The structure of the simulators, as well as their functional features, were discussed by us in the previous article, which gave rise to a series about the purpose of very specific stations, or more precisely about what work they are intended to do. This article, according to the previously proposed classification, will cover the topic of the purpose of strength training equipment in the broadest sense of the word. We will also find out what muscles they load, what they are intended for, and what characteristic features all these structures have.
Introduction
Each simulator, which is quite logical, has its own purpose. It is based on these considerations, for the convenience of presenting the material, that we have divided them into categories, or more precisely, into muscle groups that they are intended to develop. The main aspects to which we will draw your attention will be: the muscles that it loads and its purpose. In this article, we have combined load-bearing and load-bearing structures into one list, since often both categories have their own duplicate analogues, and of course for the main reason that both categories of simulators belong to strength ones.
Press mechanism
One of the most popular exercise machines in the gym, designed to work out the abs. With its help, you can exercise both with your own weight and with additional weights. When performing the approach, the athlete's hips bend, so the anterior quadriceps and lower back are also involved. It is important to make sure that the abdominal muscles are actually felt, since several muscle groups are active.
There are many variations of abdominal exercises. To find something you really like, you should try:
- twisting;
- abdominal exercises with weights;
- on a vertical bench;
- on an inclined bench.
Exercise equipment for chest muscles
The following simulators are designed to train the pectoralis major and minor muscles at different angles:
Press at an upward angle. Muscles worked: pectorals, triceps, anterior deltoid. The emphasis in the exercise is on working the upper part of the pectoral muscles. Description: both block and loaded exercise machines can be used as a replacement for bench presses with barbells or dumbbells lying at an upward angle, or as an additional exercise to them, since working on these machines with large weights does not require the presence of a spotter.
Horizontal press. Muscles worked: pectorals, triceps, anterior deltoid. The emphasis in the exercise is on working the entire volume of the pectoral muscles. Despite the different design, both machines can be used as a replacement for barbell or dumbbell bench presses lying on a horizontal bench, or as an additional exercise to them, since working with them with large weights does not require the presence of a spotter.
Butterfly (chest machine). Muscles involved: pectoralis major and minor. The emphasis in the exercise is on training the separation of the chest in the center. The differences are that the first has a handle feed lever and involves working with your arms bent at the elbows. The second involves bringing together outstretched arms, and having a combined design, it is adapted to perform exercises on the rear delts. More on this below.
Pullover. Muscles involved: the main load goes to the pectoral and serratus muscles, additional load is taken by the latissimus dorsi and abs. Working in the simulator is safer and does not require a spotter, which allows beginners to perform the exercise to master the technique. Has a handle feed lever.
The benefits of exercising on gym equipment
And even if “avid” athletes insist that exercise machines are not capable of developing muscles as much as training with free weights, nevertheless, training on exercise machines has a lot of advantages! For example, block or lever exercise machines, although they make it impossible to connect stabilizer muscles, nevertheless, actually reduce the risk of injury . This is possible thanks to the design, which allows you to maximally fix the body during the exercise. This is definitely a huge advantage and advantage of the simulators. And also, they are convenient to use.
Back muscle trainers
The following simulators are designed to train back muscles such as the teres major, infraspinatus, rhomboid, trapezius and latissimus muscles at various angles:
Vertical traction. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, rhomboid. The emphasis depends on the grip: the wider it is, the greater the load on the latissimus muscles; the narrower the grip, the more load the middle part of the back receives. The grip can be not only narrow, medium and wide, but also straight (palms facing away), reverse (palms facing you), parallel, and the pull can be done to the chest or behind the head. A simulator combined with horizontal traction has the same functions.
Horizontal thrust. Muscles involved: lats, trapezius, back extensors. The rear delta takes on additional load. The emphasis of the exercise is on the lower part of the lats, increasing their thickness. Also, the use of different handles allows you to shift the emphasis of the load with a wide, narrow, parallel, forward and reverse grip.
Vertical traction. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, biceps receive additional load. The manufacturer places emphasis on the possibility of alternating traction with one hand. Rows facing the machine and facing away from the machine, as well as the design features of attaching the handles, allow you to work the back muscles at different angles.
Gravitron (for doing pull-ups). Muscles involved: latissimus, rhomboid, teres major. The biceps receive additional load. Imitating a pull-up bar, the design has a platform and a counterweight that help people with insufficient training to perform pull-ups on their own.
Lever rod. Muscles involved: latissimus, trapezius, teres major. The rear deltoids and biceps receive additional load. The emphasis of the load is focused on the latissimus dorsi muscles and disabling the back extensors. Both designs allow for identical work and have a handle feed lever.
Back extensor. Muscles involved: rectus spinalis (extensors). The simulator can be used as a replacement for the hyperextension exercise. It is also often used in sports medicine for rehabilitation purposes to prevent spinal diseases. The block frame allows you to vary the load level.
T-bar row at an angle. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, trapezius, rhomboid. The rear deltoids and biceps also receive a load. The simulator allows you to isolate the latissimus muscles and turn off the back extensors from work. Footrests and a chest support fix the body in a stable position, thanks to which you can effectively work out your entire back.
Bent-over T-bar row. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, trapezius, rhomboid. The rear deltoids and biceps also receive a load. By and large, the simulator allows you to work out the same muscles, but the lack of fixation of the body connects the stabilizer muscles and allows you to independently choose the angle of inclination of the body in relation to the horizontal floor.
What are they and what are they used for?
It is not enough to know the operating principle of this or that sports simulator; you need to understand what elements it is designed to perform and what muscles, joints and ligaments it affects.
Power frame
Description: the simulator consists of 4 vertically located racks connected by horizontal crossbars. It is often supplemented with special pins, which are used as a stand for the barbell, as well as removable hooks on which you can pull yourself up.
Main purpose: the power rack is used by athletes as a safety rack to perform a number of exercises, such as:
- bench press;
- deadlift;
- barbell squat;
- pull-ups.
The squat is one of the most frequently performed elements on the power rack.
Technique:
- stand in the machine so that the bar is above the trapezius of the back;
- grab the barbell and remove it from the supports (feet should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart with toes slightly pointed to the side);
- inhaling, begin a smooth squat, slightly tilting your body forward;
- Having reached a position where your thighs are parallel to the floor, pause for a second and, slowly exhaling, rise up.
View this post on Instagram
Does every person have a desire to be healthy and have a strong, well-built body? Motivation is what moves us on the path to perfection! Set yourself a goal and move forward??? The harder you work, the luckier you become☺️ Start your journey in our gym #startgym ??You will succeed!?? • Address ? Kirova 25 B Opening hours ⏰ Mon-Sat Opening hours ⌚️ 8:00-22:30 Phone ☎️ 2 613-315 #sport#fitness#vladivostok#vl#sport#sportlife#sportgirl#vl#vladivostok#fitness#fitnessgirl#motivation# motivation#weight loss#workout#sportsvladivostok#sports#gym#start#startgym#second river
A post shared by ?START GYM? (@startgymfitness) on Mar 13, 2019 at 11:51pm PDT
Target muscle groups: quadriceps, calves, glutes, forearms, lower back.
Sports bench for bench press
Description: a simple exercise machine is a stable structure of 2 racks on which a barbell is attached, and a sports bench, upholstered in foam rubber and vinyl with leather. There are 2 types of design: horizontal and adjustable. The latter allows you to change the position of the body when performing a power element.
Main purpose: used for training the upper body, as well as performing various types of bench presses using a barbell or dumbbells.
Bench press technique:
- lie down on a bench, pressing your head and bending slightly at the lower back;
- lower your legs, resting them on the floor;
- take the bar with a wide grip and carefully remove it from the support mechanism;
- extend your arms with the barbell, placing them exactly above the center of your chest;
- inhaling, smoothly lower the projectile to the sternum (until it touches);
- exhaling, squeeze the bar up, fixating in the peak state for a couple of seconds.
Target muscle groups: triceps, shoulder girdle, frontal deltoids.
Hummer
Description: this simulator is a system of levers fixed on a rotary axis. This design ensures safe movement along an anatomically correct trajectory.
Main purpose: used to pump up the pectoral muscles and perform various variations of bench presses.
Hammer press
Technique:
- adjust the chair, sit in it, pressing your shoulder blades tightly;
- holding the handle, straighten your arms without fully extending your elbows;
- return to IP.
Targeted Muscle Groups: Most muscle groups in the upper body, but primarily the shoulders, pecs and triceps.
Crossover
Description: a multifunctional block-type exercise machine that can become an analogue to elements with weights and other strength exercises.
Main purpose: aimed at working out the upper and lower parts of the body.
Raising arms in a crossover
Technique:
- stand between the crossover racks and grab the handles of the simulator;
- tilt your body forward slightly, bend your arms slightly at the elbows;
- exhaling, pull your hands to the waist area;
- Inhaling, smoothly return to IP.
Target muscle groups: biceps and triceps, deltoids, pectorals, thighs, glutes and abs.
Important! The crossover can be used by both experienced and beginner athletes.
Horizontal bar
Description: this simple multifunctional exercise machine can be found not only in every gym, but also in many homes. It is a simple rack of vertical steel supports with a horizontal crossbar.
Main purpose: strengthening the muscle groups of the upper body, as well as performing pull-ups with different types of grips.
Pull-ups
Technique:
- grab the bar with any type of grip;
- sharply pull yourself up, leaving your chin beyond the line of the crossbar;
- fixate for a couple of seconds and slowly return to the IP.
Target muscle groups: biceps, triceps, shoulders, torso.
Vertical-horizontal traction
Description: the exercise machine is a system of blocks, complemented by a sports bench and 2 handles at the top and bottom, which can be pulled both from a standing and sitting position.
Main purpose: the upper block pumps up most muscle groups, but it is especially effective for the upper back.
Upper block pull
Technique:
- sit on a bench;
- take the handle with a grip slightly wider than shoulder width;
- slightly tilting the body back, pull the handle to the upper chest (not to the belt);
- smoothly return to the starting position.
Target muscle groups: latissimus dorsi, biceps, deltoids, glutes, stabilizers.
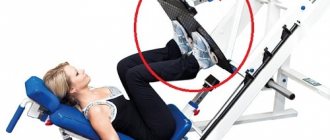
Leg extension machine
Description: the simulator consists of a seat with a back that supports the spine, leg bolsters and a weight system. Works along a given trajectory.
Main purpose: the simulator allows you to work out the quadriceps muscle using different weights, suitable for recovery from leg injuries. Additionally, the arms swing to maintain the correct body position.
Technique:
- adjust the machine and set the weight;
- sit on the seat with your ankles pressed against the bolsters;
- grab the handles with your hands, pressing your back and hips tightly;
- exhaling, raise your legs, and while inhaling, return to IP.
Target muscle groups: quadriceps, trapezius, biceps.
Leg Curl Trainer
Description: the exercise machine is a reinforced frame with a sports bench, cables, handrails and a leg bolster.
Main purpose: the equipment is designed to work with quadriceps and calf muscles. The number of weighting discs and adjustment of the amplitude of the rollers allow you to change the load on the leg muscles.
Technique:
- adjust the position of the rollers and weight;
- lie face down on the bench, resting the back of your ankles on the bolsters, and grab the handrails with your hands;
- as you exhale, bend your legs, bringing your heels to the top point;
- Inhale and gently lower back.
Target muscle groups: biceps, thighs, calves, popliteal.
Hyperextension machine
Description: the second name of the simulator is “Roman chair”. It is an adjustable frame with leg bolsters and a base cushion.
Main purpose: safe training of the muscles of the back and abdomen.
Technique:
- stand on the apparatus, placing your pelvis on the base pillow;
- rest your feet on the bolsters;
- straighten your torso and cross your arms in front of you or behind your head;
- bend over, bending your body at the waist until your body forms an angle of 90°;
- slowly raise your body.
Target muscle groups: quadratus lumbar, latissimus dorsi, popliteal, gluteal.
Bars
Description: durable steel structure of 2 racks with handles.
Main purpose: pumping up the muscles of the arms, shoulders and forearms through various types of push-ups.
Push ups
Technique:
- fixate on the apparatus with straight arms with a grip slightly wider than shoulder width;
- slightly tilting your body forward, begin to slowly lower yourself, simultaneously bending your elbows;
- hold for a second and, as you exhale, smoothly return to IP.
Push-ups are usually performed to failure.
Target muscle groups: shoulders, triceps, deltoids, lower chest area.
Smith machine
Description: power frame with a bar fixation system, ensuring safe work with the barbell.
Main purpose: allows you to work with heavy weights, performing different variations of deadlifts, squats and other strength exercises.
Technique:
- set the bar to the desired height and stand on the machine;
- Having taken the projectile onto your shoulders, begin to slowly squat until your thighs reach parallel to the floor;
- smoothly return to IP.
Target muscle groups: trapezius, triceps and shoulder girdle.
Interesting! Beginners are advised to first practice the technique of movements with an empty bar.
Scott's bench
Description: Prefabricated metal frame with bench and adjustable desk support. Some models have a barbell stand.
Main purpose: working out the biceps by bending the arms with weights.
Arm Curl
Technique:
- set the desired desk height and sit on the bench;
- rest your feet on the floor, grab the barbell with your hands on the desk;
- inhaling, straighten your arms, straightening your biceps, then return to IP.
Target muscle groups: biceps, brachialis, forearms.
Leg press machine
Description: system consisting of a platform, seat and support for awnings.
Main purpose: working out the muscles of the legs.
Technique:
- sit in the exercise machine with your feet shoulder-width apart on the platform;
- holding the stoppers with your hands, straighten your legs with effort, lifting the platform up;
- return to IP.
Target muscle groups: quadriceps, gluteus maximus, popliteus, hamstrings.
Butterfly (butterfly)
Description: the simulator is a machine with “floating” handles, a seat, a load stack with weight plates and a footrest.
Main purpose: performing isolation exercises on the chest muscles.
Reduction of hands while sitting
Technique:
- sit on the machine, press your back tightly and grab the handles;
- exhaling, light your hands together;
- while inhaling, return to IP.
Target muscle groups: pectoral, deltoid.
Treadmill
Description: a cardio exercise machine consisting of a frame, a running belt and a control system. There are 3 types: mechanical, magnetic and electronic.
Main purpose: training leg muscles.
Run
Technique:
- turn on the simulator, set the settings;
- start running.
Target muscle groups: gluteus, IT band, hamstrings, quadriceps and calves.
Be sure to check out:
Lose weight in the gym: the dream or reality of every girl Workout program in the gym for girls Workout program for the gym for men: putting together an effective set of exercises How much you need to do in the gym: research on the duration and frequency of workouts
Exercise machines for leg muscles
The following machines are used to train lower body muscles such as quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles:
Leg press. Muscles worked: entire front thigh, entire back thigh, and buttocks. The simulator can be used as an alternative to squats with a barbell, or as an additional exercise to them, since it does not require the presence of a belayer due to the presence of locking levers. The tilt level of the lounger and platform is adjustable.
Hack machine. Muscles worked: entire front thigh, entire back thigh, and buttocks. The emphasis in the exercise is on the front of the thigh and its outer side. The simulator can be used as an alternative to squats with a barbell, or as an additional exercise to them, since it does not require the presence of a belayer due to the presence of locking levers.
Smith's car. Muscles involved: the specific design of the machine allows you to work out almost all muscle groups, but is often used specifically for squats, which allows you to load the front and back of the thigh, as well as the buttocks. The counterbalanced design increases the smoothness of the rails and reduces the weight of the bar.
Hip extensor. Muscles involved: front of thigh. The emphasis in the exercise is on the medial (teardrop-shaped) muscle located above the knee. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes, as well as for the prevention of possible diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Hip flexor. Muscles involved: back (biceps) of the thigh. The calf muscles receive additional stress. The exercise allows you to focus the load on the lower part of the thigh biceps. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes, as well as for the prevention of possible diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Leg information. Muscles involved: hip adductors. The emphasis in the exercise is on the inner part of the thigh, which allows you to form its correct and beautiful shape. In sports medicine, it is often used to increase or restore the elasticity of muscle fibers in a given area.
Leg spreads. Muscles involved: hip abductors. The emphasis in the exercise is on the outer part of the thigh, which allows you to form its correct and beautiful shape. In sports medicine, it is often used to increase or restore the elasticity of muscle fibers in a given area.
Swing to the side. Muscles involved: adductor, abductor muscles of the thigh and buttocks. The machine is designed to train the inner and outer thighs. It is successfully used for figure correction, as well as for the formation of expressive and beautiful legs, making it popular among women.
Backward leg press. Muscles involved: gluteal muscle. The exercise machine is successfully used for figure correction, as well as for the formation of expressive and beautiful legs, which makes it popular among women. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes to prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Shin machine (standing). Muscles involved: calf muscle. The machine is very effective for training the lower legs and for developing strong and beautiful calves.
Shin machine (inclined). Muscles involved: calf muscle. The difference from the previous design allows you to remove the axial load from the spine.
Shin machine (sitting). Muscles involved: calves, gastrocnemius. The emphasis in the exercise is on focusing the load on the soleus muscles.
The main types of women's exercise equipment for gyms
Dividing sports equipment into exercise equipment designed for men and women is the main mistake of any novice athlete. There is a number of equipment, the use of which is performed with varying degrees of severity for representatives of the 2 genders.
In this case, the anatomical features of the human body structure and physical fitness play a more significant role than gender. All sports equipment in fitness clubs are equally applicable to both women and men. However, not all models and not all manufacturers can be recommended for exercisers.
In general, all gym equipment is divided into 3 groups:
| Name | Description | Scroll |
| Cardio equipment | They are used for aerobic exercise. That is, this type of load in which the main energy metabolism occurs with the participation of oxygen. | Treadmills, ellipsoids, exercise bikes. |
| Free weights | This is the most effective group. Exercises with free weights require training experience or the assistance of a qualified specialist. | These are barbells, dumbbells and related complexes. |
| Exercise equipment | Used for anaerobic training - a type of load in which energy metabolism occurs without the participation of oxygen. | Block, hinged, lever and other equipment. |
Arm muscle trainers
The following machines are designed to train biceps, triceps and forearms:
Biceps machine. Muscles involved: biceps. The simulator is designed to train the muscles of the arms, namely the biceps, which is achieved through a design that ensures their isolation. The seated design allows you to unload the spine, and the angle of the handles and their rotation provide the most comfortable conditions for training.
Triceps machine. Muscles involved: triceps. The machine is designed to train the muscles of the arms, namely the triceps, which is achieved through a design that ensures their isolation. The seated design allows you to unload the spine, and the angle of the handles and their rotation provide the most comfortable conditions for training.
Triceps block. Muscles involved: triceps. The anterior delta band receives additional load. The emphasis in the exercise is on fixing the spine, which prevents loosening of the body and allows you to focus on the triceps brachii muscle. This simulator is quite rare, since a crossover is often used instead. More on him later.
Bars sitting. Muscles involved: triceps, pectoral, anterior deltoids. The simulator simulates push-ups on uneven bars. The block design, or rather the adjustable weight, allows the exercise to be performed by people with an initial level of training who do not have enough strength to lift their own weight on the uneven bars.
Gravitron (for performing push-ups on uneven bars). Muscles involved: triceps, pectoral, anterior deltoids. Simulating push-ups on uneven bars, the design has a platform and counterweight that help people with insufficient training to perform push-ups on their own.
Seated French press. Muscles involved: triceps. This simulator allows you to significantly isolate the triceps and put a significant load on its inner and middle bundle. The seated design allows you to relieve the spine, and the grip angle of the handle provides the most comfortable conditions for training.
Roller block. Muscles involved: forearms. The simulator is effective for building and developing forearm muscles.
Safety precautions on simulators
There are not many safety rules when working out in the gym, but they can reduce the risk of serious injury:
- You should always check the clamps, slings and other key elements of the exercise equipment for serviceability.
- Training should always begin with a warm-up approach, that is, taking light weights, and only then move on to more serious loads.
- If you are not sure how to use the simulator, you should definitely contact a trainer.
- When a malfunction is discovered, it must also be reported to the coach.
You should always start exercising only after warming up, that is, with cardio, and only then move on to working with strength training equipment.
THE MOST USELESS TRAINERS!
Shoulder exercises
To train the front, middle and rear deltas, the following equipment is used:
Seated press. Muscles involved: anterior and middle deltoids. The simulator is effective for developing a strong and beautiful upper shoulder girdle. The seated design allows you to relieve the spine as much as possible. The handle feed lever and adjustable seat height and backrest angles make exercising on it as comfortable as possible.
Seated fly-through. Muscles involved: middle and anterior deltoids. The emphasis in the exercise is on the middle delta beams. The seated design allows you to isolate the deltoid muscles as much as possible and relieve the load on the spine. The machine can be used as an alternative or addition to dumbbell raises while standing or sitting.
Reverse fly while sitting. Muscles involved: posterior deltoids. The simulator involves raising outstretched arms, and having a combined design, it is adapted to perform chest exercises, which is implemented by changing the position of the handle levers. This was mentioned at the beginning.
What exercise machines pump up the shoulder girdle and arms?
Dumbbell Raise
Lower block thrust in a crossover
Upper block thrust in a crossover
One-handed lower pulley in a crossover
For the shoulders, free weights such as dumbbells and barbells are mostly suitable.
- To work the deltoid muscles (they are located directly above the shoulder joint), exercises are used to lift dumbbells to the sides, forward, and up. These muscles are small and get tired quickly, so about 20 repetitions will be enough for you to feel the exact location of your deltoids.
- Biceps are pumped by all exercise machines associated with bending the arm. For example, lower block rows for biceps in a block machine.
- The triceps are pumped opposite, with arm extensions. The same block simulator, but we take the top block and pull it down.
- Pull the crossover lower block with one hand
Exercise machines for abdominal muscles
The rectus and oblique abdominal muscles can be trained using the following machines:
Seated crunches. Muscles involved: rectus abdominis. Additional load is received by: serratus and intercostal muscles. The simulator allows you to specifically work the upper and middle parts of the rectus abdominis muscle. In sports medicine it is often used to prevent spinal diseases.
Twister. Muscles worked: external, internal and transverse obliques. The machine is designed to perform oblique turns and train the oblique abdominal muscles. Effective for building an athletic physique. In sports medicine it is often used to prevent spinal diseases.
Cardio equipment[edit | edit code]
Read the main article:
Cardio equipment
Cardio equipment provides an affordable and practical alternative to outdoor exercise. The most popular include:
- Treadmills;
- elliptical trainer (orbitracks);
- steppers;
- rowing machine;
- exercise bikes, etc.
- Treadmill
- Elliptical trainer
- Exercise bike
Stationary bicycles[edit | edit code]
- An exercise bike
is a sports machine that simulates riding a bicycle. The exercise bike has a seat, a palm rest, pedals and an information monitor. The intensity of the load can be controlled by changing the resistance of the pedals.
Read the main article:
Exercise bike
- A cycle trainer
is a machine that imitates a sports exercise bike, designed primarily for cycle aerobics.
Read the main article:
Cycle trainer
Running/stepping machines[edit | edit code]
- A treadmill
is an indoor running machine. Using a treadmill correctly, you can increase the endurance of the entire human body and strengthen the cardiovascular system.
Read the main article:
Treadmill
- A stepper
is a cardio exercise machine that simulates walking on steps.
Read the main article:
Stepper
- The Summit Trainer
is a cardio machine that is a cross between an elliptical ergometer and a stepper. Like the stepper, it imitates climbing steps, but has a different trajectory of movement.
Read the main article:
Summit simulator
- The adaptive AMT trainer
is a high-tech cardio trainer from PRECOR, which combines a treadmill, elliptical and stepper.
Read the main article:
Adaptive simulator AMT;
- The Counter Ladder
is a cardio machine from Versa Climber that simulates climbing a fire escape.
Read the main article:
Counterdirectional staircase;
- A climber
is a cardio exercise machine that is a staircase simulator that simulates climbing up it.
Read the main article:
Climber simulator.
Elliptical trainers[edit | edit code]
Read the main article:
Elliptical trainer
Elliptical machines are exercise machines that are a combination of stair climbing and treadmill movements. The classic elliptical trainer has two tracks for each leg, when the athlete moves his legs, they describe an elliptical motion from this and the name of the machine is derived. Some ellipsoids have magnetic motion control, which perfectly regulates the level of load on the legs.
Glider simulators or Glider[edit | edit code]
Glider simulator
Glider simulator or Glider is a machine whose movements resemble those on an elliptical trainer. However, a glider trainer is more like an aerial leg swing and describes an ellipse along the bottom of a path forward and backward, while the step on an elliptical trainer describes an ellipse along the entire perimeter. The glider also has a simpler mechanical component. In our country, the glider is not successful due to its low efficiency.
Rowing machines[edit | edit code]
Read the main article:
Rowing machine
A rowing machine is a cardio machine that simulates rowing. The simulator is designed to train the muscles of the back and arms, developing endurance and a sense of balance. Additionally, the rowing motion is gentle, making rowing safe for people of all ages, regardless of fitness level.
Multifunctional trainers
Crossover. Muscles involved: biceps, triceps, deltoids (front, middle, rear), chest, back, abs, hip abductors and adductors, hamstrings, buttocks. The design has four traction blocks: two upper and two lower, which allows, by connecting various handles, to perform a large set of exercises on all parts of the body.
Block frame. Muscles involved: biceps, triceps, deltoids (front, middle, rear), chest, back, abs, hip abductors and adductors, hamstrings, buttocks. Both designs have two traction blocks, which, by connecting various handles, allow you to perform a large range of exercises on all parts of the body.
Types of simulators
The variety of exercise equipment in the gym is divided into cardio and strength training equipment. Cardio equipment includes designs that increase endurance, such as orbiters, treadmills and exercise bikes. In the gym, they often have a separate place called the cardio zone. The rest of the simulators are called strength ones. With their help, the athlete develops strength, increases mass and improves muscle tone.
Strength training machines are divided into two types:
1. Lever - these exercise machines involve working with free weights. You can adjust the weight yourself. Their design provides space for placing cargo (weighting disks). Exercise on such machines minimizes the load on the spine and joints due to maximum fixation and stabilization of the body. For example, a machine for training the pectoral muscles is a hummer. The athlete sits in it, securely fixing his back on a vertical bench, and the levers, moving only in one direction, will not allow the load to move to the side, and thereby cause injury.
2. Block - the load in this type of simulators is built into the structure and consists of plates of the same weight. Using a design consisting of a vertical pin and a lock passing through them, you can change the weight, and this solution makes it possible to change the weight in steps (on average 5 kg). Using a block system, the athlete works with a load. The variety of such simulators is very large. An excellent example of this type of trainer would be a crossover. This machine allows you to train any muscle. Using a crossover, you can train the muscles of the chest, back, abdomen, deltoids, biceps and triceps, as well as thigh muscles. By the way, crossovers are often equipped with additional training structures, such as a horizontal bar, vertical and horizontal traction.