible for this, until evolution rewarded us with a layer of fat to protect internal organs from shocks and shocks; the fat depot will help us survive in case of famine.
In addition, it is fats that improve memory and attention. Try eating some walnuts rather than a chocolate bar before an important exam or presentation and feel the impact of healthy fats for yourself.
Try eating some walnuts instead of a chocolate bar before an important exam or presentation.
If you don't have enough fat in your diet, here's what will happen:
- the skin will be dry and scaly;
- hair will become dull, dry and begin to fall out;
- growth will slow down;
- resistance to infectious diseases will decrease;
- wound healing will worsen;
- mood problems and depression will begin;
- lack of attention.
Add red fish to your diet, it contains many healthy fats.
Confusion in the head occurs because there are, conditionally, healthy and unhealthy fats. The latter includes products from fast food places, palm oil and other additives. Such foods should be avoided in the diet.
And why do we need carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates give us energy and are converted into glucose, which fuels our brain. Carbohydrates, like fats, can be healthy and not so healthy.
- The first ones are “slow”, they take a long time to digest, give a long-lasting feeling of fullness, a lot of energy and do not provoke spikes in blood sugar.
- The second ones are “fast”, these are all our favorite sweets, buns, and flour products. Fast sugar is easily absorbed into the blood, so after eating candy we feel a sharp rise in energy, and then the same sharp decline - and again we put sweets in our mouth.
Therefore, you should still limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates in favor of complex ones.
You should limit your intake of simple carbohydrates, although this is not so easy
How to combine all this correctly?
To lose weight or gain weight, the BZHU ratio should be: 25%, 30%, 45%. To calculate BJU in grams, keep in mind that the breakdown of 1 g of protein releases 4.1 kcal, 1 g of fat - 9.3 kcal, 1 g of carbohydrates - 4.1 kcal.
We already know how to calculate our daily calorie intake. Let's say a person's daily calorie requirement is 2000 kcal. This means that per day he should receive 500 kcal from proteins (25% of 2000 kcal), 600 kcal from fats (30% of 2000 kcal) and 900 kcal from carbohydrates (45% of 2000).
Now let’s find out how much protein, fat and carbohydrates should be consumed in grams:
- proteins - 121 g (500/4.1);
- fat - 64.5 g (600/9.3);
- carbohydrates - 219.5 g (900/4.1).
And then it’s a matter of little things. Product labels indicate the amount of CBJU products. Study them carefully and consider them BZHU.
So what now, you have to count everything every day?
Not at all necessary. Here’s an observation from personal experience: once you calculate your daily calorie intake and the BJU ratio, further calculations will take place in your mind - literally “on a whim.”
Applications on your smartphone will help you calculate your norm; you can do this at any free time.
Too difficult! Is there an easier way?
Fortunately, we use a computer and the Internet, and this makes the task much easier. The Internet is full of ready-made options for a balanced diet for different amounts of calories, listed literally by gram.
For example, like this:
It is important, rather, not to count the notorious BZHU down to the gram, but to observe their general ratio in the diet.
And finally, how to create a menu for the day, taking into account the balance in the BZHU?
- Have complex carbohydrates for breakfast - whole grain porridge with the addition of fruits and nuts.
- The dinner plate should have meat (protein), a side dish (carbohydrates) and salad (fiber).
- Dinner can duplicate lunch, but without a side dish - that is, meat or egg with vegetable salad.
- Any vegetables or fruits are perfect as a snack.
Make your diet varied, add berries and fruits to it
That's all the wisdom of creating a competent and balanced diet.
We agree, at first it may seem difficult, but believe me: once you start walking, the road will appear by itself.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Previous articles in the series:
1. Building a relationship with food: 8 harmful myths about healthy eating. First issue
2. Building a relationship with food: everything about calories, how to calculate your norm
3. Building a relationship with food.
Tricky tricks that prevent us from eating for nothing VELVET
Rules for creating a menu
One of the principles of the effectiveness of the diet is to eat small portions, but often. It would be optimal to split the daily diet into five times. An important point is the correct percentage of calories between meals.
Regardless of whether the calculation is based on 1000 calories per day or according to any other option, the correct ratio is considered to be:
- 25% – breakfast
- 10% – second breakfast
- 35% – lunch
- 10% – afternoon snack
- 20% – dinner
It is advisable to include in different combinations at each meal:
- For breakfast: porridge, fruit, eggs, cottage cheese, tea or coffee
- For second breakfast: fermented milk products, fruits
- For lunch: broths, soups, meat, bread, vegetables, fish, salads
- Afternoon snack: dairy products, fruits
- For dinner: meat, vegetables, fish, salads, tea
If you have a desire to eat something from the list of not recommended foods, then you don’t have to deny yourself this. The main rule is not to go beyond the daily energy value.
The importance of proteins, carbohydrates, fats
An important component of a weight correction program is the correct distribution of carbohydrates, fats and proteins (BZHU). It is a well-known fact that a large amount of protein foods in the diet contributes to rapid weight loss, but it is important not to forget about the importance of carbohydrates and fats for the normal functioning of the body; nutritionists categorically do not recommend consuming them completely.
In order to maintain muscle mass and body weight, you need to eat at least 1-1.3 grams of protein per kilogram of weight every day. With an intensive weight loss program, this norm can increase to two grams. However, it is important to remember that overconsumption of protein foods can have unpleasant consequences. To prevent them, the daily protein intake should not exceed 35 grams. for one meal. If carbohydrates are a source of energy and nourish the brain, then fats promote the absorption of vitamins and improve the production of hormones. Proteins serve as the basis for muscle formation, being a building material. They play an important role, being defenders of our body, taking part in immune processes, preventing the penetration of viruses.
When choosing the right balanced diet, it is better to use lean turkey or chicken meat, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, fish, eggs, and rennet cheeses as a source of protein. It is worth giving up fatty meats. It is important not to get carried away with protein foods, since an excess of protein in the body can cause such negative consequences as the formation of stones, the development of pathologies of the excretory system, and intoxication of the body. In addition, an excess of protein in the body leads to the development of joint disorders, and the body’s immune function weakens.
When eating according to the BZHU system, it is important not to exceed their permissible daily intake. It is better to include complex carbohydrates and vegetable fats in your diet. The consumption of animal fats should be minimal, since they are a source of “unhealthy” cholesterol for the body.
Fats are a source of energy; when entering the body, they are almost completely converted into energy, of course, except for those that are deposited on the sides or thighs.
Fats are divided into two types:
- animals: present in fatty meats, fish, butter;
- vegetable, found in oils produced from oilseed crops.
Fats also vary in terms of their benefits to the body. Some are vital, while others are best excluded from your diet altogether.
In addition, fats contain acids:
- saturated, are formed in the human body, it is these fats that are deposited, turning into fat reserves;
- unsaturated, take part in metabolism, being an important component of the process of hormone formation.
Examples of saturated fats include margarine fats, palmitic, stearic, and other acids that form plaques, increasing the level of “unhealthy” cholesterol in the blood.
The norm for the body is considered to be a ratio of animal and vegetable fats of 70%/30%. The amount of animal fats should be limited as you age. Sources of vegetable fats can be oils produced from oilseeds and nuts. But it is important to consume even healthy fats in limited quantities, since indulgence in them can cause excess weight.
Carbohydrates play an important role as a source of nutrients and blood pressure regulators. They are divided into: simple and complex. Just 15 years ago, simple carbohydrates were considered “unhealthy,” often calling them “white death.” However, research conducted by the World Health Organization has cast doubt on this claim. Simple carbohydrates consumed in large quantities reduce the energy value of foods. In addition, they provoke a sharp release of glucose into the blood, which causes the pancreas to produce insulin.
Unlike simple carbohydrates, complex carbohydrates take longer to break down. This reduces the rate of glucose release and provides adequate nutrition to the brain. Insulin is not produced, which reduces the risk of obesity. Sources of “healthy” carbohydrates can be fresh or processed vegetables, bread made from whole grains, fruits, cereals, and the use of pasta made exclusively from durum wheat is allowed.
Recommendations
A person who decides to lose weight in calories, first of all, must decide on the value of the diet. The safest option is considered to be an individual calculation of the daily requirement. This is due to the fact that the personal characteristics of a particular person are taken into account.
If you like diets with a set calorie content, it is important to consider the following points:
- To lose weight without stress, it is better to alternate a week with critical caloric intake with a week of weight stabilization.
- It is not recommended to immediately set the bar low (800 calorie diet), as this can lead to exhaustion.
- Without harm to health, it is better not to lower the bar below 1200 kcal.
- As an exception, you can vary your daily calorie intake based on physical activity. If the day is spent passively, then you can do a fasting day and reduce the value of the diet. If the day is physically difficult, then it is appropriate to increase the calorie content to 1400 or even 2000 kcal.
- It is not advisable to be on a low-calorie diet for a long time (more than a month).
- The exit should be smooth, gradually increasing the daily calorie content by 300-500 kcal.
- Ideally, the weekly menu should include a variety of foods to get all the vitamins and minerals.
The most correct decision on choosing both the diet itself and calculating the optimal daily caloric intake is consultation with specialists. A gastroenterologist will indicate whether there are any contraindications, and a nutritionist will competently describe the nutritional scenario.
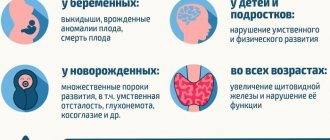
Carbohydrates and their functions
Carbohydrates give us energy. The body converts them into glucose (sugar), so their second name is saccharides. Depending on the size of the molecule and how quickly they are broken down in the body, they are divided into simple and complex.
- Simple carbohydrates (monosaccharides).
These include glucose and sucrose (table sugar). These are small molecules that are a quick source of energy as they are instantly broken down and absorbed by the body, causing a sharp jump in blood sugar levels. Simple carbohydrates are called “empty calories” because they have no nutrients and do not benefit the body. Fast carbohydrates are found in candy, cakes, fast food, sweet carbonated drinks, etc. - Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides)
. They consist of long chains of simple carbohydrates, so they are broken down and absorbed by the body more slowly, but at the same time they provide a longer lasting boost of energy and eliminate sudden changes in insulin. Polysaccharides are considered safer and promote proper digestion. What foods contain complex carbohydrates? Whole grains (pasta and baked goods), grains (rye, corn and other cereals), legumes (beans, peas, lentils), root vegetables, etc.
Example of slow and fast carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can also be:
- refined and unrefined
- plant and animal origin
Carbohydrates contain not only sugar, but also fiber and starches, which are important for digestion, the functioning of internal organs and are indispensable aids in the process of losing weight.
The daily intake of carbohydrates per day depends on many factors - gender, weight, goals (losing weight, gaining muscle mass or cutting the body), as well as the amount of physical activity. For example, a woman weighing 70 kg needs to consume about 170 g of protein to lose weight, and at least 260 g to gain muscle.