How do chondroprotectors work?
Chondroitin is part of our bones, cartilage and joints; its task is to retain moisture in the cartilage and stimulate the production of synovial fluid. Lack of chondroitin affects the health of cartilage tissue: it begins to deform, become thinner, and loses strength and elasticity. A decrease in the amount of synovial fluid affects the mobility of the joints: first there is a creaking, clicking of the joint when moving, later pain appears and the mobility of the joints worsens. Chondroitin is used for fractures, arthritis, and osteoporosis.
Glucosamine is a building material for healthy joints and cartilage, which makes them stronger and more elastic; it is also part of chondroitin. In addition, a sufficient amount of glucosamine helps prevent inflammation and pain in the joints. Glucosamine is often used for osteoarthritis, periarthritis, osteochondrosis and spondylosis.
Both glucosamine and chondroitin allow for better absorption of calcium in the body, and also participate in the process of synthesis of sulfur, which is a structural component of joints.
Numerous clinical studies of the use of chondroprotectors for osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee joint have shown their undoubted effectiveness in reducing the symptoms of this disease (reducing stiffness, restoring trophism of cartilage and joint tissue, improving the X-ray picture, reducing pain). However, recently, new data are increasingly appearing and clinical studies are being conducted evaluating the effect of chondroprotectors in diseases of the spine, chronic lumbodynia and intervertebral disc degeneration, the results of which are quite contradictory. In this article, we attempted to analyze how effective the administration of chondroprotectors is for back pain, whether they have their own antinociceptive effect, and how it is achieved, and whether these drugs can become a worthy alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other analgesics.
A Cochrane systematic review summarized the effectiveness of glucosamine from 25 randomized clinical trials [1]. According to these results, only when using original glucosamine sulfate preparations with a patented composition, an effect of relieving pain and improving joint function was observed, superior to the effect of placebo. Regarding the effectiveness of chondroitin, a review of 43 randomized controlled trials was recently published [2], including 4962 patients treated with chondroitin and 4148 patients treated with placebo. The duration of the studies ranged from 1 month to 3 years. This meta-analysis showed that during treatment with chondroitin (alone or in combination with glucosamine), there was a significant reduction in pain compared with the placebo group.
A review of 3 pooled studies of at least 2 years' duration reported a small but significant narrowing of joint space width [3]. According to the published results of a large randomized clinical trial, GAIT (Glucosamine/Chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial), assessing the effectiveness of the combination of glucosamine hydrochloride and chondroitin sulfate in the treatment of symptomatic knee OA, there was no correlation with long-term improvement of symptoms or reduction of radiological morphological changes [4, 5]. However, the results of multivariate analysis suggested that patients with moderate to severe pain at baseline experienced a relative reduction in symptoms.
To globally evaluate the effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin in OA, a large-scale LEGS study was organized [6], which involved 605 people aged 45-75 years with chronic pain in the knee joints and signs of narrowing of the joint space in the medial tibiofemoral part of the knee joint ( while maintaining the width of the medial joint space >2 mm). Patients were randomized into 4 treatment groups (once daily or 1500 mg glucosamine sulfate ( n
=152), or 800 mg chondroitin sulfate (
n
=151), or a combination of these dietary supplements (
n
=151), or placebo capsules (
n
=151).
Patients self-rated and noted in diaries the maximum level of knee pain on a 10-point scale for 7 days every 2 months for more than 1 year. The treatment did not show a significant effect on the primary outcome of the disease in the treatment groups ( p
= 0.57), and there were no significant differences in the level of reduction in knee pain between any groups of patients, including placebo. The use of pain medications (or NSAIDs/opioids) remained stable throughout the follow-up period in all groups. Symptoms of knee pain and dysfunction (WOMAC scores) decreased from baseline to year 1, with no further improvement from year 1 to year 2 in all groups.
Most clinical studies describe both pronounced structural-modifying (restoration of trophicity of cartilage and joint tissues, improvement of the X-ray picture) and symptom-modifying effects (reduction of stiffness, pain) during therapy with chondroprotectors, and the latter often occurred earlier [7].
According to an open randomized study [8], in 58 patients with knee OA, radiological symptoms on the Kellgren-Lawrence scale (I-III) with the severity of pain and the degree of motor activity of 5 or less points for each of the signs on the Lequesne scale (with a total value Lequesne index 14) and pain intensity on a visual analogue scale (VAS) >5 points, taking combination therapy with glucosamine (1500 mg) and chondroitin sulfate (1200 mg) 2 times a day, there was a significant decrease in pain syndrome according to VAS, as well as improvement in indicators according to the WOMAC and Lequesne scales after 6 months of treatment, which became more pronounced after 1 year of therapy.
In the work of L. Tant et al. [9] compared the effects of traditional NSAID therapy and physiotherapeutic treatment for chronic lumbodynia with similar therapy with the addition of glucosamine. The study involved 36 patients with chronic back pain lasting more than 12 weeks, radiological signs of lumbar arthrosis and VAS pain intensity >3 points. Already by the end of the 4th week, there was a statistically significant reduction in pain at rest in the group treated with glucosamine compared to the control group, which persisted at the 8th and 12th weeks of treatment. At week 12 of therapy, significant differences were noted between groups in terms of pain during movement according to the VAS [10].
Of interest are the results of a prospective experimental pilot clinical study conducted by R. Klein et al. [11], in which a solution of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride was injected directly into the intervertebral disc. We examined 36 patients aged from 27 to 62 years (average 46.5 years), suffering from long-term (about 8 years) chronic back pain that was not amenable to conservative and physiotherapeutic treatment. Intradiscal injections of 1-2 ml of a solution containing 0.5% chondroitin sulfate and 20% glucosamine hydrochloride were performed. In addition, injections of glucosamine hydrochloride were performed into the facet joints. As a result of therapy, 17 out of 30 patients showed a decrease in pain syndrome according to VAS by 76% compared to the initial level, and an improvement in quality of life and ability to work by 72%. In contrast, 13 patients had a minimal response to therapy, with an average reduction in VAS score of 14% and an improvement in quality of life of 8%.
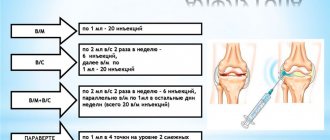
In a double-blind, multicenter clinical trial, chondroprotectors demonstrated an antinociceptive effect comparable to that of selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors [12]. The study included 606 patients over 40 years of age with radiographically confirmed knee OA and severe pain (> 301 WOMAC pain index on a scale of 0 to 500), randomized into 2 groups. In the first group, patients received chondroitin sulfate 400 mg and glucosamine hydrochloride 500 mg 3 times a day daily for 6 months; in the second - celecoxib 200 mg and placebo in the first dose, in the remaining two doses - 2 capsules of placebo. The results showed that combination therapy with glucosamine and chondroitin was comparable in effect to celecoxib, including in terms of pain. Within 6 months, there was a decrease in VAS pain by 48.0% in the chondroprotector group compared to 48.8% in the celecoxib group ( p
=0.92) (see figure). However, the effect of prescribing chondroprotectors was characterized by a gradual onset, smooth development, increase over time and stable results against the background of discontinuation of therapy, while the effect of celecoxib, although it occurred earlier and was somewhat more pronounced in the early stages of therapy, ceased to increase over time.
Dynamics of pain syndrome (VAS, mm) during therapy with glucosamine and chondroitin and celecoxib for 6 months.
The results of a pilot study conducted in Japan are quite eloquent regarding pain syndrome while taking chondroprotectors [13]. In it, one group of patients with chronic OA received chondroitin and glucosamine with the addition of antioxidants and microelements, and the other received a placebo. Already at the 4th week of treatment, a significant reduction in pain was observed in the main group, while no significant changes were noted in the placebo group. The dynamics of pain according to VAS are presented in table. 1.
Table 1. Changes in the three main characteristics of pain according to VAS (mm) during 16 weeks of therapy in the study group and the placebo group (n = 16 in each group) [13] Note. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation; * - p<0.05, ** - p<0.01 relative to the baseline (Student's t-test).
The effects of chondroprotectors have been actively studied in many Russian studies. Let's look at some of them using the example of the drug teraflex.
Theraflex is a combination of 2 salts - chondroitin sulfate (400 mg) and glucosamine hydrochloride (500 mg) in one capsule. There is another form of the drug for oral administration - teraflex advance, which contains chondroitin sulfate 200 mg, glucosamine sulfate 250 mg and ibuprofen 100 mg [14].
The feasibility of combining two main drugs with chondroprotective activity is explained by the possibility of potentiating the positive effect of each of them, which is associated with the peculiarities of the pharmacological action of glucosamine and chondroitin. They are synergists and, when used together, complement and enhance each other’s effects [15, 16]. According to the Department of Clinical Geriatrics and Organization of Gerontological Care of the Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, in women with an average age of 54.2 ± 7.6 years with postmenopause, the use of Teraflex for 6 months made it possible to significantly reduce the main manifestations of osteoarthritis (Table 2) while reducing the need in NSAIDs in 21% of patients or refusal to take NSAIDs in another 14% of patients.
Table 2. Dynamics of quantitative parameters of osteoarthritis while taking Teraflex Note. * — p<0.05; ** — p<0.01.
The possibility of using teraflex in a continuous and intermittent course was studied [17]: 50 patients received teraflex according to the usual regimen for 9 months, and 50 patients received teraflex for 3 months, then there was a 3-month break in treatment, then patients in this group received teraflex again . In general, by the end of the 9th month of the study, there were no significant differences between the effectiveness of the drug in both groups, although the severity of the effect was higher with constant use of the drug. In both groups, 34% of patients stopped taking NSAIDs.
The effect of Teraflex Advance was studied at the Institute of Rheumatology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences [18, 19] in comparable groups of 20 people with gonarthrosis, whose average age was about 58 years. Patients were randomized into 3 groups, 1 of which took Teraflex Advance at a dose of 6 capsules per day; patients of group 2 - teraflex 2 capsules per day and paracetamol in a daily dose of no more than 6 tablets (3 g); Group 3 - ibuprofen at a dose of 600-1200 mg per day (as needed). The researchers noted equal effectiveness of both forms of the drug - Teraflex and Teraflex Advance, clearly exceeding the effectiveness of ibuprofen in relation to pain, stiffness and functional impairment (WOMAC index). In another study [20], taking Teraflex Advance 2 capsules 2 times a day allowed achieving an analgesic effect after 2 weeks of use, and when taking the usual form of Teraflex (1 capsule 2 times a day) - after 2 months.
The results discussed above reliably confirm the presence of an antinociceptive effect in chondroprotectors, which is characterized by an early onset and gradual development with long-term preservation of the result even after discontinuation of therapy. Currently, the effectiveness of chondroprotectors has been studied and confirmed in many experimental and clinical studies [21–24]. They are an obligatory component of complex therapy for OA, recommended for this purpose by the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) [25] to reduce pain and improve joint function; the effect persists for several months after discontinuation of chondroprotectors; in addition, they are well tolerated by patients. The use of chondroprotectors slows down the progression of degenerative changes in the joints and spine and has a delayed anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Along with degenerative changes, inflammation plays a very important role in the development and progression of OA. In the affected joint, the production of “pro-inflammatory” cytokines, cyclooxygenase, increases, which initiates inflammatory reactions and aggravates damage to cartilage tissue and surrounding structures of the joint. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), which is expressed in OA-affected cartilage and stimulates the production of metalloproteinases, plays a key role in the cascade of proinflammatory mediators [26, 27]. In addition, IL-1β inhibits the expression of collagen and proteoglycans, stimulates the synthesis and release of eicosanoids - prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Increased production of nitric oxide triggers chondrocyte apoptosis [28].
The antinociceptive effect of chondroprotectors is probably associated with a direct effect on proinflammatory cytokines, markers of systemic inflammation.
Some in
vivo
and
in vitro
have shown that chondroprotectors have anti-inflammatory properties and are able to reduce the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the blood. One of the targets of glucosamine in chondrocytes has been shown to block the effects of interleukin-1β, thereby inhibiting inflammatory enzymes such as nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 [29]. Experiments on rats demonstrated the ability of glucosamine to alter nociception, in particular to reduce the degree of mechanical allodynia. In addition, when taking glucosamine, the formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 is inhibited and the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 is activated in the synovial membrane [30].
These interactions have also been studied in the human body - according to the VITAL (VITamins and Lifestyle) association study, in 217 men and women who took part in the experiment, there was a clear correlation between the use of chondroprotectors and the level of markers of systemic inflammation. Patients using high doses of chondroitin (14 or more tablets per week) had a 36% decrease in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in the blood and a 27% decrease in PGE-M (prostaglandin E, a metabolite in the urine) compared to baseline [31]. .
Unfortunately, the number of similar studies evaluating the relationship of glucosamine and chondroitin supplementation with other biomarkers of inflammation in the human body is very limited. Understanding the patterns and associations between the use of these drugs and inflammatory biomarkers may shed light on the biological mechanisms involved. It is important to understand the potential anti-inflammatory effects of chondroprotectors, since reducing systemic inflammation may provide impetus for new strategies for the prevention and treatment of diseases that cause it, such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases. For example, long-term use of glucosamine and chondroitin has been found to reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer [32] and lung cancer [33].
Traditionally, chondroprotectors were considered exclusively as substances that act only on the trophism of cartilage and its structure, and their effects were often associated with a direct effect on cartilage tissue and its partial restoration. However, numerous clinical studies have demonstrated that the symptom-modifying effect (reduction of pain) occurs much earlier than the structure of the cartilage tissue is restored.
The results of a number of randomized placebo-controlled studies demonstrate a pronounced antinociceptive effect of chondroprotectors, comparable to that of NSAIDs, not only in the treatment of OA, but also in chronic back pain, which opens up new opportunities for clinicians in the treatment of this condition. It should be remembered that side effects with long-term use of NSAIDs are much more frequent and dangerous than those of chondroprotectors [34, 35].
Today, ideas about the mechanisms of action of chondroprotectors have changed significantly. This is primarily due to the discovery of their independent anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. The data obtained in numerous studies confirming the ability of these drugs to inhibit proinflammatory cytokines opens up new prospects for their use in the treatment of not only arthralgia, but also other chronic pain syndromes. Of course, new research is needed to clarify important issues for clinicians regarding dosages, timing and predictors of treatment, and to assess possible undesirable effects for different types of pain syndromes.
Separately or together?
Although glucosamine and chondroitin are chondroprotectors, they are used under different circumstances. Which raises the question: should I buy chondroprotectors together or separately? Answer: it is better to give preference to a complex supplement in which the components will complement each other.
What are the advantages of the complex:
- acts in several directions at once, providing comprehensive support;
- has higher dosages, which makes it possible to cover the daily requirement with a one-time dose;
- will cost less based on price/number of capsules/dosage.
The role of chondroitin in the human body
Chondroitin performs several important functions in the human body:
- stimulates the formation of glycosaminoglycans - the main building material of connective tissue, slowing down the destruction of cartilage and promoting its restoration;
- activates the formation of hyaluronic acid, which retains water in the tissues - this is important for maintaining the elasticity necessary for full shock absorption of the joint;
- interacts with all other components of cartilage, uniting and structuring them, providing the necessary strength;
- forms small water cavities in the cartilage, increasing shock absorption;
- stimulates the production of intra-articular fluid necessary to nourish cartilage tissue and smooth movement of articular surfaces relative to each other;
- makes synovial fluid more fluid, maintaining its natural viscosity;
- reduces pain in joint diseases and increases mobility in them, including by increasing the amount and fluidity of intra-articular fluid;
- prevents the growth of blood vessels into the cartilage;
- suppresses the formation of reactive oxygen species, which accumulate in large quantities during joint aging;
- blocks enzymes that destroy connective tissue;
- suppresses lipid synthesis, thereby preventing the development of atherosclerosis in the walls of blood vessels.
Who should take it?
In situations of high physical activity, the use of these substances as supplements is especially important. Wear on joints from training occurs much faster, which can lead to a number of problems with the musculoskeletal system.
In addition, we must not forget about the injuries that often accompany weightlifting, powerlifting or bodybuilding. By taking additional complexes, which include glucosamine and chondroitin, you can significantly speed up the recovery process.
Additional intake of chondroprotectors is also necessary for elderly people, as well as those who suffer from diseases of the musculoskeletal system (arthrosis, arthritis, etc.).
How does taking chondroitin affect joints?
Once in the body, chondroitin is absorbed in the intestines and enters the connective tissue through the bloodstream, where it is used in the same way as its natural counterpart. Due to the similar structure of the substance, the body does not see the difference between internal and external chondroitin, so it actively uses chondroitin taken orally. In joints, chondroitin is “embedded” in cartilage tissue, where it stimulates metabolic processes and the formation of synovial fluid. First, it slows down and stops the destruction of cartilage, then gradually reverses the process, starting restoration. But this is only possible with a continuous and long-term intake of chondroitin into the body, therefore drugs containing it (chondroprotectors) are prescribed in long courses.
Are chondroprotectors as effective as we are told?
According to manufacturers, chondroitin and glucosamine restore cartilage tissue in the joint and protect it from destruction. They contain components that replicate the structure of hyaline cartilage, which explains this effect. To get any results, you need to take the drugs for a long time, several months.
Many patients note that even after a long period of use, chondroprotectors did not give any result at all. This is also confirmed by x-rays, in which the size of the joint space remained the same, and sometimes decreased.
Drugs with a chondroprotective effect only help people with early stages of arthrosis. At stages 2 and 3 of coxarthrosis or gonarthrosis, there is no result from them: stronger drugs are needed. In such cases, it is advisable to undergo a course of intra-articular injections of Noltrex or decide on endoprosthetics if the joint is severely damaged and conservative treatment does not help.
Proponents of chondroprotectors often remain silent about what side effects are possible after long-term use of these drugs. Watch the video on this topic and draw your own conclusions:
Release forms and recommendations
You can find chondroprotectors in several forms on the shelves of pharmacies and specialty stores. These can be capsules, tablets or powder - for systemic use. In addition, there are preparations for local action - ointments and creams. Depending on the severity of the injury or joint wear, choose between systemic and local action.
Choosing products at a pharmacy or buying them in sports nutrition stores is a matter of convenience, since not every city has points of sale of supplements for athletes. Both in the pharmacy and in the sports nutrition store, the quality level of drugs is controlled at the state level. Therefore, the risk of buying a jar or tube containing a counterfeit from a reputable chain is minimal.
For serious injuries and pain in the joint while walking, it is not recommended to opt for ointments and creams, as they provide minimal therapeutic effect. If we talk about the difference between capsules and tablets, it must be said that capsules have an advantage because the substances from them are absorbed faster, regardless of food intake.
The dosage is calculated based on the information on the packaging. It is important to remember that for preventive purposes it is less than for the treatment of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
What are synovial fluid grafts?
Synovial fluid prostheses are drugs with a completely different effect. They do not affect chondrocytes in articular cartilage and do not restore cartilage, as the manufacturers of chondroprotectors promise us. These medications:
- are injected into the joint and replenish the deficiency of synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant;
- normalize the viscosity of the joint fluid and thereby improve its shock-absorbing properties;
- push mechanically rubbing surfaces apart and stop painful sensations almost immediately after insertion.
Most synovial fluid prostheses are made based on hyaluronic acid, which is native to our body. It remains inside the joint for 6-12 months and gives exactly this result, after which the course of injections must be repeated.
Synthetic drugs based on polymers, for example polyacrylamide Noltrex, are more effective. It is not recognized by the body's immune system, so it remains inside longer (up to 1.5 years). Moreover, the substance is hypoallergenic and does not cause rejection reactions or side effects.
"Noltrex" is a synthetic synovial fluid prosthesis of prolonged action.
What the Research Says
Over the past few years, studies have regularly appeared that confirm poor results or their complete absence in the treatment of osteoarthritis with chondroprotectors.
- In 2006, an English medical journal published data that chondroitin, glucosamine, and any combination of them were not more effective than placebo. The studies were conducted on a group of patients of 1583 people.
- In 2007, American scientists concluded that chondroitin does not provide any improvement in the symptoms of arthrosis.
- In 2010, large-scale studies were carried out on a group of patients of 3800 people, which also equated the effect of chondroprotectors to placebo.
Chondroprotectors in many countries have already been equated to placebo - they don’t work
If chondroprotectors do not give the desired effect, then is it worth spending a lot of money on them and taking pills for many months, waiting for the result? Indeed, unlike this method, intra-articular injections of synovial fluid prosthesis give an almost instant effect. They pose no health risks in the short or long term. Therefore, many doctors in developed countries no longer recommend chondroprotectors to their patients, but immediately, after confirming the diagnosis, send them for injections.
Contraindications and side effects
Modern biologically active chondroprotective supplements have a minimum of contraindications. They cannot be accepted:
- for phenylketonuria
- with individual intolerance to glucosamine and chondroitin.
They are prescribed with caution and under the supervision of a doctor:
- for bleeding disorders, thrombophlebitis;
- children under 14 years of age;
- pregnant and lactating women;
- for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the acute phase.
The most common side effect of these drugs is allergic reactions. Sometimes gastrointestinal disorders are observed - abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, bloating and flatulence. Very rarely, glucosamine and chondroitin can cause headaches, sleep disturbances, dizziness, pain and swelling in the legs.
What are the benefits for athletes?
Sports achievements directly depend on the volume and intensity of training. During the training process, you often have to work on the same motor element for a long time, which overloads certain muscle groups, tendons and joints. This negatively affects the condition of cartilage tissue, which does not have time to regenerate properly. The depletion of the natural protection of cartilage and joints leads to frequent and serious injuries.
Runners leg and muscle pain on running training outdoors in summer nature, sport jogging physical injury when working out. Health and fitness concept with sore body
Chondroitin and glucosamine are recommended to be included in the diet of everyone who plays sports. A sufficient amount of these components allows you not to limit physical activity, continuing to actively train. They not only prevent joint deformation, but also effectively treat existing joint diseases.
The main role of chondroitin and glucosamine in sports nutrition:
- significantly reduce pain;
- increase the strength and elasticity of ligaments;
- do not allow abrasion of articular surfaces;
- prevent the destruction and depletion of cartilage tissue;
- prevent inflammatory processes.
To maintain healthy joints, it is important to take special supplements - chondroprotectors and saturate your diet with foods. Timely intake of supplements with glucosamine and chondroitin strengthens the ligamentous apparatus and prevents the destruction of joints.
What foods contain chondroitin and glucosamine?
The health of the musculoskeletal system largely depends on diet. For the proper functioning of joints, it is important to nourish them with useful substances. Glucosamine is quite often found in foods in the form of polymers, proteins, and collagen particles.
Foods High in Glucosamine:
- beef, veal, poultry;
- hard cheeses;
- river and sea fish (especially red fish - salmon, salmon);
- seafood (shrimp, seaweed, mussels);
- eggs;
- broccoli;
- marshmallow, jelly, marmalade;
- sprouted wheat;
- nuts.
However, the substance is unstable and easily destroyed even before it enters our body during the heat treatment of food. Therefore, even regular consumption of foods high in chondroitin and glucosamine does not guarantee the health of osteochondral tissue, especially with heavy loads, sports and age-related changes in the joints.
How are they absorbed?
Once in the body, glucosamine is absorbed by the digestive system and transported to cartilage tissue, where it is converted into chondroitin and other substances necessary for joints. To improve the absorption of glucosamine, doctors recommend taking macro- and microelements (calcium, magnesium, selenium, phosphorus, manganese, selenium), as well as vitamins B, C, A.
Dietary sulfur is also of great importance for the absorption of glucosamine and chondroitin. It acts as a conductor, increasing the permeability of cell membranes. The record-breaking foods for the content of this macronutrient are all varieties of cabbage, onions, chicken, beef, and fish.
Glucosamine/chondroitin: complex or separately
Based on the fact that the use of each component is recommended under certain circumstances due to different indications, the question arises whether complex chondroprotective drugs can be used or whether it is necessary to make a choice in favor of only one of the substances. Experts say that regardless of what caused the discomfort, it is still better to use complex therapy, since the ability to complement each other’s benefits enhances the positive effect.
Advantages of an integrated approach:
- simultaneous comprehensive action;
- complex preparations allow you to satisfy the body’s daily need for glucosamine and chondroitin in one go;
- from the point of view of rational spending of the budget, the complexes are almost twice as profitable.
You should not separate the two substances, since they do not interfere with each other's action. By activating the production of synovial fluid, it will not be superfluous to strengthen the articular ligaments and increase the elasticity of the cartilage. An integrated approach will give better results. In addition, simultaneous use of drugs will help not only restore lost joint function, but also prevent incipient pathology. It is always easier to prevent a problem than to solve it. This is especially true for joints. When cartilage production begins, there is no pain yet. It will not be possible to identify the problem until the deformation of the cartilage makes itself felt. An integrated approach will eliminate the development of pathology before it manifests itself in a decrease in quality of life
Indications for the use of glucosamine with chondroitin
The first, important factor indicating the need to take glucosamine with chondroitin is high physical activity. This can be not only the physical activity of athletes at the stadium or in the gym during training. This also includes groups of people whose daily activities involve constant movement, such as couriers who spend a lot of time on bicycles or loaders who strain their backs.
The second, no less important factor is age. In older people, the rate of synovial fluid production is reduced, and tissue elasticity is not the same as it was in youth. Any, even minor, loads lead to serious problems with the joints, since tissue cells can no longer recover at the required rhythm. People aged 65+ should discuss taking any medications with their local doctor, because there may be restrictions with certain concomitant chronic diseases.
The third factor indicating the need to supplement with chondroitin with glucosamine is the presence of injuries. Any damage to bones and joint tissues will be quickly forgotten, and motor activity will be restored if you help the body by taking chondroprotectors.