I am glad to welcome you again, friends! You can write endlessly about exercises. The reason for this is their diversity. Even for the simplest of them, you can come up with many options for implementation! What can we say about multi-joint movements?
But athletes and their coaches came up with various variations of exercises not for fun, but as a tool for achieving better results. Therefore, if you are interested in the result, you need to develop your “training” horizons!
The leader in the number of exercise variations are pull-ups. But not everyone is able to perform them from the very first training, and even more so with the correct technique. Fortunately, there is a replacement for heavy pull-ups - vertical pull-downs. It retains many of the benefits and is suitable for people of all skill levels!
Why include exercise in your workout?
There are many reasons not to avoid this exercise.
- Back workout for beginners. If you just came to the gym and want a wide back, then start with a vertical block. Because approaches to the horizontal bar are unlikely to be successful. Of course, if you are not a former workout competitor or an athlete from other sports.
By practicing this exercise, you will give your muscles a stimulus for growth, not much inferior to pull-ups. In addition, rows will serve as an effective tool for learning the technique of pull-ups.
- More experienced athletes will be helped to diversify the training process. Or they will serve as a good replacement for pull-ups during the period of mass gain. For example, bodybuilders can use rows as the main exercise for the back, due to the fact that it is difficult for them to do pull-ups due to their large muscle mass.
- Exercises on vertical blocks are used as rehabilitation for spinal injuries or diseases of the musculoskeletal system. But under the strict supervision of a specialist.
What is better to do – pull-ups or lat pull-downs?
First, you need to understand that pull-ups are the pinnacle of perfection in physical fitness and not everyone can do it for various reasons. While everyone can perform lat pull-downs - both men and girls.
The vertical block row will be an excellent springboard in preparation for pull-ups, since the target muscles in these exercises are almost the same, the only difference is in the strength and capabilities of the athlete.
If we talk about effectiveness, of course, pull-ups involve more muscles, require more strength and endurance from the athlete and bring him closer to results - increased strength, muscles and endurance.
If pull-ups are feasible at least 2-3 times, they should be included in training and developed, and various rows will be additional exercises in the uniform development of the back muscles. Otherwise, rows will be the only way to strengthen your back until the muscles are ready for pull-ups.
And also read, leading exercises to pull-ups →
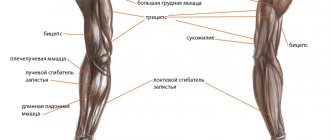
What muscles are involved?
The main part of the body worked in the exercise is the back. The assistants are the arms, shoulders and pectoral muscles. The contribution of each assistant depends on the version of the movement.
Now let's take a closer look at the anatomy.
Among the entire array of back muscles, it is the latissimus that pulls the handle of the exercise machine down. They can be helped by the round muscles, pectoral, rear deltoids and biceps. The trapezius and rhomboid muscles have their own responsible duty - moving the shoulder blades (adduction, rotation and downward movement).
You can remember a simple relationship:
- The narrower the grip, the greater the load on the arm muscles.
- The more you lean your body back, the more the trapezius and rear deltoids are loaded.
Reverse Grip Lat Pulldown
The exercise maximizes the thickness of the back muscles, especially the middle part. In this variant, the biceps of the shoulder are more involved in the work.
What muscles work
- Latissimus dorsi muscles.
- Teres major muscle.
- Rhomboid muscle.
- Pectoralis minor muscle.
- Shoulder biceps.
- Brachial muscle.
Exercise technique
- Place your palms on a wide bar, shoulder-width apart, with a reverse underhand grip, supinating your shoulder joints.
- Lower your pelvis onto the seat, lock your hips under the bolsters, slightly tilt your body back, maintaining the position throughout the approach.
- As you exhale, squeeze your shoulder blades, bringing your elbows towards your body, lower the handle to the upper part of the pectoral muscles, but do not touch them. Concentrating on the work of the back muscles, bring the shoulder blades towards each other as close as possible due to the deflection of the chest, in other words, make the chest a “wheel”.
- Try to perform the pull not with the biceps, but concentrated with the back muscles.
- As you inhale, smoothly straighten your arms at the joints, keeping your torso tilted back.
- Repeat the movement several times.
Reverse grip lat pulldown in video format
Features and Recommendations
You don't want to waste your time and energy, do you? Therefore, carefully study the execution technique. But first, there are some features of the exercise that are worth knowing!
Traction for girls
Since most girls find it difficult to do pull-ups, you can use the vertical pull-down as the main exercise to train your back muscles. But keep in mind that due to anatomical features, women’s upper body is not as strong as men’s. Therefore, train with light weight and a high number of repetitions - 15-20.
We work with our backs
Not everyone can immediately feel the latissimus muscles. Don't be upset, this is not always a sign of bad technology. There is such a thing as a neuromuscular connection. If it is not yet developed, then even with proper muscle contraction, you may not feel them. Neuromuscular connection improves over time, as long as you exercise regularly!
It's a completely different matter when you violate your technique, causing the wrong muscles to work. The reason may actually be ignorance of the technique or too much weight in the exercise, which again leads to a violation of the technique.
Elbow position
During training, pay attention to the position of your elbows, whether they are moving along the correct path. Which trajectory is correct? The one in which the forearms are directed along the cable of the simulator.
If you do deadlifts with a wide grip, your elbows should move to the sides of your body. If behind the head - strictly in the (frontal) vertical plane. When doing rows with a narrow grip - in front of the body, that is, parallel to the plane of symmetry of our body.
Cheating
Let me explain this concept. Any swinging, irregular technique, or jerking used to lift more or perform one more repetition is called cheating. He is your enemy! And that's why:
If the technique is violated, there is a risk of injury, which can nullify all your strength records.
By cheating, you are depriving your muscles of growth! After all, to gain high-quality mass, it is important to work the muscle until it fatigues, and not to lift as much as possible by any means.
How to choose a working weight
From my own experience I can say that you should start with very little weight. One with which, on the one hand, you will feel the load on the muscles, and on the other, you will be able to perform the exercise with ideal technique for 15-20 repetitions. Work with this weight, ask an experienced person to watch your technique. Try to feel the muscles that need to work (mainly the lats). Only after this increase the weight by 10-15 percent and move on to full loads.
How to determine the initial weight of the projectile? Let's look at three situations:
- You can’t do a single pull-up, or you struggle to reach the bar once. Then you should put weights on the blocks that are a third or even a quarter less than your own weight.
- You can do pull-ups, but for less than 8 reps. Then your initial weight of the burden will be from a third to half of your own.
- You can easily handle the crossbar. Performing more than 8 repetitions is not a problem for you. Then deadlifts can be done with more than half your own weight.
The calculations, as you can see, are not tricky.
How can you increase the quality of muscle contractions?
There is one subtlety that allows you to achieve better contraction of the lats. The fact is that between the handle of the simulator and our “wings” (the broadest muscles) there is also a whole chain of muscles. This chain includes the biceps, brachialis, forearms and hands. Each of them can “steal” the load from the back.
By squeezing the handle of the exercise machine in your hands so that it does not slip out from the good weight, you strain your forearms. From them, your biceps and brachialis also receive a signal to increase contraction. As a result, you seem to be shaking your back, but your arms get tired. But there is a way out! Use wrist straps (loops). By screwing them correctly onto the handle, you neutralize load thieves.
Grip Features
Which muscles will work in the exercise depends on the width of the grip and its direction. Knowing these dependencies, you can create a workout that does not leave a single area of the back unattended!
- Straight
This is the classic grip where your palms face forward. Only it can be used in wide-grip deadlifts, which develop the lats better than other variations of the exercise. In this case, the biceps receive minimal load.
Practice this grip if you want to build a wide back!
- Back
Palms face back. With this grip, the biceps is in an advantageous position, but despite this, it practically does not take on the load. And if you feel your biceps, then most likely you need to adjust your technique.
To pump up your biceps, you need to pull the handle not to the bottom of your chest, but to your chin. Moreover, the forearms will no longer be directed along the cable.
- Parallel
This grip is also called neutral. More powerful than other types of grip. This is good, as it will make it easier to hold the handle when working with serious weights.
- Wide
A wide grip is considered to be wider than the shoulders. And the farther the hands are from each other, the greater the emphasis on the lats. This type of grip requires good mobility of the shoulder joint.
Don't use too wide a grip. This is dangerous! And besides, it reduces the amplitude of the exercise.
- Narrow
A narrow grip is considered to be narrower than the shoulders. To grasp it this way, a special narrow handle with parallel handles is used. Or use a standard curved handle for a wide grip, which you need to grab with a narrow grip.
The amplitude of the exercise is slightly reduced, since the elbows have to be moved not back, but slightly to the sides.
One-arm lat pulldown
This exercise will allow you to work your back muscles more effectively. When performing the exercise on one side, the weight is not distributed on both hands, but focuses on the target muscles without the help of the stronger hand. Therefore, the craving becomes more concentrated. When choosing a working weight, divide the load with which you perform two-arm rows by two. For this exercise you will need a one-handed handle or a D-handle.
What muscles work
- Latissimus dorsi muscles.
- Teres major muscle.
- Biceps brachii.
- Shoulder muscles.
- Brachioradialis muscles.
- Lower part of the trapezius muscle.
- Rhomboid muscle.
Features of the technology
- Secure and grip the handle for one hand.
- Stand sideways, turning away from your working hand, and lower your pelvis onto the seat, while you can fix one thigh with a bolster, if this is convenient.
- Straighten your arm completely, and exhale, lower the handle to your shoulder, bringing your shoulder blade closer to the center of your back and your elbow closer to your torso. In this case, the shoulder should not turn, the elbow should look down.
- As you inhale, smoothly extend your arm to the starting position and repeat the movement.
- Then turn around in the other direction and repeat the same movement.
Seated one-arm lat pulldown in video format
Exercise technique
Depending on the width and direction of the grip, the technique changes, but only slightly. Therefore, we will consider it step by step, introducing some adjustments for different types of grip:
- The approach begins not with the traction itself, but with adjusting the “seat”. First you need to adjust the height of the rollers of the machine, which you will rest against with the front of your thighs. Align them so that your shins can be parallel to the floor.
- Depending on what you are going to do, you need to sit either a little closer to the rollers (so that your head is under the cable) or a little further. We sit closer if, according to the plan, we pull by the head and, accordingly, a little further if we do other variations.
- Sit in the machine and grab the handle with the desired grip. The thumb should go under the handle of the machine; this is called a closed grip. Make sure that the hands are positioned symmetrically relative to the middle of the handle.
- When pulling behind your head, maintain a natural arch in your lower back. In other cases, a slight additional deflection is allowed.
- At the beginning of the exercise, you need to move your shoulders slightly upward, thereby stretching the lats.
- With a smooth movement (as you exhale), begin to pull the handle towards your chest, stomach or head, depending on the movement being performed. In the first case, this is a chest pull with a wide or medium grip. In the second - with a narrow or reverse grip. And in the last one - with a wide grip on the head.
- At the same time as you pull, lower and contract your shoulder blades. There is no need to bring your shoulder blades together in the overhead pull. This is the only way you can reduce your lats to the maximum!
- Make sure your elbows remain parallel to the cable at all times.
- Lower the handle to the lowest point (not necessarily until it touches your chest, but as far as flexibility allows). Then also smoothly (while inhaling) return to the starting position.
- Complete the required number of repetitions.
Close-grip vertical pull-down (parallel)
The exercise works all parts of the latissimus dorsi and teres major muscles using a handle for a narrow parallel grip.
What muscles work
- Latissimus dorsi muscle.
- Teres major muscle.
- Biceps brachii.
- Brachial muscle.
- Brachioradialis muscle.
- Also involved: rhomboid and trapezius muscles, posterior bundles of deltoid muscles.
Features of the technology
- It is necessary to place a handle for a narrow parallel grip or an L-handle on the upper block.
- Grasp the handles and lower your pelvis onto the seat, securing your hips under the bolsters.
- Straighten your arms above your head, lengthening your spine.
- As you exhale, pull the handle toward your upper chest without touching. At the lowest point, it is important to form a deflection of the thoracic region , as if the chest is tending to the handle, bring the shoulder blades as close as possible to each other.
- As you inhale, gently release the tension, straightening your elbows completely.
- Repeat the movements.
Close-grip lat pull-down in video format
Exercise options
In addition to standard rods, there are many more specific options. They can be used as an effective tool in training your back muscles!
- Pull in different directions
You can pull the handle towards your chest, you can pull it behind your head, but what if you do these two movements alternately? This way you can first load the lats and trapezius, then “give heat” mainly to the lats!
What does it look like? Let's say you need to do 12 repetitions. Start the exercise with chest rows. After completing the repetition, change the tilt of the body to strictly vertical and perform a row behind the head for the second repetition. In order for the total number of repetitions to be 12, you need to do 6 repetitions in each method. This is some simple math!
- To the chest
Usually performed with a wide or medium straight grip. The handle does not have to be pulled all the way to your chest. You can stop at chin level.
- Per head
People usually feel the latissimus dorsi muscles better with this exercise. It is for this reason that even beginner athletes should include such deadlifts in their split. But here you need to be careful not to lower the bar until it touches your trapezius and not to pull your elbows back!
- One hand
It is also used in bodybuilding by experienced athletes who are fluent in the two-handed deadlift technique. Proper technique plays an even more important role in this version of the exercise. After all, the load acts on the torso asymmetrically and leads to unequal work of the core muscles. For beginners, the core muscles are still poorly developed, and the entire load can fall on the spine!
Using one-arm rows, you can concentrate on working only one part of the back and increase the amplitude of the exercise.
- To the belt
From the name you might think that the handle should be pulled towards the stomach. But that's not true. In accordance with the correct technique, the handle should be lowered to the level of the chest or even the chin. But at the same time, the trajectory of the handle should go towards the stomach. That is, you seem to be trying to pull the handle towards your belt, but you stop earlier.
- To the chin
Do not confuse this with the delt pull, which is also called the chin pull. In our case, we are talking about an exercise for the back muscles. If you perform chin pulls with a wide or medium grip, the rear deltoids and trapezius will receive most of the load. If you do deadlifts with a narrow grip, the load will go to the biceps.
What is the difference between pulling the upper block behind the head and to the chest?
You may not have realized this difference yet. In that case, I'll explain. The overhead row targets the lats to a greater extent than the chest row, but at the same time involves less of the trapezius.
The difference between rows and pull-ups
From a biomechanical point of view, there is only one significant difference in the exercises. Pull-ups load the biceps, but rows don't! This is explained by the fact that in deadlifts our body is on the seat and does not try to push down with our weight. It is the weight of our body in pull-ups that causes the biceps to tighten.
Wide grip lat pulldown to chest
The exercise develops back thickness by increasing the load on the middle of the latissimus muscles.
What muscles work
- Latissimus dorsi muscles.
- Teres major muscle.
- Biceps brachii.
- Shoulder muscles.
- Additionally included: trapezius muscle, rhomboid muscle, pectoralis major muscle.
Execution technique
- Place a wide handle on the upper block, grab it from above with a wide grip.
- Lower yourself into the seat with your arms extended above your head. Place your hips under the special fixing rollers.
- Lean your body back slightly, maintaining this position throughout the approach.
- As you exhale, bend your elbows and , using the efforts of your back muscles, bring your shoulder blades together , bringing the handle to the clavicular part of your chest, while protruding your chest, forming a deflection.
- Do not touch the sternum with the handle; fix the tension at the lowest point.
- As you inhale, smoothly straighten your elbows, maintaining the position of your body.
- At the top point, smoothly straighten your arms, gently stretching your shoulder joints, without jerking.
- Repeat the movement.
Upper pulley to the chest in video format
Effective lat training on a vertical block
There is no point in performing a large number of exercises on a vertical block, since approximately the same muscles work.
You need to choose two types of traction from those we talked about. For example, wide-grip and narrow-grip rows, or overhead rows and one-arm rows. The main thing is that the exercises affect different areas of the back!
An example complex might look like this:
- Wide grip rows – 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps.
- Close grip rows – 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps.
After completing the complex, you can perform stretching exercises.
Execution options
• Wide grip – more load on the back, less on the biceps;
• Narrow grip – the biceps are loaded more than the back;
• Reverse grip – the biceps are included in the work as much as possible, the latissimus, teres major and minor, and rhomboid muscles are also loaded;
• Using a neutral grip (parallel grip), palms facing each other.
Experiment and find a grip, position and method of performing the exercise so that at the end you feel the muscles and are satisfied with the workout you did.
Basic mistakes
Athletes performing deadlifts (as well as any other exercise) often make mistakes in technique.
The two most popular are:
- Rounding of the thoracic spine. Usually such a “jamb” occurs when you want to lift more. In this position of the body, not only the back muscles are used, but also the triceps muscles of the shoulder.
- Pulling your elbows back. Everything is connected with the same desire to take on new weight.
All mistakes can be avoided if you approach training headlong, understanding that there are no quick results in iron sports!
Inclusion in the training program
The vertical pull-down to the chest is suitable for both beginners and experienced practitioners.
Beginners can use it as one of the main mass-building exercises (repetition range 8-12 per approach), performing it at the beginning of the back complex.
Or it is used to maintain muscle tone of the back (15-20 repetitions). In this case, the movement is placed both at the beginning of the program and at the very end.
Intermediate and advanced levels use the vertical block row as one of the “finishing” exercises, after performing heavier pull-ups and barbell rows.
As a rule, it is placed in the middle or at the end of the program for the back muscles.
Another area of application of the vertical block is training during the drying period . At this time, using the exercise it is good to work on detailing the back.
The weights used are small or medium, the pace of the exercise is slow, with the obligatory second fixation of the handle in the lower position and additional tension of the back muscles.
What to replace
In principle, the lat pulldown is a separate and self-sufficient exercise that has its own specifics. Therefore, if it is replaced in the program, it is with other movements performed in the same block.
This can be a pull-down of the upper block behind the head, or a pull-down of the upper block with a reverse grip to the chest.
But from a biomechanical point of view, this movement is close to pull-ups on the bar. For those who find it difficult to do pull-ups with their own weight, an alternative option in Gravitron is suitable.
Work of muscles and joints
When performing block rows with a reverse grip to pump up the latissimus dorsi muscles, the latissimus muscles, teres major muscle, trapezius muscle, forearm and biceps receive the main load. When an athlete wants to focus the load on the biceps, then in addition to the target muscle, the latissimus is also loaded, and all other muscle groups do not receive the load. The bottom line is that the biceps is a small muscle, so training it together with other muscles is problematic, since it is difficult for the body to use it. In this regard, there is a need for its careful isolation, although if the biceps is genetically predisposed to growth, then on the contrary it can interfere with the development of the latissimus muscles, then it is necessary to select exercises for the back that do not allow the biceps to steal the load.
The number of working joints that are involved during the performance of the lat pulldown with a reverse grip again depends on the emphasis on what the athlete is performing the exercise. If the target muscle is the latissimus, then the load is distributed between the shoulder and elbow joints, just as with a regular lat pulldown. If an athlete sets himself the task of loading the biceps, then the work occurs in only one joint - the elbow, and the shoulders are fixed. The need for such isolation arises because otherwise it is impossible to exclude unnecessary muscle groups from work. However, both options for performing deadlifts are safe, since the weight does not put pressure on the joints from above, but, on the contrary, pulls them upward.
Contraindications and restrictions for training
Vertical traction in the simulator, like other types of physical activity, has a number of contraindications for implementation.
This load is not recommended for people who have:
- injuries to the shoulder girdle, hands or elbows;
- hernia or protrusion in the thoracic spine;
- diseases that result in the inability to perform exercises with the proper range of motion of the upper limbs;
- pathologies (including inflammatory processes) in joints and bones.
Vertical traction is considered one of the safest types of exercises and is practiced even in rehabilitation centers for the recovery of people after injuries and complex operations, the consequences of which do not allow a person to be fully mobile.